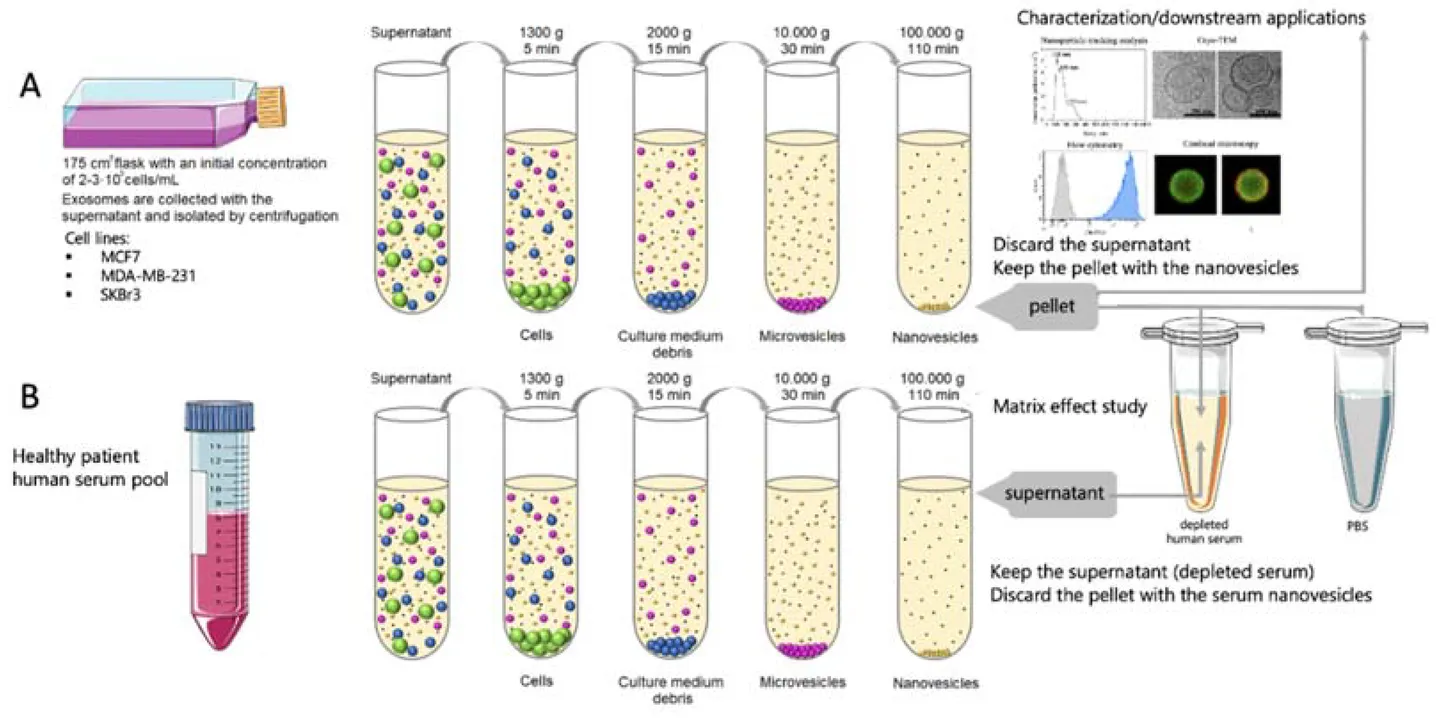
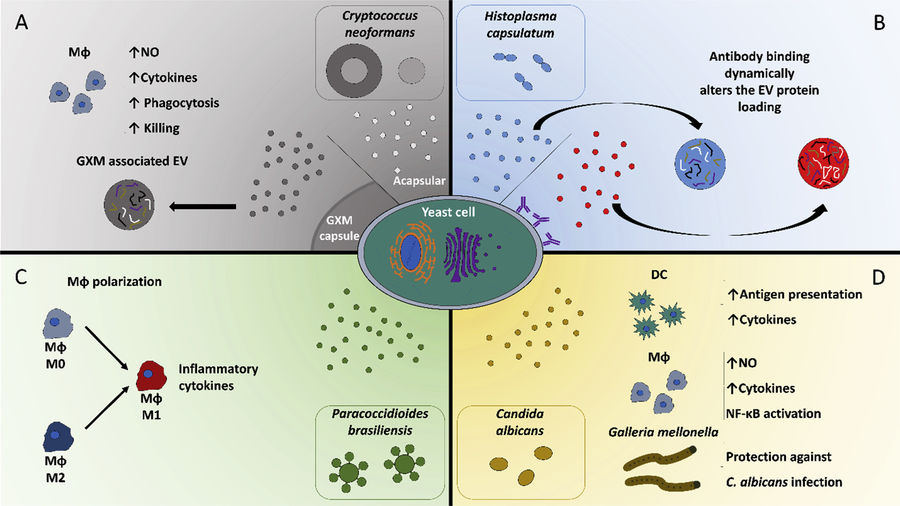
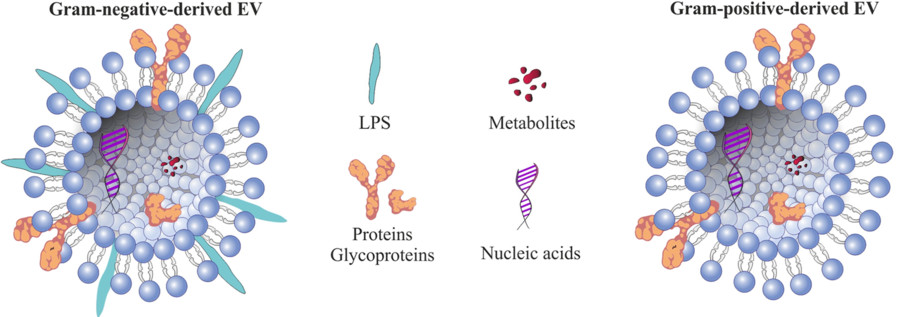
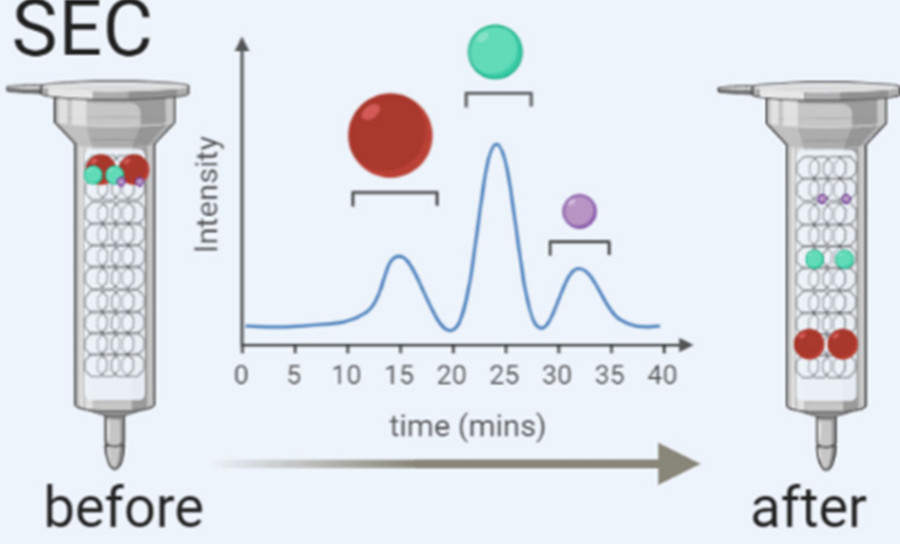
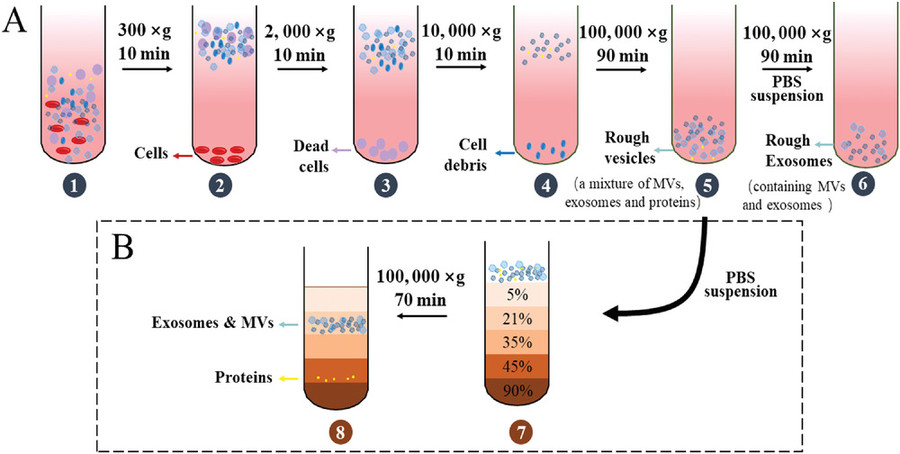
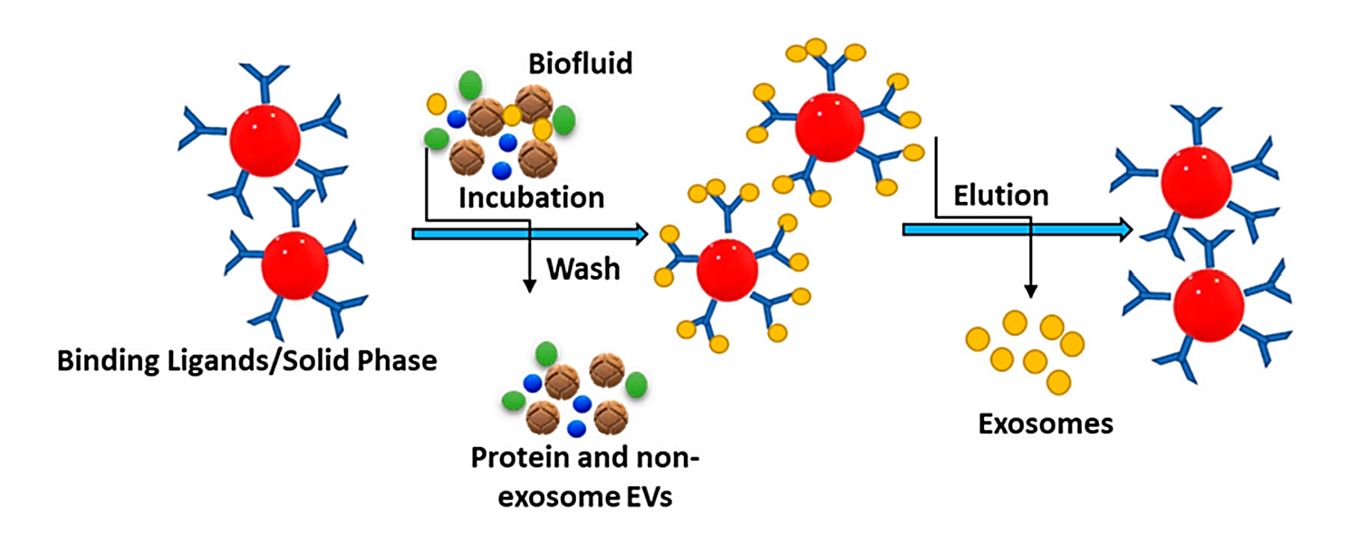
Immunoaffinity-Based Exosome Isolation Service
At Creative Biostructure, we provide immunoaffinity-based exosome isolation services designed to selectively enrich exosome subpopulations from complex biological samples. This technique leverages high-specificity antigen-antibody interactions to capture exosomes expressing specific surface markers such as CD9, CD63, CD81, or tumor-associated antigens, enabling highly targeted isolation with superior purity.
What Is Immunoaffinity-Based Exosome Isolation?
Exosomes are nanosized extracellular vesicles (30-150 nm) released by nearly all cell types, containing proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids reflective of their cell of origin. Among various isolation techniques, immunoaffinity capture stands out for its ability to isolate source-specific or biomarker-enriched exosomes.
This method uses antibodies immobilized on magnetic beads or solid supports to bind surface proteins present on exosomes. Common targets include:
- Tetraspanins (CD9, CD63, CD81): These are widely recognized as canonical markers for general exosome identification and enrichment.
- Tumor-associated antigens (e.g., CSPG4, EpCAM, HER2): These are used to selectively capture exosomes originating from tumor cells, often referred to as tumor-derived exosomes (TEX).
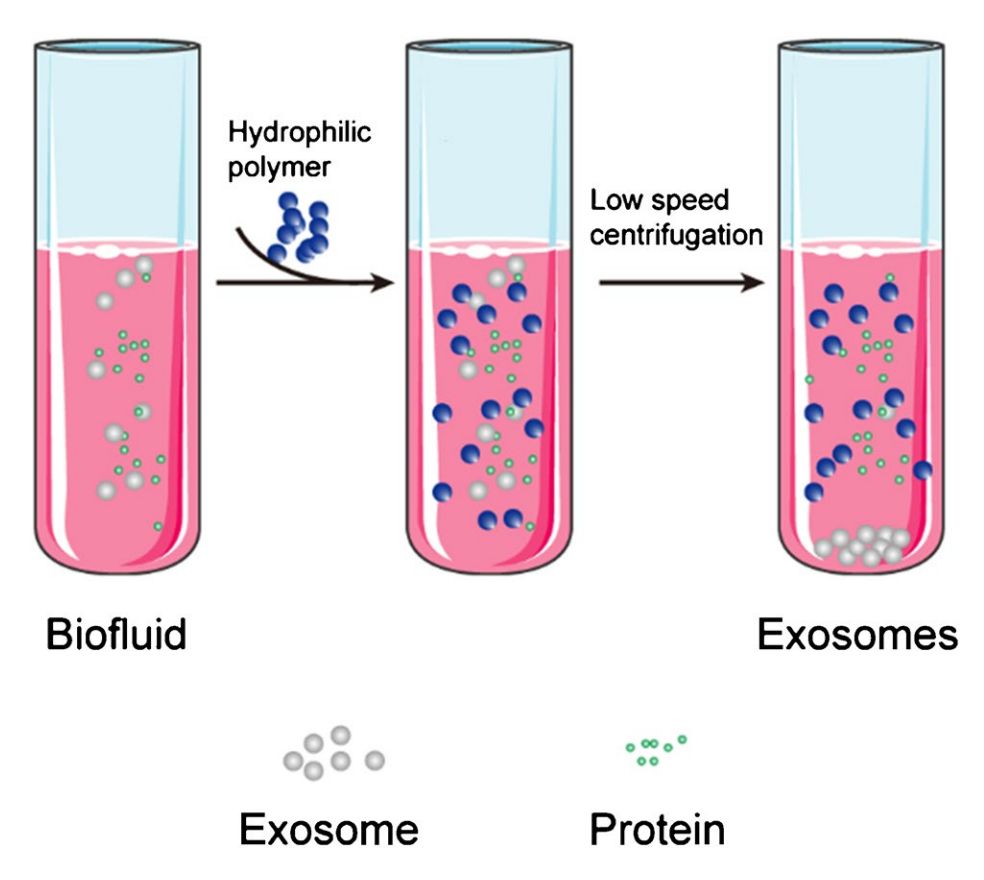
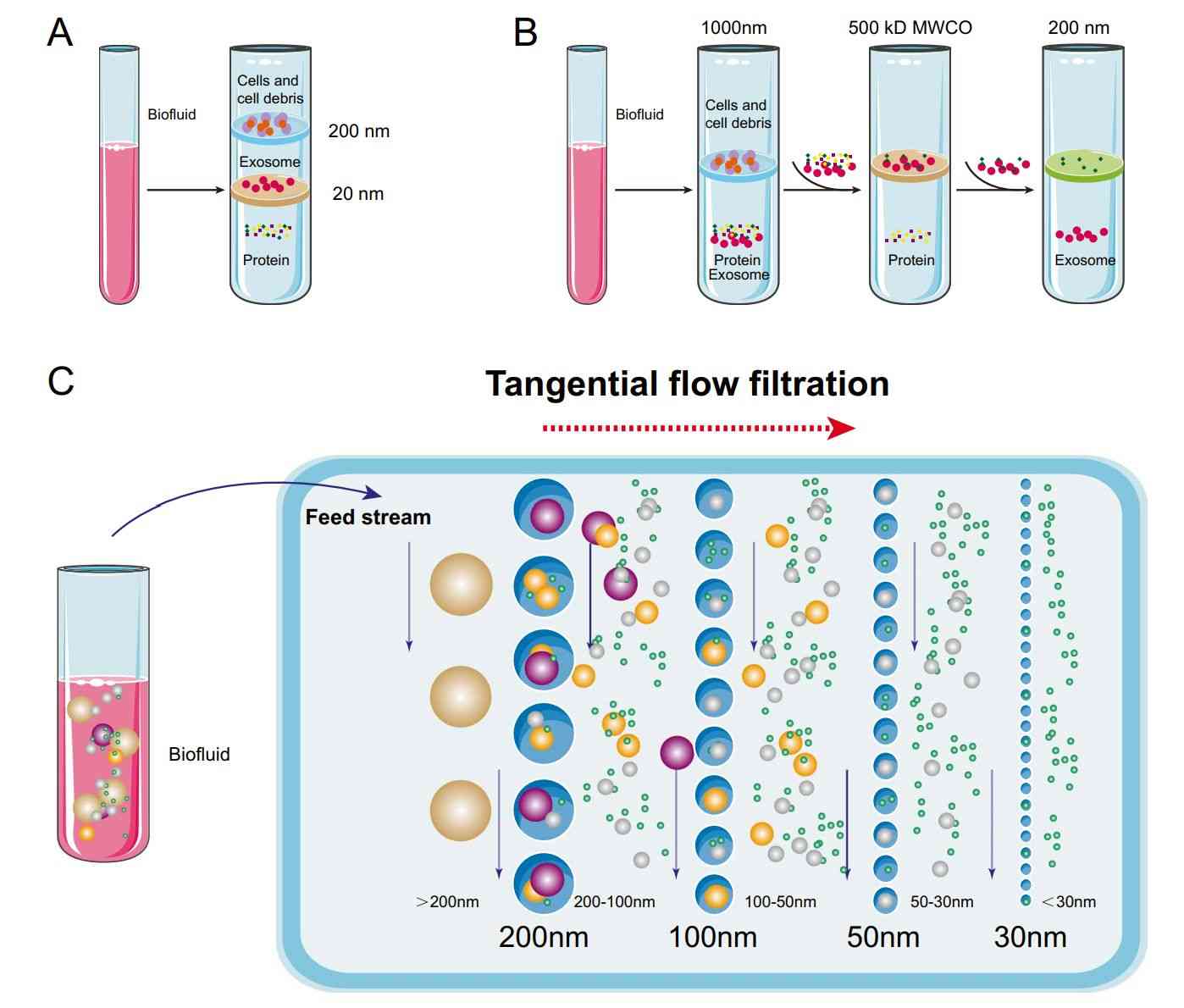
By selectively binding to surface proteins, immunoaffinity isolation offers higher specificity compared to conventional physical separation methods such as ultracentrifugation or size exclusion chromatography (SEC).
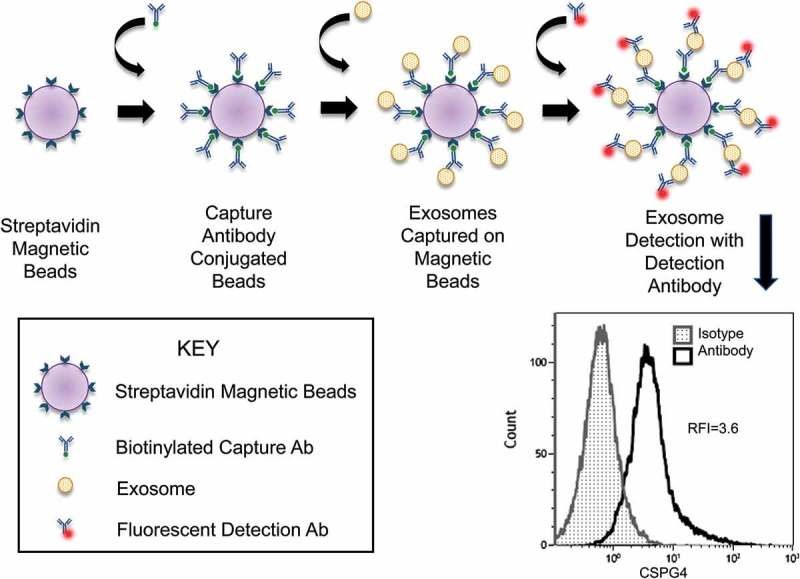 Figure 1. Flow Cytometry Detection of CSPG4⁺ Exosomes Captured on Beads. (Sharma P, et al., 2018)
Figure 1. Flow Cytometry Detection of CSPG4⁺ Exosomes Captured on Beads. (Sharma P, et al., 2018)
Research Applications of Immunoaffinity-Based Exosome Isolation
- Biomarker Discovery: Enriching exosomes from defined cell types improves detection of disease-associated RNAs, proteins, or lipids.
- Immune Profiling: Isolation of vesicles carrying immune-related markers (e.g., PD-L1, MHC) facilitates studies on cell communication and immune modulation.
- Engineered Exosome Characterization: Purify modified exosomes using tag-specific antibodies to validate delivery vehicles for functional studies.
- Subpopulation Analysis: Capture of specific exosome subsets (e.g., CD9+, CSPG4+) supports heterogeneity profiling and cargo comparisons.
- Quality Control in Bioproduction: Isolate exosomes from cell lines to assess production consistency and vesicle composition.
Our Immunoaffinity-Based Exosome Purification Workflow
Our immunoaffinity capture workflow is meticulously designed to ensure high-efficiency isolation of exosome subpopulations while preserving their biological integrity. Each step is optimized for reproducibility, specificity, and compatibility with downstream analyses.
Sample Preparation
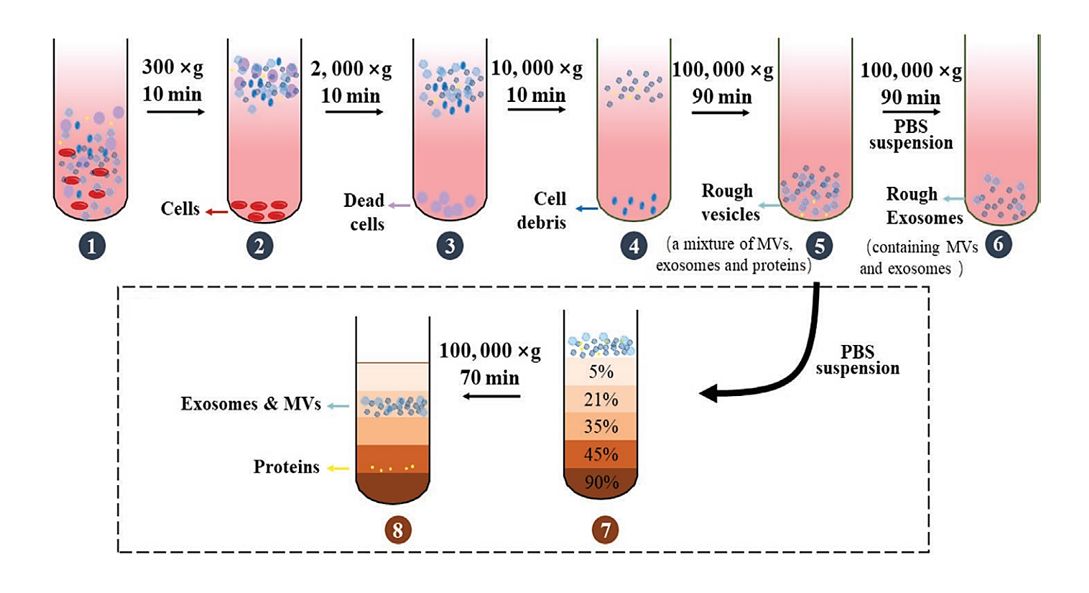
Plasma, serum, urine, CSF, or culture media are clarified by sequential centrifugation, removing cells and debris. Filtration and optional concentration prepare samples for exosome enrichment.
Pre-enrichment via Size Exclusion Chromatography (optional)
For complex fluids like plasma, an optional mini-SEC step reduces protein and lipoprotein contaminants, enhancing antibody binding and improving immunocapture efficiency.
Surface Marker Identification and Antibody Selection
Marker selection is tailored to source and goals: CD9, CD63, CD81 for general capture, CSPG4/EpCAM for tumor focus. Clients may provide custom antibodies or request in-house development.
Antibody Conjugation and Bead Preparation
Biotinylated monoclonal antibodies are coupled to streptavidin-coated beads or solid matrices, with validated binding capacity to ensure low non-specific binding and high capture efficiency.
Immunocapture and Binding Reaction
Exosome fractions are incubated with antibody-coated beads under controlled conditions, using pre-optimized protein, antibody, and bead ratios to maximize binding without saturation.
Magnetic Separation and Washing
Bead-bound exosomes are magnetically separated, then gently washed with PBS to remove non-target proteins and vesicles while preserving exosome integrity.
Elution or On-Bead Analysis
Captured exosomes may be eluted for downstream use or analyzed on-bead via flow cytometry, proteomics, RNA assays, or Western blot validation.
This flexible workflow supports both small-scale discovery research and high-throughput biomarker validation studies. Each stage can be adapted to accommodate unique experimental goals, specific antibody preferences, or regulatory documentation needs.
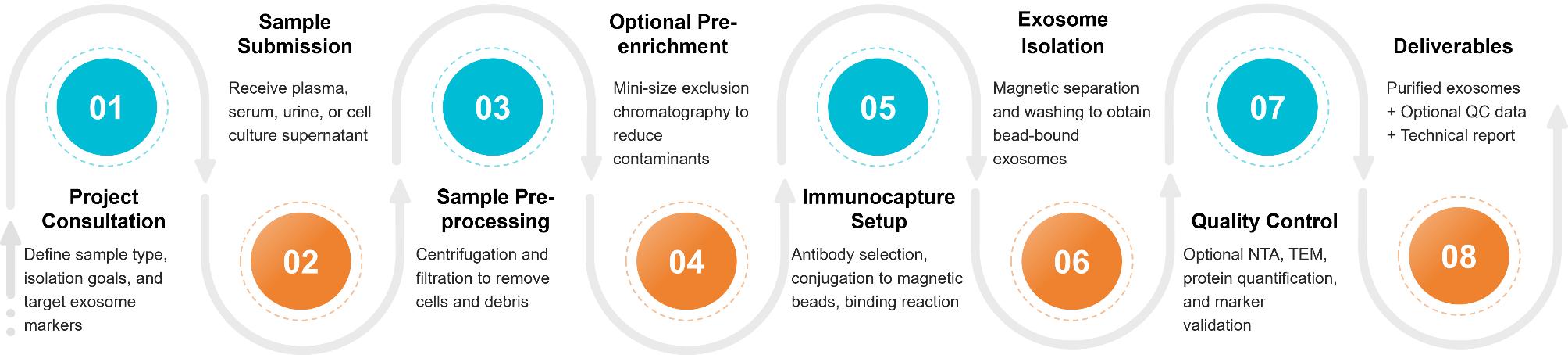 Figure 2. Project Workflow for Exosome Isolation via Immunoaffinity Capture. (Creative Biostructure)
Figure 2. Project Workflow for Exosome Isolation via Immunoaffinity Capture. (Creative Biostructure)
Sample Requirements
Our immunoaffinity capture platform is optimized for isolating exosomes that express specific surface markers such as CD9, CD63, CD81, or disease-associated antigens. To ensure successful and reproducible exosome purification, please review the following sample compatibility guidelines:
Sample Types Suitable for Immunoaffinity-Based Exosome Isolation
The following sample types are well-suited for antibody-based exosome isolation:
- Cell Culture Supernatants: Suitable for adherent or suspension cells from human, animal, or engineered cell lines. We recommend using serum-free or exosome-depleted FBS media. Harvest after 48-72 hours of culture with pre-centrifugation and 0.22 µm filtration.
- Plasma and Serum: Rich in exosomes carrying canonical and disease-specific surface markers. Samples must be non-hemolyzed and collected using EDTA or heparin tubes. At least 1 mL per sample is recommended.
- Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) and Urine: Applicable for studies targeting exosome biomarkers from neurological or renal origins. Minimum volume of 5 mL is advised for effective yield.
- Tumor Tissue Lysates: After enzymatic digestion and clarification, exosomes from tumor-derived tissue can be selectively captured if tumor-specific surface antigens are known and accessible.
For uncommon organisms or engineered systems, we recommend preliminary consultation to determine antibody compatibility and project feasibility.
General Guidelines
- Storage: Store all samples at -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
- Shipping: Transport samples on dry ice with appropriate labeling.
- Metadata: Include details on sample type, organism source, known target markers, and intended downstream applications.
If you are unsure whether your sample is compatible with immunoaffinity capture, please contact our technical support team for personalized guidance.
Quality Control and Deliverables
To ensure the reliability and reproducibility of our immunoaffinity-based exosome isolation, every project is accompanied by rigorous quality control and comprehensive documentation. Our QC pipeline verifies exosome identity, integrity, and capture specificity using industry-standard techniques.
Quality Control Options
| Items | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA) | Provides particle size distribution and concentration data |
| Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) | Offers morphological validation of isolated exosomes |
| Protein Quantification | Total protein content measured using BCA or Bradford assay to assess sample yield |
| Surface Marker Validation | Flow cytometry or WB analysis can be performed to confirm the expression of target exosome markers such as CD63, CD81, CD9, or custom-selected antigens. |
| Contaminant Assessment (Optional) | Evaluation of potential impurities such as albumin or high-density lipoproteins (HDLs) upon request |
Standard Deliverables
- Purified Exosome Sample: Supplied in PBS or custom buffer. Can be eluted from beads or preserved in bead-bound format based on intended downstream use.
- Technical Report, including:
- Detailed information on processing steps
- Antibody and bead specifications
- Capture conditions
- Reagent lot numbers
- Quality Control Summary: Contains size distribution plots, protein quantification data, and optional TEM or flow cytometry results.
If you have specific deliverable needs, such as proteomic readiness or downstream RNA isolation, our technical team can adjust the workflow accordingly.
Key Features of Our Exosome Isolation via Immunoaffinity Capture
- High specificity and purity of isolated exosomes
- Ability to enrich exosomes from specific cell types or disease states
- Compatibility with downstream applications including proteomics and biomarker profiling
- Available for biofluids, cell culture supernatants, and tissue-derived samples
- Custom antibody integration or use of client-provided antibodies
Case Study
Case: Immunoaffinity-Based Isolation of Melanoma-Derived Exosomes from Human Plasma
Background
To address the challenge of isolating tumor-derived exosomes (TEX) from mixed extracellular vesicle (EV) populations in human plasma, researchers developed an immunoaffinity-based method to capture melanoma-derived exosomes (MTEX) using a monoclonal antibody specific to CSPG4, a surface antigen highly expressed on melanoma cells.
Methods
Plasma samples from melanoma patients were processed using:
- Mini-SEC to reduce plasma protein contamination
- Biotinylated anti-CSPG4 monoclonal antibody for immunocapture
- Streptavidin-coated magnetic beads for separation and enrichment
Characterization included:
- Flow cytometry for surface marker detection (CSPG4, CD63)
- Protein quantification using BCA assay
- Marker profiling with melanoma-associated antigens (e.g., TYRP2, MelanA)
Results
- MTEX capture from melanoma cell line supernatants reached ~98% efficiency with 1 μg antibody, 5 μg exosome protein, and 100 μL beads
- In plasma samples, MTEX protein recovery ranged from 22% to 58%, correlating with disease stage
- Captured MTEX were CD63+ and enriched with melanoma-associated proteins, while non-captured exosomes lacked these markers
- High reproducibility was observed across replicates (intra-class correlation coefficient >0.97)
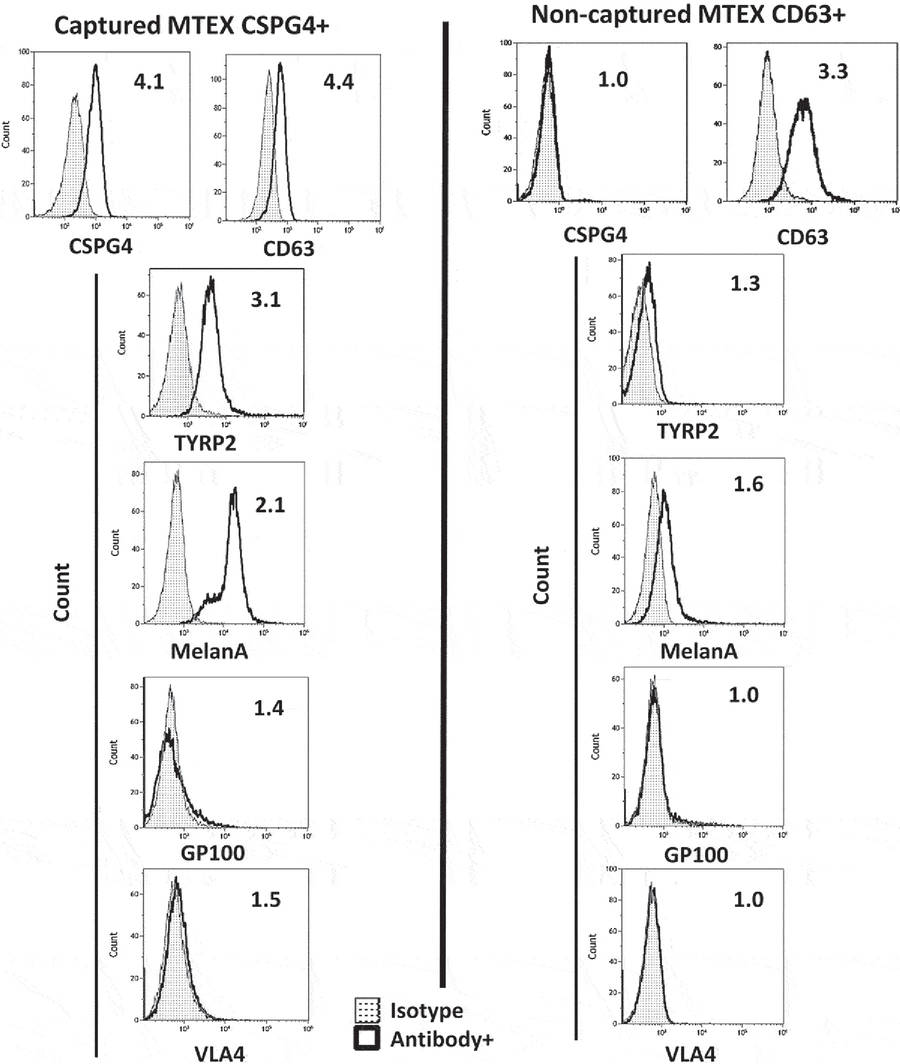 Figure 3. Flow Cytometry Analysis of Melanoma-Associated Antigens on Immunocaptured MTEX. (Sharma P, et al., 2018)
Figure 3. Flow Cytometry Analysis of Melanoma-Associated Antigens on Immunocaptured MTEX. (Sharma P, et al., 2018)
Conclusion
This study demonstrated that combining SEC pre-purification with antibody-mediated immunocapture allows reliable, selective isolation of MTEX from plasma. The method enables detailed exosome phenotyping and supports downstream applications such as biomarker discovery and tumor-specific cargo analysis.
If you are seeking a reliable and specific method to isolate exosome subpopulations for your research, our immunoaffinity capture service is the ideal solution. Whether your focus is biomarker discovery, immune profiling, or exosome quality control, Creative Biostructure offers customizable workflows and validated antibodies to meet your needs. Feel free to contact us to explore your project needs or receive a customized quote tailored to your specifications.
References
- Sharma P, Ludwig S, Muller L, et al. Immunoaffinity-based isolation of melanoma cell-derived exosomes from plasma of patients with melanoma. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles. 2018, 7(1): 1435138.
Frequently Asked Questions
For any inquiries, our support team is ready to help you get technical support for your research and maximize your experience with Creative Biostructure.