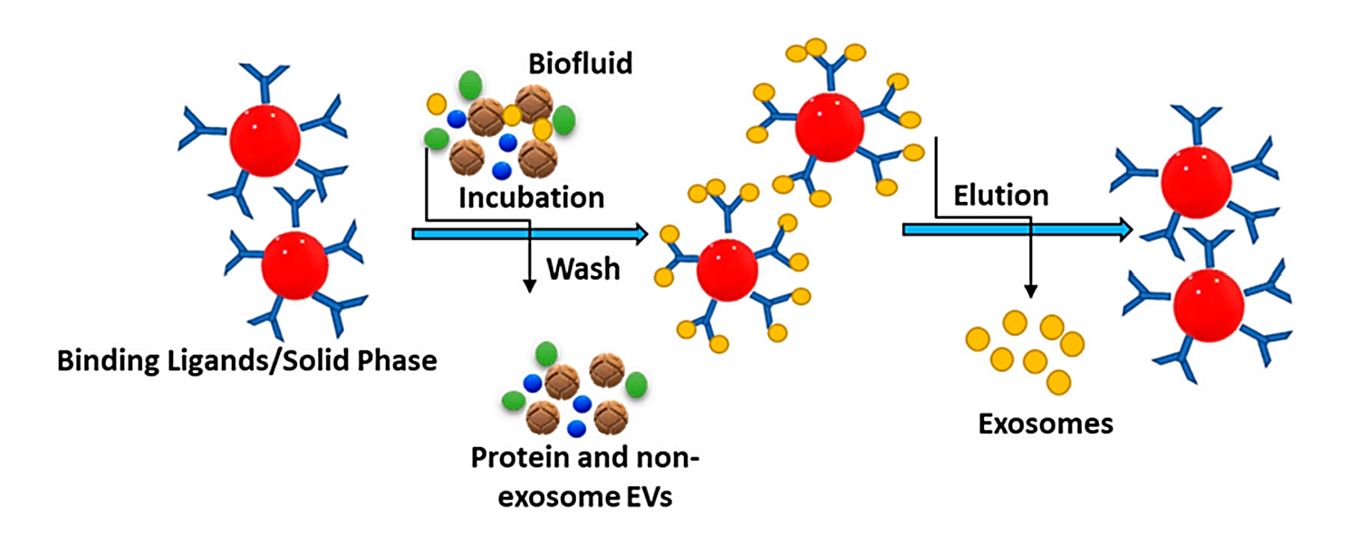
Ultracentrifugation-Based Exosome Purification Service
At Creative Biostructure, we offer a high-performance ultracentrifugation-based exosome purification service tailored for academic and industrial researchers. Leveraging our expertise in extracellular vesicle (EV) workflows, we isolate highly pure and functionally intact exosomes from a variety of biofluids and cell culture systems. Our service is designed to support applications such as biomarker discovery, disease modeling, and drug delivery system development.
Why Choose Ultracentrifugation for Exosome Isolation and Purification?
Ultracentrifugation remains the gold standard for exosome purification due to its exceptional ability to separate vesicles based on size and density. As nanovesicles typically ranging from 30 to 150 nm, exosomes require precise and reproducible protocols to ensure minimal contamination from proteins, lipoproteins, or other extracellular vesicles (e.g., microvesicles, apoptotic bodies). Our protocols have been refined through years of hands-on experience and literature-supported optimization.
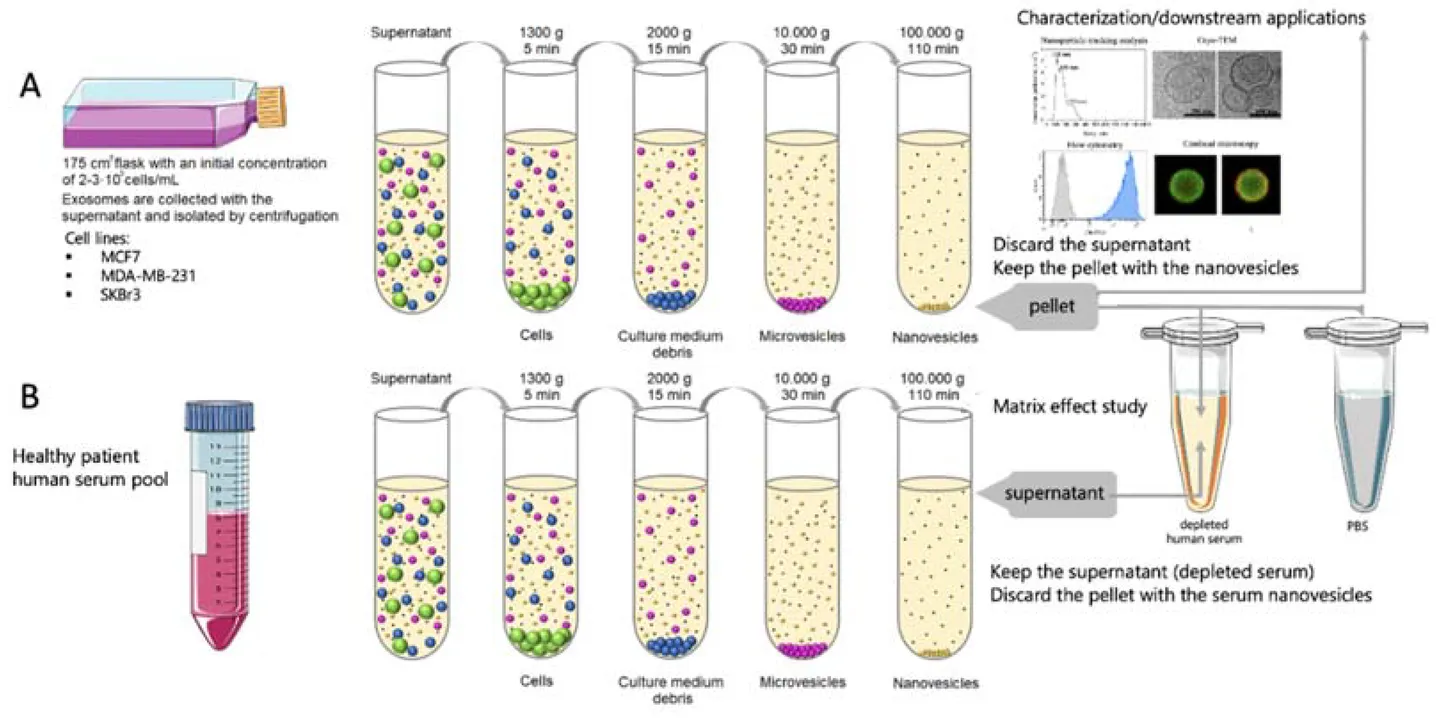
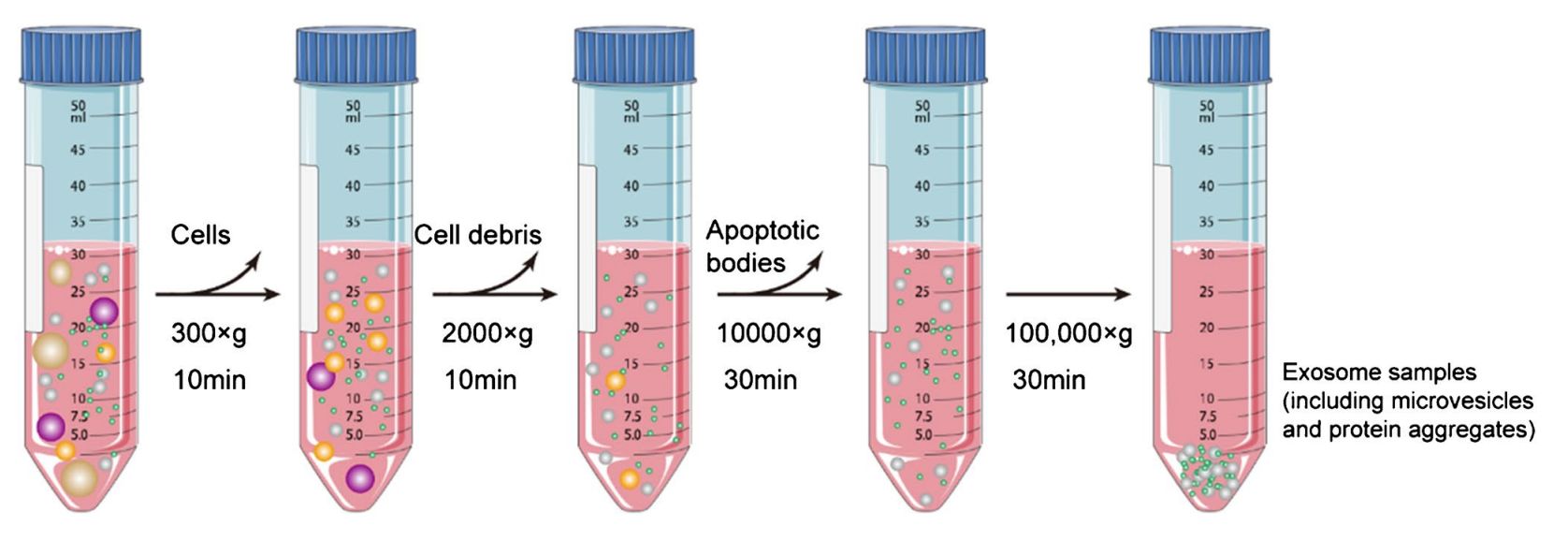
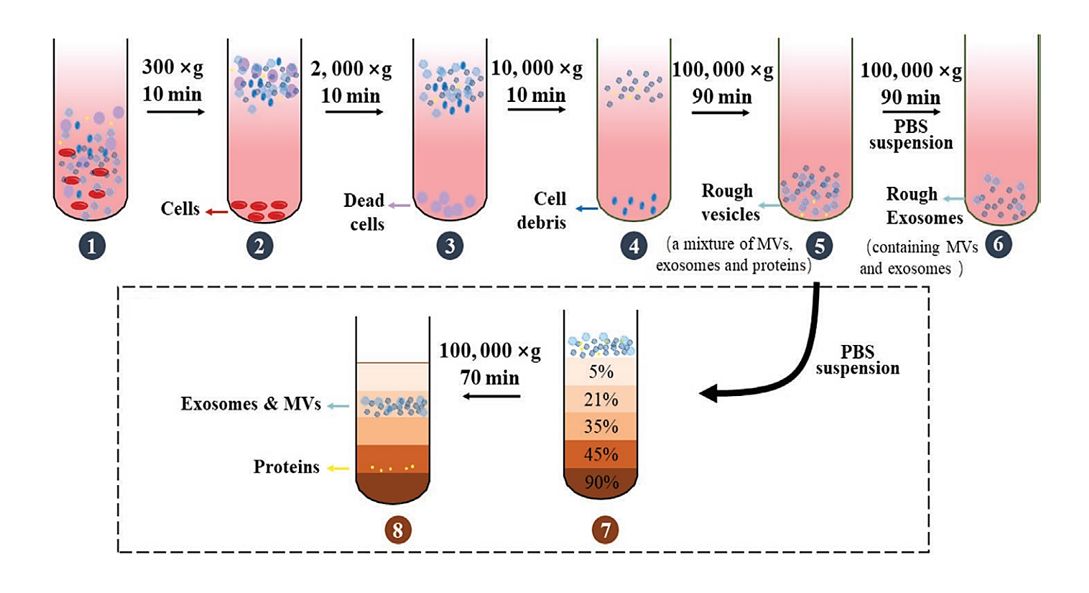
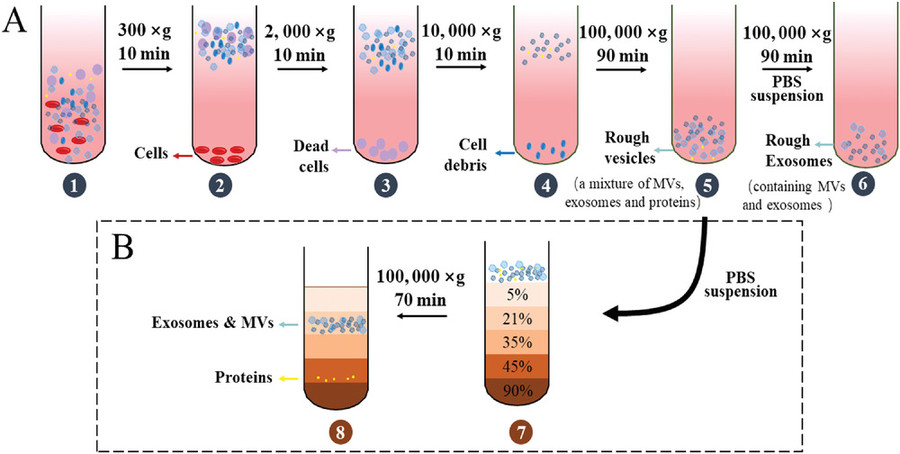 Figure 1. Differential Centrifugation and Density Gradient Centrifugation for Exosome Isolation. (A) Differential centrifugation removes cells, debris, and proteins through sequential spins at increasing centrifugal force to yield crude exosomes. (B) Density gradient centrifugation separates extracellular vesicles and proteins based on their density by layering the sample over a gradient solution, allowing finer separation of exosomes from contaminants. (Xie Y, et al., 2022)
Figure 1. Differential Centrifugation and Density Gradient Centrifugation for Exosome Isolation. (A) Differential centrifugation removes cells, debris, and proteins through sequential spins at increasing centrifugal force to yield crude exosomes. (B) Density gradient centrifugation separates extracellular vesicles and proteins based on their density by layering the sample over a gradient solution, allowing finer separation of exosomes from contaminants. (Xie Y, et al., 2022)
Our Ultracentrifugation Techniques for Exosome Purification
At Creative Biostructure, we offer multiple ultracentrifugation-based workflows tailored to your downstream application needs. These techniques are designed to maximize yield, purity, or biomarker compatibility depending on sample type and research goals.
| Technique | Description | Typical Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Differential Ultracentrifugation (DUC) | Sequential centrifugation at increasing speeds to remove debris, apoptotic bodies, and isolate exosomes based on size and density. | Routine purification from plasma, serum, urine, or cell culture media |
| Cushioned Differential Ultracentrifugation (C-DUC) | Uses a dense cushion (e.g., sucrose or iodixanol) at the bottom of the tube to protect vesicles during pelleting. | Preserving structural integrity for functional or morphological studies |
| Isopycnic Density Gradient Ultracentrifugation | Forms a continuous gradient (e.g., iodixanol) during spin; exosomes settle at their equilibrium density, minimizing contaminants. | High-purity recovery for proteomics, RNA sequencing, and biomarker validation |
| Equilibrium Zonal DGUC | Pre-layered gradient steps allow exosome subpopulations to migrate and stabilize at discrete density interfaces. | Fractionation of exosome subtypes and comparative studies |
| Rate Zonal DGUC | Exosomes are separated by sedimentation rate through a linear gradient, ideal for differentiating vesicles of similar size but distinct shape. | Advanced biophysical studies or subtype-specific isolation from complex fluids |
To enhance performance, our ultracentrifugation protocols can be flexibly combined with additional purification strategies, enabling scalable and application-specific solutions. Each of the above techniques can be optionally paired with:
- Ultrafiltration (UF): For sample volume reduction and buffer exchange prior to or after ultracentrifugation
- Polymer-Based Precipitation: For high-yield pre-enrichment before DGUC or when processing large sample batches.
- Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC): For fine purification after ultracentrifugation, SEC separates exosomes from free proteins and non-vesicular contaminants based on size.
Our Exosome Purification Workflow via Ultracentrifugation
Exosome isolation by ultracentrifugation involves a multi-step process that separates vesicles based on size and density using progressively increasing centrifugal forces. The general workflow includes:
- Low-speed centrifugation (300-2,000×g): Removes cells and large debris.
- Medium-speed centrifugation (10,000-20,000×g): Eliminates apoptotic bodies and large microvesicles.
- High-speed ultracentrifugation (100,000×g for 1-2 hours): Pellets exosomes based on their small size (~30-150 nm) and density.
- Washing step: The exosome pellet is resuspended in PBS or other buffers and centrifuged again to remove residual contaminants.
- (Optional) Density gradient ultracentrifugation: A sucrose or iodixanol gradient can be used to further purify exosomes from proteins or other vesicles.
This method is widely considered the gold standard for exosome purification due to its reproducibility and compatibility with downstream applications like RNA analysis, proteomics, and functional assays.
 Figure 2. Project Workflow for Exosome Isolation and Purification by Ultracentrifugation. (Creative Biostructure)
Figure 2. Project Workflow for Exosome Isolation and Purification by Ultracentrifugation. (Creative Biostructure)
Sample Requirements
Creative Biostructure offers exosome and EV purification services from a wide range of biological sources. Whether you're working with mammalian systems, microbial cultures, or plant-based matrices, our protocols are tailored to ensure optimal yield, purity, and biological activity.
Supported Sample Types
- Cell Culture Supernatants: Adherent or suspension cells from human, animal, or engineered lines
- Animal Tissue Samples: Liver, brain, lung, tumor tissue, etc.; enzymatic digestion available
- Body Fluids: Plasma, serum, urine, saliva, cerebrospinal fluid, milk, etc.
- Plant: Leaves, roots, fruits, or callus cultures, etc.
- Fungal Extracellular Vesicles: Derived from yeast, filamentous fungi, or pathogenic species
- Bacterial Extracellular Vesicles (BEVs): Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria under aerobic or anaerobic conditions
- Protozoa-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: Including Plasmodium, Trypanosoma, Leishmania, and other parasites
- Custom Samples: Contact us to discuss compatibility with uncommon matrices or novel organisms
Minimum Volume Requirements
- Biofluids: ≥1 mL
- Cell supernatants: ≥10 mL
- Tissue (wet weight): ≥ 50 mg (species-dependent)
All samples should be freshly collected or stored at -80°C, and must avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles to preserve vesicle integrity.
Quality Control and Deliverables
To ensure the reliability, purity, and reproducibility of each exosome or EV preparation, Creative Biostructure implements a comprehensive quality control (QC) and characterization process. All assays are conducted using validated instruments and reagents under standardized operating procedures.
Quality Control Assays
| Assay | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA) | Measures particle size distribution and vesicle concentration |
| Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) | Visualizes vesicle morphology and confirms lipid bilayer structure |
| Western Blot or ELISA | Detects exosomal surface markers (CD9, CD63, CD81) to confirm identity |
| Protein Quantification (BCA Assay) | Quantifies total protein content, supporting loading consistency |
| Optional: Endotoxin Testing | Ensures safety and suitability for immunology or in vivo applications |
Standard Deliverables
Upon completion of the project, clients will receive:
- Purified exosomes or EVs in user-defined buffer (e.g., PBS, HEPES)
- Comprehensive technical report, including:
- Sample processing summary
- Instrumental QC results (with graphs and images)
- Marker expression analysis
- Fraction map (if DGUC applied)
- Optional add-ons: Aliquoting, long-term storage, or buffer exchange
Our QC framework aligns with MISEV (Minimal Information for Studies of Extracellular Vesicles) guidelines and supports compatibility with downstream applications such as RNA sequencing, mass spectrometry, flow cytometry, and therapeutic loading.
Key Advantages of Our Exosome Purification Service
- High-purity exosome preparations with minimal protein or lipoprotein contamination
- Adaptable protocols for various sample types and research objectives
- Expert consultation for project planning and downstream assay compatibility
- Stringent quality control using validated analytical platforms
- Scalable processing volumes for both discovery and translational research
Case Study
Case: Comparison of Exosome Isolation Methods from Bovine Serum
Background
To determine the most suitable exosome isolation strategy for bovine serum, researchers conducted a rigorous comparison of three commonly used methods: ultracentrifugation alone (UC), ultracentrifugation combined with size exclusion chromatography (US), and the exoEasy membrane affinity kit (EE).
Key Observations
Yield:
- UC had the highest particle count (1.78 × 10¹¹ particles/mL).
- US and EE showed lower yields but differed in purity and RNA content.
Purity:
- US samples showed no albumin contamination and expressed TSG101, CD81, and HSP70.
- UC and EE samples contained albumin and lacked some exosomal markers.
RNA Integrity:
- EE showed the strongest small RNA bands (25-200 nt).
- US had moderate small RNA presence; UC showed weak signals.
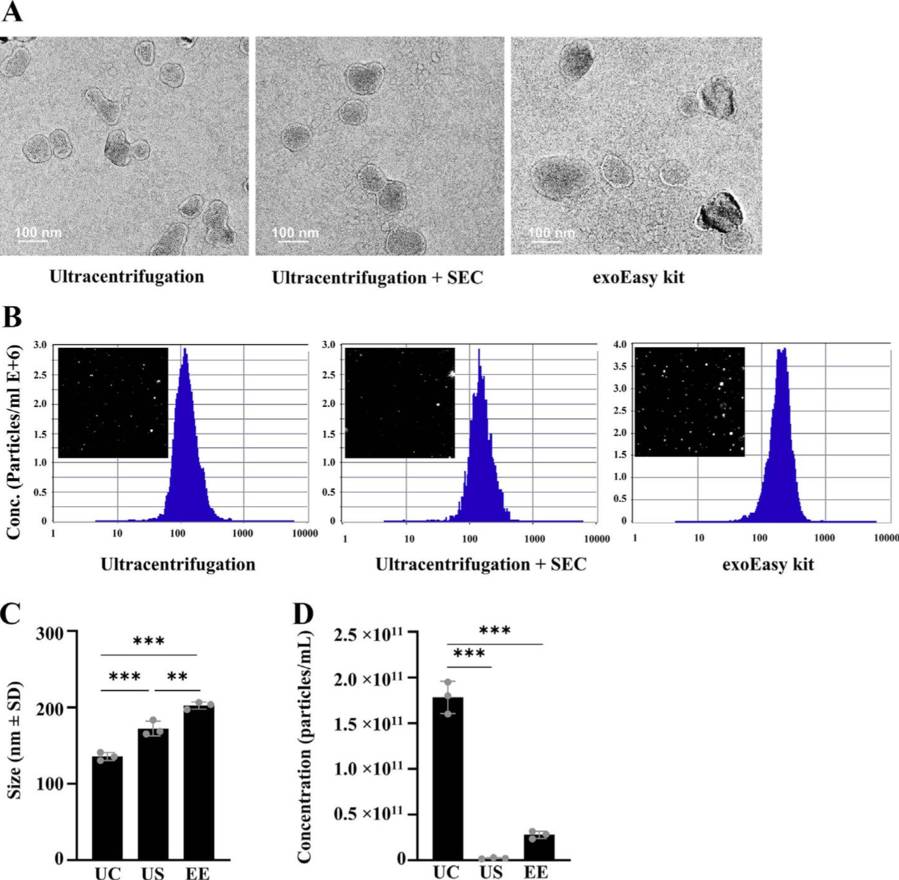 Figure 3. Exosomes isolated from bovine serum using ultracentrifugation, ultracentrifugation combined with SEC, and the exoEasy kit were characterized by TEM and NTA. (Bok E Y, et al., 2024)
Figure 3. Exosomes isolated from bovine serum using ultracentrifugation, ultracentrifugation combined with SEC, and the exoEasy kit were characterized by TEM and NTA. (Bok E Y, et al., 2024)
Structural Quality:
- TEM showed intact vesicles in US samples; UC samples appeared damaged.
- US had the highest particle-to-protein ratio (2.83 × 10⁸ particles/μg), indicating better purity.
Conclusion
The US method offers the best purity and marker retention, making it suitable for proteomics. EE is more effective for small RNA extraction, while UC is ideal when high particle yield is needed.
At Creative Biostructure, we combine gold-standard ultracentrifugation techniques with flexible customization to deliver exosome preparations that meet the highest scientific standards. Whether you're working on fundamental EV biology, biomarker discovery, or therapeutic development, our team is ready to support your project from sample to data. Contact us to discuss your specific requirements or request a personalized quotation.
References
- Chhoy P, Brown C W, Amante J J, et al. Protocol for the separation of extracellular vesicles by ultracentrifugation from in vitro cell culture models. STAR Protocols. 2021, 2(1): 100303.
- Liu W, Ma Z, Kang X. Current status and outlook of advances in exosome isolation. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry. 2022, 414(24): 7123-7141.
- Xie Y, Xu X, Lin J, et al. Effective Separation of Cancer‐Derived Exosomes in Biological Samples for Liquid Biopsy: Classic Strategies and Innovative Development. Global Challenges. 2022, 6(9): 2100131.
- Bok E Y, Seo S Y, Lee H G, et al. Exosomes isolation from bovine serum: qualitative and quantitative comparison between ultracentrifugation, combination ultracentrifugation and size exclusion chromatography, and exoEasy methods. Journal of Animal Science and Technology. 2024, 66(5): 1021.
Frequently Asked Questions
For any inquiries, our support team is ready to help you get technical support for your research and maximize your experience with Creative Biostructure.