Structural Research of Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptors
Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptors (FGFRs) are a family of receptor tyrosine kinases expressed on cell membranes, which play a crucial role in the development and adult cells. Dysregulation of FGFRs is implicated in cancers. Because of their functional importance, FGFRs have been identified as promising drug targets for various cancers. A number of small-molecule inhibitors have been developed against this family of kinases. By elucidating the structure and function of FGFRs, disease mutation sites, and drug-binding sites associated with FGFRs can be revealed. This provides significant clues for disease treatment and drug design.
The FGFR structure comprises a structural extracellular domain, a transmembrane region, and a kinase intracellular region. The most studied region of FGFR proteins is the intracellular tyrosine kinase structural domain. In addition to the primary helix, the C-lobe contains a short helix between the activation loop (A-loop) and the αF helix, called the EF helix. This helix is conserved in all FGFR members and other protein kinases. The active site, which binds ATP and substrate proteins, is located in the cleft between the two lobes. The C-lobe is tightly folded with the αF helix to form a hydrophobic core, which is surrounded by other secondary fragments. In addition to the primary helix, the C-lobe contains a short helix between the activation loop (A-loop) and the αF helix, called the αEF helix. This helix is conserved in all FGFR members and other protein kinases.
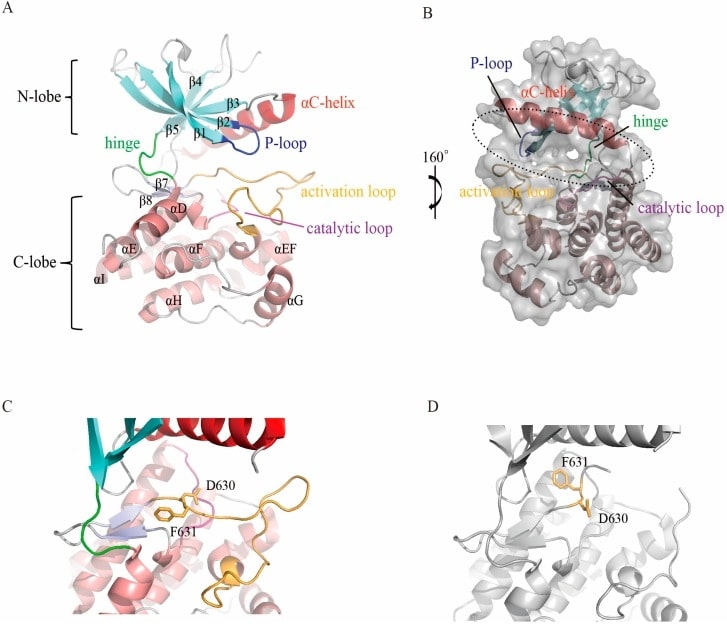 Figure 1. Structure of the FGFR kinase domain. (Dai S, et al., 2019)
Figure 1. Structure of the FGFR kinase domain. (Dai S, et al., 2019)
| Protein | Organism | Method | Resolution | PDB Entry ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FGFR3 Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 transmembrane dimer: Homo sapiens | Homo sapiens | Solution NMR | / | 2LZL |
Table 1. Structural research of FGFRs.
In recent years, great progress has been made in the study of FGFR structure by applying various structural biology methods and techniques. For example, FGFR crystals have been obtained by X-ray crystallography and diffracted using X-rays to determine their high-resolution three-dimensional structure. Single-particle cryo-electron microscopy has been used to resolve FGFR structure and their interactions with ligands. Biophysical techniques, including nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and mass spectrometry, are used for FGFR conformation, dynamics, and interactions.
As a leading service provider in protein structural biology, Creative Biostructure offers scientists and researchers access to a wide range of services and resources related to FGFRs. We can provide services such as protein crystallization screening and optimization, X-ray crystallography analysis, cryo-electron microscopy, and protein structure modeling and prediction. If you are researching the structure and function of proteins in the field of FGFRs, we are the ideal partner for you! For more information, please contact us.
Reference
- Dai S, et al. Fibroblast growth factor receptors (fgfrs): structures and small molecule inhibitors. Cells. 2019; 8 (6): null.