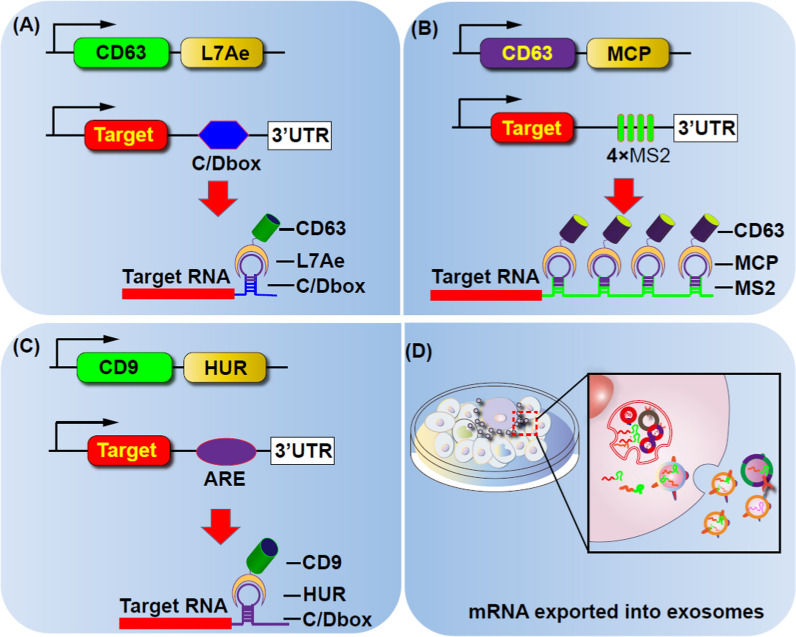
Exosome Protein Delivery
Therapeutic proteins (like monoclonal antibodies) have transformed medicine, but they are generally limited to extracellular targets. Delivering active enzymes, transcription factors, or CRISPR-Cas9 ribonucleoproteins (RNPs) into the cytoplasm or nucleus remains a formidable challenge due to the cell membrane barrier and rapid lysosomal degradation.
We provide specialized exosome protein delivery solutions. Unlike synthetic carriers that often denature fragile proteins, exosomes provide a native, biocompatible environment. We utilize both genetic engineering (endogenous loading) and active loading (exogenous loading) strategies to deliver functional proteins to hard-to-reach intracellular compartments, treating conditions ranging from lysosomal storage disorders to cancer.
Overcoming the Barriers of Protein Therapeutics
Why use exosomes for protein delivery? They solve the "last mile" problem of intracellular trafficking.
- Cytosolic Access: The biggest hurdle for protein drugs is getting out of the endosome. Exosomes facilitate endosomal escape via membrane fusion, releasing the bioactive protein directly into the cytoplasm.
- Preserving Bioactivity: The exosomal lumen protects enzymes and transcription factors from proteases in the blood, maintaining their tertiary structure and catalytic activity.
- Reduced Immunogenicity: Encapsulation masks the protein from neutralizing antibodies (ADAs), allowing for repeat dosing of potentially immunogenic enzymes (e.g., in Enzyme Replacement Therapy).
- Crossing Biological Barriers: Exosome-encapsulated proteins can traverse the Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB), enabling the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases with therapeutic enzymes (e.g., Catalase, Neprilysin).
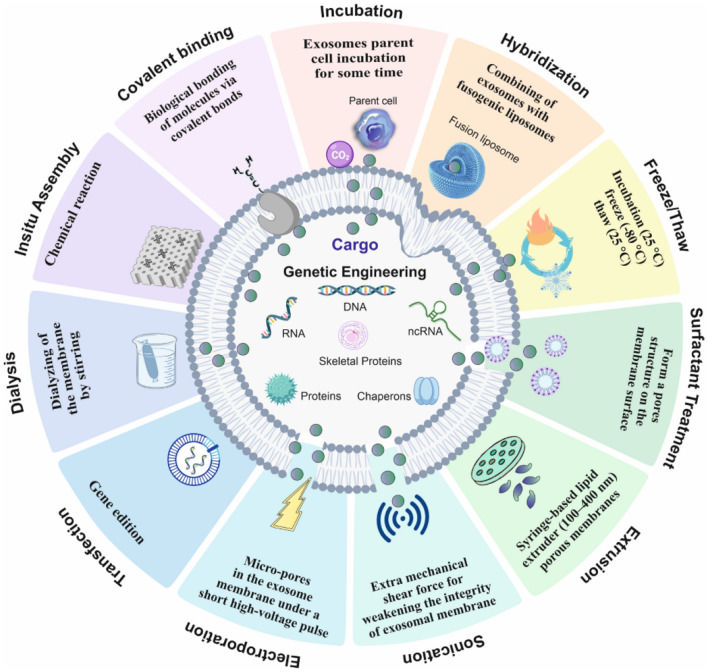
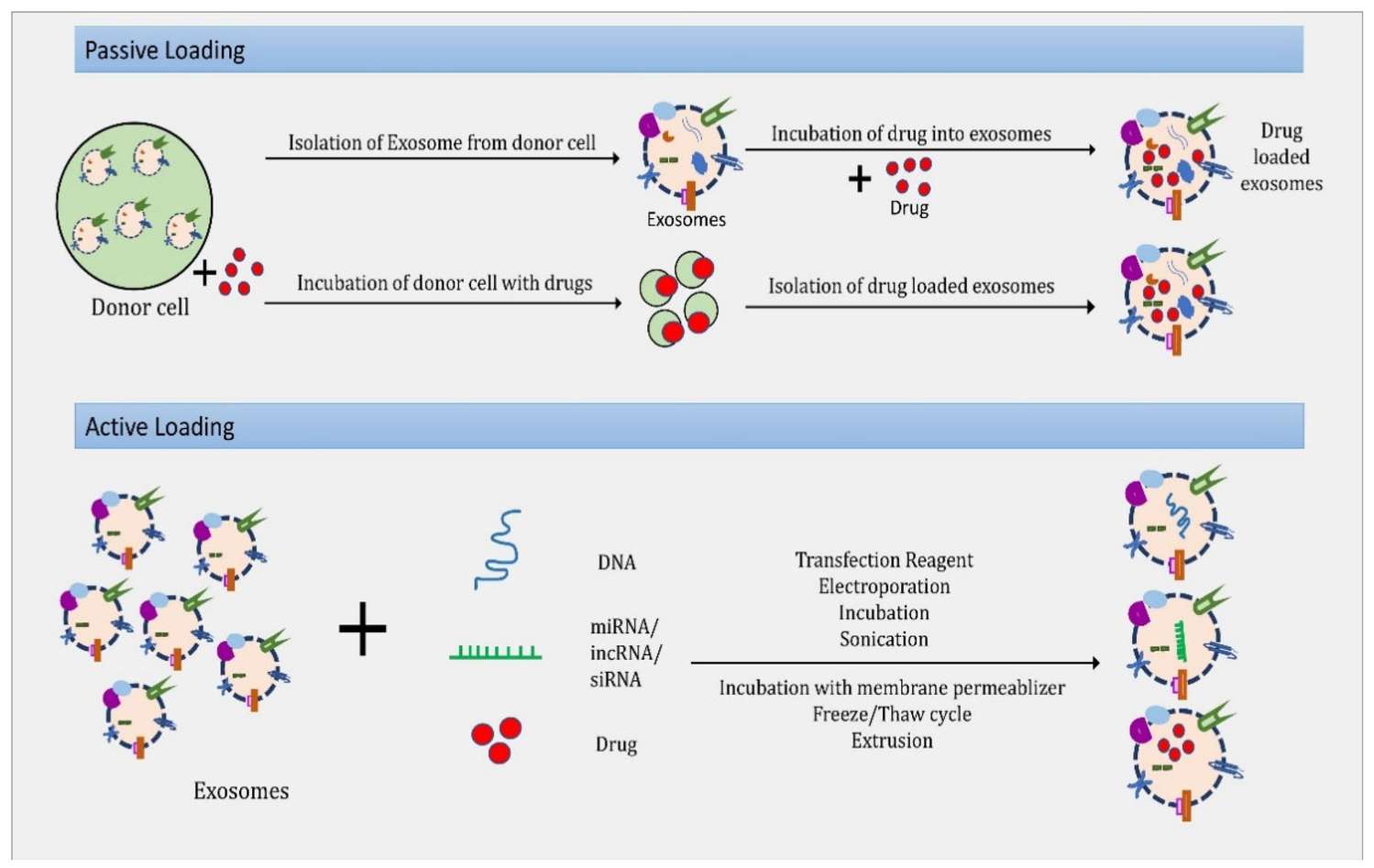
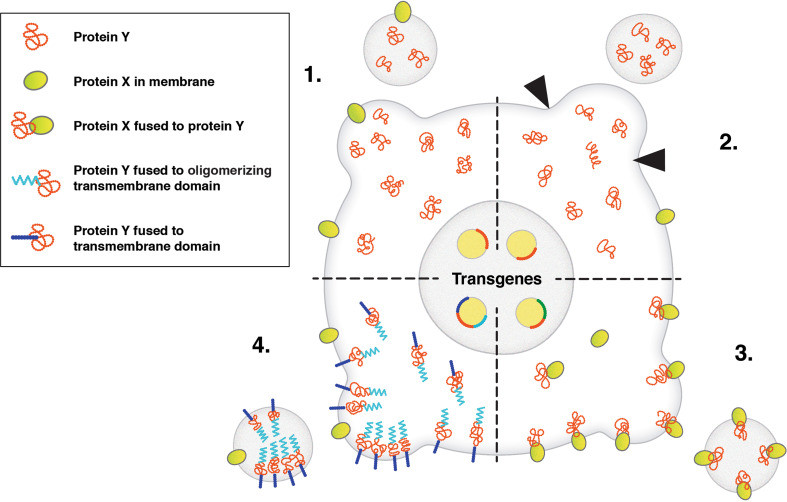 Figure 1. Strategies for loading proteins into extracellular vesicles (EVs) to enhance their content. (Hall J, et al., 2016)
Figure 1. Strategies for loading proteins into extracellular vesicles (EVs) to enhance their content. (Hall J, et al., 2016)
Our Specialized Protein Loading Workflow
Protein loading is complex. We offer two distinct pathways depending on your protein's size and stability.
| Loading Strategy | Our Specialized Approach & Solution | Key Services Applied |
|---|---|---|
| Endogenous Loading (Genetic Engineering) | "Cellular Factories": We transfect producer cells with plasmids encoding your protein fused to an exosome-sorting scaffold (e.g., CD63, Lamp2b, or Nef). The cell's machinery automatically packages the protein into exosomes during biogenesis. Ideal for surface display or secreted proteins. | Genetically Engineered Exosome Surface Display, Upstream Process Development (Cell Culture Optimization) |
| Exogenous Loading (Post-Isolation) | "Active Encapsulation": For purified proteins (like Cas9 RNPs or Catalase), we use physical methods to force them into isolated exosomes. We optimize Sonication, Freeze-Thaw cycles, or Saponin permeabilization to maximize loading efficiency while preserving enzymatic activity. | Exosome Protein and Peptide Loading, Downstream Purification & Formulation |
| Purification & QC | Removing Free Protein: "Free" protein can confuse efficacy data. We use Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC) to rigorously separate drug-loaded exosomes from unencapsulated proteins. We quantify final loading using Western Blot and specific enzymatic activity assays. | Exosome Purification by Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC), Exosome Characterization by Western Blotting |
| Functional Validation | Proving Intracellular Activity: We don't just show uptake. We validate that the protein works. For example, using gene editing efficiency assays for Cas9, or substrate turnover assays for metabolic enzymes. | In Vitro Exosome Functional Assays, Exosome Cellular Functional Assays |
Core Technologies for Your Protein Program
We address the specific technical challenges of maintaining protein stability and function.
Optimized Active Loading Protocols
Preserving Structure: Harsh loading methods can denature proteins. We have optimized protocols for mild sonication and freeze-thaw, balancing membrane disruption with protein stability. We test multiple conditions (temperature, cycles, buffer composition) to determine the optimal window that maximizes Encapsulation Efficiency (EE%) without compromising the protein's catalytic function.
Scaffold-Mediated Loading
Targeted Packaging: For proteins that are hard to load physically, we use biology. We engineer producer cells to express your protein of interest fused to exosomal sorting domains (like the XP tag or lipid-anchored motifs). This recruits the protein into the exosome pathway naturally, resulting in high yields of "self-loaded" exosomes.
Intracellular Activity Assays
Cytosolic Delivery Verification: Distinguishing between protein stuck in endosomes vs. protein in the cytoplasm is critical. We utilize subcellular fractionation and functional reporter assays (e.g., Cre-LoxP recombination systems) to definitively prove that your cargo has reached the cytosol and executed its function.
Application Spotlight: Delivering Antioxidant Enzymes to the Brain
This analysis highlights one of the most famous examples of exosome protein delivery: using physical loading to deliver active enzymes across the blood-brain barrier.
Featured Technologies:
- Active Protein Loading (Sonication/Freeze-Thaw)
- In Vivo Biodistribution
Literature Interpretation:
Parkinson's Disease is driven by oxidative stress, but antioxidant enzymes like Catalase cannot cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and are rapidly degraded if injected. Researchers developed a method to load Catalase into exosomes using various techniques (sonication, freeze-thaw, saponin). The study found that sonication and saponin methods yielded high loading efficiency with preserved enzymatic activity. Remarkably, the Catalase-loaded exosomes accumulated in neurons in vitro and crossed the BBB in vivo, providing significant neuroprotection in Parkinson's mouse models. This outcome demonstrates that active loading strategies can transform large, unstable enzymes into potent CNS therapeutics, validating the formulation capabilities of our platform.
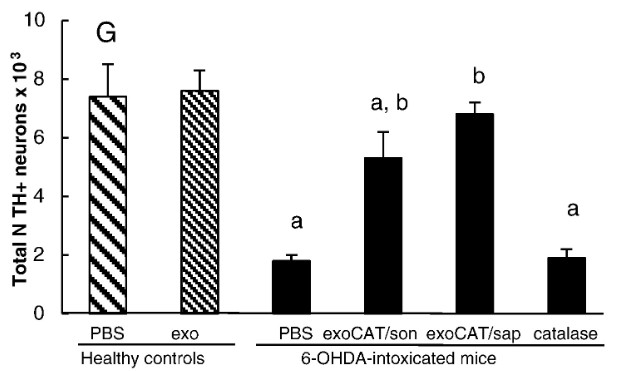 Figure 2. Exosomal formulations show neuroprotective effects, with intranasal (i.n.) exoCAT treatment leading to a threefold increase in DA neuron survival compared to PBS controls. (Haney MJ, et al., 2015)
Figure 2. Exosomal formulations show neuroprotective effects, with intranasal (i.n.) exoCAT treatment leading to a threefold increase in DA neuron survival compared to PBS controls. (Haney MJ, et al., 2015)
Start Your Protein Delivery Project
We make getting started straightforward. Our process is designed to be collaborative and transparent.
How It Works: Our Project Pathway
 Figure 3. Our workflow for optimizing the loading of functional proteins into engineered exosomes. (Creative Biostructure)
Figure 3. Our workflow for optimizing the loading of functional proteins into engineered exosomes. (Creative Biostructure)
Ready to deliver your therapeutic enzyme or transcription factor? Our scientific team is available for a free consultation to discuss your protein delivery strategy. Contact us today to discuss your project.
References
- Hall J, Prabhakar S, Balaj L, et al. Exosomes as New Generation Vehicles for Drug Delivery: Biomedical Applications and Future Perspectives. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Apr;36(3):417-27.
- Haney MJ, Klyachko NL, Zhao Y, et al. Exosomes as drug delivery vehicles for Parkinson's disease therapy. J Control Release. 2015 Jun 10;207:18-30.