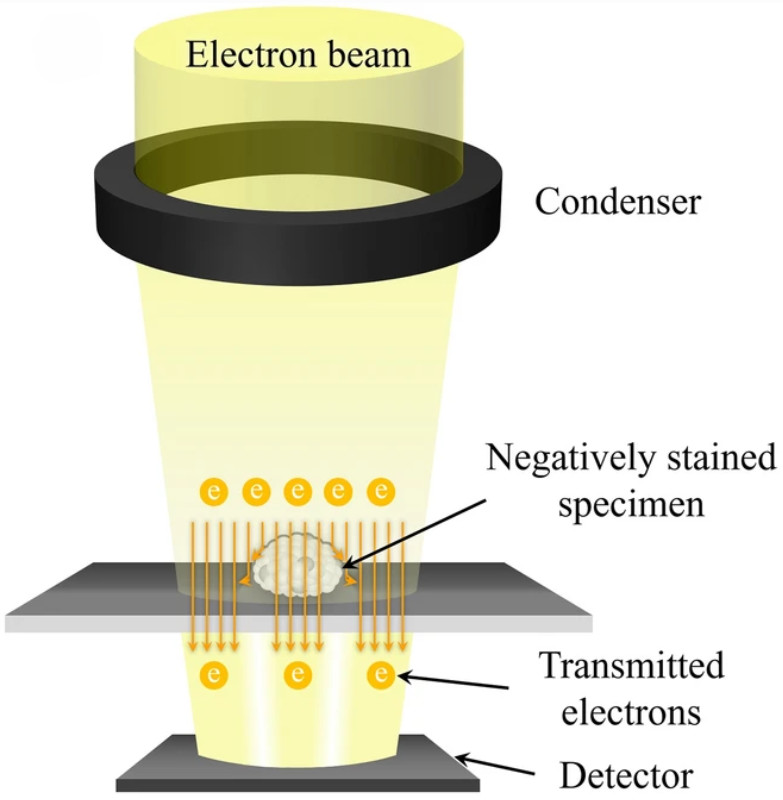
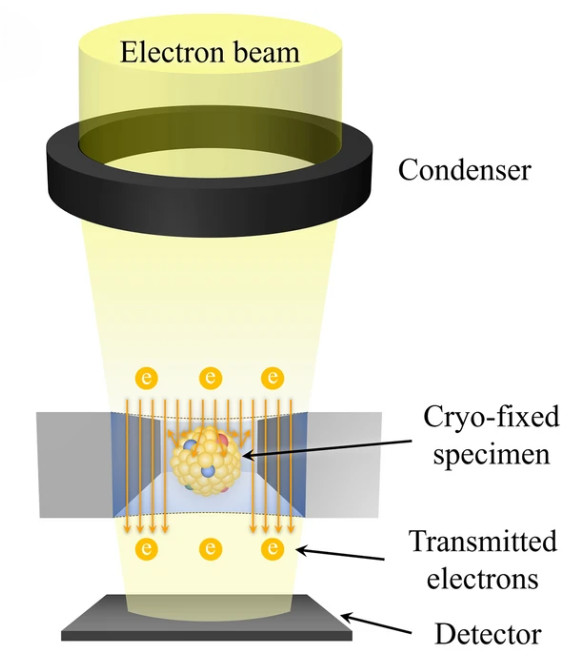
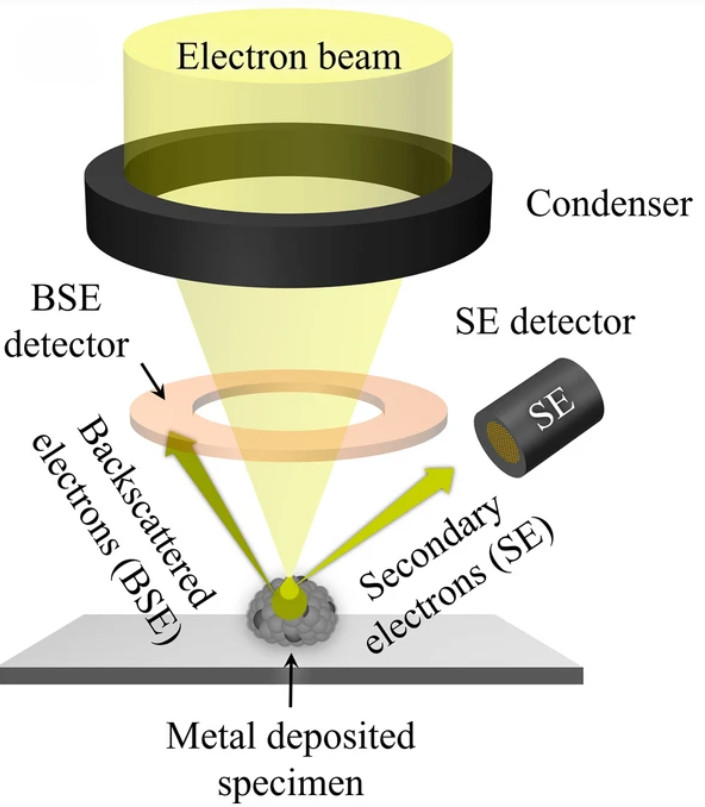
Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)-Based Exosome Characterization Service
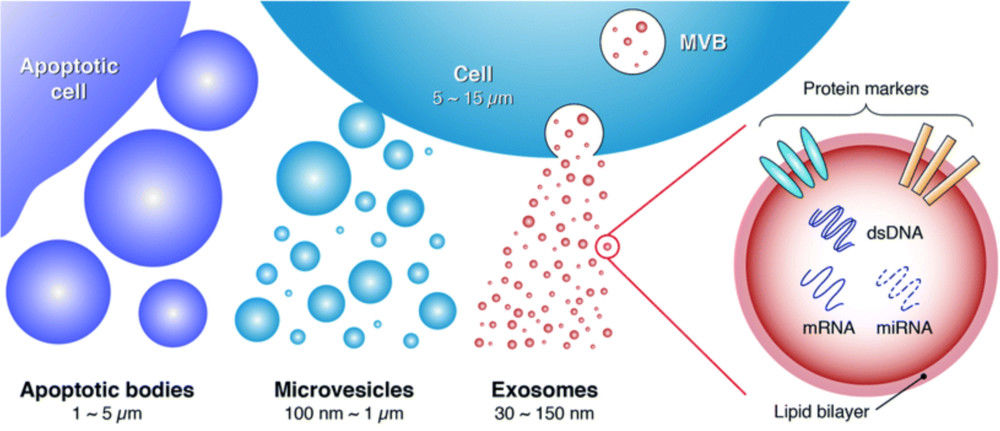
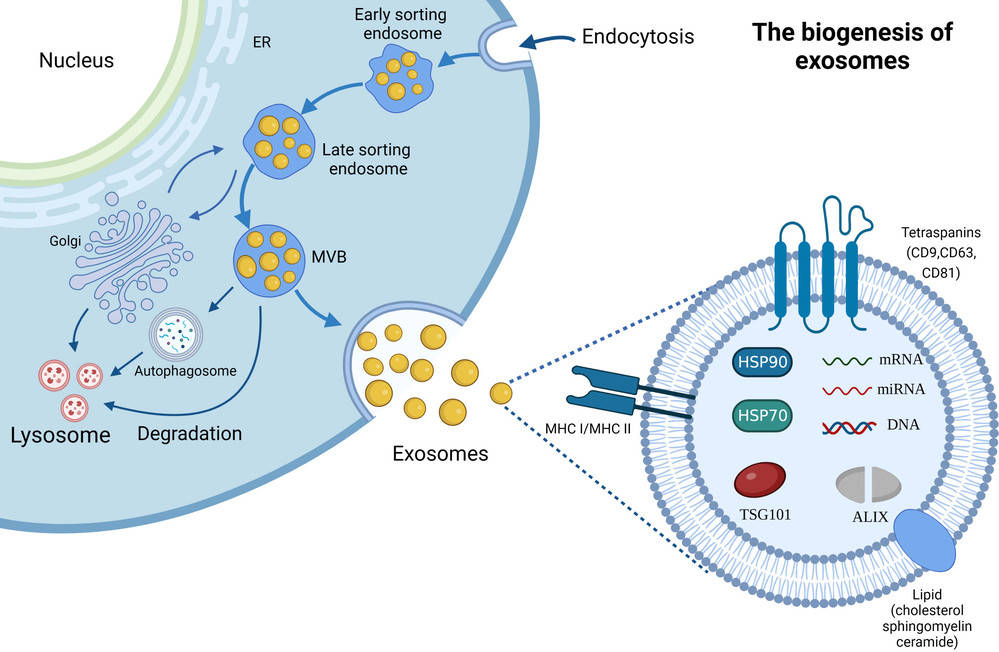
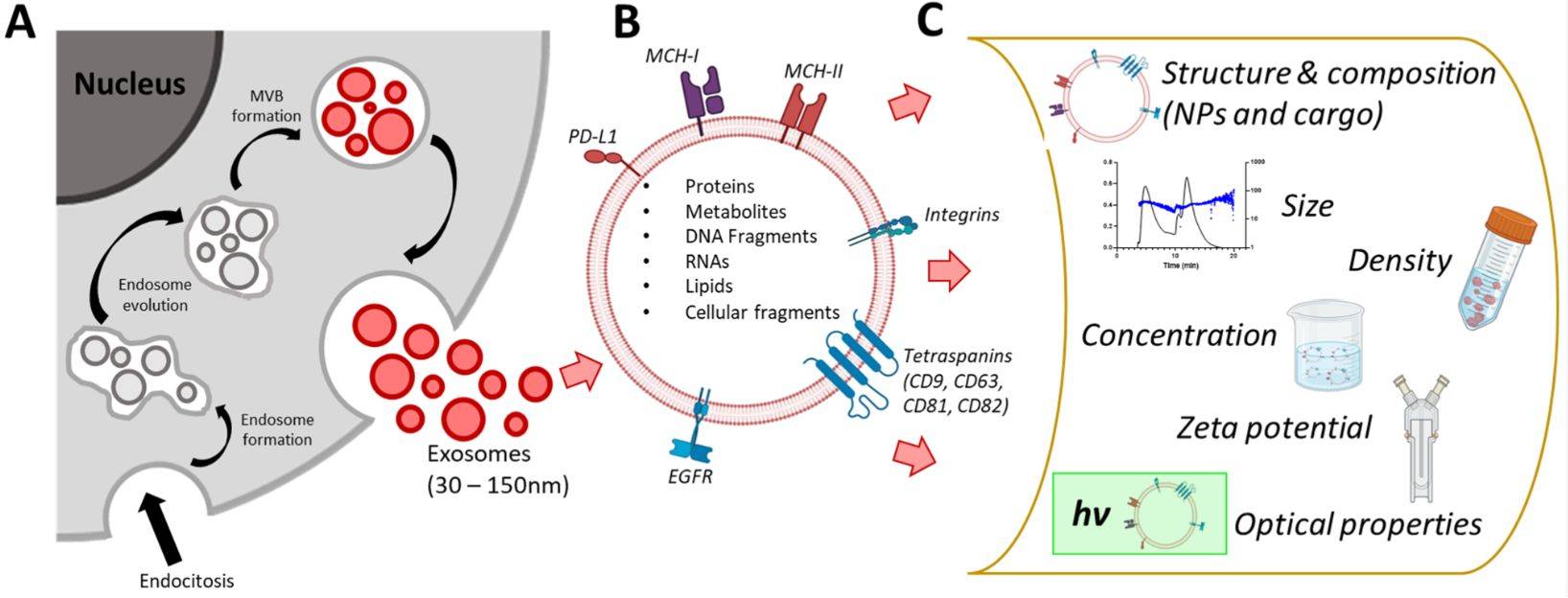
Exosomes, as a major class of extracellular vesicles (EVs), are tiny membrane-bound structures that transport proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids between cells, influencing physiological processes and disease mechanisms. To fully explore their biological roles and therapeutic potential, researchers require precise methods to assess both their morphology and mechanical features.
Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) provides a unique solution by offering high-resolution, label-free imaging at the single-vesicle level while also capturing nanomechanical characteristics. At Creative Biostructure, our AFM exosome characterization service follows international MISEV2023 standards, delivering data with the accuracy and reproducibility needed for both research publications and applied development projects.
Why Choose AFM for Exosome Analysis?
AFM offers several advantages over other exosome characterization techniques:
- Label- and stain-free imaging for preserving vesicle integrity.
- 3D topographical mapping of individual vesicles, revealing morphology at the nanoscale.
- Nanomechanical property measurements such as stiffness, adhesion, and elasticity, which are linked to exosome composition and biological function.
- Single-vesicle analysis, enabling the study of heterogeneity within EV populations.
- Discrimination of exosomes from contaminants, such as salts or protein aggregates, based on mechanical fingerprints.
These unique features make AFM an indispensable tool in exosome research, especially for studies involving drug delivery, cancer diagnostics, and biomarker discovery.
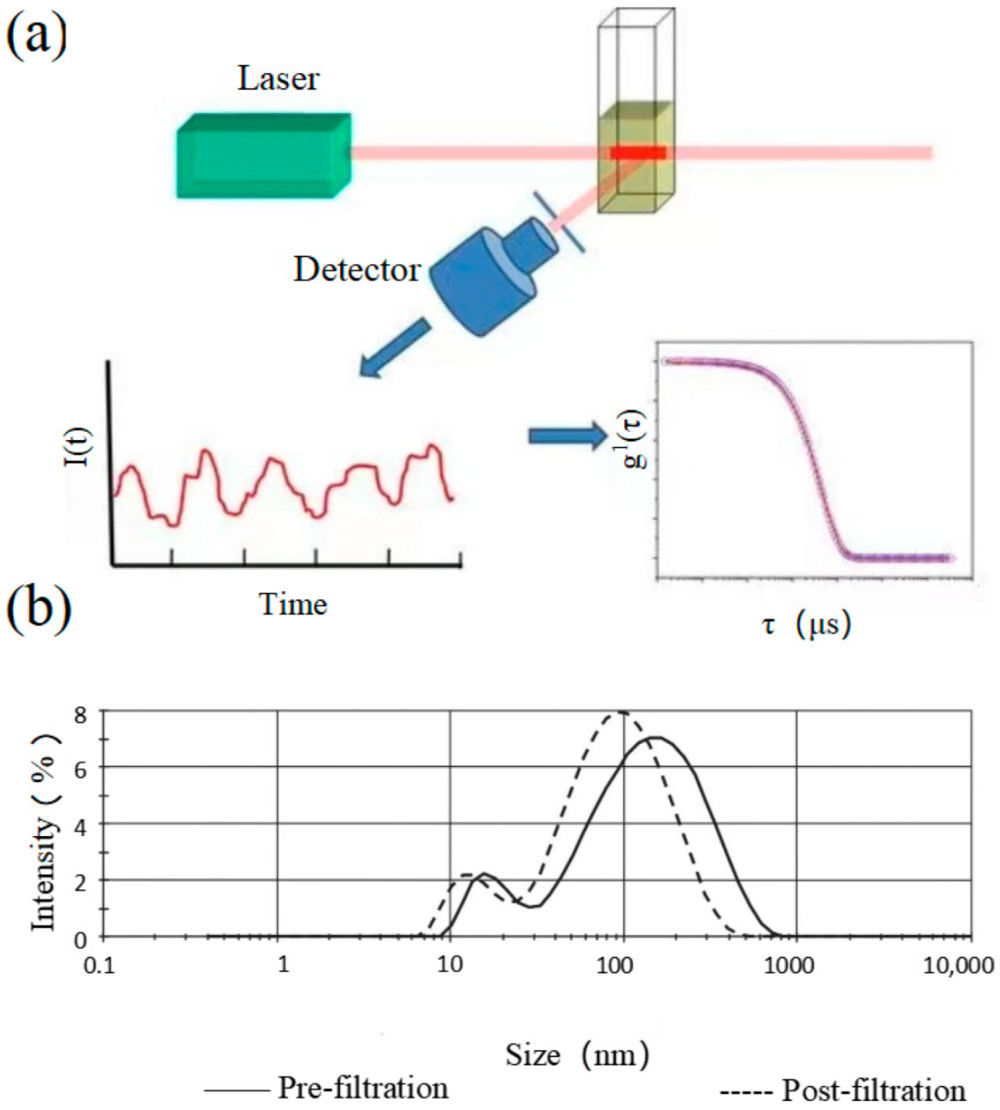
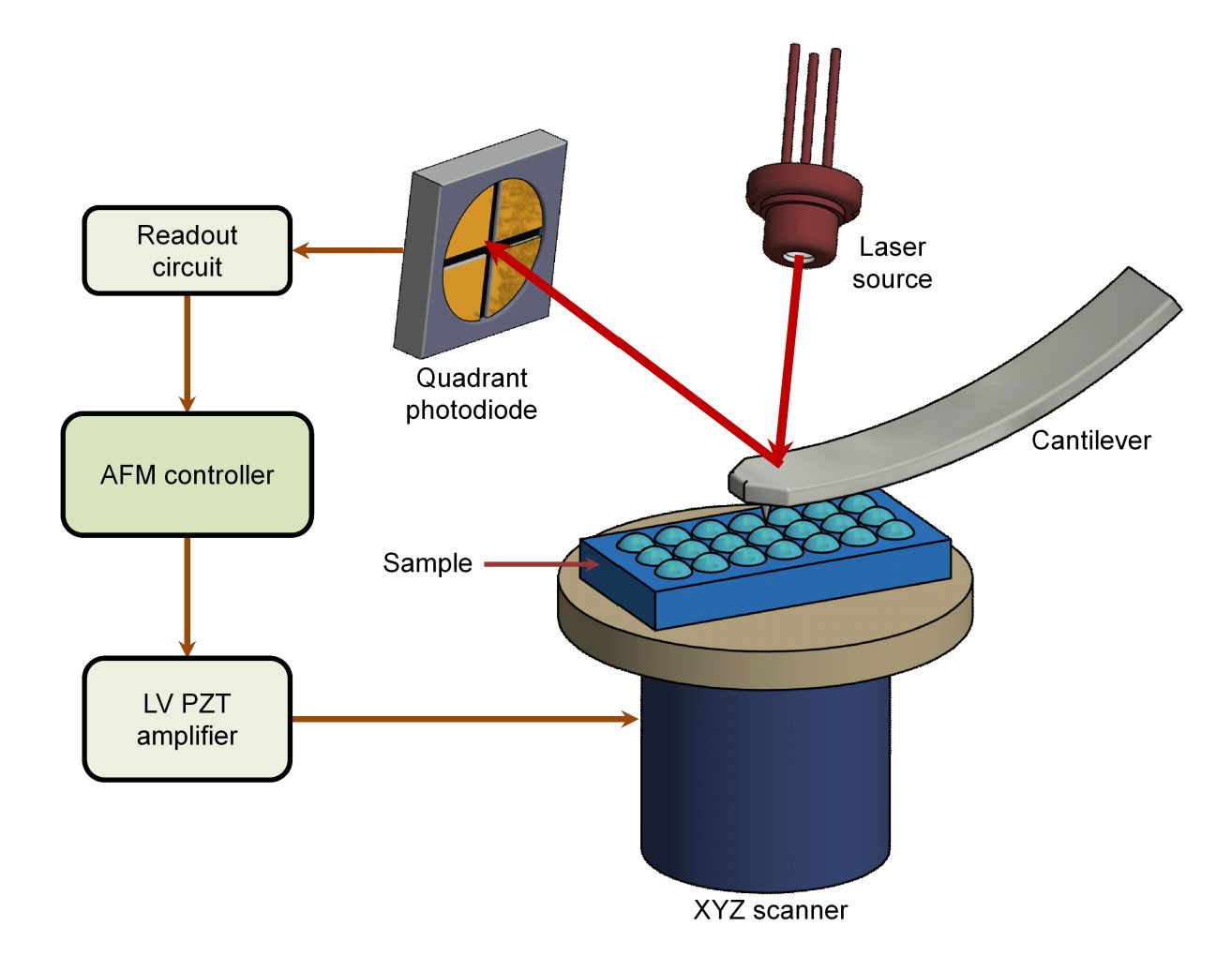
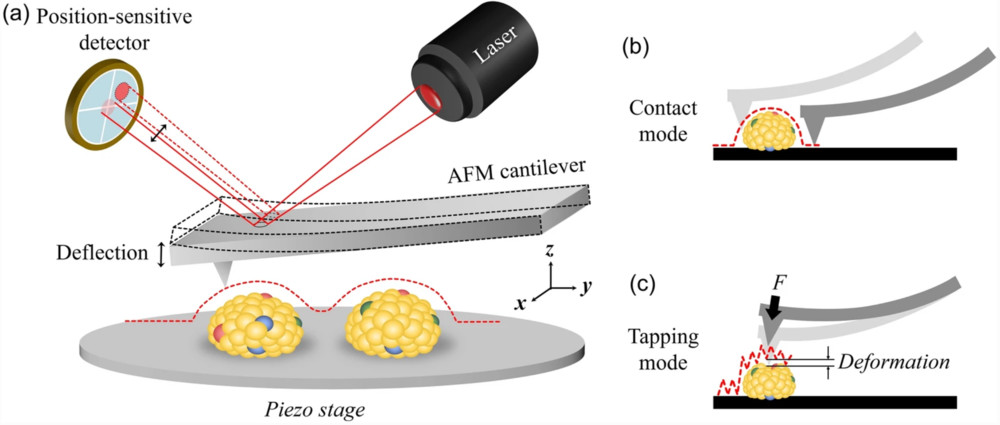 Figure 1. Schematic representation of AFM applied to EV characterization. (a) Principle of AFM signal detection. (b) Contact mode acquires high-resolution topographic data of EV surfaces. (c) Tapping mode measures EV membrane deformation and provides mechanical properties such as rigidity and adhesion by applying controlled force through the AFM tip. (Kwon Y, et al., 2022)
Figure 1. Schematic representation of AFM applied to EV characterization. (a) Principle of AFM signal detection. (b) Contact mode acquires high-resolution topographic data of EV surfaces. (c) Tapping mode measures EV membrane deformation and provides mechanical properties such as rigidity and adhesion by applying controlled force through the AFM tip. (Kwon Y, et al., 2022)
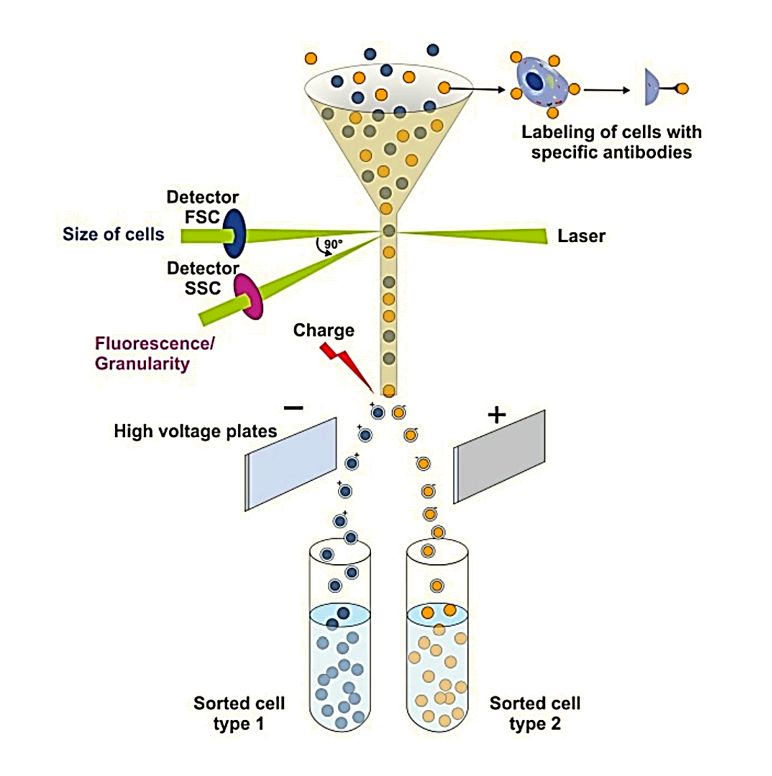
AFM vs. TEM, NTA and Flow Cytometry for Exosome Characterization
| Method | Key Features | How AFM Adds Value |
|---|---|---|
| TEM | High-resolution structural imaging | Provides additional nanomechanical data |
| NTA | Measures bulk size distribution and concentration | Offers single-vesicle shape and stiffness analysis |
| Flow Cytometry | Detects surface markers at the population level | Enables single-vesicle protein-ligand interaction studies |
AFM, when combined with these complementary techniques, gives a more complete understanding of exosome morphology, mechanics, and function.
Our AFM Exosome Characterization Workflow
At Creative Biostructure, we follow a structured and transparent process to ensure accuracy, reproducibility, and compliance with MISEV2023 guidelines. From the initial consultation to the delivery of final results, every step is designed to provide clients with reliable and publication-ready data.
Project Consultation
Each project starts with a consultation to define goals and sample needs, followed by tailored AFM mode selection and a study design suited to the application.
Sample Preparation
Clients may submit purified exosomes or raw material for in-house exosome isolation, after which suitable substrates such as mica are prepared, deposition and immobilization steps are carefully controlled, and all concentrations and timings are thoroughly documented.
AFM Imaging
The most suitable imaging mode, whether contact, tapping, or force mapping, is selected to capture high-resolution topography and three-dimensional vesicle morphology, with probe specifications such as curvature radius and spring constant carefully recorded.
Quantitative Morphometry
Vesicle dimensions and structural descriptors are extracted using defined heuristics for object selection and classification, allowing clear differentiation between intact vesicles, collapsed EVs, and non-vesicular particles.
Nanomechanical Measurements
Force spectroscopy is applied to evaluate stiffness, elasticity, and adhesion, with validated contact mechanics models used to calculate Young's modulus and related parameters, followed by comparative analysis of different exosome populations to reveal functional differences.
Data Analysis and Interpretation
Morphological and mechanical datasets are integrated and statistically evaluated to confirm trends and remove artifacts, with results interpreted in context to support biomarker discovery, drug delivery research, and diagnostic applications.
Comprehensive Reporting and Delivery
All acquisition conditions, probe parameters, and analysis models are transparently reported, with results delivered as publication-ready figures and tables alongside both raw and processed data, and optional follow-up consultations are available to support interpretation or manuscript preparation.
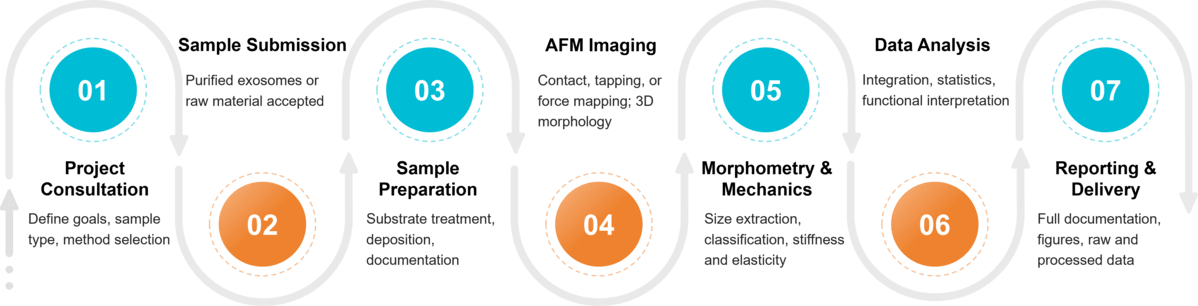 Figure 2. Project Workflow for Exosome Characterization by Atomic Force Microscopy. (Creative Biostructure)
Figure 2. Project Workflow for Exosome Characterization by Atomic Force Microscopy. (Creative Biostructure)
Quality and Compliance Standards
We adhere strictly to MISEV2023 recommendations, including:
- Transparent reporting of sample handling, deposition, and imaging protocols.
- Documentation of AFM probe specifications and acquisition conditions.
- Clear description of contact mechanics models for force spectroscopy.
- Distinction between EVs, non-vesicular contaminants, and collapsed vesicles.
This ensures that our clients' results meet international standards of rigor, reproducibility, and transparency.
Sample Requirements for AFM Analysis
To ensure reliable and reproducible AFM results, we recommend the following sample requirements:
| Requirement | Description |
|---|---|
| Sample Type | Pre-purified exosomes or raw material (e.g., cell culture supernatant, biofluid) |
| Purity | Free of large debris, apoptotic bodies, and excessive protein aggregates |
| Concentration | Sufficient particle density for deposition; typically ≥109 particles/mL |
| Volume | Minimum of 50-100 µL per measurement |
| Buffer Conditions | Preferably PBS or physiological buffer; avoid high salt or detergent levels |
| Storage & Shipping | Fresh or frozen at -80 °C; ship on dry ice to maintain vesicle integrity |
What Deliverables Will You Receive
- Raw and processed AFM data files
- High-resolution images of exosome morphology
- Quantitative measurements of vesicle size and mechanical properties
- Publication-ready figures and tables
- Full documentation of experimental conditions and analysis models
- Technical report with interpretation of key findings
Applications of AFM in Exosome Research
Our AFM service supports a wide range of research objectives:
- Morphological imaging: Determining vesicle shape, height, and size distribution.
- Ultrastructural insights: Identifying collapsed vesicles, surface irregularities, or membrane deformation.
- Mechanical characterization: Measuring Young's modulus, rigidity, bending modulus, and adhesion forces.
- Protein interaction studies: Assessing receptor-ligand or antigen-antibody interactions on vesicle surfaces.
- Contaminant discrimination: Differentiating exosomes from non-vesicular particles by analyzing contact angles and deformation patterns.
- Disease-related research: Correlating exosome stiffness with tumor aggressiveness or evaluating biophysical properties relevant to therapeutic delivery.
Advantages of Our Service
- Cutting-edge AFM instrumentation for nanoscale precision.
- Expertise in both imaging and mechanical characterization of exosomes.
- Data interpretation by a team with extensive structural biology experience.
- Tailored reporting that supports academic publications, grant applications, and industrial R&D.
Case Study
Case: Biomechanical Profiling of Blood Plasma EVs Using AFM
Background
This study applied AFM to blood plasma-derived vesicles to evaluate their nanomechanical signatures and clarify their structural features in both air and liquid environments.
Methods
- Sample Source: Blood plasma from three healthy volunteers.
- Isolation: EVs purified by ultracentrifugation and analyzed with NTA, DLS, and immunoprecipitation using exosomal (CD9, CD63, CD81) and exomere (ApoM, HSP90) markers.
- AFM Analysis: Conducted in PeakForce QNM mode to capture high-resolution morphology and force spectroscopy data in air and liquid conditions.
Results
- Two EV populations were confirmed: exosomes (~97 nm) and smaller exomeres (~28 nm by DLS, ~16 nm by AFM in liquid).
- Exosomes: Showed an internal cavity with central adhesive sites and reversible deformation in liquid; Young's modulus averaged 4.7 MPa.
- Exomeres: Displayed peripheral adhesive regions, minimal deformation, and slightly higher stiffness with a Young's modulus around 8.8 MPa.
- Air imaging revealed artifacts such as cup-shaped vesicles caused by irreversible indentation, but also highlighted distinct adhesive patterns distinguishing exosomes from exomeres.
Conclusion
AFM enabled the direct measurement of size, elasticity, and adhesive properties of blood plasma vesicles, offering a powerful approach to differentiate exosomes from exomeres. The findings demonstrated that exomeres exhibit higher stiffness and peripheral adhesion compared to exosomes, providing new insights into how nanomechanical properties correlate with biological function.
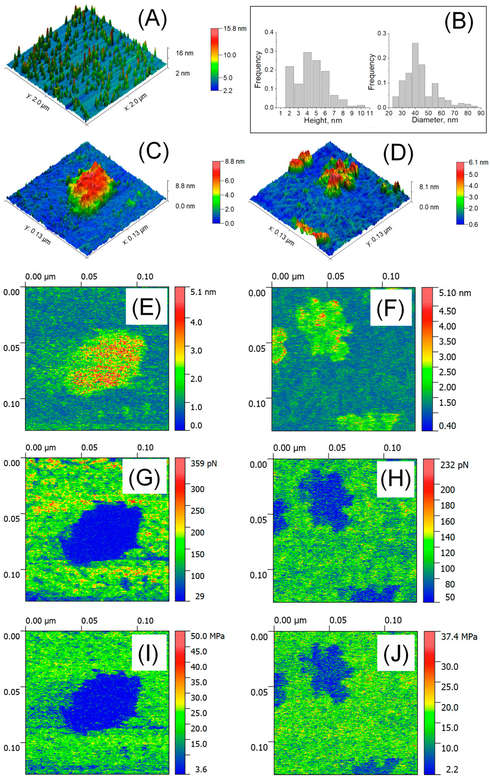 Figure 3. AFM characterization of EVs in liquid. (A) Large-scale AFM image (2 × 2 μm²). (B) Size distribution analysis of EVs (n = 207-254). (C) High-resolution AFM image (129 × 129 nm²) of a single exosome. (D) Visualization of single exomeres and aggregates. (E-F) Deformation parameter measurements. (G-H) Adhesion force analysis. (I-J) Determination of Young's modulus for EV mechanical properties. (Bairamukov V, et al., 2020)
Figure 3. AFM characterization of EVs in liquid. (A) Large-scale AFM image (2 × 2 μm²). (B) Size distribution analysis of EVs (n = 207-254). (C) High-resolution AFM image (129 × 129 nm²) of a single exosome. (D) Visualization of single exomeres and aggregates. (E-F) Deformation parameter measurements. (G-H) Adhesion force analysis. (I-J) Determination of Young's modulus for EV mechanical properties. (Bairamukov V, et al., 2020)
At Creative Biostructure, we use advanced AFM technology and exosome expertise to deliver reliable, publication-ready results. Our team offers tailored support for research and development. Contact us to discuss how our AFM service can advance your project.
References
- Sharma S, LeClaire M, Gimzewski J K. Ascent of atomic force microscopy as a nanoanalytical tool for exosomes and other extracellular vesicles. Nanotechnology. 2018, 29(13): 132001.
- Bairamukov V, Bukatin A, Landa S, et al. Biomechanical properties of blood plasma extracellular vesicles revealed by atomic force microscopy. Biology. 2020, 10(1): 4.
- Kwon Y, Park J. Methods to analyze extracellular vesicles at single particle level. Micro and Nano Systems Letters. 2022, 10(1): 14.
- Welsh J A, Goberdhan D C I, O'Driscoll L, et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles (MISEV2023): From basic to advanced approaches. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles. 2024, 13(2): e12404.
Frequently Asked Questions
For any inquiries, our support team is ready to help you get technical support for your research and maximize your experience with Creative Biostructure.