Creative Biostructure offers high-quality transmembrane proteins with NAD(P)-binding Rossmann-fold domains by our first-class Mempro™ cell-free protein production services. Our Mempro™ cell-free expression system can best preserve the native activity of transmembrane proteins.
Transmembrane proteins with NAD(P)-binding Rossmann-fold domains superfamily can be divided into two families: tyrosine-dependent oxidoreductases family and flavin-containing amine oxidoreductase family. The tyrosine-dependent oxidoreductases family, termed the SDR family (short-chain dehydrogenases/reductases) as well. This family has already been identified almost 140 enzymes currently. Members in SDR family includes pteridine reductase 1, corticosteroid 11-beta-dehydrogenase, isozyme 1, tropinone reductase 2, and sorbitol dehydrogenase. Most tyrosine-dependent oxidoreductases share a catalytic center based on tyrosines. All of them play a pivot role in metabolisms of amino acids, carbohydrates, lipids, and hormones. While flavin-containing amine oxidoreductase family is composed of various amine oxidases, including GlpO (alpha-glycerophosphate oxidase), protoporphyrinogen oxidase, and monoamine oxidase A and B. They are closely related to the metabolism of amine.
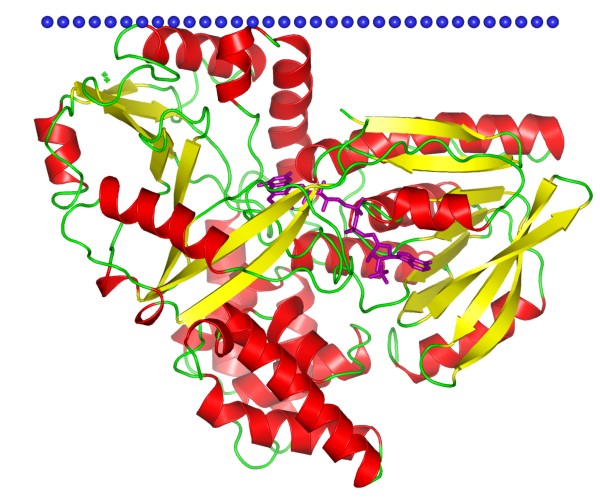 Figure 1. The structural model of alpha-glycerophosphate oxidase (GlpO). (OPM Database)
Figure 1. The structural model of alpha-glycerophosphate oxidase (GlpO). (OPM Database)
Creative Biostructure can provide various strategies for high-quality Mempro™ cell-free transmembrane proteins with NAD(P)-binding Rossmann-fold domains production, including:
• Mempro™ Transmembrane Proteins with NAD(P)-binding Rossmann-fold Domains Production in Bacterial Extract
E. coli S30 extract is commonly employed for membrane protein production. Mempro™ protein expression by bacterial extract system provides you the enhancement of expression of the transmembrane proteins with NAD(P)-binding Rossmann-fold domains, and easy to perform scale up the high-yield production.
• Mempro™ Transmembrane Proteins with NAD(P)-binding Rossmann-fold Domains Production in Wheat Germ
Creative Biostructure can provide eukaryotic translation system for transmembrane proteins with NAD(P)-binding Rossmann-fold domains production in wheat germ system. This system facilitates the membrane proteins performing correct folding and post-translational modifications and maintaining the best structural and functional features.
• Mempro™ Transmembrane Proteins with NAD(P)-binding Rossmann-fold Domains Production in Rabbit Reticulocyte
Crude rabbit reticulocyte lysate is the renewed system for eukaryotic membrane protein production, providing multiple options for the optimization of the production protocols, such as the availability of materials, protein origin and complexity, downstream processing, etc.
• Mempro™ Transmembrane Proteins with NAD(P)-binding Rossmann-fold Domains Production in Baculovirus
Baculovirus expression system from Autographa californica nucleopolyhedrovirus (AcNPV) is also a major host for transmembrane proteins with NAD(P)-binding Rossmann-fold domains expression, which is developed in the early stage that transfected insect cells in combination with vectors derived from the baculovirus.
Creative Biostructure can also provide Mempro™ plant-based virus-like particles (VLPs) production services, Mempro™ animal-free recombinant protein production services and Mempro™ membrane protein production services. Please feel free to contact us for a detailed quote.
References:
B. Persson, et al. (1995). Short-chain dehydrogenases/reductases (SDR). Biochemistry, 34(18): 6003-6013.
F. Bernhard, et al. (2013). Cell-free expression - making a mark. Cur. Opin. Struct. Biol., 23: 374-380.
K. L. Kavanagh, et al. (2008). The SDR superfamily: functional and structural diversity within a family of metabolic and regulatory enzymes. Cell Mol. Life Sci., 65(24): 3895-3906.