Exosomal mRNA Sequencing Service
Exosomal mRNA is a critical cargo in exosomes, carrying full-length genetic information of functional genes from donor cells to recipient cells, directly reflecting transcriptional activity. Creative Biostructure's exosome mRNA sequencing service captures full-length mRNA transcripts, enabling comprehensive analysis of gene expression changes, alternative splicing events, and fusion genes in exosomes. Powered by advanced Illumina sequencing technology and optimized mRNA-specific workflows, we deliver high-quality data to our clients.
Why is Exosomal mRNA Sequencing Service Important?
Exosomal mRNA sequencing service is critically important for both basic research and clinical applications, as it opens a unique window into cellular activity and intercellular communication. Exosomes carry cell-type-specific mRNA cargo that reflects the functional state of their parent cells, offering a non-invasive method to access biologically significant information that is often inaccessible through traditional methods. By employing high-throughput sequencing, this service enables the comprehensive profiling of these mRNA molecules, allowing researchers to identify novel biomarkers for early disease diagnosis, monitor treatment response in real time, and uncover fundamental mechanisms underlying disease progression. In precision medicine, it provides particularly valuable insights for understanding cancer biology, neurodegenerative disorders, and developing targeted therapies, ultimately bridging the gap between basic science and clinical practice.
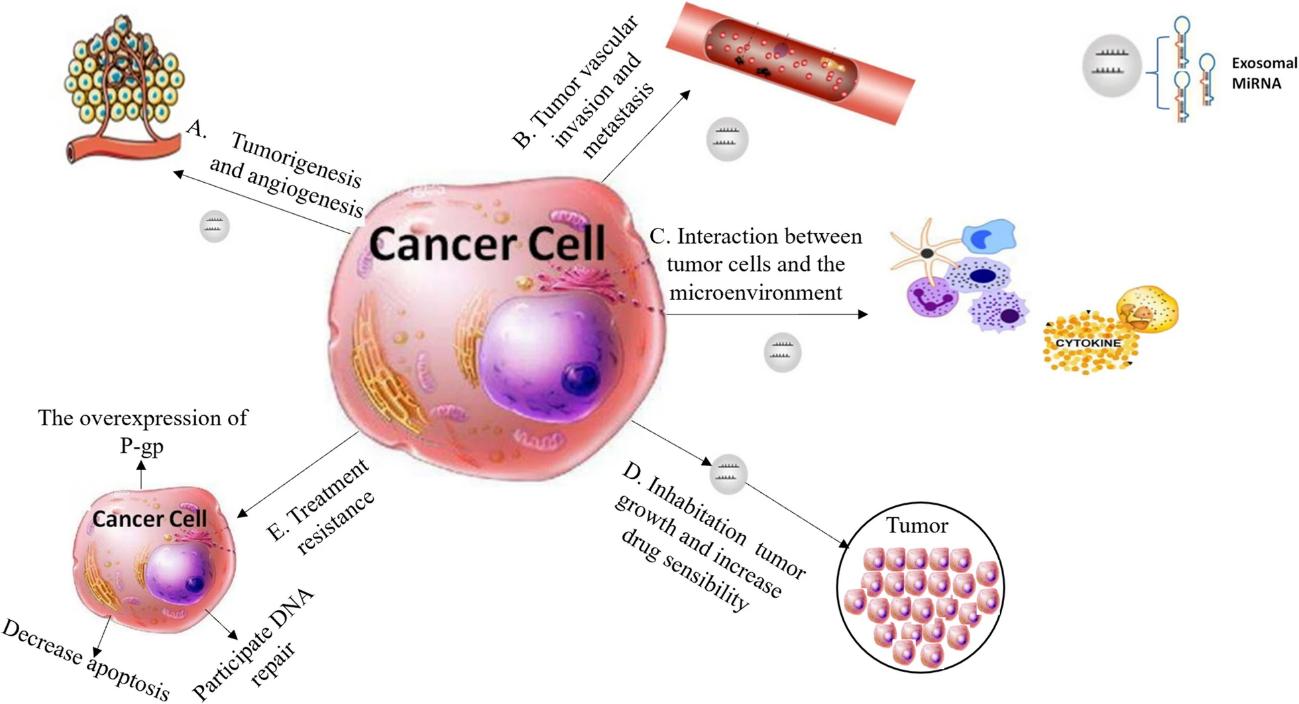
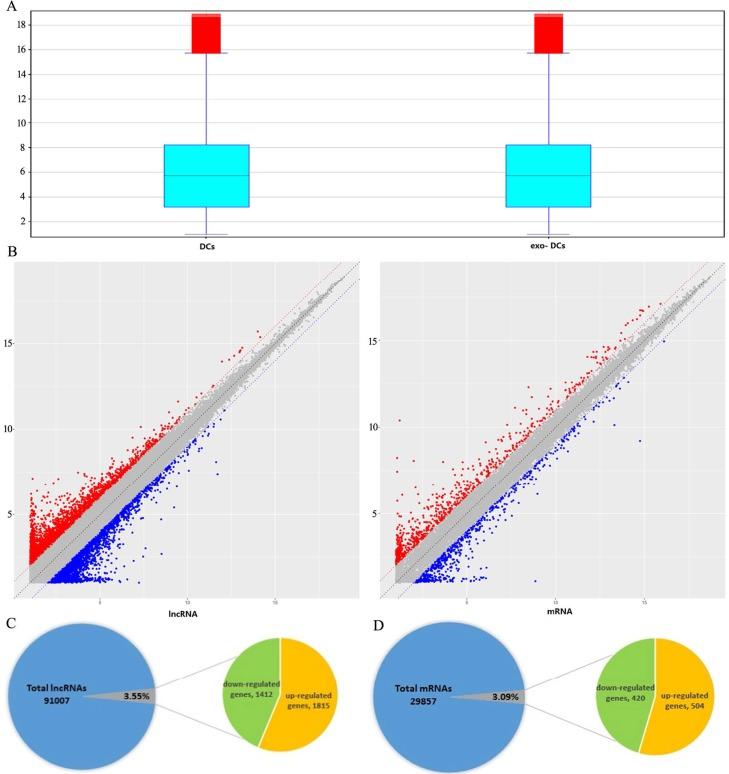
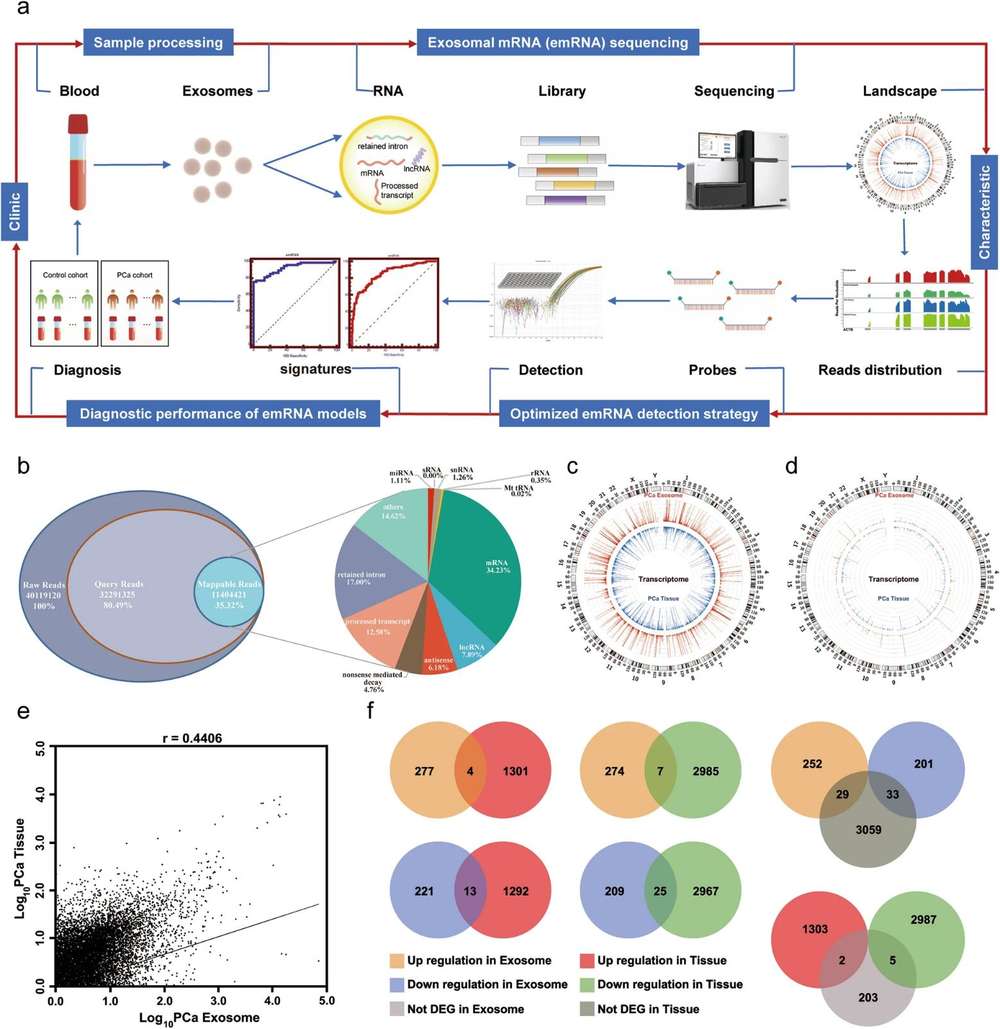 Figure 1. Circulating exosomal mRNA profiling identifies novel signatures
for the detection of prostate cancer. (Ji J, et al., 2021)
Figure 1. Circulating exosomal mRNA profiling identifies novel signatures
for the detection of prostate cancer. (Ji J, et al., 2021)
Our Exosomal mRNA Sequencing Service
We adopt the Illumina NovaSeq 6000 high-throughput sequencing platform, tailored for exosomal mRNA's characteristics (longer length, lower abundance vs. small RNA):
| Technology | Description |
|---|---|
| PolyA+ Enrichment Technology | Uses magnetic beads with oligo(dT) probes to specifically capture mRNA (excluding rRNA, tRNA, and small RNA/miRNA), achieving ≥98% rRNA removal rate and ensuring mRNA purity. |
| Strand-Specific Library Construction | Preserves the transcriptional direction of mRNA (sense/antisense), which is essential for analyzing antisense mRNA regulation and avoiding false positive results from reverse strands. |
| High Read Depth Configuration | 30-50 million clean reads per sample, covering low-abundance exosomal mRNA (down to 1 copy per cell) and supporting accurate detection of alternative splicing isoforms. |
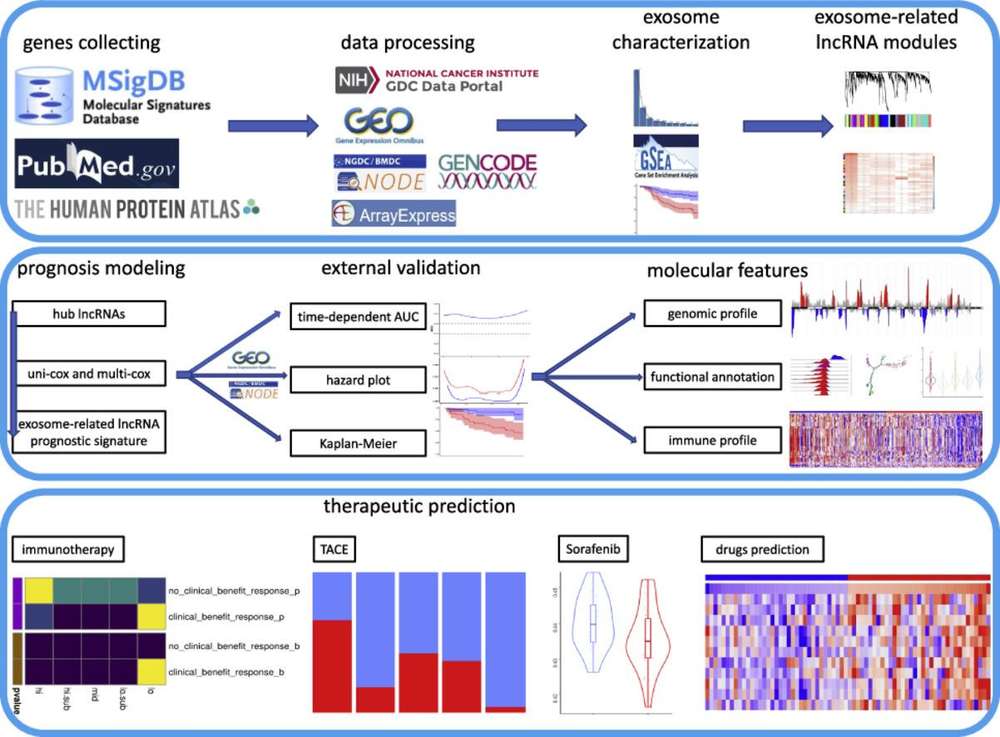
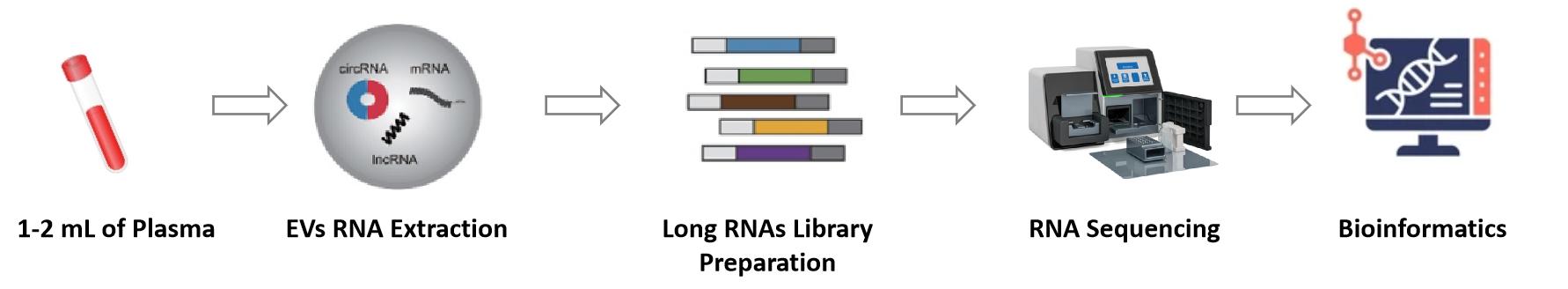
Workflow of Exosomal mRNA Sequencing Analysis
Exosome Isolation
For raw samples (e.g., serum, cell supernatants), use "ultracentrifugation + size-exclusion chromatography" to isolate exosomes. This method effectively removes lipoprotein contamination (a major interference for mRNA extraction), which is more precise than the simple centrifugation used in small RNA sequencing.
mRNA-Specific Extraction
Use RNase-free kits with PolyA+ magnetic beads to extract mRNA from exosomes; add DNase I to eliminate genomic DNA contamination (critical for avoiding false positive gene expression results).
Strand-Specific Library Prep
- Fragment mRNA into 200-300 bp segments (optimized for mRNA length, not small
RNA's 18-30 bp).
- Synthesize first-strand cDNA with reverse transcriptase (labeled with dUTP to
mark the reverse strand).
- Digest the reverse strand with UDG enzyme to retain only the forward
strand, then add Illumina adapters to construct libraries.
High-Throughput Sequencing
Load libraries onto the Illumina NovaSeq 6000 platform for paired-end sequencing (2×150 bp), ensuring sufficient coverage for alternative splicing detection.
mRNA-Focused Data Analysis
- Basic Analysis: FastQC (quality control of raw reads), STAR (genome alignment
with splice junction recognition), HTSeq (gene/isoform quantification);
- Advanced Analysis:
DESeq2/edgeR (differential gene expression screening), rMATS (alternative splicing event
identification), STAR-Fusion (fusion gene detection), GO/KEGG/GSEA (functional enrichment of
differential genes).
 Figure 2.
Workflow of exosomal mRNA sequencing analysis. (Creative Biostructure)
Figure 2.
Workflow of exosomal mRNA sequencing analysis. (Creative Biostructure)
Supported Sample Range
Raw Samples:
- Serum/plasma: ≥200 μL, no hemolysis (hemoglobin degrades mRNA).
- Cell culture supernatants: ≥10 mL, freshly collected (avoid long-term storage).
- Cerebrospinal fluid: ≥100 μL, stored at -80°C immediately.
- Urine: ≥500 μL, add RNA protection agent at collection.
Final Delivery
Clients receive a comprehensive, publication-ready report including:
- QC Report: mRNA integrity (RIN value), rRNA removal rate, library concentration/uniformity, sequencing Q30 score, and alignment rate.
- Raw & Processed Data: FASTQ files (raw reads), BAM files (aligned reads), gene/isoform expression matrix (TPM/FPKM values).
- Advanced Analysis Results:
- Differential gene list (fold change ≥2, p<0.05) with volcano plots and heatmaps.
- Alternative splicing events (skipped exons, alternative 5'/3' splice sites) with rMATS statistics.
- Fusion gene list (if detected) with breakpoint coordinates and annotation.
- Functional Interpretation: GO/KEGG enrichment analysis (focused on biological processes like "cell proliferation" "metabolic pathway") and GSEA analysis of differential gene sets.
Applications of Exosomal mRNA Sequencing
- Alternative Splicing in Disease: Study how exosomal mRNA splicing variants drive disease.
- Fusion Gene Biomarker Discovery: Identify exosomal fusion mRNA as cancer biomarkers.
- Transcriptional Response to Therapy: Monitor changes in exosomal mRNA expression during treatment.
- Tissue-Specific Communication Research: Analyze organ-specific mRNA in exosomes to study inter-organ communication.
Advantages of Our Exosomal mRNA Sequencing Profiling Services
- mRNA-Specific Capture: PolyA+ enrichment ensures no small RNA/miRNA interference, focusing on functional gene transcripts.
- Splicing & Fusion Detection: Unique ability to analyze alternative splicing and fusion genes.
- High Transcriptional Resolution: Strand-specific libraries reveal antisense mRNA regulation, providing deeper insights into transcriptional mechanisms.
- Reliable Low-Abundance Detection: 30-50 million reads cover low-abundance exosomal mRNA, avoiding missed detection of key functional genes.
- Expert Data Interpretation: Our team of computational biologists specializes in mRNA analysis, not just general sequencing, ensuring accurate interpretation of splicing and fusion results.
Case Study
Case: Biomarker Discovery and Clinical Relevance via Serum Exosomal mRNA-seq in Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (NHL)
Background
The clinical utility of mRNA cargo in exosomes is unclear, although exosomes have potential as non-invasive biomarkers. This study aimed to investigate the feasibility of exosomal mRNA sequencing for monitoring disease status and predicting outcomes in non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) patients.
Methods
- Isolation of exosomes by ultracentrifugation.
- Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA).
- Characterization of exosomes.
- Sequencing of exosomal mRNA.
Conclusion
Exosomal mRNA sequencing was performed successfully in 26 cases (79%, 26/33), whereas the remaining seven cases were not completed due to their small amount of RNA. The exosomal mRNA sequencing of DLBCL showed gene expression profiles consistent with activated B-cell-like and germinal center type.
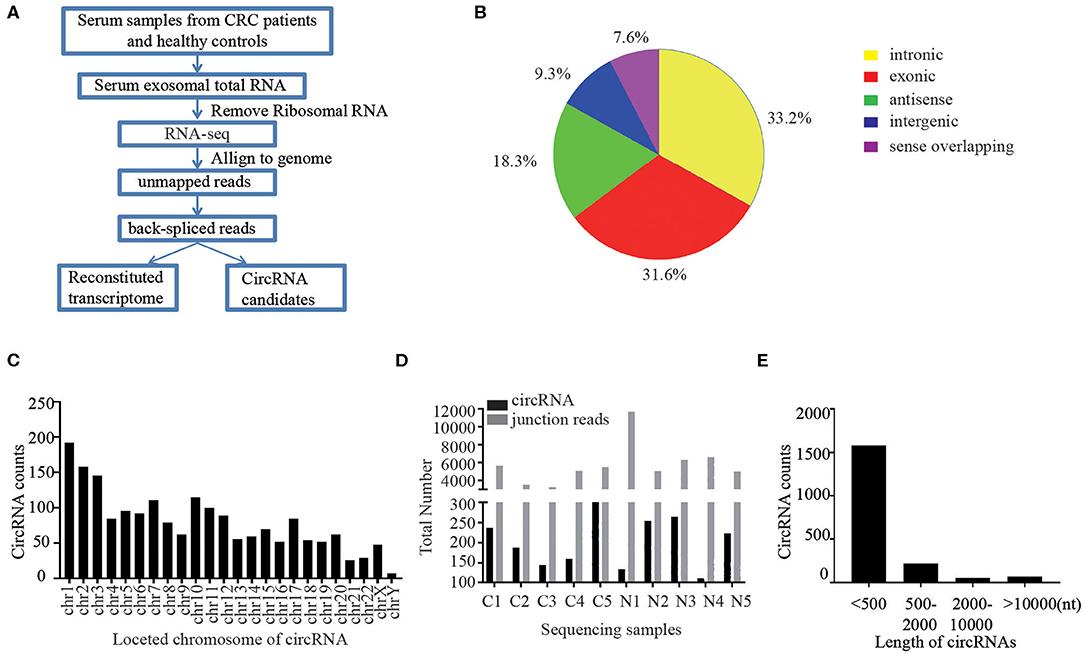
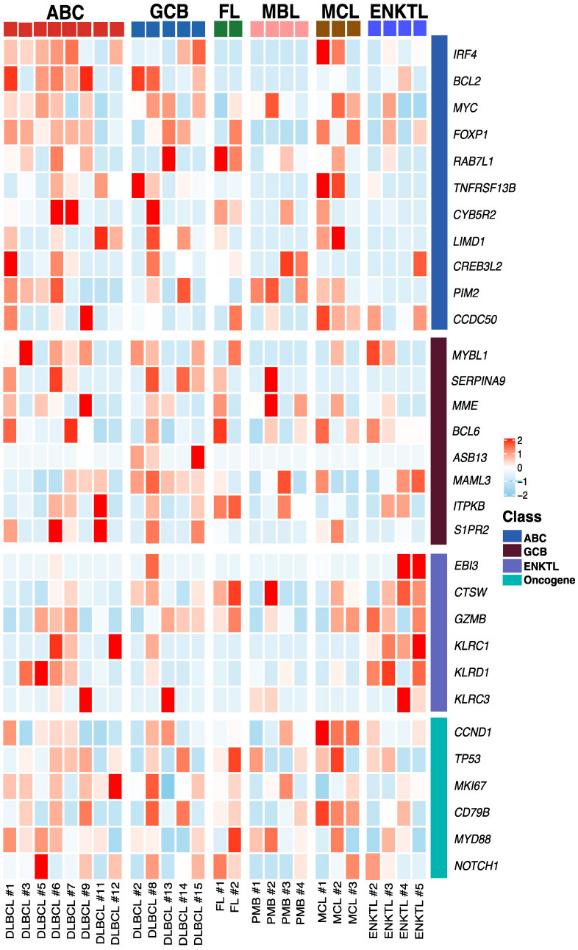 Figure 3. Exosomal mRNA expression profile in
patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma heatmap of mRNA expression levels for selected genes at
baseline. (Bang Y H, et al., 2022)
Figure 3. Exosomal mRNA expression profile in
patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma heatmap of mRNA expression levels for selected genes at
baseline. (Bang Y H, et al., 2022)
Creative Biostructure is committed to providing clients with highly effective solutions. Whether in exploring disease mechanisms, discovering biomarkers, or conducting translational medicine research, we are dedicated to offering reliable support to help clients make progress in the field of exosome research. Please cntact us for more detailed information. We will be happy to assist you.
References
- Bang Y H, Shim J H, Ryu K J, et al. Clinical relevance of serum-derived exosomal messenger RNA sequencing in patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Journal of Cancer. 2022, 13(5): 1388.
- Ji J, Chen R, Zhao L, et al. Circulating exosomal mRNA profiling identifies novel signatures for the detection of prostate cancer. Molecular cancer. 2021, 20(1): 58.
Frequently Asked Questions
For any inquiries, our support team is ready to help you get technical support for your research and maximize your experience with Creative Biostructure.