Kidney Disease Exosome Profiling Services
Kidney disease is often called a "silent killer" because traditional biomarkers like Serum Creatinine and BUN only rise after significant loss of renal function (often >50%). By then, structural damage like fibrosis is frequently irreversible. Exosomes offer a solution to this diagnostic lag. Abundant in urine, exosomes originating from podocytes and tubular cells provide a non-invasive "liquid biopsy" that mirrors the real-time status of the nephron, identifying injury at the molecular level long before functional decline.
We provide a holistic Kidney Disease Exosome Research Solution. Whether you are identifying early markers of Diabetic Nephropathy in urine, unraveling the mechanism of Renal Fibrosis (EMT), or testing the regenerative potential of MSC exosomes in AKI, our platform integrates specialized urinary isolation techniques, fibrosis models, and omics profiling to advance nephrology research.
Critical Frontiers in Nephrology Research
Current research focuses on overcoming the limitations of traditional renal markers and understanding the cellular crosstalk driving disease progression.
- The Diagnostic "Blind Spot": Current markers (Creatinine/Proteinuria) are lagging indicators. There is an urgent need for sensitive biomarkers (e.g., exosomal NGAL, KIM-1, or podocyte-specific miRNAs) that detect Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) or early Diabetic Kidney Disease (DKD) before tissue damage becomes permanent.
- Podocyte Injury & Loss: Podocytes are incapable of regeneration. Their detachment or injury is a key initiating event in focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) and DKD. Tracking "podocyte-derived exosomes" in urine is considered the holy grail for monitoring glomerular health non-invasively.
- Renal Fibrosis (The Final Pathway): Regardless of the primary cause, Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) progresses via fibrosis. Investigating the crosstalk between injured tubular epithelial cells and fibroblasts (via exosomes) is key to understanding Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) and collagen deposition.
- Tubulointerstitial Inflammation: Research is mapping how exosomes released by stressed tubular cells recruit macrophages and promote a pro-inflammatory microenvironment, accelerating the maladaptive transition from AKI to CKD.
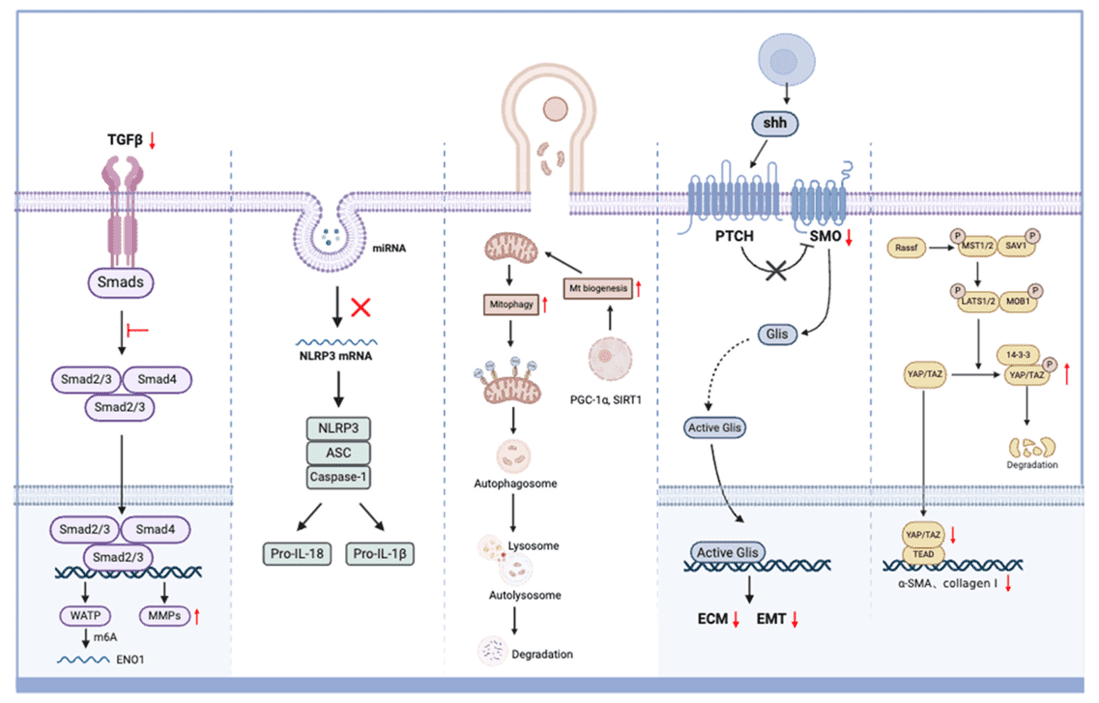 Figure 1. Signal pathways involved in MSC-mediated treatment of DKD, highlighting MSC effects on TGF-β, EMT, NLRP3, mitochondrial quality, and ECM regulation. (Cheng J, et al., 2024)
Figure 1. Signal pathways involved in MSC-mediated treatment of DKD, highlighting MSC effects on TGF-β, EMT, NLRP3, mitochondrial quality, and ECM regulation. (Cheng J, et al., 2024)
Comprehensive Service Portfolio for Kidney Disease
We offer an integrated matrix of services tailored to address these nephrology challenges, from non-invasive discovery to therapeutic validation.
| Research Focus | Our Specialized Approach & Solution | Key Services Applied |
|---|---|---|
| Early Diagnosis (Biomarkers) | Urinary Exosome Profiling: We isolate exosomes from urine (removing Tamm-Horsfall protein interference) and profile miRNAs or proteins to detect early tubular or glomerular injury. | Biofluid Exosome Isolation |
| Fibrosis & EMT (Phenotype) | Cellular Functional Assays: We utilize TGF-beta induced EMT models (HK-2 cells). We treat cells with exosomes and measure phenotypic changes (e.g., E-cadherin loss, migration) to assess anti-fibrotic efficacy. | In Vitro Exosome Functional Assays |
| Mechanism Verification (Target) | miRNA Target Validation: How do exosomal miRNAs protect podocytes? We use Dual Luciferase Reporter Assays to verify if a specific miRNA binds to the 3'UTR of fibrosis/apoptosis-related genes. | Exosome Dual-luciferase Reporter Gene Assay |
| In Vivo Efficacy (Animal Models) | AKI & CKD Models: We perform UUO (Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction) for fibrosis or Ischemia-Reperfusion (IRI) for AKI. We evaluate renal function (BUN/Cr) and fibrosis (Masson's Trichrome). | In Vivo Exosome Functional Assays |
Featured Technologies for Nephrology
High-Throughput Urinary Exosome Isolation Platform (TFF & SEC)
We utilize a state-of-the-art Tangential Flow Filtration (TFF) system combined with Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC) to address the challenges of processing large-volume urine samples inherent to nephrology research. This industrial-grade platform is capable of processing sample volumes from 0.5 L up to 500 L, effectively concentrating dilute urinary exosomes while minimizing pore clogging and removing non-vesicular contaminants. Unlike traditional ultracentrifugation, this method maintains the structural integrity and biological activity of the exosomes, ensuring high-quality input for downstream functional studies.
Nanoscale Single-Vesicle Analysis Engine (NanoFCM)
Our Nano-Flow Cytometry (NanoFCM) technology provides a high-resolution solution for characterizing kidney-derived exosomes, overcoming the limitations of conventional flow cytometry. With a detection limit as low as 40 nm , this system allows for the simultaneous assessment of particle size distribution, concentration, and phenotypic analysis of surface proteins (e.g., CD9, CD63, CD81). This precise profiling capability is critical for distinguishing specific exosome subpopulations released by podocytes or renal tubular cells from complex urine matrices.
Deep-Dive Multi-Omics Discovery Pipeline
To facilitate the discovery of novel biomarkers for renal diseases such as CKD and AKI, we employ a comprehensive multi-omics platform featuring DIA (Data-Independent Acquisition) Proteomics and Full-Length Transcriptome Sequencing. The DIA technology divides the mass spectrometry scan range into fixed windows to fragment all precursors, achieving near-complete and unbiased coverage of low-abundance proteins. Complemented by high-throughput sequencing that captures miRNAs, mRNAs, and lncRNAs, this pipeline generates high-dimensional data essential for elucidating disease mechanisms.
Application Spotlight: Urinary Exosomes Reveal Diabetic Injury
This case study demonstrates the power of urinary exosomes as a non-invasive window into the kidney, detecting damage before standard clinical markers.
Featured Technologies:
- Urinary Exosome Isolation
- Small RNA Sequencing
Literature Interpretation:
Diabetic Nephropathy (DN) is often diagnosed too late. Researchers aimed to find early diagnostic markers in urine. By isolating exosomes from the urine of Type 2 Diabetes patients and performing Small RNA Sequencing, they identified a specific panel of miRNAs (including miR-4534) that were significantly upregulated in patients with early-stage DN compared to those without nephropathy. Crucially, these exosomal miRNA levels correlated with the degree of tubular injury and glomerular filtration rate (GFR) better than albuminuria. This study validates that urinary exosome cargo reflects specific pathological changes in the kidney, supporting our platform for non-invasive biomarker discovery.
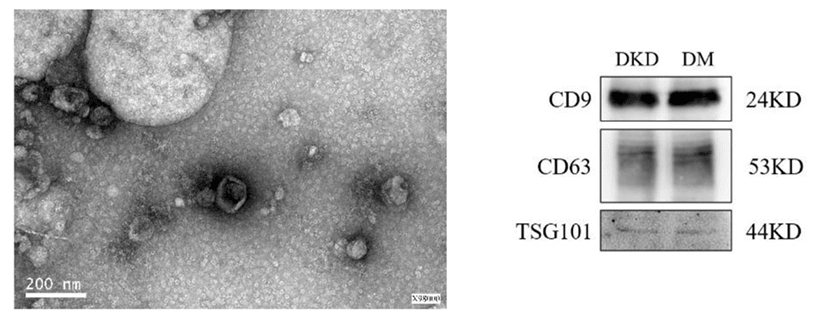 Figure 2. Electron microscopy images of exosomes and their characterization using specific markers. Exosomes appear cup-shaped and under 200 nm in diameter, with detectable markers CD9, CD63, and TSG101 in DKD and DM groups. (Zhao Y, et al., 2020)
Figure 2. Electron microscopy images of exosomes and their characterization using specific markers. Exosomes appear cup-shaped and under 200 nm in diameter, with detectable markers CD9, CD63, and TSG101 in DKD and DM groups. (Zhao Y, et al., 2020)
Start Your Kidney Research Project
Leverage our comprehensive platform to accelerate your discovery, from urinary biomarkers to anti-fibrotic therapies.
How It Works: Our Project Pathway
 Figure 3. Workflow for discovering urinary biomarkers, elucidating fibrosis mechanisms (EMT), and validating therapeutic efficacy in kidney disease models. (Creative Biostructure)
Figure 3. Workflow for discovering urinary biomarkers, elucidating fibrosis mechanisms (EMT), and validating therapeutic efficacy in kidney disease models. (Creative Biostructure)
Ready to find the next breakthrough in AKI or CKD? Our nephrology experts are available to build a custom study plan tailored to your needs. Contact us today to discuss your project.
References
- Cheng J, Zhang C. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy: Therapeutic Opportunities and Challenges for Diabetic Kidney Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 30;25(19):10540.
- Zhao Y, Shen A, Guo F, et al. Urinary Exosomal MiRNA-4534 as a Novel Diagnostic Biomarker for Diabetic Kidney Disease. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020 Aug 28;11:590.