Structural Research of Mammalian Cell Entry (MCE) Proteins
Mammalian Cell Entry (MCE) is a plasminogen (PLG) binding protein that can be detected from normal human serum (NHS) to produce plasminase (PLA) in the presence of a PLG activator. Members of the MCE protein family form a hexamer assembly with a central channel capable of mediating lipid transport. The binding of MCE is also observed with the leukocyte cell receptors αLβ2 and αMβ2, suggesting the involvement of this protein in the host immune response.
The E. coli MCE protein MlaD forms a ring in the intima associated with the ABC transporter complex. A soluble lipid-binding protein, MlaC, transports lipids between mad and the outer membrane protein complex. The EM structure of two other E. coli MCE proteins showed that YebT forms an elongated tube consisting of seven stacked MCE rings, while PqiB adopts a syringe-like structure. Both YebT and PqiB can generate channels of sufficient length to span the periplasmic space. These channels are involved in lipid transport between organelle membranes.
On the intima side, MCE domain heterohexamers attach to YrbEAB penetrating enzymes to form transmembrane channels. Mkl (MceG) interacts with YrbEAB on the cytoplasmic side, and the membrane will act as a driving force for transport in an ATP-dependent manner. X-ray crystallography and low-temperature electron microscopy have been used to study the structure of MCE proteins. The structural information obtained from experiments can help scientists gain insight into the lipid transport mechanisms in living organisms.
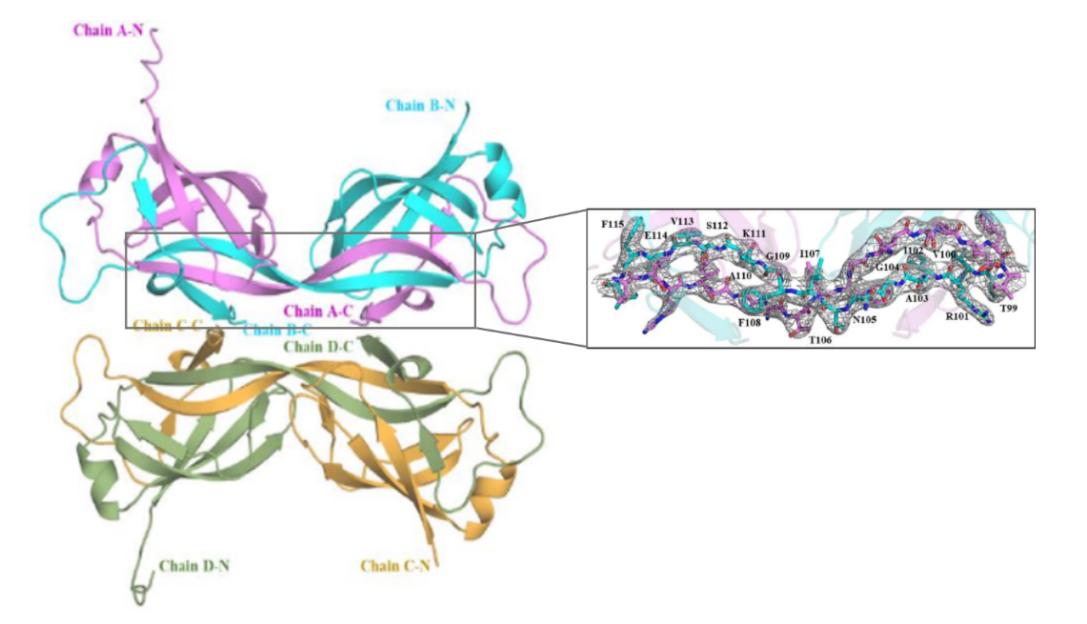 Figure 1. Crystal structure of the MtMce4A39-140- with 4 molecules in the asymmetric unit. (Asthana P, et al.,
2021)
Figure 1. Crystal structure of the MtMce4A39-140- with 4 molecules in the asymmetric unit. (Asthana P, et al.,
2021)
| Protein | Organism | Method | Resolution | PDB Entry ID |
| MCE protein MlaD, core MCE domain | Escherichia coli O157:H7 | X-ray diffraction | 2.15 Å | 5UW8 |
| MCE protein PqiB, periplasmic domain | Escherichia coli K-12 | Cryo-EM single particle analysis | 3.96 Å | 5UVN |
| MCE protein MlaD, periplasmic domain | Escherichia coli O157:H7 | X-ray diffraction | 2.85 Å | 5UW2 |
| Se-Met labelled MCE domain of Mce4A | Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv | X-ray diffraction | 3.61 Å | 7AI2 |
| MCE domain of Mce4A | Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv | X-ray diffraction | 2.90 Å | 7AI3 |
| Lipophilic envelope-spanning tunnel protein (LetB), domains MCE2-MCE3 | Escherichia coli K-12 | X-ray diffraction | 2.15 Å | 6VCI |
| YebT domain1-4 | Escherichia coli K-12 | Cryo-EM single particle analysis | 3.10 Å | 6KZ3 |
| YebT domain 5-7 | Escherichia coli K-12 | Cryo-EM single particle analysis | 3.00 Å | 6KZ4 |
| Phospholipid binding protein MlaC | Escherichia coli K-12 | X-ray diffraction | 1.501 Å | 5UWA |
| Acinetobacter MlaFEDB complex in ATP-bound Vtrans1 conformation | Acinetobacter baumannii | Cryo-EM single particle analysis | 4.00 Å | 7D08 |
| A. baumannii MlaBDEF complex bound to APPNHP | Acinetobacter baumannii | Cryo-EM single particle analysis | 3.90 Å | 6Z5U |
Table 1. Structural research of mammalian cell entry (MCE) proteins.
To study the structure of membrane proteins, cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) and X-ray crystallography are commonly used. Structural analysis of membrane proteins is beneficial to the study of biomolecular functions. It also helps in the development of new targeted drugs.
Creative Biostructure has long been committed to the study of structural biology and membrane proteins. We have extensive experience in determining membrane protein structures using single particle analysis (SPA). In addition to the structural determination of membrane proteins, we can accurately analyze biomolecules, including but not limited to nucleic acids, ribosomes, small proteins, protein complexes, protein-ligand complexes, and viruses. If you are interested in our services, please contact us and we will provide you with a professional and comprehensive solution.
References
- Asthana P, et al. Structural insights into the substrate-binding proteins Mce1A and Mce4A from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. IUCrJ. 2021. 28(8):757-774.
- Kumar, et al. Analysis of expression profile of mammalian cell entry (mce) operons of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Infection and Immunity. 2003. 71: 6083 - 6087.
- Cosate MR, et al. Mammalian cell entry (Mce) protein of Leptospira interrogans binds extracellular matrix components, plasminogen and β2 integrin. Microbiol Immunol. 2016. 60(9):586-598.
- Ekiert DC, et al. Architectures of Lipid Transport Systems for the Bacterial Outer Membrane. Cell. 2017. 169(2):273-285.