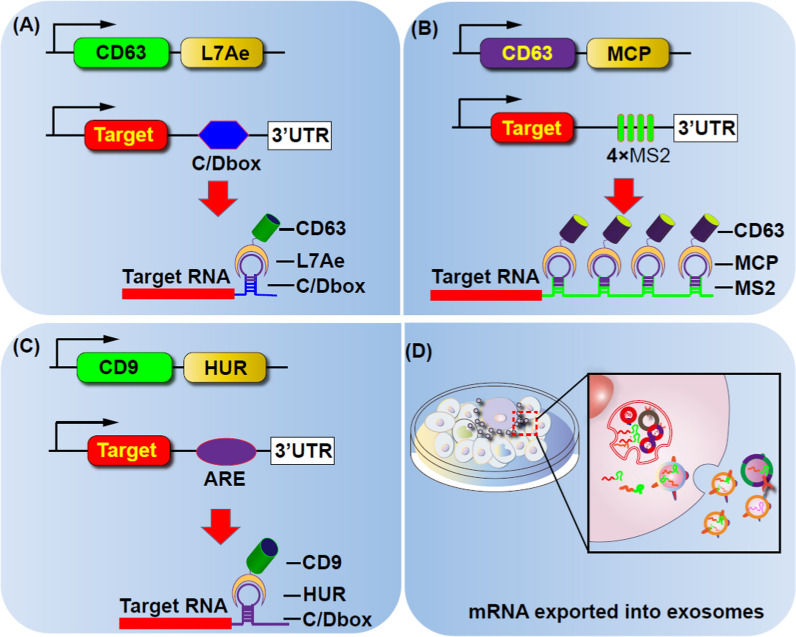
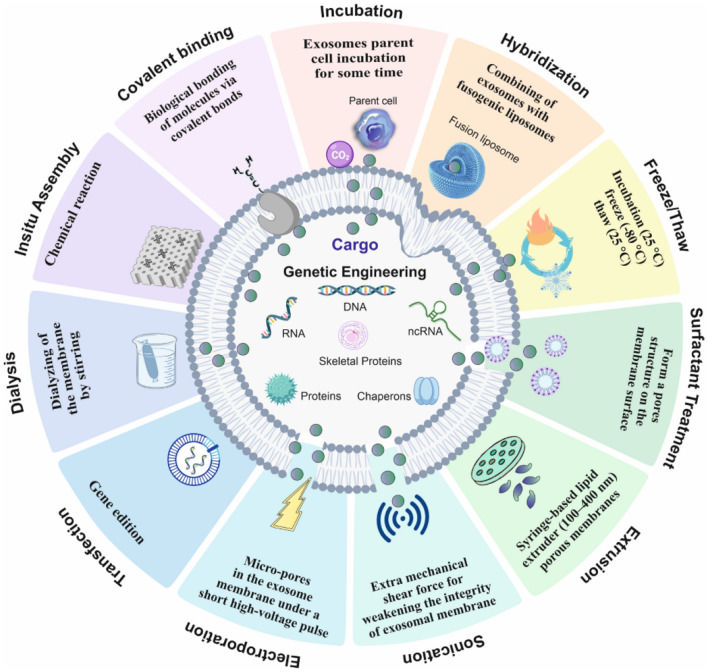
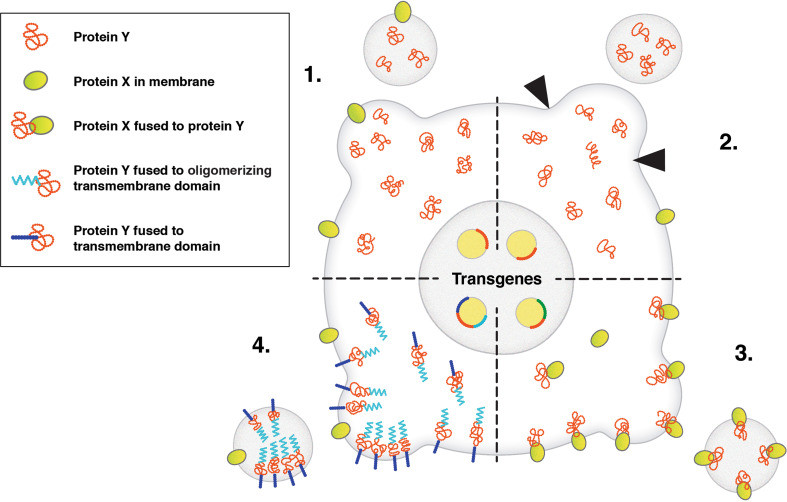
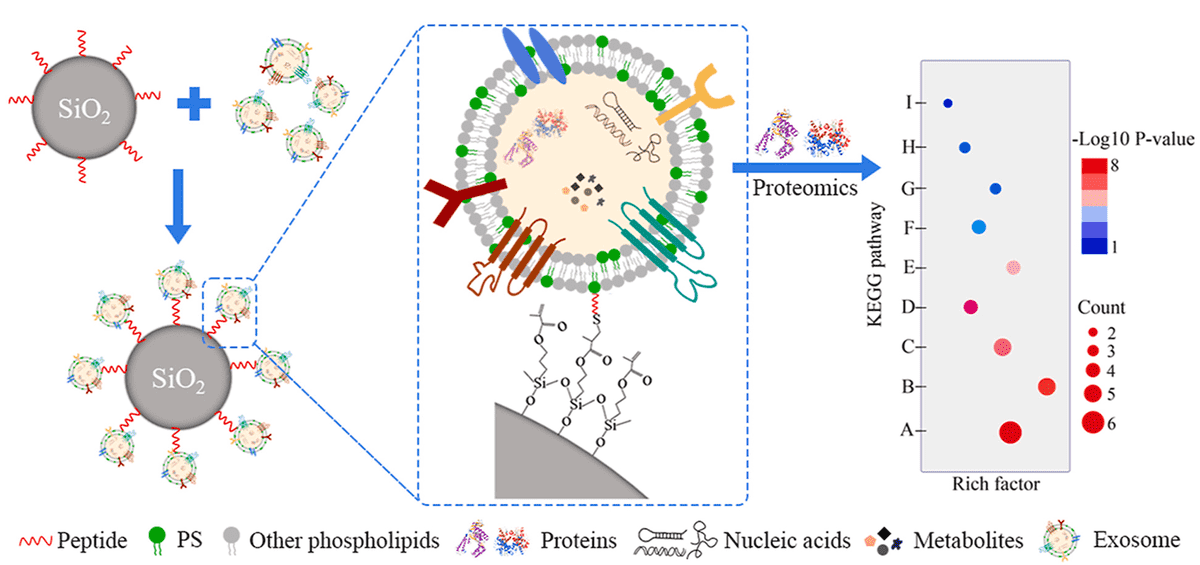
Exosome Small Molecule Delivery
Many potent small molecule drugs (e.g., chemotherapeutics, kinase inhibitors) fail in the clinic due to poor solubility, rapid clearance, or severe systemic toxicity. Even when delivered, tumor cells often develop Multidrug Resistance (MDR), pumping the drug out before it can act.
We provide specialized exosome small molecule delivery solutions. We utilize the natural lipid bilayer of exosomes to solubilize hydrophobic drugs and engineer them for targeted delivery. Our platform helps you transform toxic compounds into precision therapies, enhancing their therapeutic index and bypassing cellular resistance mechanisms.
The Exosome Advantage for Small Molecules
Why choose exosomes over synthetic liposomes or free drugs? Exosomes offer unique biological properties that solve the limitations of traditional pharmacokinetics.
- Solubilizing Hydrophobic Drugs: The lipid membrane of exosomes provides a natural reservoir for hydrophobic compounds (e.g., Curcumin, Paclitaxel), improving their stability and bioavailability without toxic solvents.
- Overcoming Multidrug Resistance (MDR): Exosomes enter cells via endocytosis/fusion, effectively bypassing surface drug efflux pumps (like P-glycoprotein). This allows for intracellular accumulation of the drug in resistant tumor cells.
- Reducing Off-Target Toxicity: By directing the drug specifically to the disease site (via surface engineering), exosomes significantly reduce accumulation in healthy organs (e.g., reducing Doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity).
- Deep Tissue Penetration: Their nanoscale size and deformability allow exosomes to penetrate dense tumor stroma (ECM) more effectively than larger carriers.
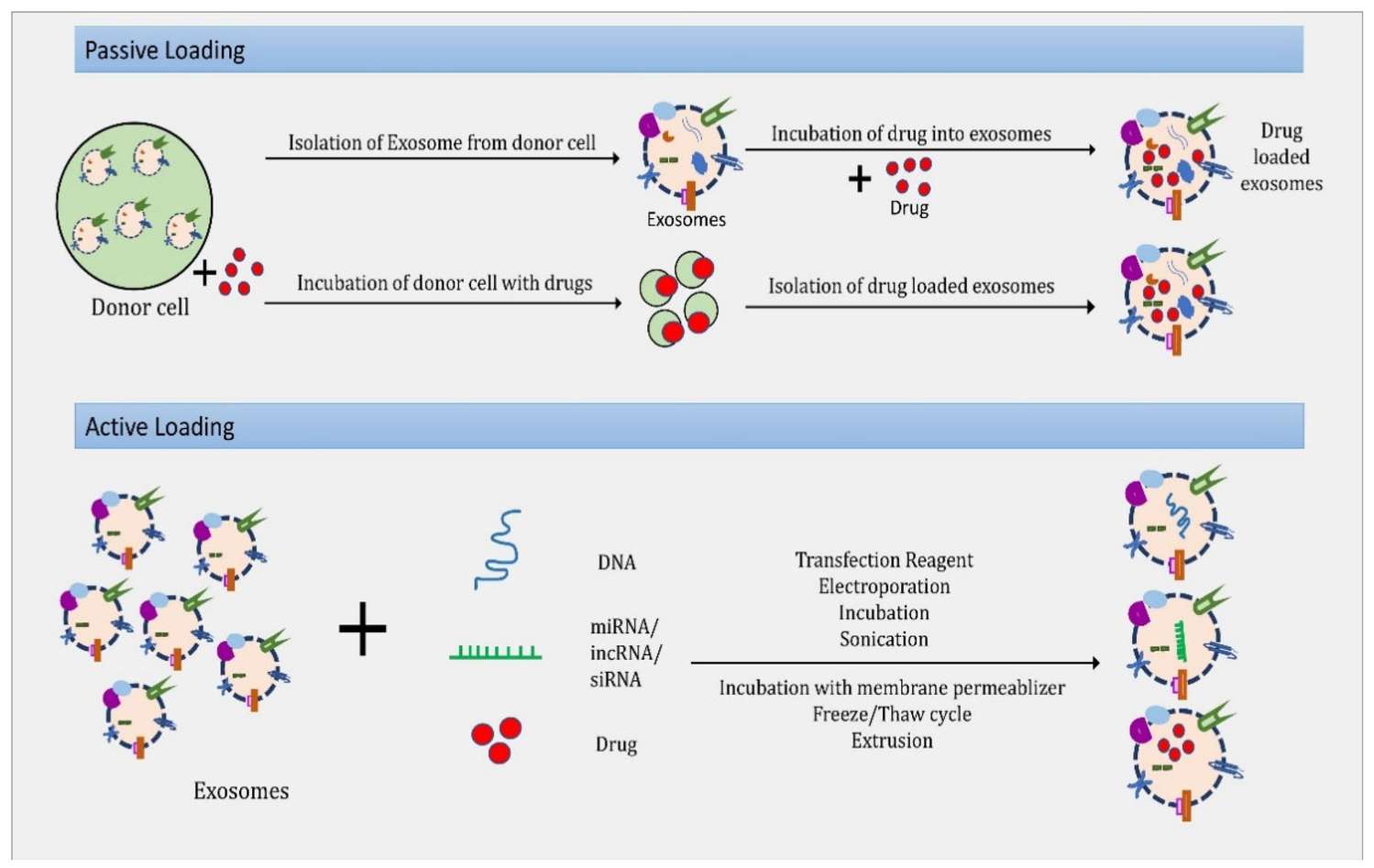 Figure 1. Passive loading involves drug incubation with exosomes, while active loading includes transfection, electroporation, and extrusion to incorporate drugs into exosomes for enhanced therapeutic efficacy. (Rajput A, et al., 2022)
Figure 1. Passive loading involves drug incubation with exosomes, while active loading includes transfection, electroporation, and extrusion to incorporate drugs into exosomes for enhanced therapeutic efficacy. (Rajput A, et al., 2022)
Our Specialized Small Molecule Loading Workflow
Loading efficiency is the critical metric. We offer a range of loading technologies optimized for the chemical properties (Hydrophilic vs. Hydrophobic) of your drug.
| Drug Property | Our Specialized Approach & Solution | Key Services Applied |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrophobic Drugs | Passive & Co-Incubation Loading: We optimize incubation conditions (Temperature, pH, Surfactant) to allow lipophilic drugs to naturally partition into the exosome membrane. We validate the Drug-to-Lipid Ratio to ensure high payload capacity. | Exosome Nucleic Acid Loading, Exosome Protein-to-Particle Ratio Measurement |
| Hydrophilic Drugs | Active Loading Technologies: Water-soluble drugs require force to enter. We utilize Electroporation or Sonication to transiently open membrane pores. We create pH gradients to actively pump and retain the drug inside the vesicle. | Exosome Small Molecule Loading, Downstream Purification & Formulation |
| Purification & QC | Removing Free Drug: Free (unencapsulated) drug causes toxicity and biases data. We use Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC) to strictly separate drug-loaded exosomes from free molecules. We quantify Encapsulation Efficiency (EE%) using HPLC or Spectrophotometry. | Exosome Purification by Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC), Exosome Purity Analysis |
| Efficacy Validation | IC50 & Apoptosis Assays: We compare the cytotoxicity of "Free Drug" vs. "Exo-Drug" in target cells. We typically aim to demonstrate a lower IC50 value (higher potency) for the exosome formulation. | In Vitro Exosome Functional Assays, In Vivo Exosome Functional Assays |
Core Technologies for Your Drug Program
We address the specific technical challenges of small molecule formulation.
Sonication & Electroporation Loading
Maximizing Loading Efficiency: Simple mixing is often insufficient. We employ controlled sonication and electroporation protocols to actively load small molecules. Our process is optimized to maximize drug uptake while minimizing damage to the exosome membrane and surface proteins, ensuring the vehicle remains functional.
Tumor-Targeting Surface Engineering
Precision Delivery: To further reduce systemic toxicity, we engineer exosomes to display targeting ligands (e.g., iRGD peptide or Anti-EGFR antibodies). This ensures that the cytotoxic payload is delivered preferentially to tumor cells, sparing healthy tissues like the heart and liver.
Multidrug Resistance (MDR) Models
Proving Resistance Reversal: We provide specific cell models (e.g., Dox-resistant breast cancer lines) to test your formulation. We track the intracellular accumulation of fluorescent drugs to demonstrate that your exosome formulation successfully evades efflux pumps and kills resistant cells.
Application Spotlight: Delivering Hydrophobic Drugs to the Brain
This analysis highlights how exosomes can solubilize hydrophobic small molecules and deliver them across biological barriers that stop traditional drugs.
Featured Technologies:
- Hydrophobic Drug Loading (Passive Mixing)
- Biodistribution Tracking
Literature Interpretation:
Curcumin is a potent anti-inflammatory small molecule, but it is highly hydrophobic (poorly soluble) and has very low bioavailability, making it difficult to use as a drug. Researchers encapsulated Curcumin into exosomes using a simple incubation method. The lipid bilayer of the exosomes successfully solubilized the drug. The Exosome-Curcumin formulation demonstrated significantly higher stability and solubility. More importantly, when injected, these exosomes successfully crossed the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and inhibited brain inflammation in mice, whereas free Curcumin failed to reach the brain. This outcome demonstrates that exosome encapsulation is an effective strategy to enhance the solubility and bioavailability of hydrophobic small molecules, aligning with the formulation capabilities of our platform.
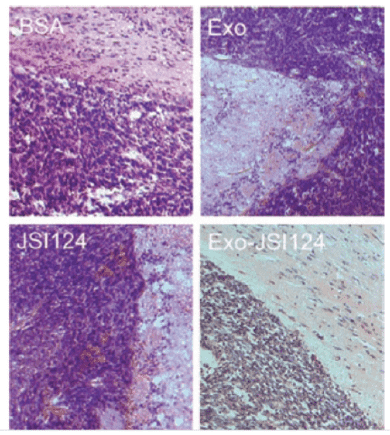 Figure 2. HE staining results of brain tumor sections in mice treated with various agents. Exo-JSI124 treatment inhibits brain tumor growth in vivo. (Zhuang X, et al., 2011)
Figure 2. HE staining results of brain tumor sections in mice treated with various agents. Exo-JSI124 treatment inhibits brain tumor growth in vivo. (Zhuang X, et al., 2011)
Start Your Drug Delivery Project
We make getting started straightforward. Our process is designed to be collaborative and transparent.
How It Works: Our Project Pathway
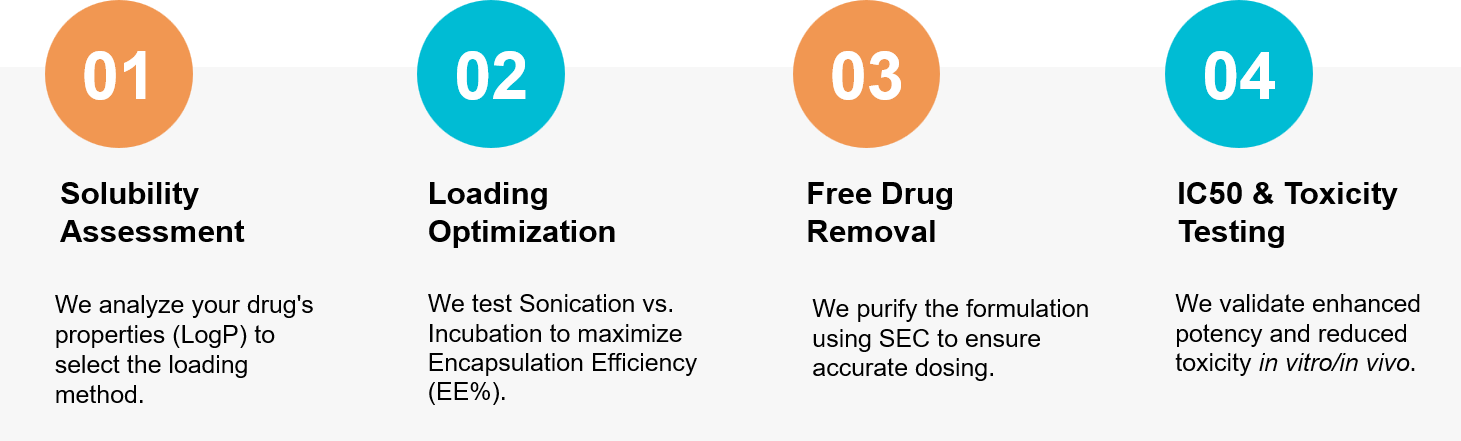 Figure 3. Our workflow for optimizing the loading and purification of small molecule drugs in exosomes. (Creative Biostructure)
Figure 3. Our workflow for optimizing the loading and purification of small molecule drugs in exosomes. (Creative Biostructure)
Ready to improve the solubility and safety of your lead compound? Our scientific team is available for a free consultation to discuss your small molecule delivery strategy. Contact us today to discuss your project.
References
- Rajput A, Varshney A, Bajaj R, et al. Exosomes as New Generation Vehicles for Drug Delivery: Biomedical Applications and Future Perspectives. Molecules. 2022 Oct 27;27(21):7289.
- Zhuang X, Xiang X, Grizzle W, et al. Treatment of brain inflammatory diseases by delivering exosome encapsulated anti-inflammatory drugs from the nasal region to the brain. Mol Ther. 2011 Oct;19(10):1769-79.