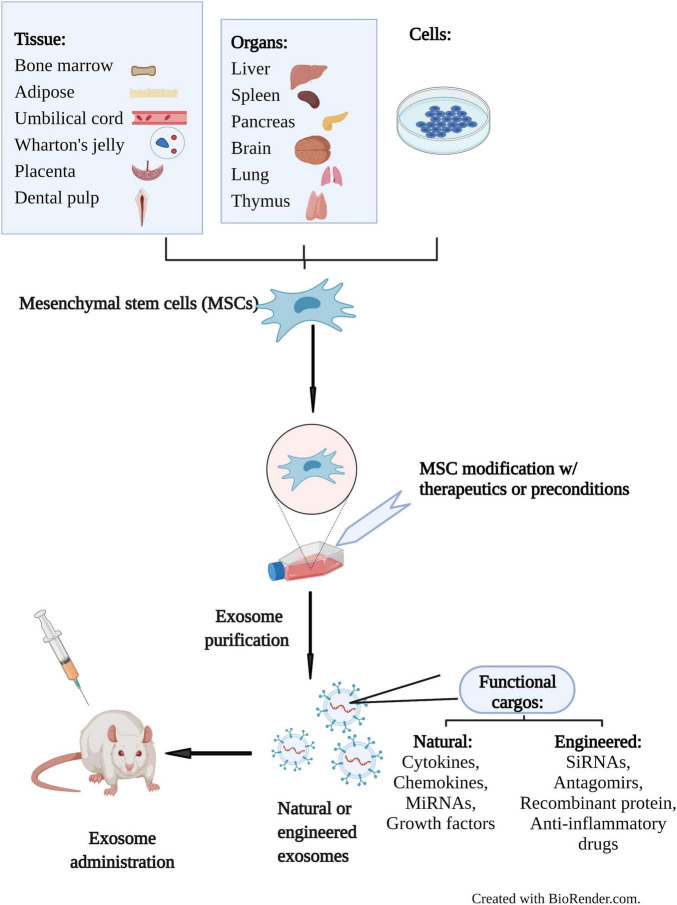
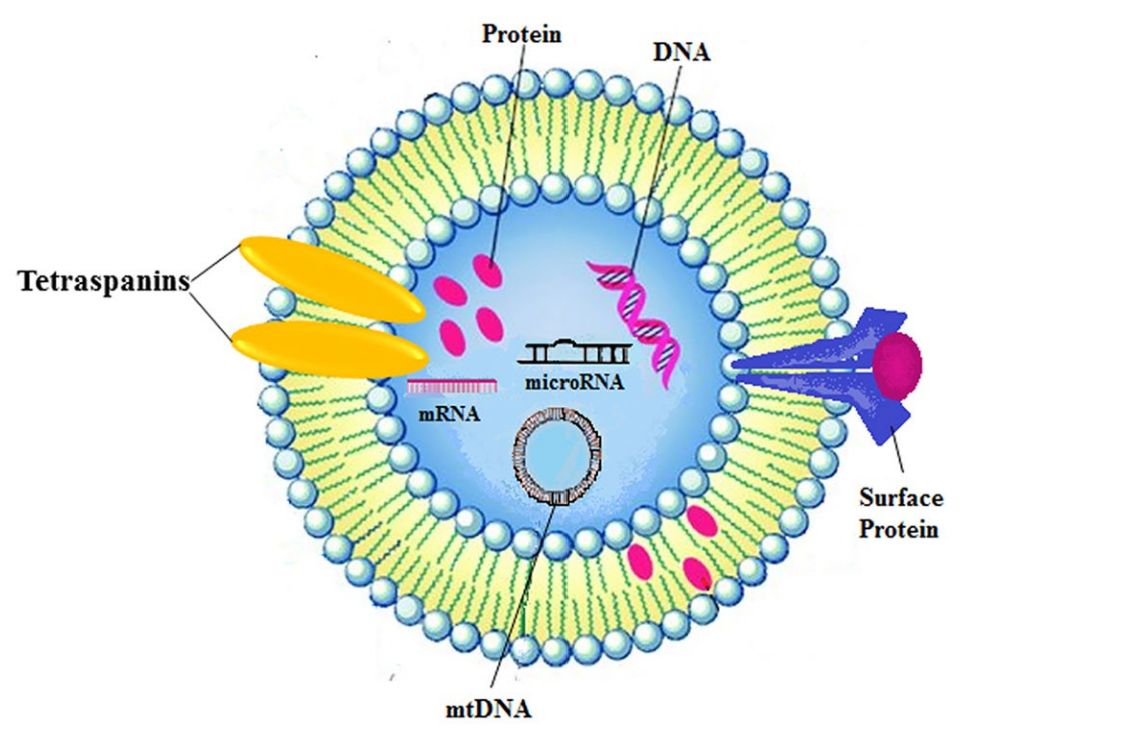
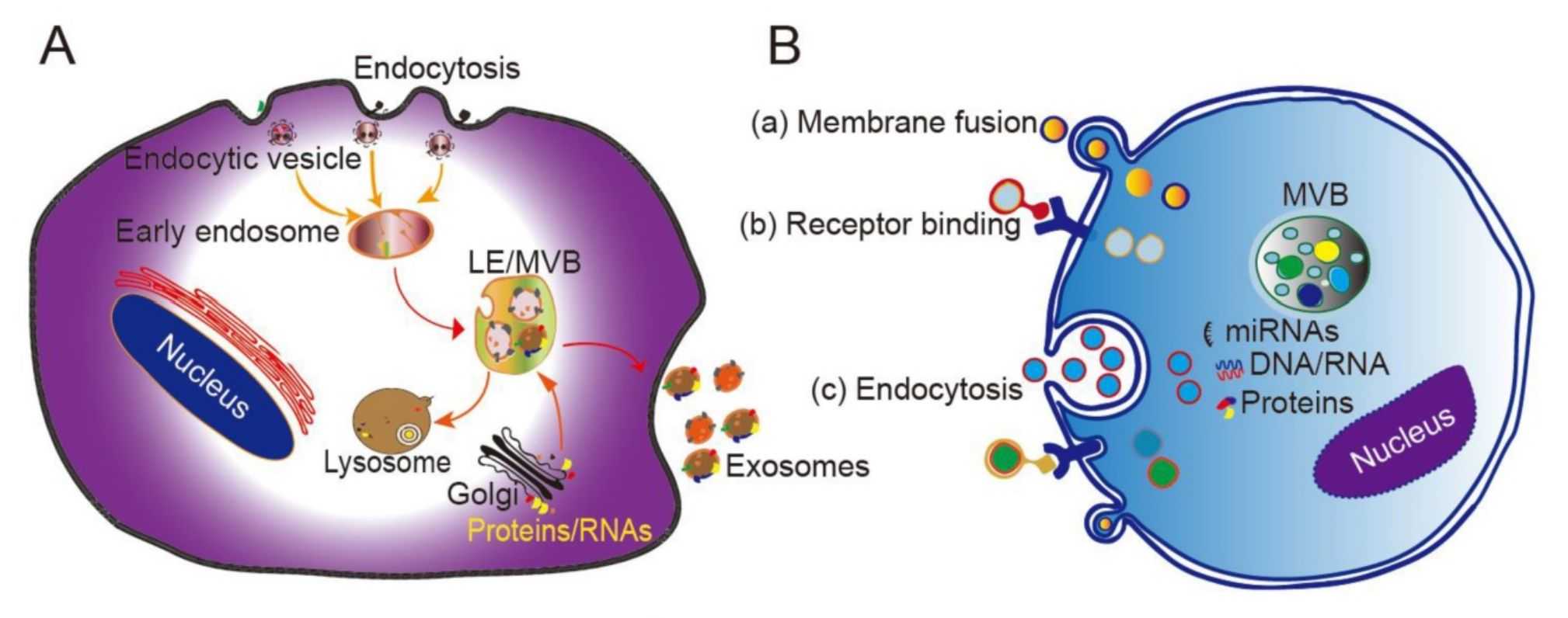
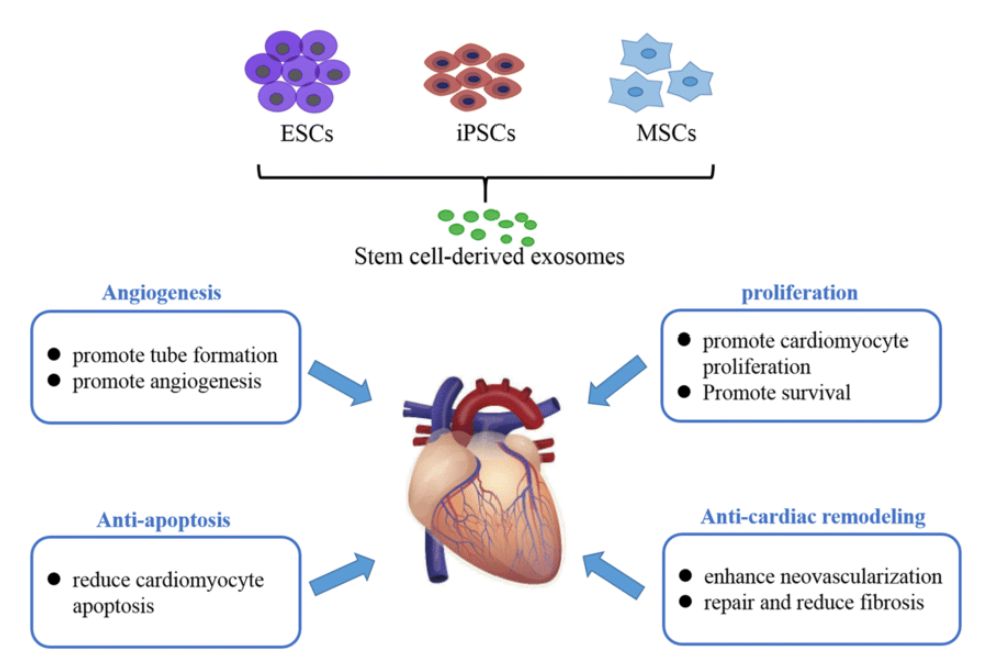
Exosome Tracing and Tracking Services
Exosome tracing is a vital experimental technique used to visualize and monitor the journey of exosomes. It allows researchers to answer critical questions about an exosome's fate: where do they go, which cells do they target, and what is their pathway of internalization? This process can be monitored in vitro (in cell culture) or in vivo (in a living animal).
Why Perform Exosome Tracing and Tracking?
A functional assay tells you what your exosomes do, but a tracking assay tells you where they do it. For any exosome-based therapeutic or targeted drug delivery system, demonstrating specific homing and biodistribution is non-negotiable.
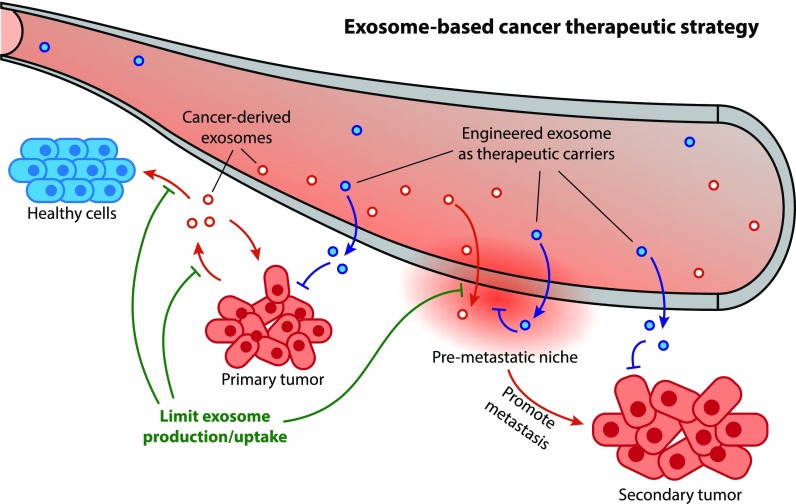
- Validate Targeted Delivery: In vivo exosome tracking provides visual, definitive proof that your engineered exosomes are homing to the target tumor or organ, not just accumulating in the liver or spleen.
- Elucidate Biological Pathways: Use live-cell imaging to understand the how and where of cellular uptake. Does your exosome internalize and co-localize with the endosome? This provides critical mechanistic data.
- Guide In Vivo Efficacy Studies: Before running a complex and expensive in vivo efficacy study (part of our In Vivo Exosome Functional Assays), a biodistribution study confirms the exosome reaches the target, de-risking the project.
- Understand Inter-organ Communication: For basic research, tracking endogenous exosomes in vivo helps reveal their role in complex biological processes, such as in vivo tracking of macrophage exosomes.
![]() Figure 1. Schematic overview of in vivo exosome imaging modalities and labeling strategies. (Hong S, et al., 2025)
Figure 1. Schematic overview of in vivo exosome imaging modalities and labeling strategies. (Hong S, et al., 2025)
Our Exosome Tracing and Tracking Portfolio
Our platform is designed to provide high-resolution visual evidence of your exosome's biological pathway, from dynamic intracellular movement to whole-body biodistribution.
In Vitro Exosome Tracking (Live-Cell Imaging)
This service focuses on the dynamic, real-time visualization of exosome uptake, distinct from the endpoint quantification offered in our Exosome Cellular Functional Assays. We answer how and where your exosomes are internalized.
- Live-Cell Confocal Microscopy:
- Service: We use high-resolution confocal microscopy to perform live tracking of your fluorescently labeled exosomes (e.g., exosomes stained with cell tracker) as they are internalized by recipient cells. This allows for dynamic monitoring of the entire uptake process.
- Key Readouts: Time-lapse videos of internalization, co-localization analysis with endosomes or lysosomes (e.g., LysoTracker), and 3D reconstruction of exosome localization.
- High-Content Imaging (HCI) Uptake:
- Service: An automated, high-throughput imaging platform to screen and quantify exosome uptake. This is ideal for comparing the targeting efficiency of multiple engineered exosome candidates simultaneously.
- Key Readouts: Quantified fluorescence intensity per cell, number of fluorescent puncta, and comparative uptake efficiency scores.
In Vivo Exosome Tracking (Biodistribution)
This is the core of our exosome tracking in vivo service, designed to map the systemic fate of your exosomes in animal models.
- Optical Imaging (Fluorescence / Bioluminescence):
- Service: We use your pre-labeled exosomes (with NIR dyes like DiR or bioluminescent reporters like Luciferase). Exosomes are administered to animal models (e.g., tumor-bearing mice), and their whole-body biodistribution is monitored over time using an in vivo imaging system (IVIS).
- Key Readouts: Time-course images showing exosome accumulation in target organs or tumors (e.g., at 2h, 4h, 24h, 48h).
- Ex Vivo Organ Validation:
- Service: Following the final in vivo imaging time point, we perform a terminal study. Major organs (liver, spleen, lung, kidney, brain, tumor) are harvested, and their fluorescent or bioluminescent signal is quantified. This provides precise, quantitative data on final exosome accumulation.
- Key ReadDouts: Quantitative graph of Radiant Efficiency (fluorescence) per organ.
- Radionuclide Imaging (PET/SPECT) Support:
- Service: For deep-tissue quantification, we are equipped to support studies using exosomes labeled with radionuclides (e.g., ⁸⁹Zr, ⁶⁴Cu). This enables high-resolution, tomographic in vivo tracking via PET or SPECT imaging for superior quantitation.
Prerequisite: Exosome Labeling
To be visualized, your exosomes must first be stablely labeled with a fluorescent or bioluminescent reporter. Our Exosome Tracing and Tracking Services are performed on client-provided, pre-labeled exosomes.
This prerequisite is essential as it ensures that the signal we are tracking originates from your exosomes and not from free, unbound dye.
For clients who require labeling, please inquire about our related labeling services.
Our End-to-End Project Workflow
We manage every step, from selecting the right imaging modality to acquiring the final biodistribution images.
Key Service Steps
Strategy & QC
We consult with you on the optimal strategy (e.g., NIR dye for in vivo, GFP for in vitro) and perform critical QC on your pre-labeled exosomes to ensure removal of free dye.
Dynamic In Vitro Imaging
For in vitro studies, we perform live-cell imaging on high-sensitivity confocal systems to capture the internalization pathway in real-time.
In Vivo & Ex Vivo Analysis
For in vivo studies, we manage the full animal protocol, including exosome administration, time-course IVIS imaging, and final ex vivo organ harvest and quantification.
Project Workflow (For Flowchart)
![]() Figure 2. Exosome Tracing and Tracking Service Project Workflow. (Creative Biostructure)
Figure 2. Exosome Tracing and Tracking Service Project Workflow. (Creative Biostructure)
Sample Requirements
Client-Provided Labeled Exosomes:
- Quantity: ≥ 1x10¹² particles (highly dependent on labeling method and in vivo study design; please inquire).
- Purity: Purified, pre-labeled exosomes are required. Free dye must be removed.
- Buffer: Suspended in sterile PBS.
Client-Provided Cell Lines:
- For in vitro tracking: Target recipient cell lines.
- For genetic labeling: Exosomes from parent cell line already expressing the reporter (e.g., CD63-GFP).
Standard Deliverables
A Comprehensive Project Report: Details the imaging parameters, animal models, and a full scientific interpretation of the tracking data.
Raw and Analyzed Data: All raw images (IVIS, confocal) and processed data files.
Publication-Ready Figures:
- In Vitro: High-resolution confocal images, co-localization maps, and time-lapse videos (if applicable).
- In Vivo: Time-course IVIS images of animal biodistribution.
- Ex Vivo: Ex vivo organ imaging panel and quantitative graphs of signal intensity per organ.
Scientific Consultation: A final meeting to discuss the biodistribution results and their implications for your therapeutic program.
Case Study
Case: In Vivo Tracking Shows Pancreatic Cancer Exosomes Target Tumors
Background: Researchers hypothesized that exosomes derived from pancreatic cancer (PC) cells might have an intrinsic tropism (natural homing) towards their cells of origin. To test this, they needed to perform in vivo exosome tracking.
Methodology & Findings: Exosomes from PANC-1 (pancreatic cancer) cells were labeled with a fluorescent dye. These labeled exosomes were injected into mice bearing two different tumor types: a PANC-1 tumor and a B16-F10 melanoma tumor.
- In Vivo Tracking: In vivo biodistribution studies showed that the PANC-1-derived exosomes preferentially accumulated in the PANC-1 tumor mass.
- Ex Vivo Validation: Ex vivo analysis of the harvested tumors confirmed this finding, showing favored accumulation in the "self-tissue" (PANC-1) tumor over the melanoma tumor.
Conclusion: This study successfully used in vivo and ex vivo tracking to provide direct evidence of an exosome's intrinsic tumor-homing properties. This demonstrates the critical value of exosome tracking in vivo to validate a targeted delivery strategy before loading the exosome with a therapeutic drug.
![]() Figure 3. In vivo organ biodistribution of PANC-1 Exo in tumour-bearing NSG mice. Ex vivo imaging showed higher liver accumulation of Exo compared to free dye. (Xu L, et al., 2020)
Figure 3. In vivo organ biodistribution of PANC-1 Exo in tumour-bearing NSG mice. Ex vivo imaging showed higher liver accumulation of Exo compared to free dye. (Xu L, et al., 2020)
Ready to map where your exosomes go and how they get there? We design in vitro and in vivo tracing studies, confirm uptake and co-localization, and quantify biodistribution with clear visuals. Contact us for a free consultation and a tailored imaging plan.
References
- Hong S, Jo HC, Kim HL, et al. In vivo exosome imaging: applications of diverse visualization techniques. BMB Rep. 2025 Aug;58(8):340-349.
- Xu L, Faruqu FN, Liam-Or R, et al. Design of experiment (DoE)-driven in vitro and in vivo uptake studies of exosomes for pancreatic cancer delivery enabled by copper-free click chemistry-based labelling. J Extracell Vesicles. 2020 Jun 19;9(1):1779458.
Frequently Asked Questions
For any inquiries, our support team is ready to help you get technical support for your research and maximize your experience with Creative Biostructure.