Milk Derived Exosome Development
One of the biggest hurdles in exosome therapy is scalability. Human cells are expensive to culture and yield limited vesicles. Bovine Milk Exosomes, however, are abundant, cost-effective, and surprisingly compatible with the human body. They naturally survive the harsh acidic environment of the stomach, making them the premier candidate for oral drug delivery and nutritional carriers.
We provide specialized Milk Derived Exosome Development solutions. From scalable isolation using industrial dairy processing techniques to drug loading and safety validation, we help you transform bovine milk into a high-value source of therapeutic nanovesicles for oral biologics and functional foods.
The Advantages of Bovine Milk Exosomes
Why use milk? Because it is the only exosome source available at an industrial scale that is GRAS (Generally Recognized As Safe).
- Oral Bioavailability: Milk exosomes are evolutionarily designed to survive digestion to deliver immune signals from mother to offspring. This natural "armor" allows them to transport fragile cargos (like siRNA or peptides) across the gut barrier into systemic circulation.
- Massive Scalability: A single liter of milk contains ~1014 exosomes. Compared to cell culture media, milk offers a yield that is orders of magnitude higher and significantly cheaper.
- Cross-Species Compatibility: Bovine milk exosomes show remarkable homology with human vesicles. They are non-immunogenic and can be taken up by human cells, facilitating the delivery of therapeutic cargos without triggering allergic reactions (once casein is removed).
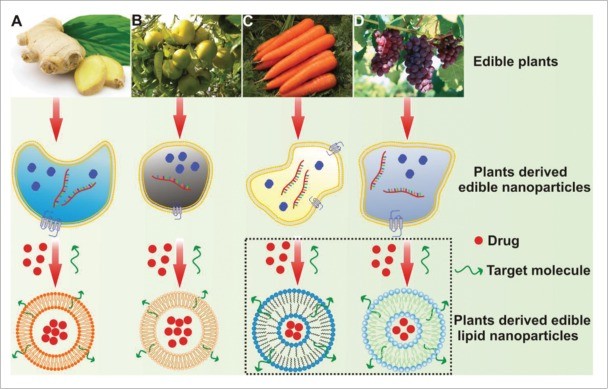
- Versatile Cargo: They can be loaded with both hydrophilic (siRNA, proteins) and hydrophobic (Curcumin, Paclitaxel) drugs, making them a universal platform.
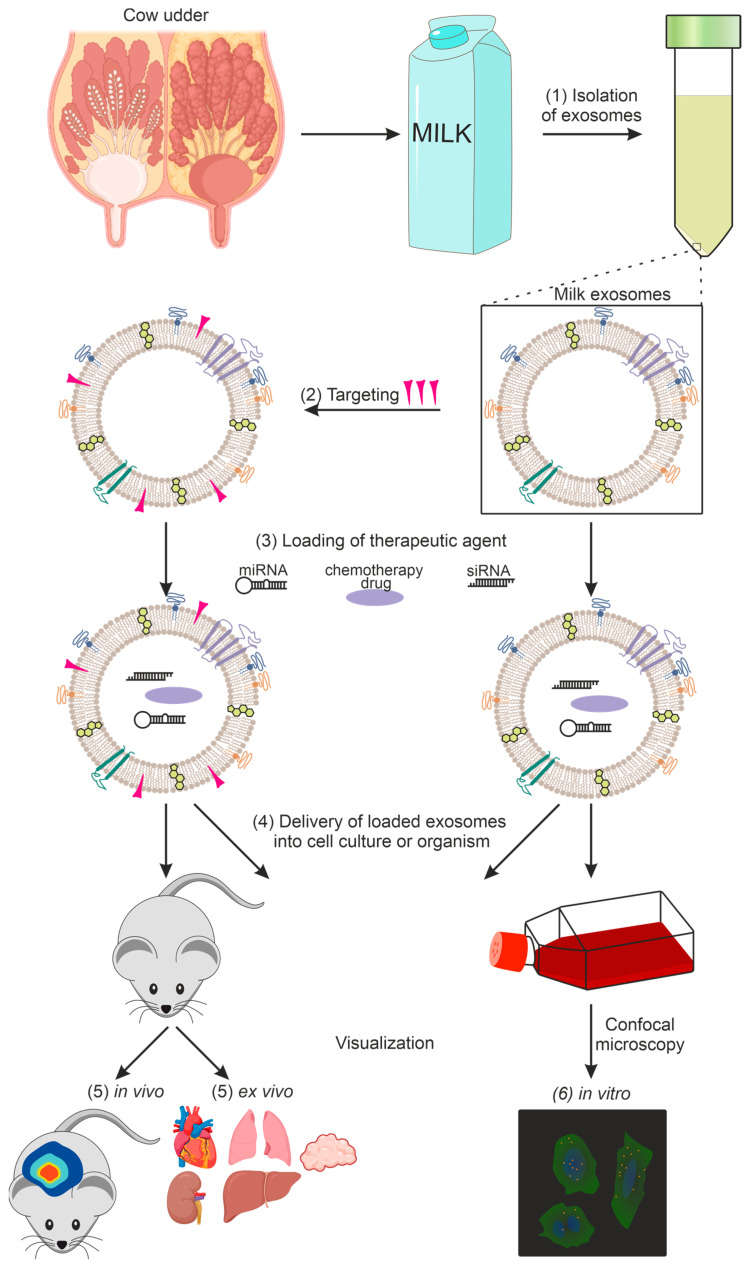 Figure 1. Exosome-based therapeutic delivery process including isolation, targeting, loading, delivery, and imaging. (Timofeeva AM, et al., 2023)
Figure 1. Exosome-based therapeutic delivery process including isolation, targeting, loading, delivery, and imaging. (Timofeeva AM, et al., 2023)
Our Milk Exosome Development Workflow
Processing milk requires specialized steps to remove abundant proteins like casein while preserving vesicle integrity.
| Discovery Phase | Our Specialized Approach & Solution | Key Services Applied |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-Processing | Casein Removal: Casein micelles mimic the size of exosomes. We employ Acid Precipitation (Isoelectric Point) and enzymatic treatment to efficiently remove casein and fat globules before isolation, preventing contamination. | Biofluid Exosome Isolation |
| Industrial Isolation | Tangential Flow Filtration (TFF): For large volumes, ultracentrifugation is impractical. We utilize industrial TFF systems to concentrate exosomes from liters of whey, providing a scalable process suitable for pilot production. | Exosome Isolation by Tangential Flow Filtration (TFF) |
| Cargo Loading | Active Encapsulation: We utilize Electroporation or Sonication to load your active ingredient (e.g., siRNA or small molecules) into the purified milk exosomes. We optimize loading efficiency to ensure maximum potency per dose. | Exosome Nucleic Acid Loading, Exosome Small Molecule Loading |
| Safety & Stability | Digestive Simulation: We test the loaded exosomes in Simulated Gastric Fluid (pH 2.0) to verify cargo protection. We also screen for potential allergens (residual Beta-lactoglobulin) to ensure food safety. | Exosome Contaminant Detection |
Core Technologies for Oral Delivery
We utilize specific technologies to validate the "Oral Route" for therapeutics.
Scalable TFF Isolation
From Liters to Grams: Isolating exosomes from milk is a volume game. Our customized TFF protocols allow us to process 10L-100L of bovine milk rapidly, removing lactose and soluble proteins while recovering high-purity exosomes. This makes it feasible to produce grams of exosome powder for animal studies or clinical trials.
Drug Loading Optimization
Turning Milk into Medicine: We specialize in loading difficult-to-deliver drugs. Whether it's a hydrophobic chemotherapy drug (like Paclitaxel) or a fragile nucleic acid (miRNA), we optimize the loading buffer and energy conditions to maximize encapsulation efficiency (>20%) without aggregating the vesicles.
Digestive Stability Assays
Survival Test: A carrier is useless if it dissolves in the stomach. We subject your loaded exosomes to a sequential digestion model (Pepsin/HCI -> Pancreatin/Bile). We quantify the remaining intact exosomes and the retention of the cargo, providing proof that your drug will reach the intestine.
Application Spotlight: Milk Exosomes as Oral Drug Carriers
This analysis demonstrates the groundbreaking potential of using bovine milk exosomes to deliver chemotherapy drugs orally, bypassing the need for injections.
Featured Technologies:
- Milk Exosome Drug Loading
- In Vivo Efficacy Testing
Literature Interpretation:
Many potent drugs (like Paclitaxel) have poor oral bioavailability and severe toxicity when injected. Researchers isolated exosomes from commercial bovine milk and loaded them with Paclitaxel. They administered these "Exo-Pac" formulations orally to mice with lung cancer. The oral milk exosomes successfully delivered the drug to the tumor site, inhibiting tumor growth significantly better than the free drug. Remarkably, the exosome formulation showed reduced systemic toxicity compared to the standard IV injection. This study confirms that bovine milk exosomes are a robust, biocompatible, and orally bioavailable drug delivery vehicle.
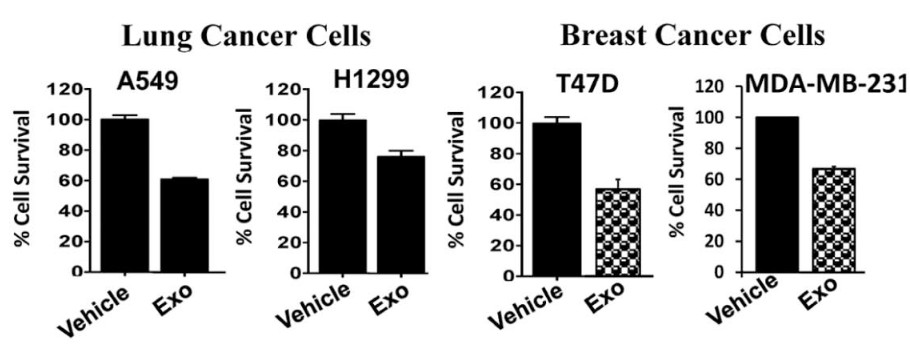 Figure 2. Milk exosomes inhibit proliferation of lung (A549 and H1299) and breast (T47D and MDA-MB-231) cancer cells, as measured by MTT assay after 72 hours of treatment with 50 μg/ml exosomal protein. (Munagala R, et al., 2016)
Figure 2. Milk exosomes inhibit proliferation of lung (A549 and H1299) and breast (T47D and MDA-MB-231) cancer cells, as measured by MTT assay after 72 hours of treatment with 50 μg/ml exosomal protein. (Munagala R, et al., 2016)
Start Your Oral Delivery Project
We make getting started straightforward. Our process is designed to be collaborative and transparent.
How It Works: Our Project Pathway
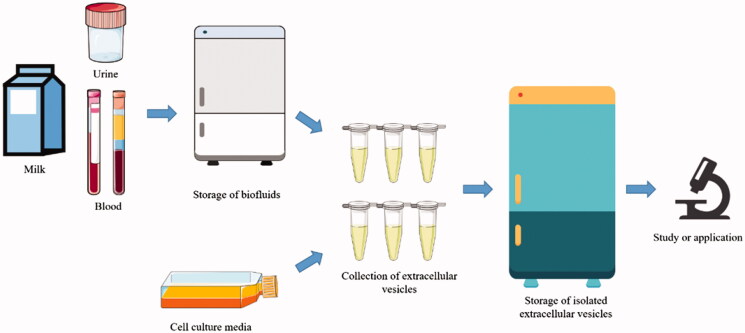
 Figure 3. Our industrial workflow for converting bovine milk into a scalable, orally bioavailable drug delivery system. (Creative Biostructure)
Figure 3. Our industrial workflow for converting bovine milk into a scalable, orally bioavailable drug delivery system. (Creative Biostructure)
Ready to bypass injections with an oral exosome solution? Our formulation scientists are available for a free consultation to discuss your specific drug delivery challenge. Contact us today to discuss your project.
References
- Timofeeva AM, Paramonik AP, Sedykh SS, et al. Milk Exosomes: Next-Generation Agents for Delivery of Anticancer Drugs and Therapeutic Nucleic Acids. Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 15;24(12):10194.
- Munagala R, Aqil F, Jeyabalan J, et al. Bovine milk-derived exosomes for drug delivery. Cancer Lett. 2016 Feb 1;371(1):48-61.