Exosome Labeling
Creative Biostructure is engaged in offering comprehensive solutions for exosome study. We offer various technologies applied for exosome characterization and visualization. With efficient exosome labeling methods coupled with professional detection equipment, Creative Biostructure provides you high resolution exosome characterization and visualization service at the single-particle level.
The Importance of Exosome Labeling Analysis
Exosomes are believed to play an important role in intercellular communication under both normal and pathological conditions. They can interact with their target through many processes, including fusion with the plasma, ligand-receptor binding, and internalization through clathrin-dependent endocytosis pathways. Following labeling, the exosome can be traced and can be analyzed on individuals. For example, the exosome uptake process can be visualized directly by labeling fluorescent dye. Creative Biostructure offers specialized exosome visualization service with high accuracy, specificity, and sensitivity.
Creative Biostructure provides various label methods for different targets. Our labeling methods can eliminate background from auto-fluorescence and take less time, facilitating in vivo exosome tracking, biodistribution, and kinetic studies.
- Labeling of lipid. Membrane lipid can be labeled with several dyes, such as PKH26, a widely used amphiphilic lipid dye. Besides, PHK67 and CM-DiI (a structurally similar to PKH26 but water-soluble dye) are also available for customers.
- Labeling of nucleic acid. SYTO RNASelect dye can be used for exosome nucleic acid binding.
- Labeling of protein. We use 5-(and-6)-Carboxyfluorescein Diacetate Succinimidyl Ester or CFDA-SE for protein binding.
- Labeling of other targets. We also offer unique label services for other metabolites with higher sensitivity and fewer background contaminants.
We also offer the latest technologies for fluorescent signal analysis and exosome characterization.
- Individual analysis. The fluorescent signal can be detected by flow cytometry and fluorescent microscopy.
- Characterization of exosome. At Creative biostructure, several technologies are available for characterization of the size and concentration of exosomes in a solution. These technologies include transmission electron microscopy (TEM), dynamic light scattering (DLS), nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA), tunable resistive pulse sensing (TRPS), nanofluidics methods, etc..
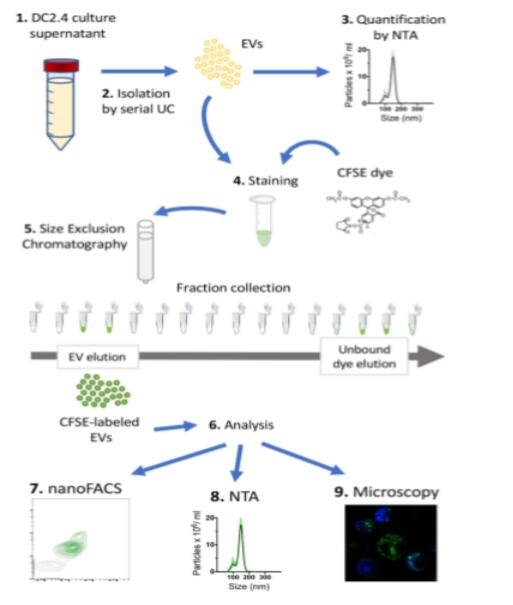 Figure 1 The workflow for the CFSE-labeled EV using DC2.4 cell cultures which produce EV containing supernatants. (Morales-Kastresana et al., 2017)
Figure 1 The workflow for the CFSE-labeled EV using DC2.4 cell cultures which produce EV containing supernatants. (Morales-Kastresana et al., 2017)
Creative Biostructure takes every effort to make your research success. We insist on offering high quality service with more flexible methods and accuracy results. We always work together with customers to solve specific challenges and chase highest-level customer satisfaction. Welcome to contact us for more details and find out how it helps your research.
Ordering process
References:
- Morales-Kastresana A.; et al. Labeling extracellular vesicles for nanoscale flow cytometry. Scientific report. 2017, 7(1): 1878.
- Dominkuša P. P.; et al. PKH26 labeling of extracellular vesicles: Characterization and cellular internalization of contaminating PKH26 nanoparticles. BBA - Biomembranes. 2018, 1860: 1350-1361.
