Exosome Gut Absorption and Delivery Studies
Developing an oral exosome therapeutic or functional food is a journey through a hostile environment. The stomach's acid and the intestine's enzymes destroy most biological carriers. Even if they survive, crossing the tight junctions of the intestinal epithelium remains a formidable barrier. Understanding if, how, and how much of your exosome payload reaches the bloodstream is critical for commercial success.
We provide comprehensive Exosome Gut Absorption and Delivery Studies. We utilize industry-standard Simulated Gastrointestinal (GI) Models and Caco-2 Transwell Systems to rigorously validate the stability, transport mechanism, and final bioavailability of your oral exosome formulations.
Unlocking the "Black Box" of Oral Delivery
To claim oral efficacy, you must prove your exosomes can overcome three distinct physiological barriers.
- Gastric Stability: Can the vesicles withstand pH 2.0 and pepsin digestion? We identify if your carrier needs enteric coating or if natural sources (like milk/plant) offer sufficient protection.
- Intestinal Mucus Penetration: Before reaching the cells, exosomes must diffuse through the thick mucus layer. We analyze surface properties (Zeta potential, PEGylation) that influence mucus interaction.
- Epithelial Transcytosis: How do they cross the gut wall? We distinguish between paracellular transport (between cells) and active transcytosis (through cells via receptors like FcRn), helping you optimize the uptake pathway.
- Systemic Bioavailability: It's not enough to be absorbed; they must reach the target organ. We track the biodistribution of orally administered exosomes to the liver, brain, or bone.
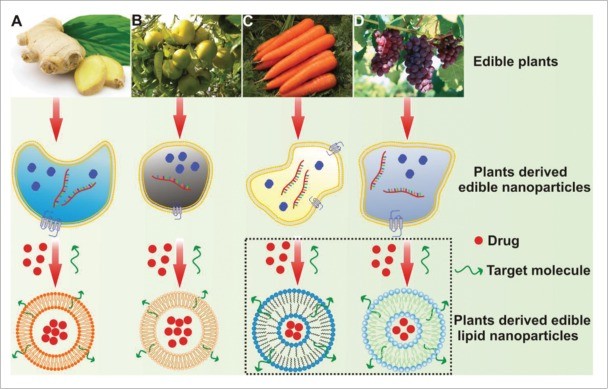
 Figure 1. Various controlled drug delivery methods: (A) Intra-tumoral, (B) Local, (C) Photo-thermal combined with drug systems, (D) Ultrasound-assisted microbubble delivery. (Ketabat F, et al., 2019)
Figure 1. Various controlled drug delivery methods: (A) Intra-tumoral, (B) Local, (C) Photo-thermal combined with drug systems, (D) Ultrasound-assisted microbubble delivery. (Ketabat F, et al., 2019)
Our Absorption Study Workflow
We offer a sequential testing pipeline, moving from simple test tubes to complex living models.
| Study Phase | Our Specialized Approach & Solution | Key Services Applied |
|---|---|---|
| Simulated Digestion (INFOGEST) | In Vitro Stability: We follow the standardized INFOGEST static digestion protocol, covering the Oral, Gastric, and Intestinal phases. We sample at each stage to quantify surviving exosomes and cargo retention (e.g., siRNA integrity). | Gastrointestinal Functional Evaluation of Exosomes, Exosome Stability and Bioavailability Assessment |
| Intestinal Barrier Model | Transwells Model: We culture cells until they differentiate into a polarized monolayer mimicking the human small intestine. We apply exosomes apically and measure their transport to the basolateral (blood) side over time. | In Vitro Exosome Functional Assays |
| Mechanism Elucidation | Pathway Blocking: Is uptake active or passive? We use specific inhibitors (e.g., metabolic inhibitors or receptor blockers) in the Caco-2 model to identify the exact endocytic pathway utilized by your exosomes. | Immunomodulation and Inflammation Assays |
| In Vivo Bioavailability | Pharmacokinetics (PK): We administer labeled exosomes orally to animals and collect serial blood samples. We calculate key PK parameters (Cmax, Tmax, AUC) to quantify the absolute oral bioavailability of your product. | Exosome Tracing and Tracking |
Core Technologies for GI Research
We deploy specific assays to mimic the human digestive tract.
Caco-2/HT-29 Co-Culture Models
Mimicking the Gut Wall: A simple Caco-2 monolayer lacks mucus. We establish Co-Cultures of Caco-2 (absorptive cells) and HT-29-MTX (mucus-secreting goblet cells). This creates a physiologically relevant model with a functional mucus layer, allowing us to test if your exosomes can penetrate the mucus barrier before absorption.
Fluorescence Transport Tracking
Visualizing Transcytosis: We label exosomes with lipophilic dyes (DiR/DiI) or load them with fluorescent cargo. Using Confocal Microscopy on Transwell inserts, we visualize the exosomes entering the apical surface, trafficking through endosomes, and exiting the basolateral side, providing visual proof of gut crossing.
Simulated Gastric Fluid (SGF) Assays
Stress Testing: We subject your formulation to Simulated Gastric Fluid (containing Pepsin, pH 1.2-2.0) for 2 hours. We then use NTA and Western Blot to assess structural damage. This serves as the critical checkpoint for any oral formulation candidate.
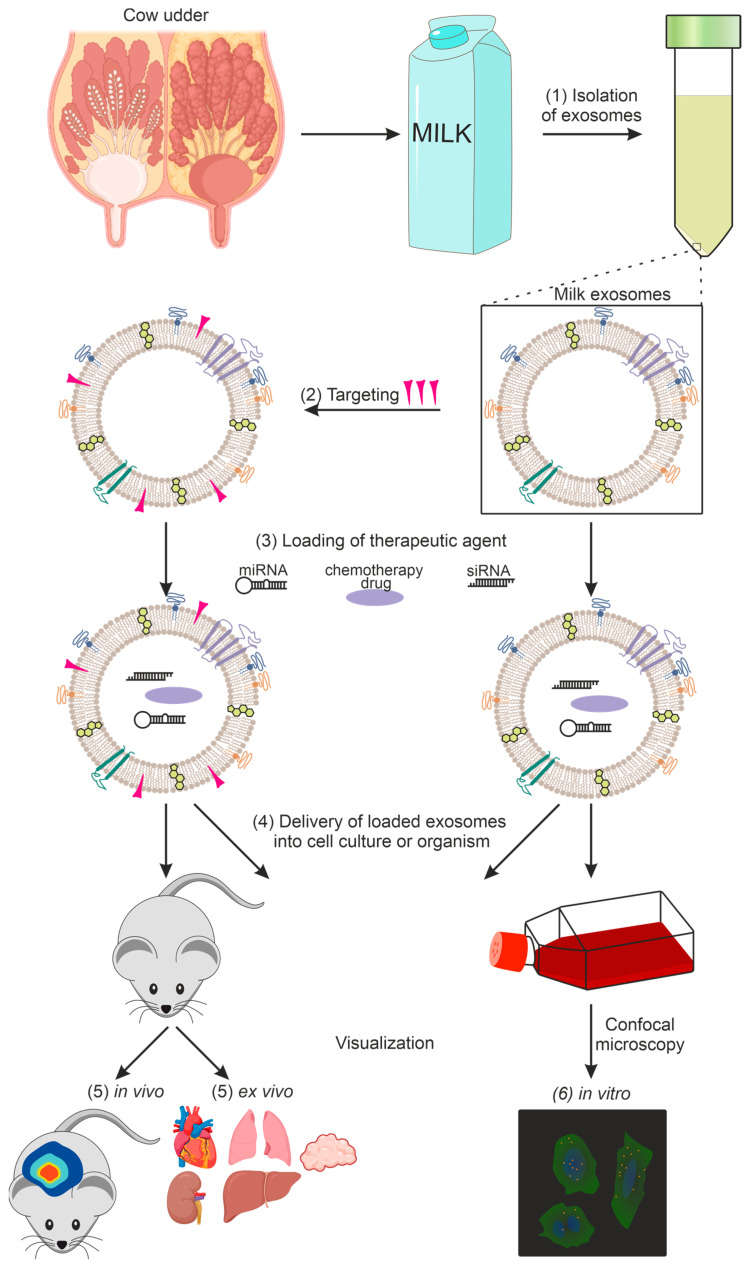
Application Spotlight: Milk Exosomes Cross the Intestinal Barrier
This analysis demonstrates the unique ability of bovine milk exosomes to survive digestion and enter systemic circulation, serving as a benchmark for oral delivery studies.
Featured Technologies:
- Pharmacokinetic Analysis
- Cargo Tracking (qPCR)
Literature Interpretation:
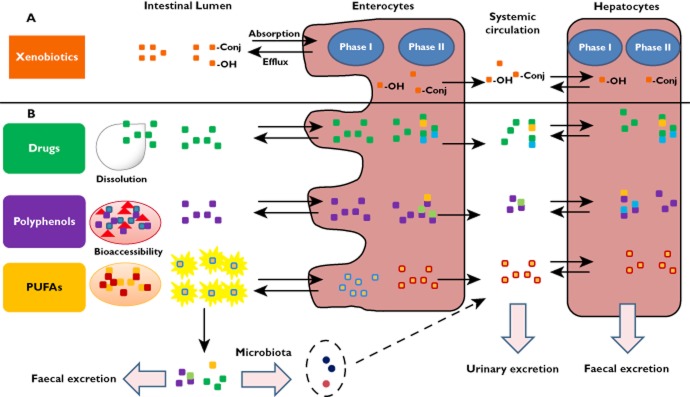
To determine if dietary exosomes actually enter the bloodstream or are simply digested, researchers orally administered bovine milk exosomes to mice and tracked the distribution of exosome-specific microRNAs. The study confirmed that milk exosomes possess remarkable bioavailability. Following oral intake, bovine-specific miRNAs accumulated in the liver, spleen, and brain within hours. The study further suggested that this uptake is likely mediated by the neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) in the gut epithelium, which recognizes surface proteins on the milk exosomes. This validates the feasibility of the oral route for exosome therapeutics and establishes the Caco-2/animal PK model as the standard for assessing absorption.
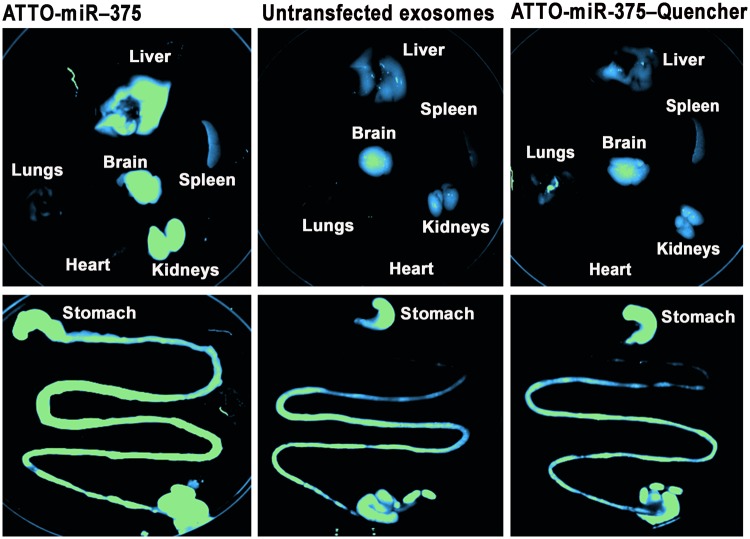 Figure 2. Dual-label assessment of microRNA degradation in mice using milk exosomes. (Manca S, et al., 2018)
Figure 2. Dual-label assessment of microRNA degradation in mice using milk exosomes. (Manca S, et al., 2018)
Start Your Oral Delivery Project
Navigating the complexities of the gastrointestinal tract requires precise modeling. We provide a clear, data-driven pathway to validate your oral delivery strategy.
How It Works: Our Project Pathway
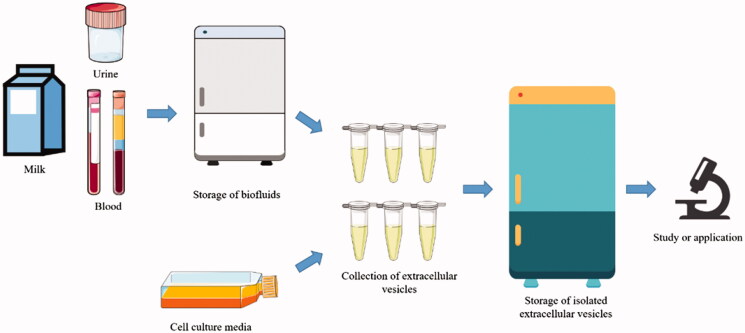
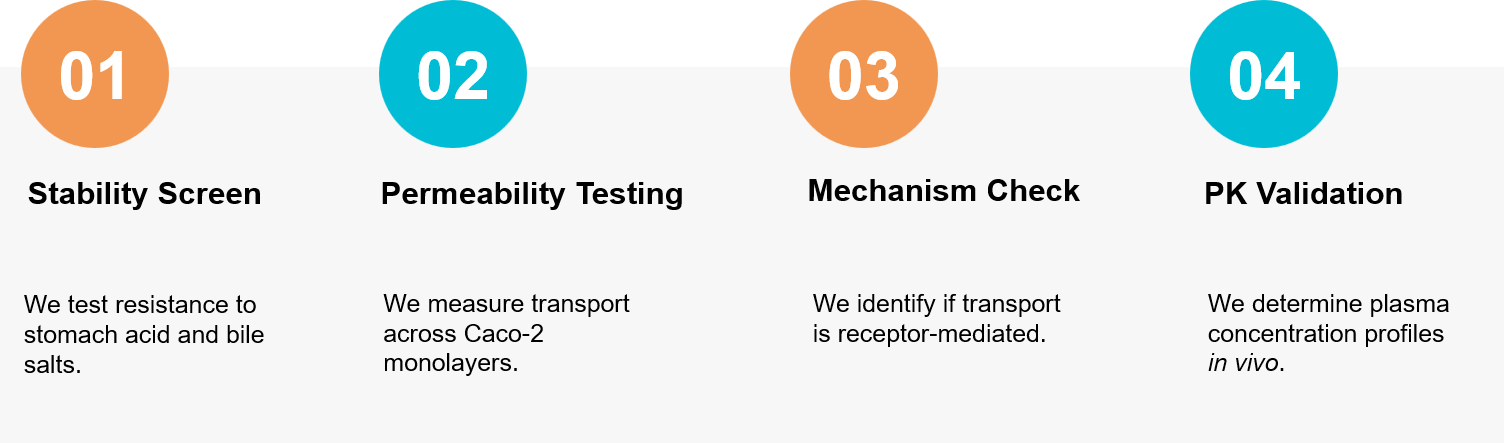 Figure 3. Our comprehensive workflow for assessing the gastrointestinal stability and intestinal absorption of orally administered exosomes. (Creative Biostructure)
Figure 3. Our comprehensive workflow for assessing the gastrointestinal stability and intestinal absorption of orally administered exosomes. (Creative Biostructure)
Ready to eliminate the guesswork from your oral formulation? Our scientists are available to discuss your specific absorption challenges. Contact us today to discuss your project.
References
- Ketabat F, Pundir M, Mohabatpour F, et al. Controlled Drug Delivery Systems for Oral Cancer Treatment-Current Status and Future Perspectives. Pharmaceutics. 2019 Jun 30;11(7):302.
- Manca S, Upadhyaya B, Mutai E, et al. Milk exosomes are bioavailable and distinct microRNA cargos have unique tissue distribution patterns. Sci Rep. 2018 Jul 27;8(1):11321.