Alzheimer Disease Exosome Research Services
Alzheimer's Disease (AD) pathology begins decades before cognitive decline. Traditional diagnostics like PET scans and CSF taps are invasive and costly, limiting wide-scale screening. Neuron-derived exosomes (NDEs) provide a revolutionary alternative: they act as "brain windows," carrying neuropathological hallmarks (Aβ42, p-Tau181) across the Blood-Brain Barrier into peripheral circulation.
We provide specialized Alzheimer's Disease Exosome Research solutions. We focus on the enrichment of neural exosomes from plasma using L1CAM/L1 protein capture and the ultrasensitive detection of phosphorylated Tau and synaptic proteins. Whether you are developing a non-invasive screening test or investigating how exosomes propagate Tau pathology, our platform offers the sensitivity required for neuro-discovery.
Critical Frontiers in AD Research
Alzheimer's research is racing to identify pathology before irreversible neuronal loss occurs.
- Pre-Symptomatic Diagnosis: AD pathology (Amyloid and Tau) begins decades before symptoms. The field urgently needs accessible blood biomarkers to screen populations and select candidates for clinical trials.
- Pathological Propagation: AD is characterized by the spread of Tau tangles across brain networks. Understanding how exosomes facilitate this "prion-like" seeding and transmission between neurons is a central research theme.
- Synaptic Dysfunction: Cognitive decline correlates best with synapse loss, not just plaque load. Investigating exosomal synaptic proteins serves as a proxy for monitoring synaptic health in living patients.
- Neuroinflammation: Microglia play a dual role in AD. Research is decoding how exosomes mediate the switch between neuroprotective and neurotoxic microglial states.
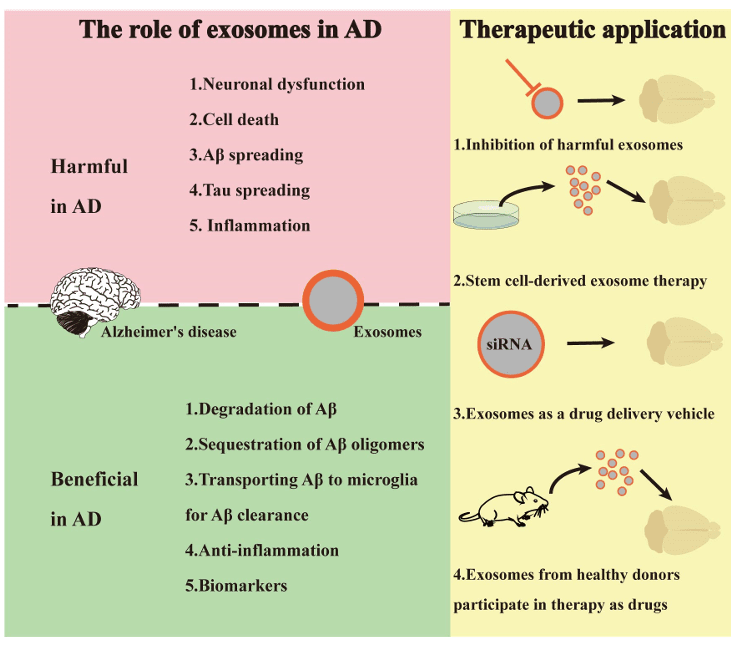 Figure 1. Dual roles and therapeutic applications of exosomes in Alzheimer's disease (AD). (He A, et al., 2023)
Figure 1. Dual roles and therapeutic applications of exosomes in Alzheimer's disease (AD). (He A, et al., 2023)
Our Alzheimer's Research Workflow
We offer a pipeline optimized for low-abundance neural markers in blood and functional seeding assays.
| Research Phase | Our Specialized Approach & Solution | Key Services Applied |
|---|---|---|
| Neural Enrichment | L1CAM Immuno-Capture: Exosomes from the brain are diluted by those from blood cells. We use Anti-L1CAM (CD171) biotinylated antibodies to selectively pull down neuron-derived exosomes from plasma, enhancing the signal of brain markers by >10-fold. | Exosome Isolation by Immunoaffinity Capture |
| Ultrasensitive Detection | Targeted Quantification: We utilize advanced Exosome Quantification technologies (such as Simoa or high-sensitivity ELISA) to measure femtogram levels of p-Tau181/217. We also use Digital PCR for absolute quantification of nucleic acid markers. | Exosome Quantitative Proteomics, Exosomal lncRNA Sequencing |
| Pathological Seeding | FRET Biosensors: We treat HEK293-Tau-biosensor cells with patient exosomes. If the exosomes contain pathological Tau seeds, they induce aggregation in the cells, measurable by FRET fluorescence. This quantifies the "seeding activity." | Exosome-protein Interactions Assay, Exosome Cellular Functional Assays |
| In Vivo Propagation | Intracerebral Injection: We inject AD-patient exosomes into the hippocampus of Tau-transgenic mice. We analyze the spatial spread of Tau pathology to distant brain regions over time using Immunohistochemistry (IHC). | Exosome Tracing and Tracking, In Vivo Exosome Functional Assays |
Core Technologies for AD Biomarkers
We utilize technologies specifically chosen for their sensitivity in detecting brain-derived signals in the periphery.
L1CAM+ Exosome Isolation
The "Brain Liquid Biopsy": L1CAM is a cell adhesion molecule highly expressed in neurons. By performing Immuno-Affinity Capture targeting L1CAM, we enrich the fraction of exosomes that originated in the CNS. This step is critical for distinguishing brain-derived Amyloid-beta or Tau from systemic background, enabling high-specificity diagnosis from a simple blood draw.
Phosphoproteomics for p-Tau Profiling
Mapping the Tangles: Hyperphosphorylation of Tau is the hallmark of AD. Our Targeted Phosphoproteomics service focuses on detecting specific epitopes (Threonine 181, 217, 231) on Tau protein within exosomes. p-Tau217, in particular, has emerged as a high-performance biomarker that rivals PET scans in diagnostic accuracy.
AD Brain Organoid Models
Modeling Neurodegeneration: We generate Cerebral Organoids from iPSCs derived from familial AD patients (e.g., PSEN1 mutant). We study how exosomes released by these "mini-brains" accumulate Aβ plaques and trigger tau phosphorylation, providing a human-relevant model for drug screening that outperforms 2D cultures.
Application Spotlight: Proteomic Signatures and Toxicity of Brain-Derived EVs
This analysis highlights the power of combining deep proteomic profiling with functional assays to uncover the pathogenic role of brain-derived extracellular vesicles.
Featured Technologies:
- Exosome Quantitative Proteomics
- In Vitro Cellular Functional Assays (Tau Seeding)
Literature Interpretation:
To bridge the gap between fluid biomarkers and actual brain pathology, researchers isolated extracellular vesicles (EVs) directly from post-mortem brain tissues of Alzheimer's disease (AD) patients and healthy controls. Utilizing Quantitative Mass Spectrometry, the study identified a specific proteomic signature in AD-derived EVs, characterized by the enrichment of neuron-specific proteins like ANXA5, VGF, and GPM6A. Beyond molecular profiling, the study assessed biological function by adding these brain-derived EVs to biosensor cells. The results demonstrated that AD-EVs, but not control EVs, possessed potent Tau seeding activity, actively inducing the aggregation of Tau proteins in recipient cells. This landmark study confirms that EVs are not just passive byproducts but active carriers of neurotoxicity, validating the necessity of integrated proteomic and functional seeding platforms.
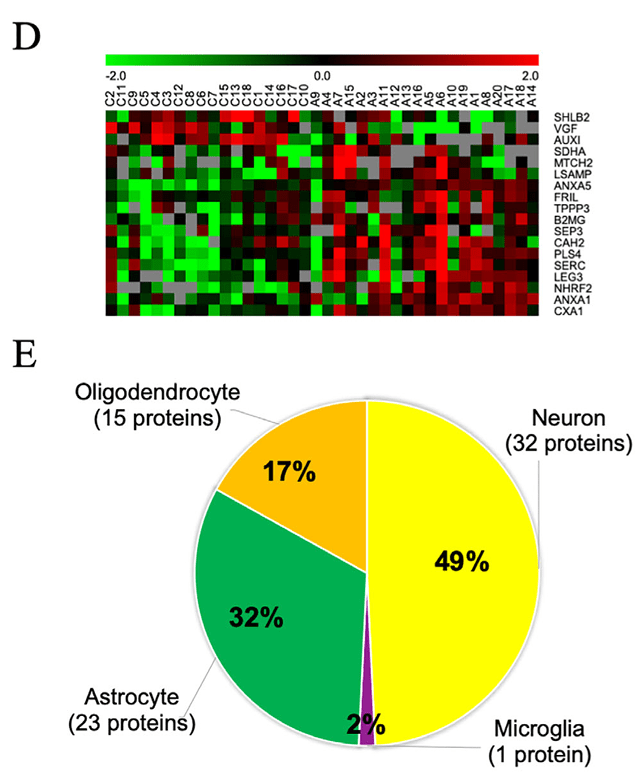 Figure 2. Protein expression analysis in Alzheimer's disease (AD). (D) Heat map of differentially expressed proteins, with red indicating upregulation and green downregulation. (E) Enrichment analysis of brain cell type-specific markers among brain-derived extracellular vesicle (EV) proteins, color-coded by cell type. (Muraoka S, et al., 2020)
Figure 2. Protein expression analysis in Alzheimer's disease (AD). (D) Heat map of differentially expressed proteins, with red indicating upregulation and green downregulation. (E) Enrichment analysis of brain cell type-specific markers among brain-derived extracellular vesicle (EV) proteins, color-coded by cell type. (Muraoka S, et al., 2020)
Start Your AD Research Project
Advance your research on neurodegeneration with our specialized CNS exosome platform.
How It Works: Our Project Pathway
 Figure 3. Our specialized workflow for isolating neuron-derived exosomes from blood and validating their potential as biomarkers for early Alzheimer's disease diagnosis. (Creative Biostructure)
Figure 3. Our specialized workflow for isolating neuron-derived exosomes from blood and validating their potential as biomarkers for early Alzheimer's disease diagnosis. (Creative Biostructure)
Ready to validate the next generation of Alzheimer's biomarkers? Our neuroscience team is available to discuss your L1CAM enrichment strategy. Contact us today to discuss your project.
References
- He A, Wang M, Li X, et al. Role of Exosomes in the Pathogenesis and Theranostic of Alzheimer's Disease and Parkinson's Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 4;24(13):11054.
- Muraoka S, DeLeo AM, Sethi MK, et al. Proteomic and biological profiling of extracellular vesicles from Alzheimer's disease human brain tissues. Alzheimers Dement. 2020 Jun;16(6):896-907.