Site-directed Mutagenesis Libraries
Creative Biostructure has strong expertise in custom mutagenesis library construction services using site-directed mutagenesis technique. The site-directed mutagenesis library offers a great technology for protein function and active center studies.
Site-directed mutagenesis (SDM), also termed site-specific mutagenesis or oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis, is a molecular biology technique that is an important research tool for for investigating the structure and biological activity of DNA, RNA, and protein molecules, and for protein engineering. SDM creates specific and targeted alterations (such as insertions, deletions and substitutions) through in vitro procedure.
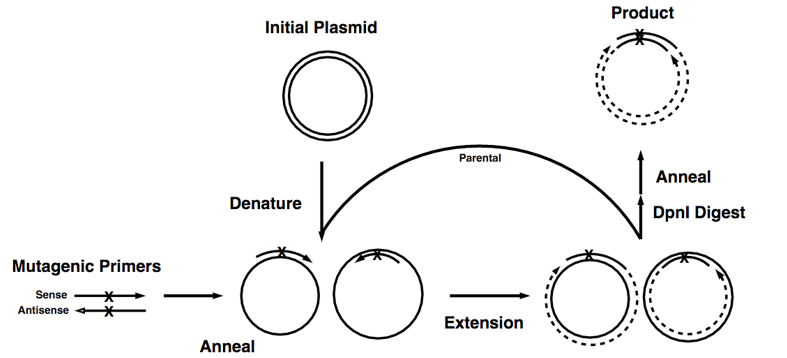 Figure 1. The basic process of site-directed mutagenesis.
Figure 1. The basic process of site-directed mutagenesis.
Creative Biostructure is capable of utilizing custom pre-designed oligonucleotide primers to generate a desired mutation in a double-stranded DNA plasmid. This synthetic primers contain the desired mutations which will be finally selected and checked by DNA sequencing. However, this single-primer extension method is ineffecient owing to a low yield of mutants. Creative Biostructure has also developed many approaches to improve the efficiency fo site-directed mutagenesis, including but not limited to:
- Cassette mutagenesis
Cassette mutagenesis technique needs not involve primer extension using DNA polymerase, in which a fragment of DNA containing the mutation gene of interest and restriction enzyme sites is synthesized, and then inserted into a plasmid. Strikingly, this method can generate mutants at close to 100% efficiency, however, is limited by the availability of suitable restriction sites flanking the site that is to be mutated.
- PCR site-directed mutagenesis
This methods can generate a larger DNA fragment to cover two convenient restriction enzyme sites. These fragments containing the desired mutation in sufficient quantity can be separated from the original, unmutated plasmid by gel electrophoresis, which may then be inserted in the original context using standard recombinant molecular biology techniques.
- Whole plasmid mutagenesis
This technique is highly efficient but relatively simple, easy to perform. The key procedure of this method is a pair of complementary mutagenic primers are employed to amplify the entire plasmid using high-fidelity DNA polymerase. The reaction generates a nicked, circular DNA. The methylated template plasmid DNA and other DNA produced from Escherichia coli strains can be eliminated by enzymatic digestion with a restriction enzyme such as DpnI. While the mutated plasmid, which is generated in vitro and is therefore unmethylated, would be left undigested. Then the digested products can be directly transformed into E. coli strains to generate disried mutagenesis library.
- In vivo site-directed mutagenesis methods
Creative Biostructure can adapt different strategies to perform in vitro site-directed mutagenesis, such as transplacement "pop-in pop-out", direct gene deletion and site-specific mutagenesis with PCR and one recyclable marker (or using using long homologous regions), and in vivo site-directed mutagenesis with synthetic oligonucleotides.
Please feel free to contact us to discuss your project!
Ordering Process
References:
M. Laible and K. Boonrod (2009). Homemade Site Directed Mutagenesis of Whole Plasmids. J. Vis. Exp., 27: 1135.
Site-directed mutagenesis. (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Site-directed_mutagenesis)

