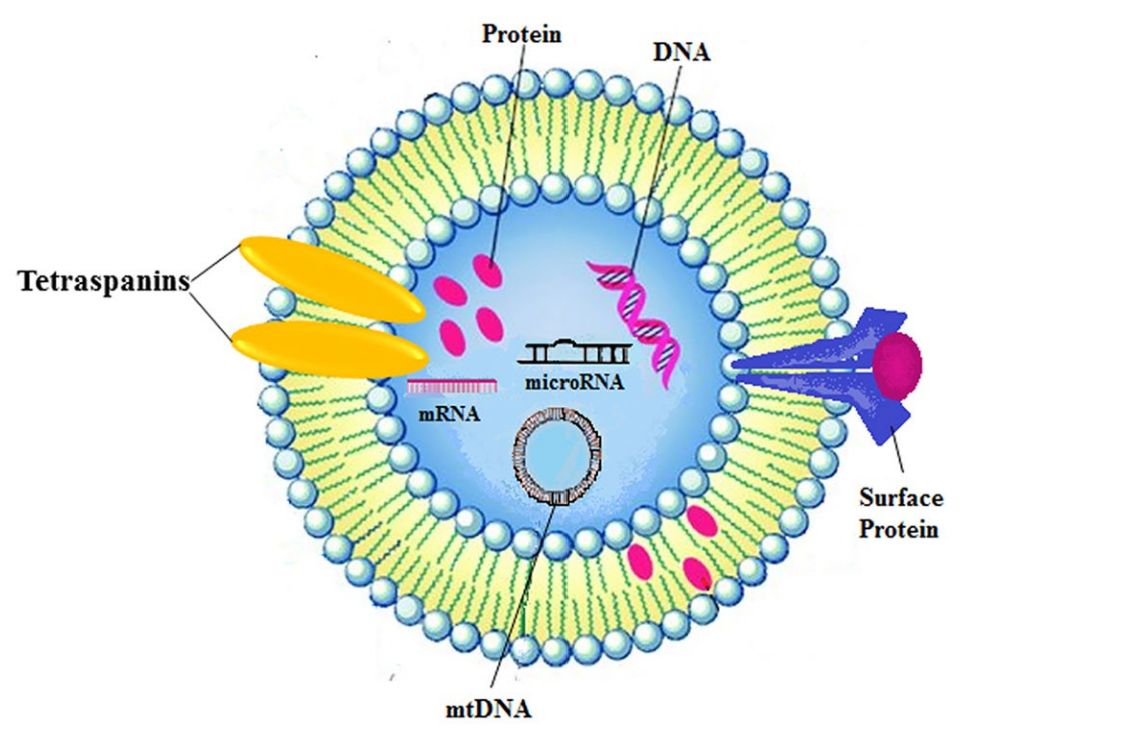
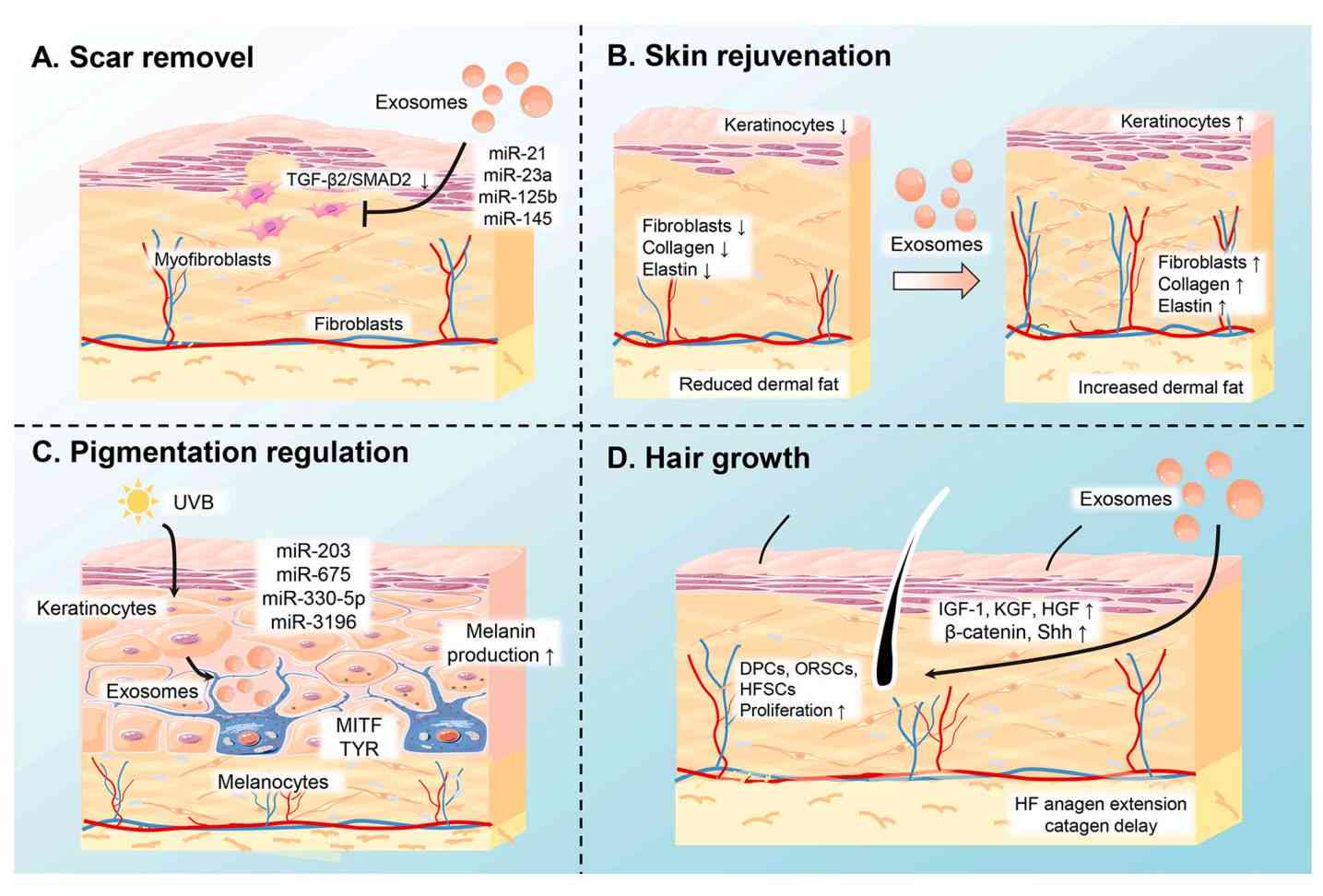
Exosome Angiogenesis and Stem Cell Functional Assays
Angiogenesis and stem cell functional assays are experimental methods used to quantify how stem cell-derived exosomes modulate key processes in tissue regeneration. These assays provide direct evidence of an exosome's pro-regenerative bioactivity by measuring functional outcomes, such as the formation of new blood vessel networks (angiogenesis) or the modulation of stem cell behavior (e.g., exosome stem cell differentiation).
Why Validate Regenerative Exosome Function?
The field of regenerative medicine is rapidly evolving from cell-based therapies to "cell-free" exosome stem cell therapy. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes (MSC-Exos) are being intensely studied for therapeutic applications ranging from skin (exosomes vs stem cells for face) and hair restoration to repairing damaged tissues.
While these clinical applications show promise, they all depend on one critical factor: exosome function. Before preclinical studies or therapeutic use, researchers must prove that their exosomes can actually cause a biological effect.
Our assays provide this essential validation. We help researchers and biotech companies developing stem cell exosome therapeutics to answer key questions:
- For Angiogenesis: Can your exosomes promote the formation of new blood vessels, a critical step in wound healing and tissue repair?
- For Stem Cell Function: Can your exosomes protect other stem cells from damage or guide their differentiation?
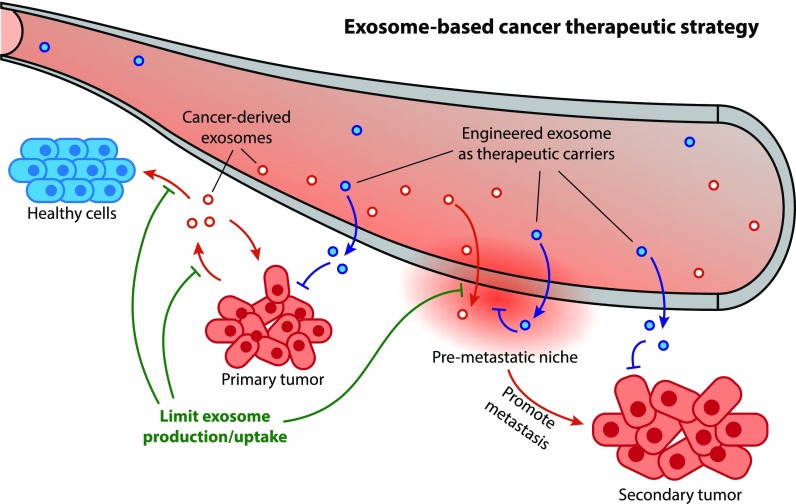
- For Oncology: Do cancer stem cell exosomes drive tumor angiogenesis?
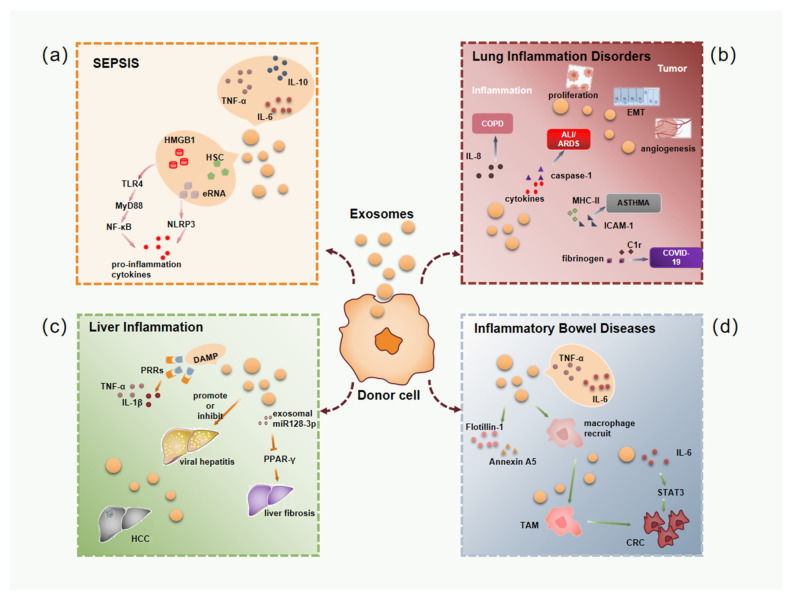
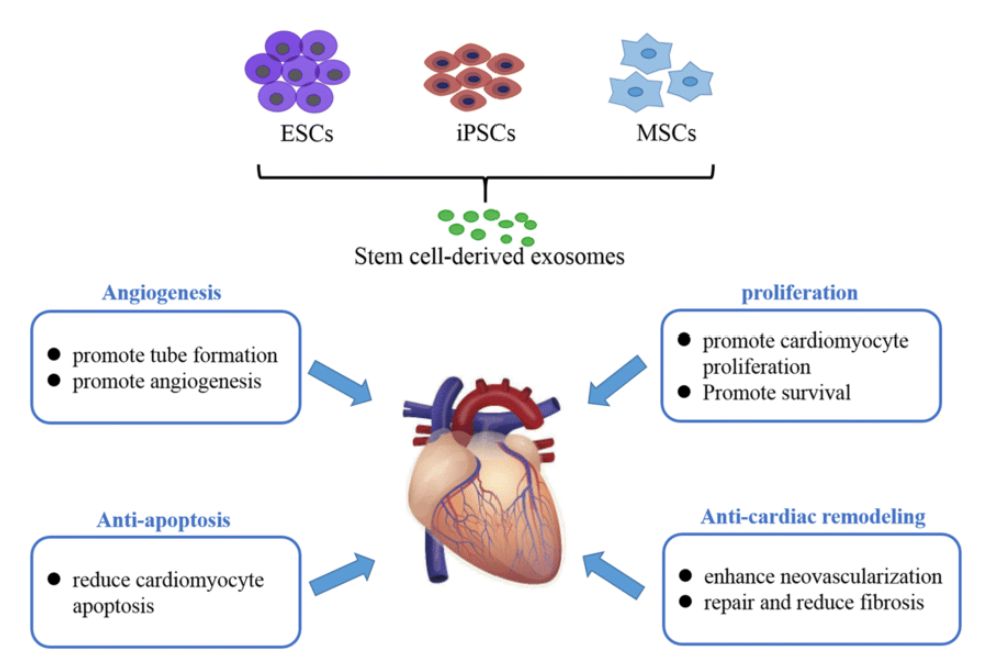
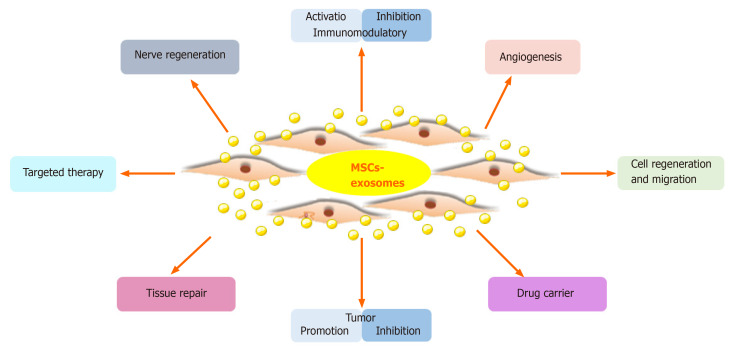 Figure 1. Properties and functions of MSC-Exos. MSC-Exos promote tissue repair through apoptosis suppression, cell regeneration, immune regulation, and angiogenesis. (Ma ZJ, et al., 2020)
Figure 1. Properties and functions of MSC-Exos. MSC-Exos promote tissue repair through apoptosis suppression, cell regeneration, immune regulation, and angiogenesis. (Ma ZJ, et al., 2020)
Our Exosome Angiogenesis and Stem Cell Assay Portfolio
We offer two specialized service packages to quantify the function of your exosomes in regenerative medicine and oncology.
Angiogenesis Functional Assays
This service package quantifies the specific impact of your exosomes on endothelial cells (e.g., HUVECs) to assess angiogenic potential.
- Tube Formation Assay (HUVEC)
- The gold-standard assay for in vitro angiogenesis. We quantify the formation of capillary-like networks following exosome treatment.
- Key Readouts: Total tube length, node count, and network complexity.
- Endothelial Cell Migration Assay
- Measures the ability of exosomes to promote endothelial cell migration, a key step in wound healing.
- Key Readouts: Wound closure percentage over time (Scratch Assay).
- Endothelial Cell Proliferation Assay
- Quantifies the mitogenic effect of your exosomes specifically on endothelial cells.
- Key Readouts: Cell proliferation index (e.g., BrdU, WST-1).
- Angiogenesis-Related Gene Expression
- Uses RT-qPCR to measure exosome-induced changes in key angiogenic genes (e.g., VEGF, HIF-1α), essential for hypoxia exosome angiogenesis studies.
Stem Cell Functional Assays
This service package assesses how your exosomes modulate the core behaviors of stem cells, such as mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) or cancer stem cells (CSCs).
- Exosome-Mediated Stem Cell Differentiation
- Evaluates the ability of your exosomes to drive exosome stem cell differentiation into specific lineages (e.g., osteogenesis, adipogenesis).
- Key Readouts: Lineage-specific staining (Alizarin Red, Oil Red O) and marker gene expression.
- Stem Cell Self-Renewal & Proliferation
- Assesses the impact of exosomes on "stemness" and proliferation, critical for both regenerative medicine and cancer stem cell research.
- Key Readouts: Colony-Forming Unit (CFU) assays or spheroid formation efficiency.
- Stem Cell Protection & Survival Assays
- Measures the ability of your exosomes to protect stem cells from apoptosis under stress conditions (e.g., hypoxia, oxidative stress).
- Key Readouts: Cell viability and apoptosis markers (e.g., Annexin V/PI).
Preclinical Research Support (In Vivo Next Steps)
To validate the therapeutic potential observed in your in vitro assays, the next crucial step is demonstrating functional efficacy in preclinical animal models. Confirm whether your exosomes can effectively promote angiogenesis (e.g., improve blood flow in ischemia models) or facilitate tissue repair and regeneration (e.g., accelerate wound healing or bone repair) in vivo.
For detailed in vivo study designs, models, and functional readouts, please see our dedicated In Vivo Exosome Functional Assays.
Our End-to-End Project Workflow
We manage every step of your project, from initial design to final data interpretation, ensuring transparency and collaboration.
Key Service Steps
Our standard workflow includes the following key steps:
Model Selection & Consultation
Our scientists consult with you to select the right cell model for your goal, such as HUVECs for angiogenesis or mesenchymal stem cells for differentiation studies.
Assay Execution & Optimization
We execute the treatment of your exosome samples on the selected cell models, using optimized concentrations and time points, and include all necessary positive and negative controls (e.g., VEGF for angiogenesis).
Quantitative Data Acquisition
We acquire high-resolution images from the tube formation or migration assays and perform quantitative analysis. For differentiation or proliferation assays, we use plate readers or flow cytometry.
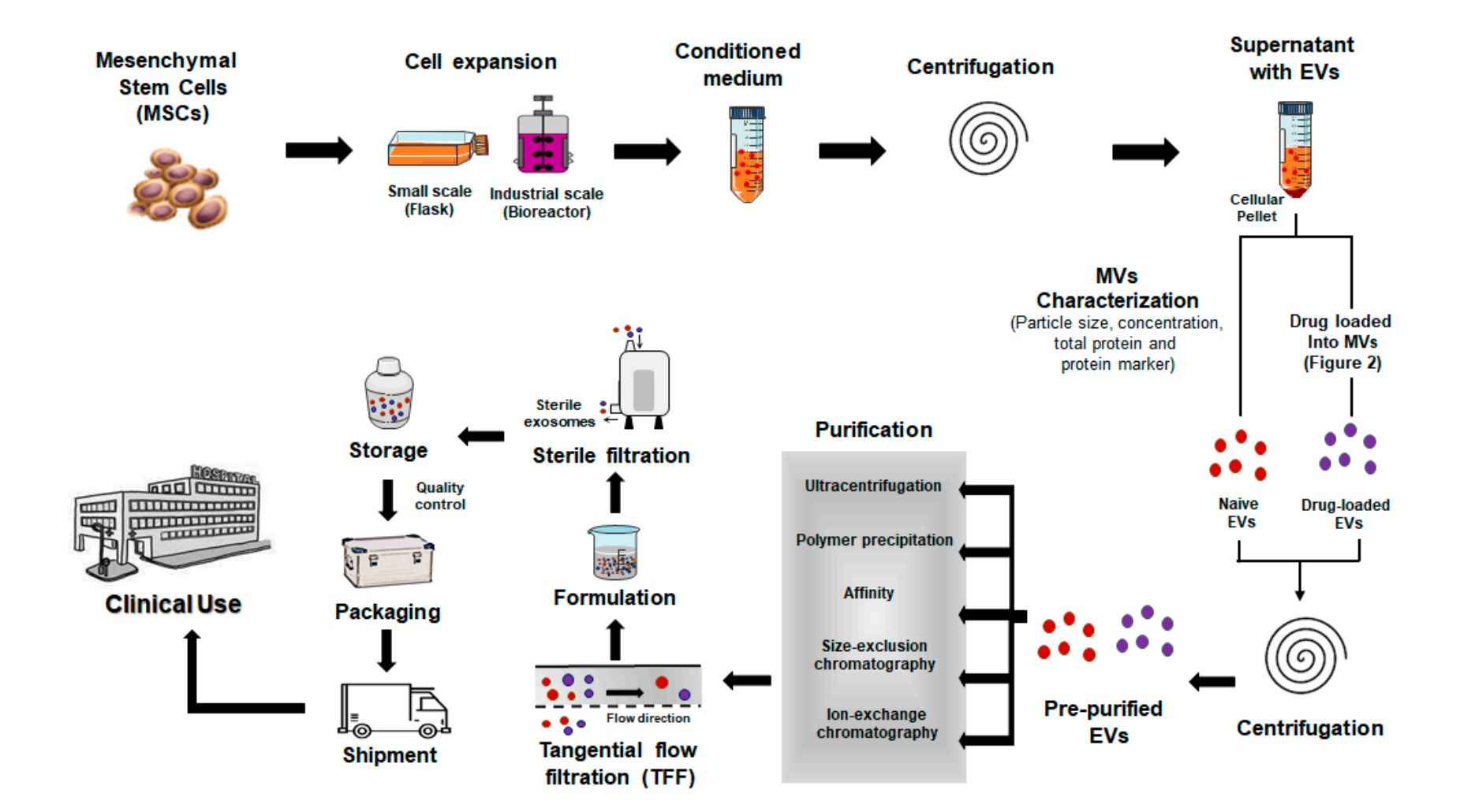
Project Workflow
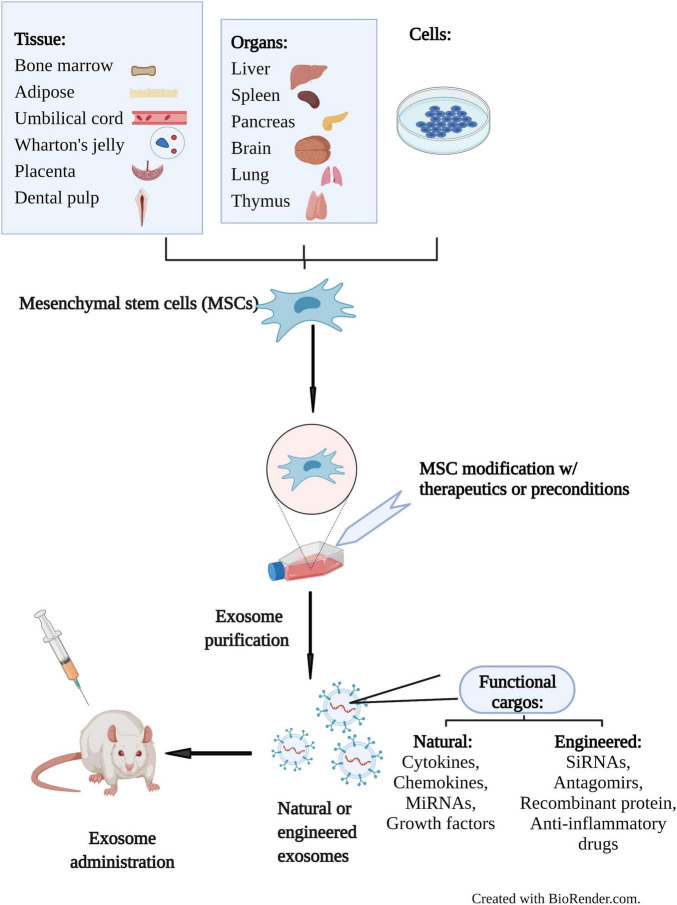
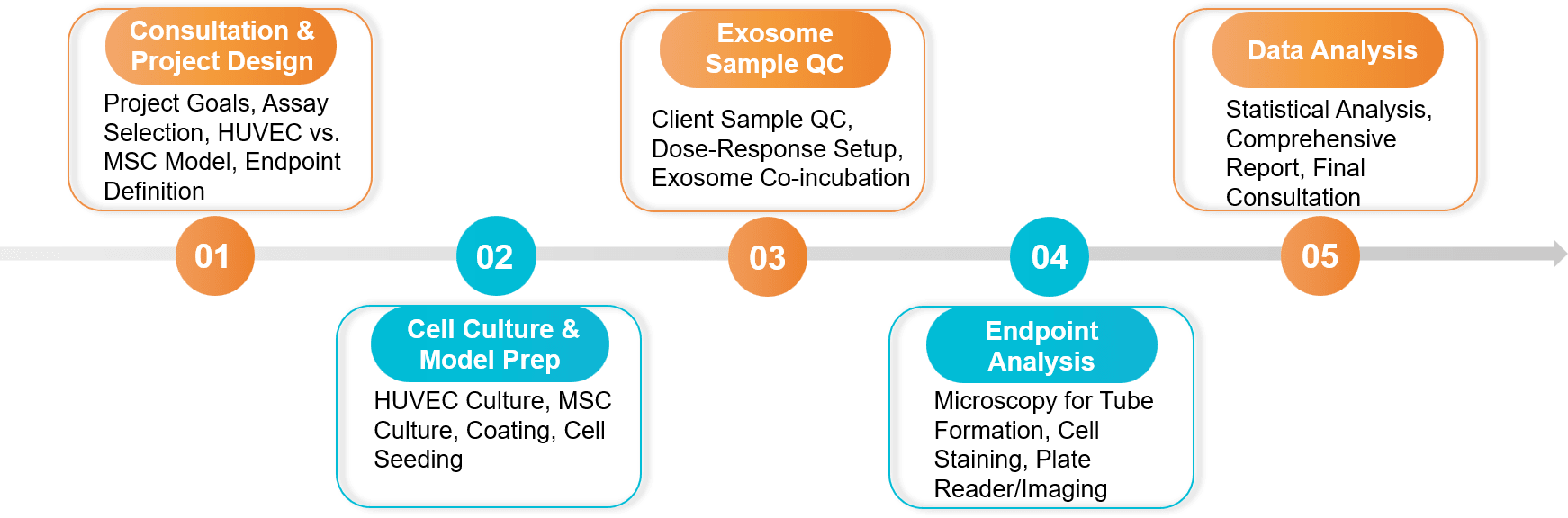 Figure 2. In Vitro Exosome Functional Assay Project Workflow. (Creative Biostructure)
Figure 2. In Vitro Exosome Functional Assay Project Workflow. (Creative Biostructure)
Sample Requirements
Client-Provided Exosomes:
- Quantity: ≥ 1x10¹⁰ particles (assay-dependent, please inquire).
- Purity: Purified exosomes (by UC, SEC, affinity, etc.) are required. We strongly recommend providing NTA and Western Blot characterization data.
- Buffer: Suspended in sterile PBS or a compatible culture-grade buffer.
Cell Models: We can source HUVECs, MSCs, and other standard cell lines, or use client-provided cell lines.
Standard Deliverables
- A comprehensive project report detailing the experimental design, protocols, and results.
- Raw and analyzed data.
- Publication-ready figures (e.g., high-resolution images of tube networks, migration plots, differentiation staining, and quantification graphs).
- A final consultation call to discuss the data and next steps.
Case Study
Case: Placenta-Derived MSC Exosomes Stimulate Angiogenesis In Vitro
Background: Researchers investigated whether exosomes from human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells (PMSCs) could serve as a "cell-free" alternative for therapeutic angiogenesis. The hypothesis was that these exosomes carry and transfer pro-angiogenic cargo to endothelial cells.
Methodology & Findings: To test this hypothesis, researchers co-cultured the PMSC-derived exosomes with HUVECs (Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells). They then performed two key in vitro functional assays: a Tube Formation Assay and a Cell Migration Assay. The results demonstrated that HUVECs treated with PMSC exosomes showed a significant increase in the formation of capillary-like tube networks compared to controls. Furthermore, the exosomes significantly promoted the migration of the endothelial cells.
Conclusion: This study successfully used in vitro angiogenesis assays to provide direct evidence that placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell exosomes are pro-angiogenic. The findings demonstrate the critical value of using functional assays, like tube formation and cell migration, to validate the therapeutic potential of stem cell-derived exosomes.
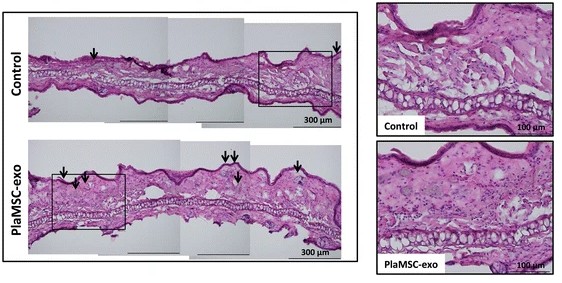 Figure 3. Histological sections of murine auricles 3 days post-PlaMSC-exo infusion, showing increased small blood vessels (arrows). (Komaki M, et al., 2017)
Figure 3. Histological sections of murine auricles 3 days post-PlaMSC-exo infusion, showing increased small blood vessels (arrows). (Komaki M, et al., 2017)
Ready to validate the regenerative power of your exosomes? Our experts will design targeted angiogenesis and stem cell assays, quantify outcomes, and align endpoints with your claims. Contact us for a free consultation and a tailored study plan.
References
- Ma ZJ, Yang JJ, Lu YB, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes: Toward cell-free therapeutic strategies in regenerative medicine. World J Stem Cells. 2020 Aug 26;12(8):814-840.
- Komaki M, Numata Y, Morioka C, et al. Exosomes of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells stimulate angiogenesis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017 Oct 3;8(1):219.
Frequently Asked Questions
For any inquiries, our support team is ready to help you get technical support for your research and maximize your experience with Creative Biostructure.