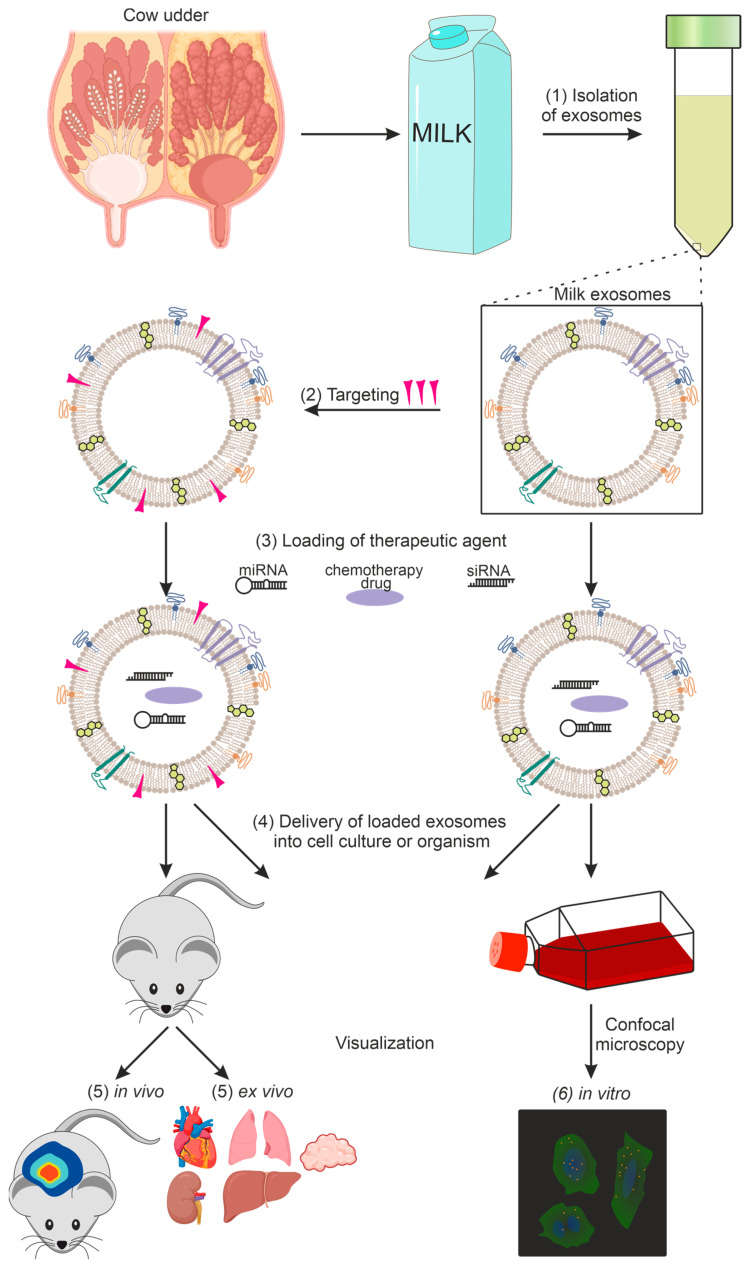
Edible Plant Derived Exosome Development
The nutraceutical industry faces a persistent challenge: many potent phytochemicals (like curcumin, anthocyanins, and peptides) suffer from poor oral bioavailability. They are degraded by stomach acid or poorly absorbed in the gut. Edible Plant-Derived Exosomes (PDEs) offer a revolutionary solution.
We provide specialized Edible Plant Derived Exosome Development solutions. We isolate high-purity nanovesicles from food sources like Ginger, Grapes, Citrus, and Broccoli. These natural carriers protect active nutrients from digestion and facilitate targeted delivery to the gut and liver, enabling the creation of next-generation functional foods and medical nutrition products.
Why Edible Exosomes for Functional Foods?
Plant exosomes are more than just nutrients; they are nature's own delivery vehicles that facilitate cross-kingdom communication.
- Digestive Stability: The robust lipid bilayer of plant exosomes withstands low pH (stomach acid) and digestive enzymes (pepsin/pancreatin), ensuring the cargo reaches the intestine intact.
- Enhanced Absorption: Unlike free compounds, exosomes are actively taken up by intestinal epithelial cells and macrophages, significantly boosting the bioavailability of hydrophobic nutrients.
- Gut Microbiome Modulation: Plant exosomes can selectively target gut bacteria, promoting a healthy microbiome balance (prebiotic effect) and reducing gut inflammation.
- Scalable & Sustainable: Sourced from everyday produce, plant exosomes offer a cost-effective, sustainable, and "GRAS" (Generally Recognized As Safe) path for mass-market supplementation.
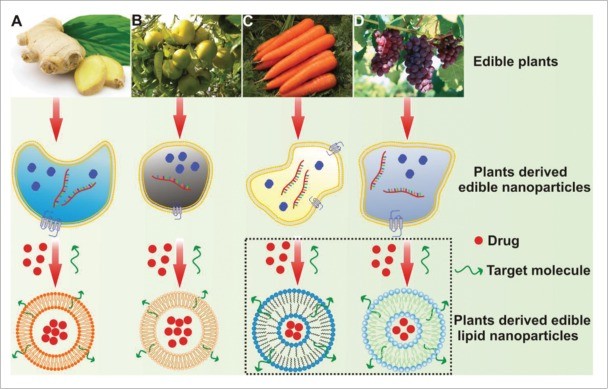 Figure 1. Plant-derived edible nanoparticles and drug-loaded lipid nanoparticles from ginger, grapefruit, carrot, and grape. Extraction and fabrication methods are detailed, highlighting the novel application of carrot and grape-derived lipid nanoparticles. (Zhang M, et al., 2016)
Figure 1. Plant-derived edible nanoparticles and drug-loaded lipid nanoparticles from ginger, grapefruit, carrot, and grape. Extraction and fabrication methods are detailed, highlighting the novel application of carrot and grape-derived lipid nanoparticles. (Zhang M, et al., 2016)
Our Nutraceutical Development Workflow
We offer a "Farm-to-Functional Ingredient" pipeline designed for food-grade safety and efficacy.
| Discovery Phase | Our Specialized Approach & Solution | Key Services Applied |
|---|---|---|
| Source Selection & Prep | Bioactive Screening: We analyze different plant cultivars to identify those with the highest vesicle yield and bioactive cargo (e.g., specific miRNAs or lipids). We utilize food-grade juicing and homogenization protocols. | Plant-Derived Exosome Isolation |
| Food-Grade Isolation | Scalable Purification: We employ Tangential Flow Filtration (TFF) and gradient centrifugation without toxic solvents. This ensures the final isolate is free from fiber, starch, and pesticides while maintaining high purity. | Exosome Isolation by Tangential Flow Filtration (TFF) |
| Nutrient Loading | Active Encapsulation: We can use plant exosomes as carriers for other nutrients. We optimize loading protocols (e.g., incubation, sonication) to encapsulate vitamins or curcumin into the vesicles, creating a "super-carrier." | Exosome Small Molecule Loading |
| Digestive Stability Testing | Simulated GI Tract: We test the formulation in Simulated Gastric/Intestinal Fluids (SGF/SIF) to verify vesicle survival. We measure particle count and cargo retention after exposure to acid and enzymes. | Gastrointestinal Functional Evaluation of Exosomes, Exosome Stability and Bioavailability Assessment |
Core Technologies for Functional Ingredients
We utilize specific technologies to validate oral efficacy and gut health benefits.
Large-Scale Plant Vesicle Isolation
Industrial Scalability: Lab-scale kits don't work for food production. We utilize industrial TFF systems capable of processing liters of plant juice. Our workflow removes plant pigments and sugars that cause instability, yielding a concentrated, clean vesicle suspension ready for freeze-drying or liquid formulation.
Gut Barrier & Absorption Models
Proving Bioavailability: We utilize Caco-2 cell monolayers (an in vitro model of the intestinal wall) to measure the transcytosis rate of your plant exosomes. We verify that the vesicles can cross the gut barrier and enter circulation, providing data to support "High Absorption" claims.
Anti-Inflammatory Gut Assays
Targeting Colitis & IBD: Many plant exosomes (like Ginger) naturally reduce gut inflammation. We provide functional assays using LPS-stimulated macrophages or colitis mouse models. We measure the reduction of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-6, TNF-a) to validate the soothing effect of your ingredient on the digestive tract.
Application Spotlight: Ginger Exosomes Repair Gut Lining
This analysis highlights the therapeutic potential of edible plant exosomes in treating intestinal inflammation and restoring gut health.
Featured Technologies:
- Edible Plant Exosome Isolation
- Gastrointestinal Functional Evaluation
Literature Interpretation:
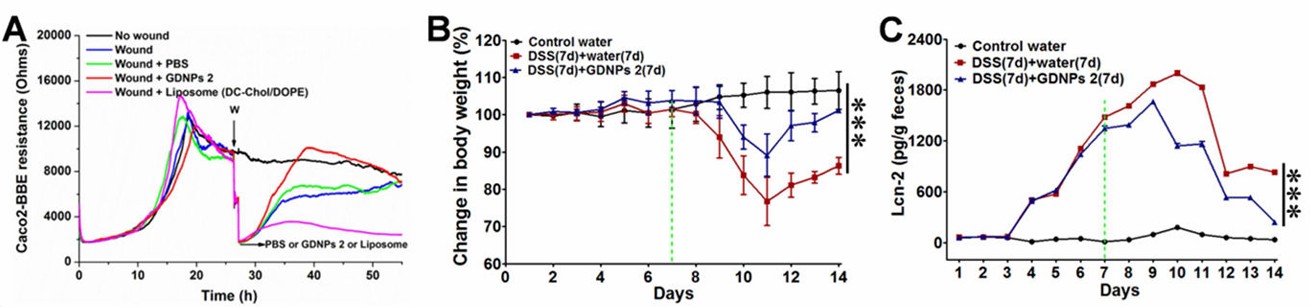 Figure 2. GDNPs 2 enhance wound healing in both in vitro and in vivo models. (A) Healing acceleration in intestinal epithelial monolayers, (B) Monitoring of body weight changes, and (C) Analysis of Lcn-2 levels. (Zhang M, et al., 2016)
Figure 2. GDNPs 2 enhance wound healing in both in vitro and in vivo models. (A) Healing acceleration in intestinal epithelial monolayers, (B) Monitoring of body weight changes, and (C) Analysis of Lcn-2 levels. (Zhang M, et al., 2016)
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) compromises the gut barrier. Researchers isolated exosome-like nanoparticles (ELNs) from edible ginger (GDNPs 2) and administered them orally to mice with colitis. The study found that these ginger-derived vesicles survived gastric digestion and were preferentially taken up by intestinal epithelial cells and macrophages. Biologically, they induced the expression of anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-22) and promoted the repair of the damaged intestinal mucosa. These findings demonstrate that orally administered plant exosomes serve as active biological agents that can target gut tissues and resolve inflammation, validating their potential as functional food ingredients for digestive health.
Start Your Functional Food Project
We make getting started straightforward. Our process is designed to be collaborative and transparent.
How It Works: Our Project Pathway
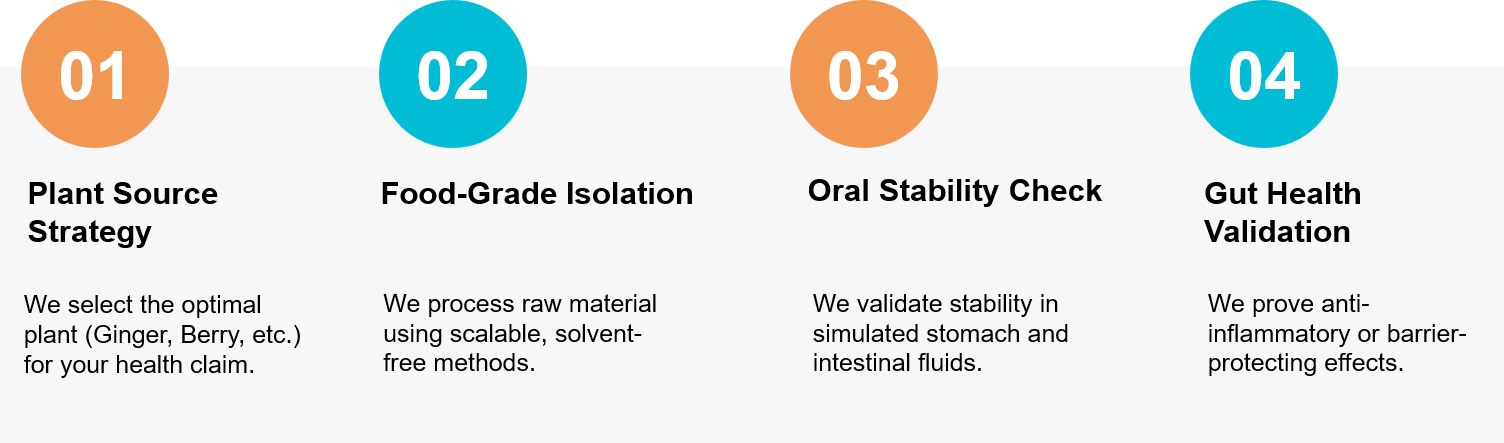 Figure 3. Our workflow for transforming raw botanical sources into stable, bioactive exosome ingredients for the nutraceutical industry. (Creative Biostructure)
Figure 3. Our workflow for transforming raw botanical sources into stable, bioactive exosome ingredients for the nutraceutical industry. (Creative Biostructure)
Ready to revolutionize your supplement line with plant nanovesicles? Our food scientists are available for a free consultation to discuss your product development strategy. Contact us today to discuss your project.
References
- Zhang M, Viennois E, Xu C, et al. Plant derived edible nanoparticles as a new therapeutic approach against diseases. Tissue Barriers. 2016 Feb 11;4(2):e1134415.
- Zhang M, Viennois E, Prasad M, et al. Edible ginger-derived nanoparticles: A novel therapeutic approach for the prevention and treatment of inflammatory bowel disease and colitis-associated cancer. Biomaterials. 2016 Sep;101:321-40.