Exosome Transcriptome Profiling Services
Exosomal RNA has emerged as one of the most informative and non-I nvasive molecular windows into cellular function, disease progression, and therapeutic response. To help researchers decode this rich layer of biological information, Creative Biostructure offers Exosome Transcriptome Profiling Services, a suite of specialized next-generation sequencing (NGS) and microarray solutions optimized for the unique challenges of extracellular vesicle (EV) RNA.
Our platform integrates high-purity exosome isolation, low-input RNA library preparation, deep sequencing, and advanced bioinformatics, enabling comprehensive exploration of mRNA, miRNA, lncRNA, circRNA, and whole-transcriptome signatures across diverse sample types.
Why Profile Exosomal RNA
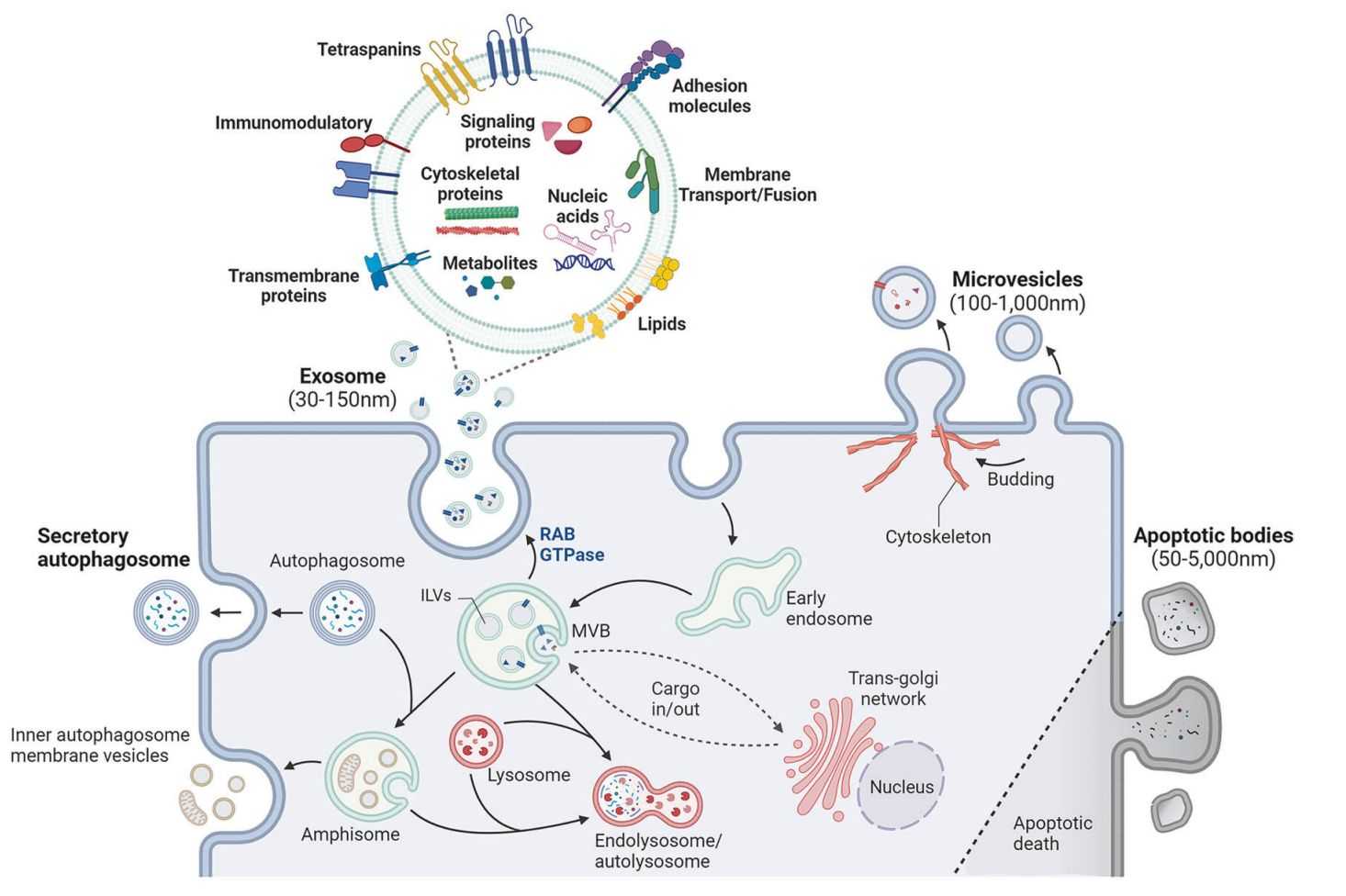
Exosomes carry a selective cargo of nucleic acids, proteins, metabolites, and lipids that reflect the physiological and pathological state of their originating cells. Exosomal RNA is particularly valuable because:
- It enables non-invasive biomarker discovery using plasma, urine, CSF, saliva, and other biofluids
- It reflects dynamic intercellular communication, including immune regulation and tumor-stromal signaling
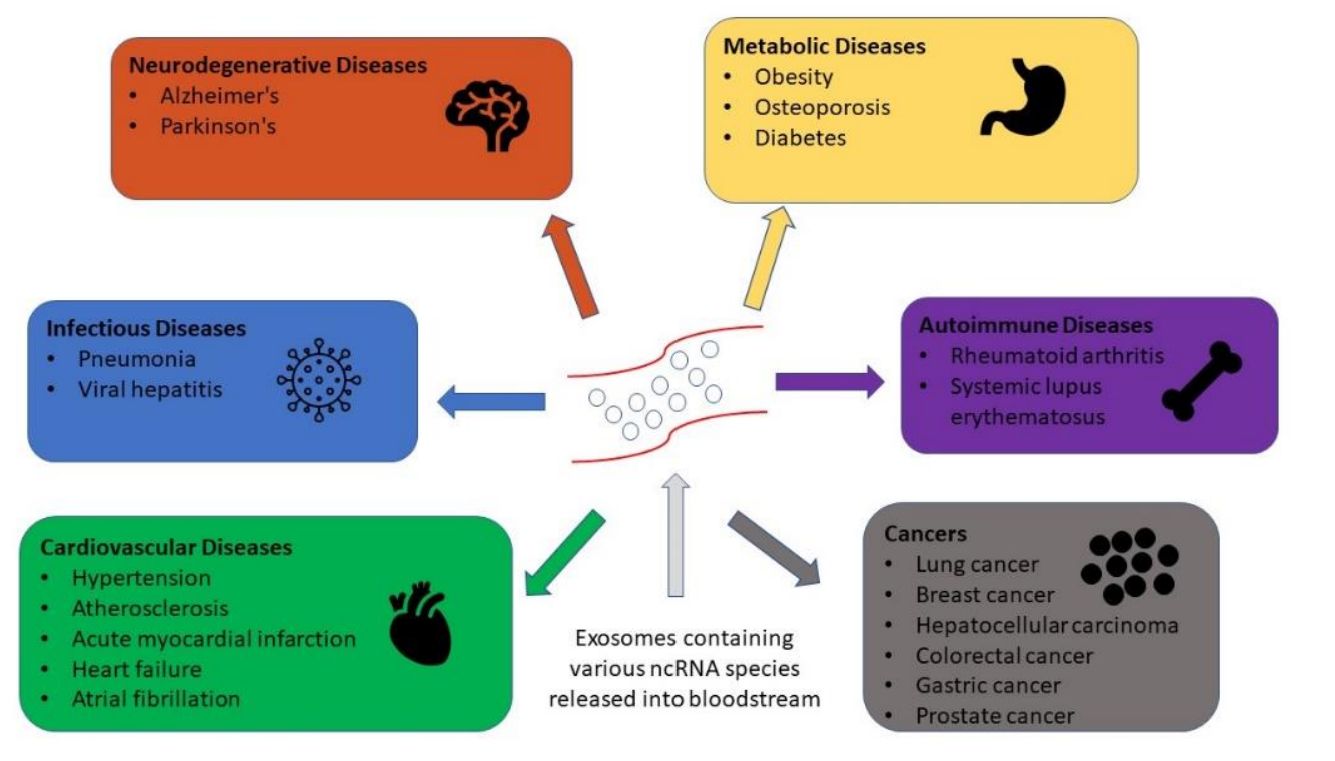
- It captures early molecular changes in cancer, neurodegeneration, cardiovascular disorders, inflammation, and infectious disease
- It is protected from degradation by the vesicle membrane, improving stability compared to cell-free RNA
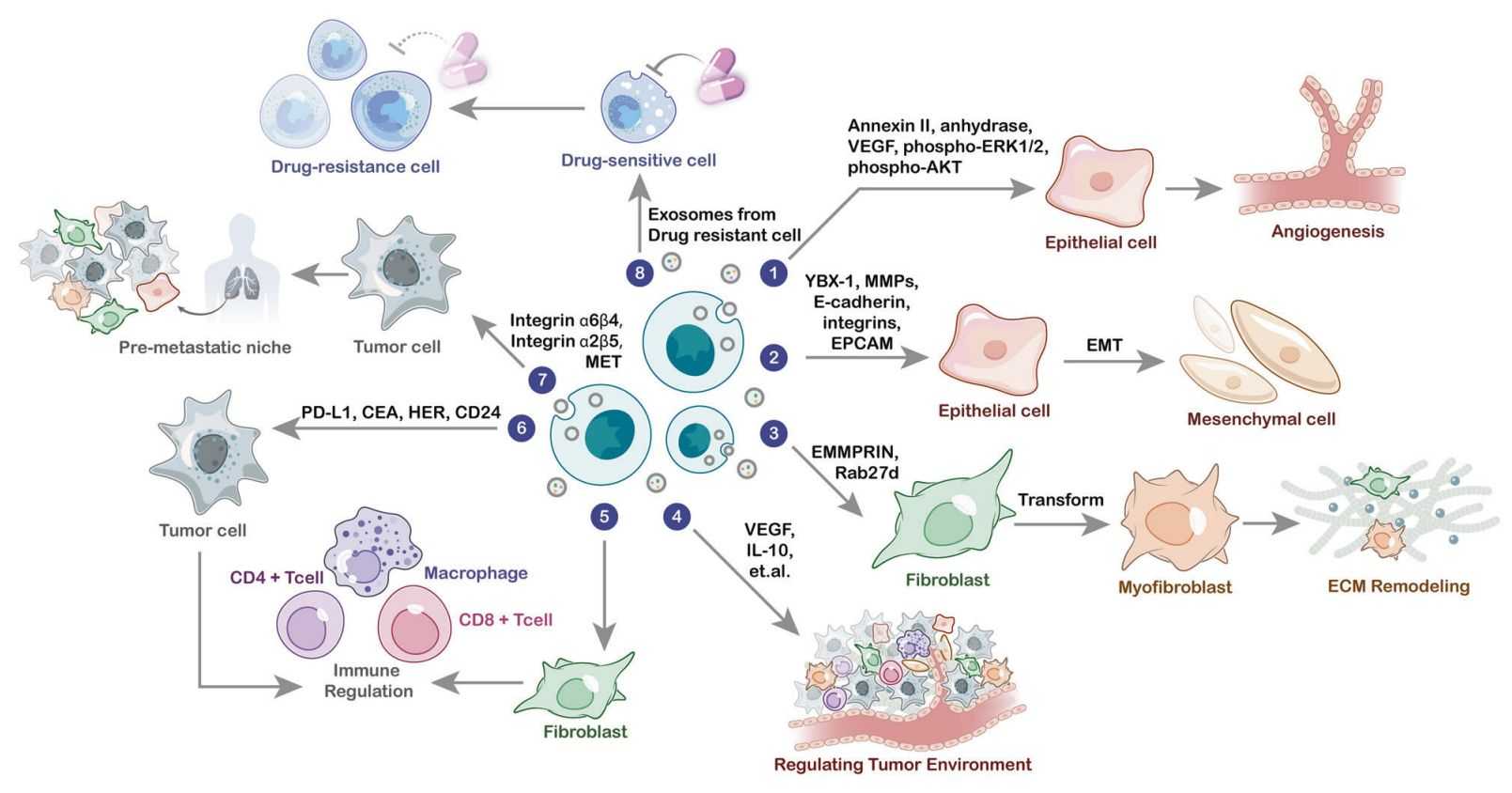
- It provides insights into therapeutic response, resistance mechanisms, and longitudinal monitoring
Together, these advantages make exosomal transcriptomics a powerful tool for precision research and translational discovery.
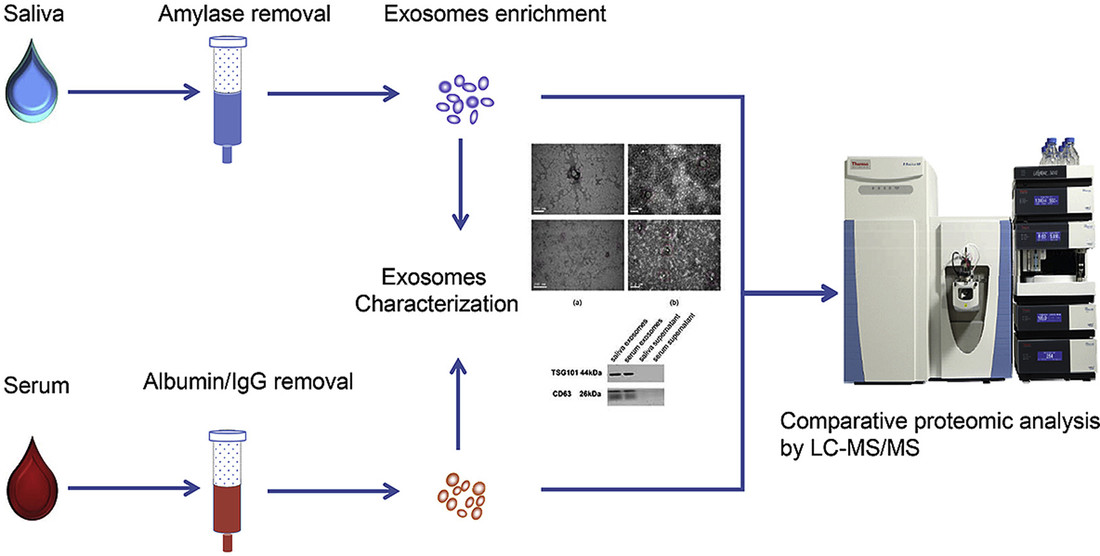
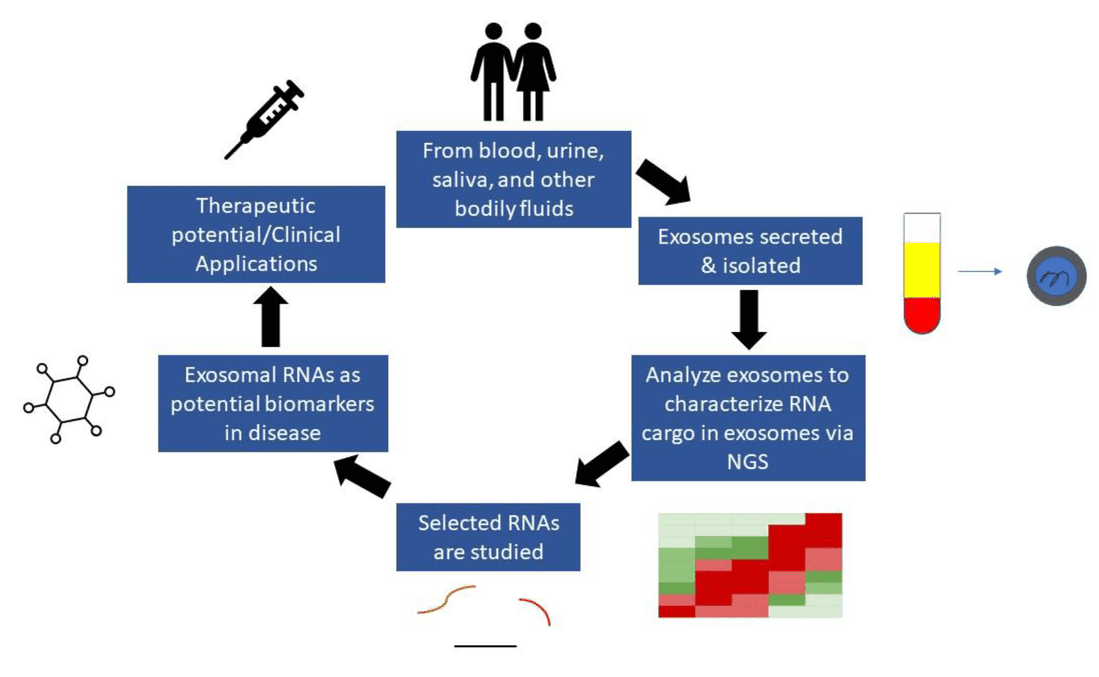 Figure 1. Exosome RNA Biomarker Discovery via NGS. (Elkommos-Zakhary M, et al., 2022)
Figure 1. Exosome RNA Biomarker Discovery via NGS. (Elkommos-Zakhary M, et al., 2022)
Our Exosomal Transcriptome Sequencing Portfolio
Creative Biostructure provides a complete set of specialized NGS and array services, each built for the distinct characteristics of different exosomal RNA classes:
Exosomal Small RNA & miRNA Sequencing
High-sensitivity detection of small RNAs (miRNA, piRNA, snoRNA, etc.) with optimized adapters and low-input workflows.
Exosomal mRNA Sequencing
Quantification of coding transcripts, low-abundance mRNA species, and pathway-level activation.
Exosomal lncRNA Sequencing
Deep profiling of non-coding transcripts involved in gene regulation, chromatin remodeling, and disease mechanisms.
Exosomal circRNA Sequencing
Circular RNA enrichment and identification using specialized algorithms and RNase-R–based workflows.
Exosomal Whole Transcriptome Sequencing (RNA-seq)
Full coverage of coding and non-coding RNA, delivering the broadest view of exosomal transcriptional activity.
Exosomal RNA Microarray Profiling
Cost-effective expression profiling for targeted panels or large cohort studies.
Standard Workflow
Our exosome transcriptome analysis pipeline has been optimized for low-input and highly fragmented RNA, ensuring maximum coverage and accuracy.
Preprocessing and exosome characterization
We isolate exosomes, assess size and concentration by NTA, confirm morphology by TEM or Cryo EM, verify markers such as CD9 CD63 CD81, and treat with RNase to remove free RNA.
RNA extraction
We extract total exosomal RNA using low input methods that recover both small and long RNA species, then perform DNase treatment and cleanup to remove genomic DNA and inhibitors before library preparation.
Library construction
We prepare libraries tailored to each RNA class, including small RNA libraries with size selection, long RNA libraries after rRNA depletion or polyA capture, circRNA enrichment, or total RNA libraries for whole transcriptome studies.
High throughput sequencing
Libraries are sequenced on Illumina instruments with read length and depth adjusted to project goals, providing reliable detection of low abundance exosomal transcripts and accurate quantification across samples.
Bioinformatics and data reporting
Our pipeline performs quality control, alignment, quantification, and normalization, then identifies differentially expressed RNAs, explores functional enrichment, builds regulatory networks, and delivers clear figures and reports.
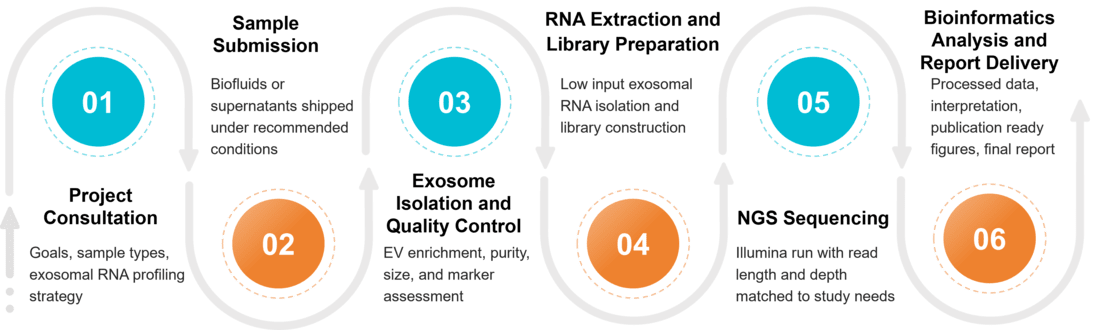 Figure 2. Project Workflow for Exosome Transcriptome Profiling. (Creative Biostructure)
Figure 2. Project Workflow for Exosome Transcriptome Profiling. (Creative Biostructure)
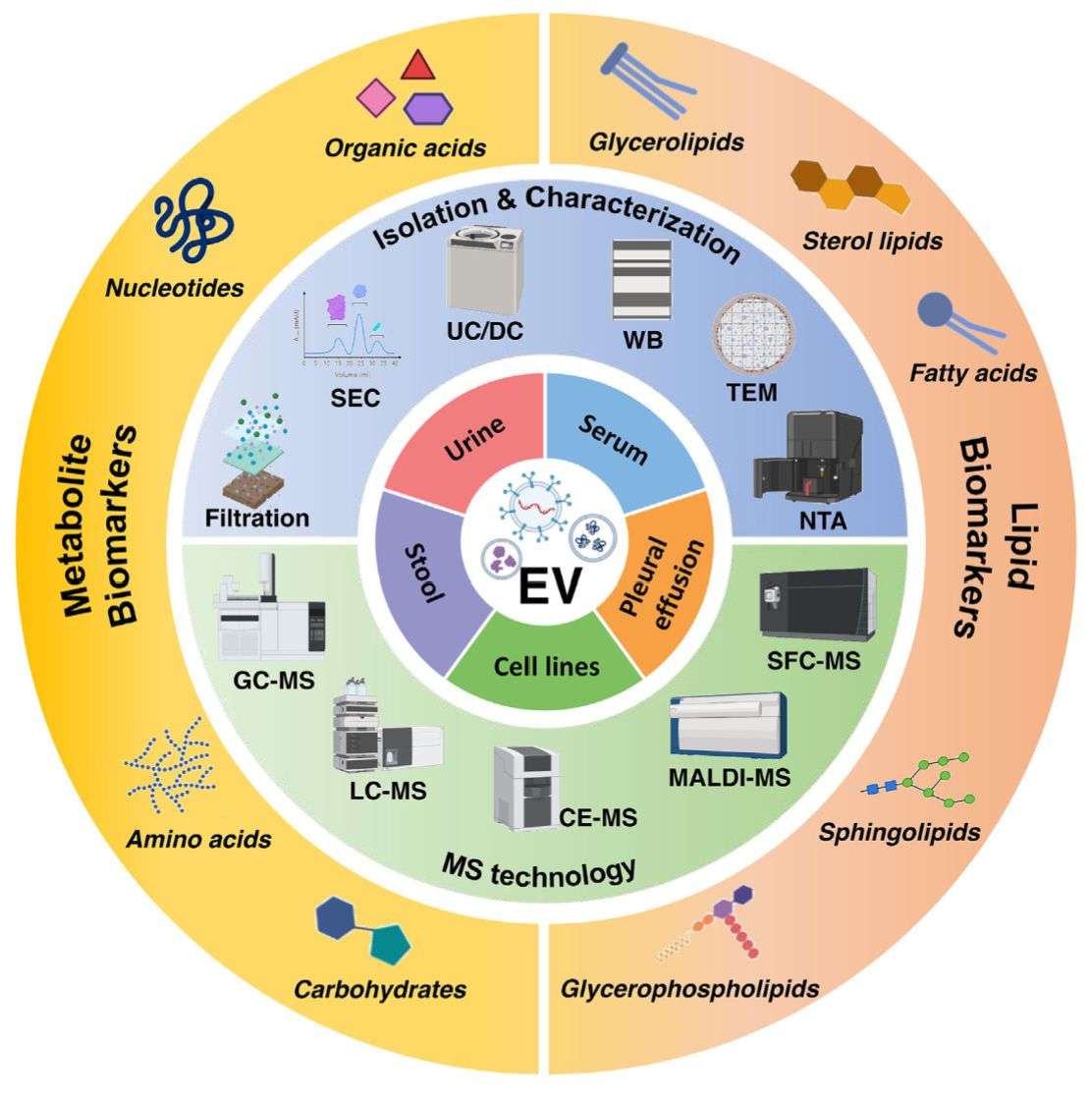
Sample Types & Exosome Isolation Expertise
We accept a wide range of research sample types:
- Plasma or serum
- Urine
- Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
- Saliva
- Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF)
- Cell culture supernatants
To ensure high-purity vesicles and reproducible RNA recovery, our laboratory applies MISEV2023-aligned isolation standards, including:
- Differential ultracentrifugation
- Density gradient purification
- Size-exclusion chromatography (SEC)
- Immunoaffinity enrichment targeting CD9/CD63/CD81
- Tangential flow filtration (TFF) for large-volume concentration
Every batch undergoes rigorous EV quality control, such as Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA), Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM), Cryo-Electron Microscopy (Cryo-EM), and surface marker detection.
Reporting & Deliverables (Publication-Ready)
Our standard deliverables include:
- Project summary report
- EV characterization data
- Library QC statistics
- Raw FASTQ files
- Processed count tables
- Differential expression datasets
- Functional enrichment analyses
- ceRNA and interaction network diagrams
- Figures in both PNG and vector-friendly formats (PDF/SVG)
Customized analysis pipelines are available upon request.
Key Applications
Our exosomal transcriptome profiling services are widely used in:
- Cancer biomarker discovery and minimal residual disease monitoring
- Neurological and neurodegenerative disease research
- Cardiovascular disease transcriptomics
- Immune regulation and inflammation studies
- Drug-response evaluation and resistance mechanism analysis
- Cell-cell communication and microenvironment modeling
- Precision medicine and therapeutic development
Why Choose Creative Biostructure
- Expertise in Exosome Biology: Our scientists specialize in extracellular vesicles, ensuring accurate isolation, minimal contamination, and optimized RNA recovery.
- Ultra-Sensitive, Low-Input RNA Workflows: We routinely generate high-quality libraries from picogram-level RNA.
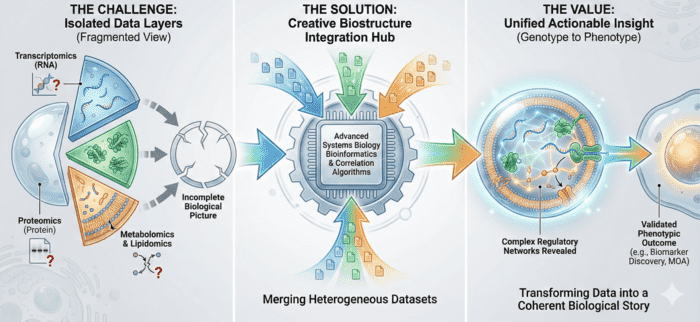
- Integrated Multi-Omics: Combine transcriptomics with exosomal proteomics, exosomal lipidomics and exosomal metabolomics for a complete understanding of EV cargo.
- High-Quality Data Deliverables: We provide transparent QC, reproducible workflows, and analyst-curated reports suitable for publication or regulatory submission.
- Compliance With MISEV2023 and Industry Best Practices: Our processes are continuously updated to reflect the latest EV standards and guidelines.
- Experienced Bioinformatics Team: Specialists in EV-specific computational analysis, including novel RNA discovery and complex network interpretation.
Case Study
Case: Bovine Adipocyte Exosomal RNA Profiling Highlights Selective Packaging
Background
Researchers compared RNAs in bovine white adipocytes and their secreted exosomes to see whether exosomal RNA reflects cellular content or is selectively sorted for signaling.
Methods
Exosomes from adipocyte-conditioned medium were confirmed by TEM, NTA, and CD63/ALIX Western blot, then exosomal and cellular RNAs were profiled by DNBSEQ/BGISEQ-500 for mRNA, lncRNA, and miRNA analysis.
Results
Only 1236 RNAs overlapped between cells and exosomes, while >21,000 remained cell-restricted, indicating strong selection. Exosomal mRNAs were enriched in ribosomal and protein synthesis pathways, and network analysis linked exported miRNAs/lncRNAs to proliferation and apoptosis signaling.
Conclusion
Bovine adipocytes selectively load specific mRNAs, miRNAs, and lncRNAs into exosomes rather than passively releasing cellular RNA, supporting a directed EV-mediated communication mechanism and providing a reference dataset for adipogenesis and metabolic research.
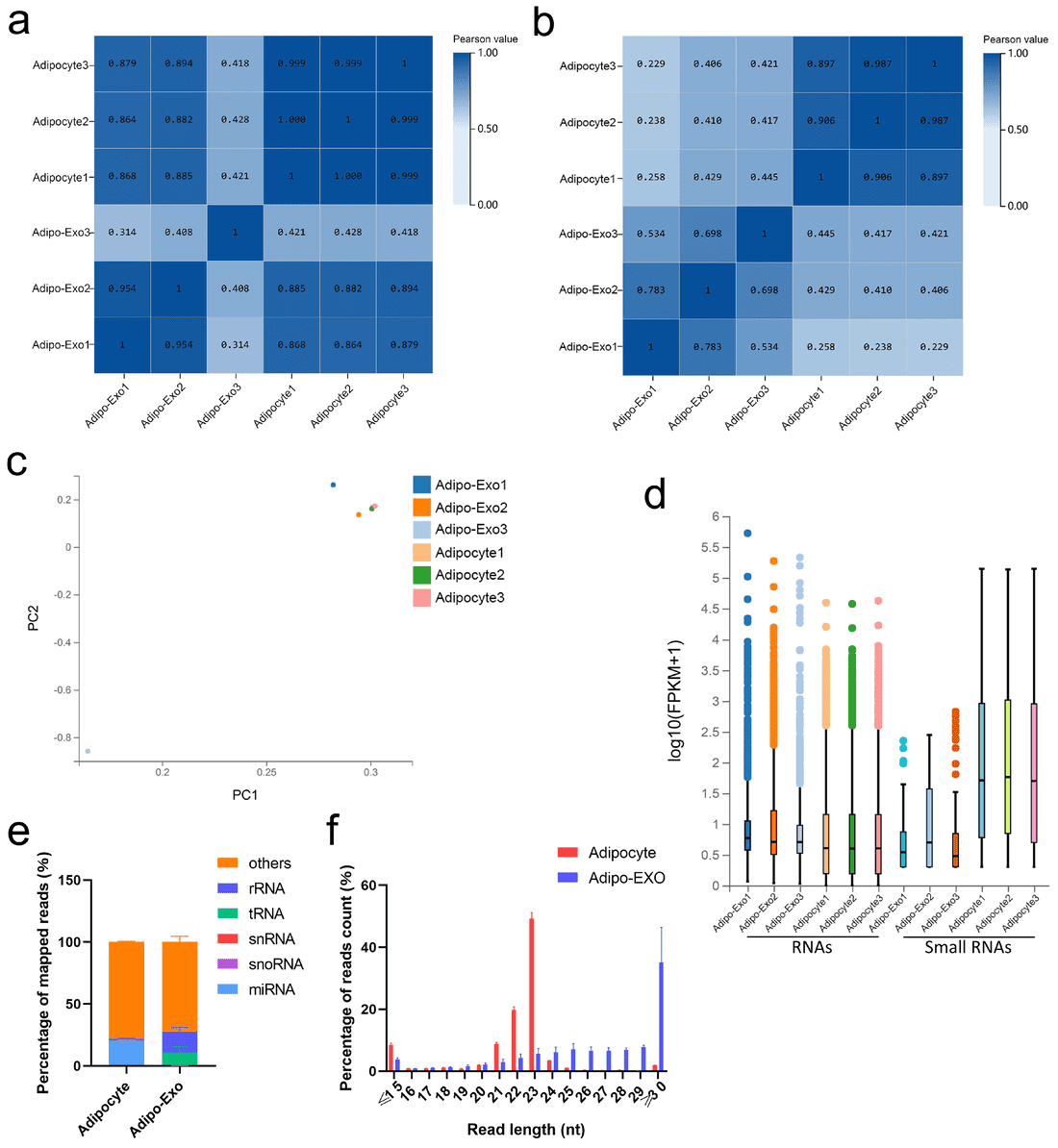 Figure 3. RNA-Seq Data Analysis of Adipocyte and Exosome RNAs. (a-b) Pearson correlation heatmaps for total RNA and small RNA from adipocyte-derived exosomes vs. adipocytes. (c) PCA of normalized RNA-seq data. (d) Box plot of detected RNAs. (e) Proportions of small RNA classes. (f) Length and frequency distributions of total small RNAs. (Yue B, et al., 2020)
Figure 3. RNA-Seq Data Analysis of Adipocyte and Exosome RNAs. (a-b) Pearson correlation heatmaps for total RNA and small RNA from adipocyte-derived exosomes vs. adipocytes. (c) PCA of normalized RNA-seq data. (d) Box plot of detected RNAs. (e) Proportions of small RNA classes. (f) Length and frequency distributions of total small RNAs. (Yue B, et al., 2020)
Ready to turn exosomal RNA into actionable insights? Our MISEV2023-aligned workflow couples high-purity EV isolation, low-input library prep, deep sequencing, and expert bioinformatics to deliver publication-ready biomarker and pathway readouts. Contact us for a free consultation, a tailored panel design, NDA support, and a fast, accurate quotation.
References
- Yue B, Yang H, Wu J, et al. Characterization and transcriptome analysis of exosomal and nonexosomal RNAs in bovine adipocytes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020, 21(23): 9313.
- Elkommos-Zakhary M, Rajesh N, Beljanski V. Exosome RNA sequencing as a tool in the search for cancer biomarkers. Non-coding RNA. 2022, 8(6): 75.
Frequently Asked Questions
For any inquiries, our support team is ready to help you get technical support for your research and maximize your experience with Creative Biostructure.