Application of Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) in Biology
The atomic force microscope is a member of the scanning probe microscope family. It has nanoscale resolution and is easy to operate. It is one of the most essential tools for studying nanotechnology and material analysis. The atomic force microscope uses the relationship between the atomic force between the probe and the sample to obtain the surface morphology of the sample. So far, atomic force microscopes have developed many analytical functions, and atomic force microscopy technology has become an indispensable and essential analytical instrument in today's scientific research. With the development of science and technology, life science began to develop in the direction of quantitative science. The research focus of most experiments has become biological macromolecules, especially the relationship between the structures of nucleic acids and proteins and their related functions. Because of the wide working range of AFM, biomedical samples can be directly imaged in the natural state (air or liquid), and the resolution is also high. Therefore, AFM has become one of the essential tools for studying biomedical samples and biomacromolecules.
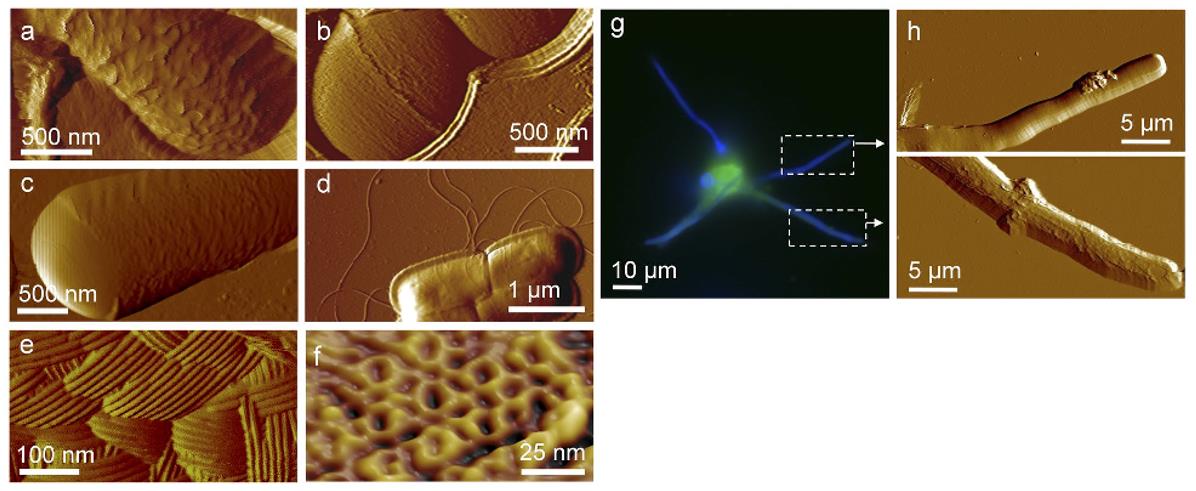 Figure 1. AFM captures structural details of microbial cell surfaces.
Figure 1. AFM captures structural details of microbial cell surfaces.
Biological Applications of Our AFM Service
The biological application of AFM provided by Creative Biostructure mainly includes three aspects: the observation of the surface morphology of biological cells, the observation and research of the structure and other properties of biological macromolecules, and the observation of the force spectrum curve between biological molecules.
Observation of biological cell surface morphology
AFM can be used for morphological observation of cells and image analysis. Quantitative parameters such as cell surface area, thickness, width, and volume can be obtained by observing the cell surface morphology and three-dimensional structure. With rich experience and advanced instruments, Creative Biostructure can provide customers with high-quality data on the surface morphology of biological samples.
Research on the structure and properties of biological macromolecules
AFM can also observe the results and properties of biological macromolecules. The samples observed are protein, DNA, RNA, nuclear acids-protein complex, cell, virus, etc. This helps to understand biocompatibility, protein purification, in vitro cell growth, the intermediate conformation of DNA replication and recombination, analysis of DNA-protein interaction, virus conformation, etc., all play an essential role. Creative Biostructure has always been an expert in protein structure, so we can use our experience to analyze customer data better.
Observation of force spectrum curves between biological molecules
AFM's essential function is to measure various interaction forces on the surface of biomolecules. This is very meaningful for understanding the structure and physical properties of biomolecules. The two molecules were immobilized on the substrate and probe tip of the AFM, respectively. The probe tip with one molecule is continuously approached and separated from another molecule on the substrate in the vertical direction. Currently, the interaction force between the two molecules is a function of their relative distance. The functional relationship between force and distance is called the force spectrum curve.
Creative Biostructure can offer you the different applications of AFM in biological samples, giving you the information, you need to do a great job. Please feel free to contact us for more information or a detailed quote.
Ordering Process
References
- Dufrêne Y F. Atomic force microscopy in microbiology: new structural and functional insights into the microbial cell surface. MBio. 2014, 5(4): 10.1128/mbio. 01363-14.
- Heath G R., et al. Localization atomic force microscopy. Nature. 2021, 594(7863): 385-390.
