Structural Research of Sterol-Sensing Domain (SSD) Proteins
Sterol-sensing structural domains (SSDs) are found in various membrane proteins and play essential roles in cholesterol metabolism, transportation, and signal transduction. Containing SSD proteins, such as sterol regulatory element binding protein (SREBP) - clearance activating protein (Scap), Niemann Pick release type C1 (NPC1), 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase (HMGCR), and patched, their structures reveal the importance of a conserved core for sterol dependent function.
Conformational analysis of SSD protein in HMGCR
HMGCR is the rate-limiting enzyme for cholesterol synthesis and a target for cholesterol-lowering statins. TM 2-6 of HMGCR contains a 170 amino acid SSD. Researchers report the cryo-electron microscopic structure of the HMGCR-UBIAD1 complex and find that rearrangements of the TM in the SSD allow the recruitment of proteins that initiate HMGCR degradation, a key reaction in the regulatory system controlling cholesterol synthesis. The rearrangement allowed the recruitment of proteins that initiate HMGCR degradation, a critical reaction in the regulatory system controlling cholesterol synthesis.
Advances in research on SSD protein action mechanisms
Researchers further analyzed the SSD conformation in both HMGCRs to gain insight into the mechanism of the sterol sensing response. By comparing the structure of HMGCR with that of other SSD-containing proteins (Insig-bound Scap), it is hypothesized that SSDs cannot bind to Insigs and resist ERAD when HMGCR adopts conformation B. However, adopting conformation A promotes HMGCR binding to Insig for subsequent ubiquitination and ERAD.
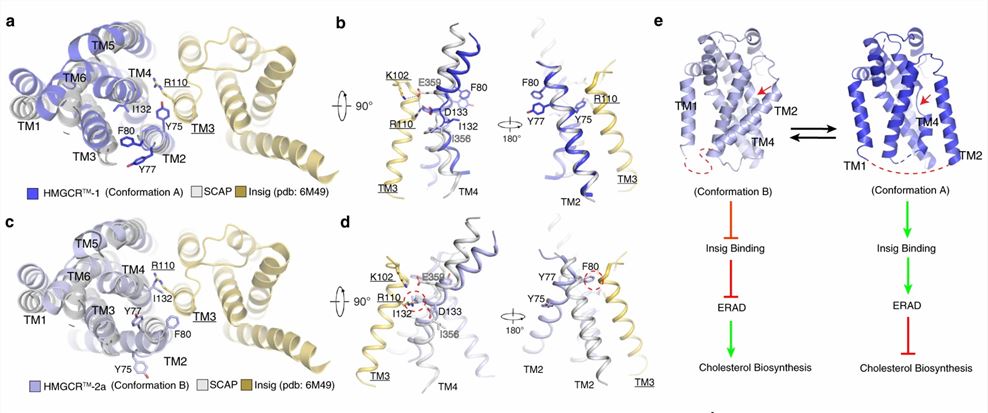 Figure 1. Structural comparison of HMGCR with Insig-bound Scap reveals dynamic features of SSDs. (Chen H, et al., 2022)
Figure 1. Structural comparison of HMGCR with Insig-bound Scap reveals dynamic features of SSDs. (Chen H, et al., 2022)
| Protein | Organism | Method | Resolution | PDB Entry ID |
| NPC1 | Homo sapiens | Cryo-EM single particle analysis | 3.6 Å | 6W5R |
| NPC1L1 | Homo sapiens | Cryo-EM single particle analysis | 3.34 Å | 7N4U |
| NPC1-NPC2 complex | Homo sapiens | Cryo-EM single particle analysis | 4 Å | 6W5V |
| Delta N-NPC1L1-CLR | Homo sapiens | Cryo-EM single particle analysis | 2.69 Å | 7DFW |
| Delta N-NPC1L1-EZE | Homo sapiens | Cryo-EM single particle analysis | 3.58 Å | 7DFZ |
| Full-length hNPC1L1-Apo | Homo sapiens | Cryo-EM single particle analysis | 3.03 Å | 7DF8 |
| Niemann-Pick type C protein NCR1 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C | X-ray diffraction | 3.5 Å | 6R4L |
| Cholesterol-bound NPC1L1 | Homo sapiens | Cryo-EM single particle analysis | 3.58 Å | 7N4V |
| NPC1-like intracellular cholesterol transporter 1 (NPC1L1) | Rattus norvegicus | Cryo-EM single particle analysis | 3.7 Å | 6V3F |
| NPC1L1 mutant-W347R | Homo sapiens | Cryo-EM single particle analysis | 3.33 Å | 7N4X |
| NPC1-like intracellular cholesterol transporter 1 (NPC1L1) in complex with an ezetimibe analog | Rattus norvegicus | Cryo-EM single particle analysis | 3.5 Å | 6V3H |
| Itraconazole-bound NPC1 | Homo sapiens | Cryo-EM single particle analysis | 4.02 Å | 6UOX |
| Niemann-Pick type C protein NPC2 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C | X-ray diffraction | 2.8 Å | 6R4M |
| Niemann-Pick type C protein NPC2 with ergosterol bound | Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C | X-ray diffraction | 2.9 Å | 6R4N |
| Scap L1-L7 / Fab 4G10 complex focused refinement | Gallus gallus | Cryo-EM single particle analysis | 2.9 Å | 7LKF |
| Scap D435V L1-L7 domain / Fab complex focused map | Gallus gallus | Cryo-EM single particle analysis | 3.5 Å | 7LKH |
| HMGCR-UBIAD1 Complex State 1 | Cricetulus griseus | Cryo-EM single particle analysis | 3.23 Å | 8DJM |
| HMGCR-UBIAD1 Complex State 2 | Cricetulus griseus | Cryo-EM single particle analysis | 3.33 Å | 8DJK |
| Niemann-Pick C1 protein | Homo sapiens | X-ray diffraction | 3.335 Å | 5U74 |
| Ptch1 | Homo sapiens | Cryo-EM single particle analysis | 3.9 Å | 6DMB |
| Ptch1 with three mutations L282Q/T500F/P504L | Homo sapiens | Cryo-EM single particle analysis | 4.1 Å | 6DMO |
Table 1. Structural research of the sterol-sensing domain (SSD) proteins.
Structural analysis is essential to the research of proteins and other biomolecules, and Creative Biostructure's experts use a variety of cutting-edge techniques to provide clients with high-quality structural information, such as X-ray crystallography, cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM), and NMR spectroscopy.
Whether you need to explore the action mechanisms of SSD proteins involved in cholesterol metabolism and signaling pathways or the structure and functions of other biomolecules, we have the expertise and resources to deliver results beyond your expectations. Please contact us to learn more about our structural analysis services and how we can help advance your research.
References
- Chen H, et al. Regulated degradation of HMG CoA reductase requires conformational changes in sterol-sensing domain. Nat Commun. 2022. 13(1): 4273.
- Wu X, et al. Structural advances in sterol-sensing domain-containing proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 2022. 47(4): 289-300.