Neurological Disease Exosome Solutions
The greatest obstacle in neurology is the Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB). It blocks therapeutics from entering and prevents biomarkers from leaving, making diagnosis and treatment of neurodegenerative diseases notoriously difficult.
We provide end-to-end neurological exosome solutions. Exosomes are the unique exception—they can cross the BBB bidirectionally. Whether you are developing a liquid biopsy for Alzheimer's using plasma L1CAM+ exosomes, or engineering a targeted vehicle for exosome therapy for neurological disorders, our platform bridges the gap between the peripheral blood and the Central Nervous System (CNS).
Why Exosomes are Critical for Neuroscience
Why focus on exosomes and the blood-brain barrier? They offer a "peripheral window" into brain health that no other technology can match.
- Non-Invasive Brain Biopsy: Neuronal exosomes (enriched via surface markers like L1CAM) circulate in the blood. Isolating them allows you to analyze the molecular state of neurons via a simple blood draw, bypassing the need for invasive CSF collection or brain biopsies.
- Crossing the BBB: Exosomes are natural nanocarriers that can traverse the BBB via receptor-mediated transcytosis, solving the delivery bottleneck for CNS drugs.
- Early Detection: Pathogenic proteins (e.g., Amyloid-beta, Alpha-synuclein) are often packaged into exosomes years before clinical symptoms appear, enabling pre-symptomatic diagnosis.
- Modulating Neuroinflammation: Mesenchymal Stem Cell (MSC) exosomes show profound potential in dampening neuroinflammation and promoting neurogenesis after Stroke or TBI.
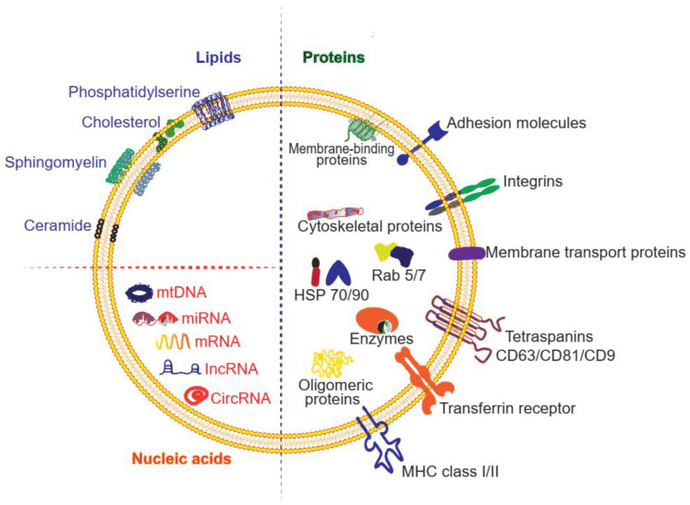
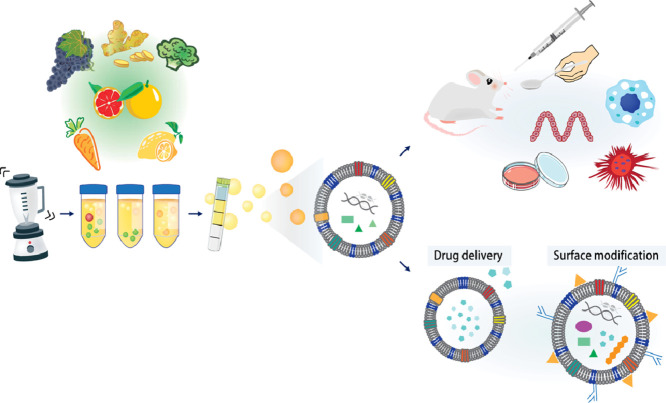
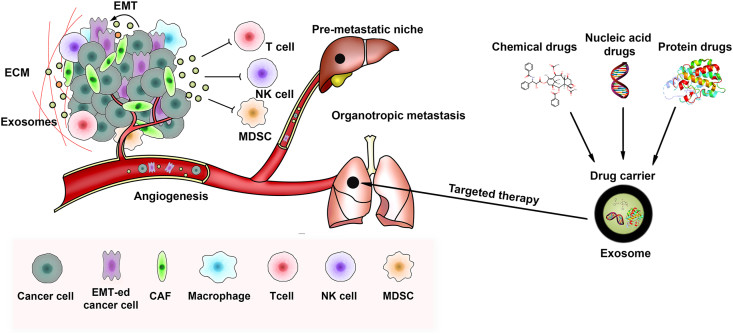
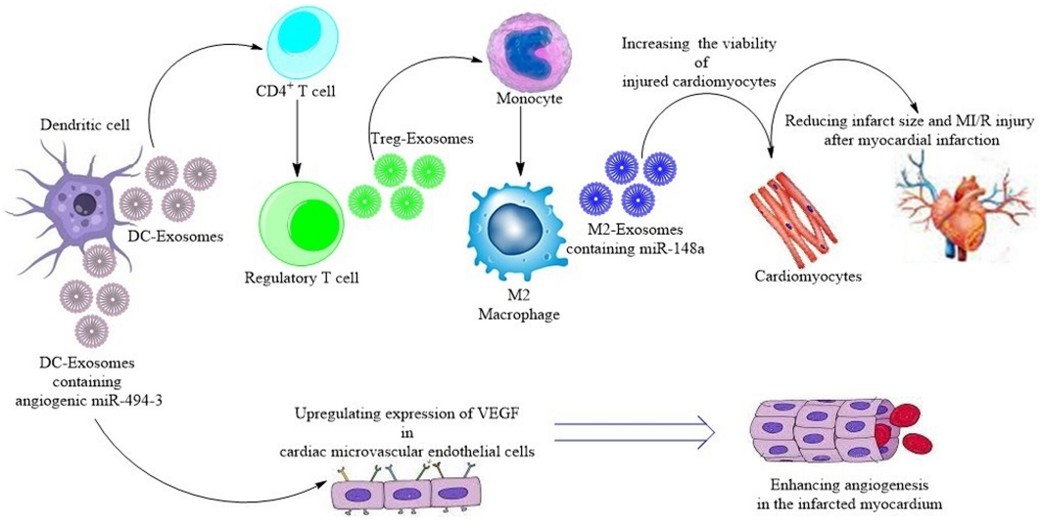
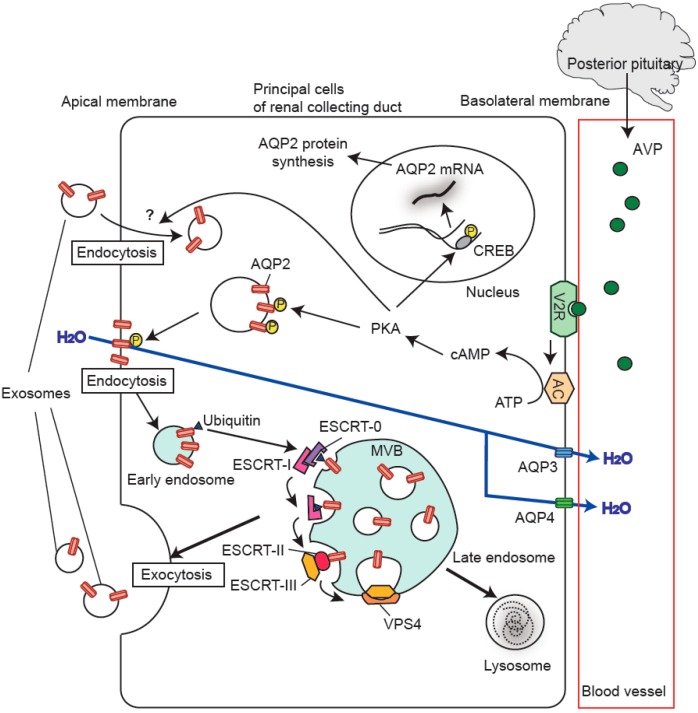
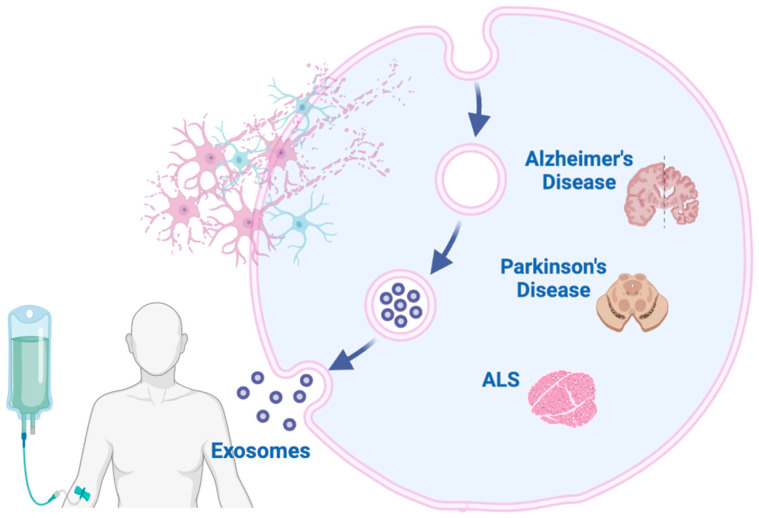 Figure 1. Exosomal biomarkers for diagnosing neurodegenerative disorders. Exosomes from brain and peripheral cells contain disease-specific molecules that can be used for early detection and monitoring of conditions like Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and ALS. (Spinelli S, et al., 2025)
Figure 1. Exosomal biomarkers for diagnosing neurodegenerative disorders. Exosomes from brain and peripheral cells contain disease-specific molecules that can be used for early detection and monitoring of conditions like Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and ALS. (Spinelli S, et al., 2025)
Our Integrated CNS Research Platform
We provide specialized tools to handle the low abundance of CNS exosomes and the complexity of brain tissues.
| Service Pillar | Key Services & Technologies We Provide |
|---|---|
| Neuronal Exosome Enrichment | The "Needle in a Haystack": Neuronal exosomes are rare in blood. We use L1CAM/NCAM Immunoaffinity Capture to specifically isolate neuron-derived exosomes from plasma or serum, ensuring your data reflects CNS status, not systemic noise. |
| CNS Biomarker Profiling | Deep Multi-Omics: We profile the cargo of enriched CNS exosomes. This includes quantifying pathogenic proteins (Tau, Aβ42) via High-Sensitivity ELISA and sequencing CNS-specific miRNAs linked to synaptic dysfunction. |
| BBB Crossing Models | In Vitro Validation: We utilize Transwell BBB models to test the ability of your engineered exosomes (or drug formulations) to cross the endothelial barrier. |
| Neuro-Functional Assays | Testing Efficacy: For therapeutic projects, we validate efficacy using assays for neurite outgrowth, microglia polarization (Anti-inflammation), and protection against oxidative stress (ROS assay). |
Neurological Applications We Support
Our platform provides specialized research models and profiling services for the major neurodegenerative and acute CNS conditions. We help you navigate the complexities of the Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB) and low-abundance CNS biomarkers.
Alzheimer's Disease Exosome Research
Alzheimer's pathology begins decades before symptoms appear. We support the discovery of preclinical biomarkers by isolating neuronal-derived exosomes (L1CAM+) from plasma. Our workflow includes ultra-sensitive quantification of Aβ42, p-Tau181/217, and synaptic proteins (e.g., neurogranin, SNAP-25). Beyond diagnostics, we offer models to investigate how exosomes mediate the spreading of Tau pathology or fail in their clearance duties, providing a complete picture of disease progression.
Parkinson's Disease Exosome Research
Evidence suggests that pathogenic alpha-synuclein aggregates spread through the brain via exosomes in a "prion-like" manner. We help you track this propagation. Our services include detecting oligomeric alpha-synuclein in patient biofluids and using in vitro models to study how exosomes transmit toxicity between neurons and glia. We also support the development of exosome-based delivery systems to transport neurotrophic factors (e.g., GDNF) or gene-silencing agents directly to dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra.
Huntington's Disease Exosome Research
Huntington's is a monogenic disorder ideal for targeted intervention. We profile exosomes to detect mutant Huntingtin (mHtt) protein and disease-associated miRNAs, validating their potential as biomarkers for disease onset. Furthermore, we support therapeutic research focusing on exosome-mediated delivery of ASOs (Antisense Oligonucleotides) or siRNA to silence the Htt gene. Our blood-brain barrier models allow you to verify that your therapeutic cargo can successfully reach the striatum.
Stroke Exosome Research
In ischemic stroke, the primary goal is neuroprotection and remodeling. We investigate the therapeutic potential of MSC exosomes to modulate the post-stroke immune response (shifting microglia from pro-inflammatory M1 to restorative M2 phenotype). Our functional assays assess angiogenesis (new vessel growth), neurogenesis, and axonal sprouting in the penumbra region. We provide comprehensive in vivo stroke models (MCAO) to validate improvements in motor function and infarct volume reduction.
Advantages of Our Neuro-Platform
Neuroscience research demands higher sensitivity and specificity than any other field. We have optimized our platform to overcome the unique physiological barriers of the CNS.
Proprietary L1CAM+ Neuronal Enrichment
Solving the "Signal-to-Noise" Problem: Total plasma exosomes are dominated by vesicles from platelets and immune cells, drowning out the CNS signal. We utilize advanced Immunoaffinity Capture protocols targeting neuronal surface markers (L1CAM, NCAM). Unlike generic precipitation kits, our workflow selectively enriches neuron-derived exosomes, increasing the sensitivity for brain biomarkers by up to 50-fold. This allows you to detect CNS pathology in a standard blood draw with unprecedented clarity.
Ultra-Sensitive Biomarker Detection
Pushing the Limits of Detection: CNS proteins (like p-Tau217 or oligomeric a-synuclein) exist in blood at ultra-low levels. Standard bulk assays often fail to distinguish effective signals from background noise. We utilize High-Sensitivity ELISA and advanced Nano-Flow Cytometry (nFCM). NanoFCM allows us to analyze exosomes at the single-particle level, identifying the specific sub-population of vesicles carrying your target neuronal markers, providing a resolution far superior to conventional methods.
Validated BBB-Crossing Engineering
Overcoming the Delivery Barrier: Getting drugs into the brain is the biggest hurdle in neuro-therapeutics. We don't just theorize; we engineer. We offer validated surface modification services to display brain-targeting peptides (e.g., RVG29, Angiopep-2, TfR ligands) on the exosome surface. We then validate this targeting efficiency using in vivo bioluminescence imaging and ex vivo brain tissue analysis to prove your therapeutic cargo actually reaches the parenchyma.
Application Spotlight: Predicting Alzheimer's Years in Advance
This analysis highlights the revolutionary power of neuronal exosome isolation for early diagnosis, the holy grail of neuro-research.
Featured Technologies:
- L1CAM+ Exosome Isolation
- Biomarker Protein Quantification
Literature Interpretation:
This pioneering study changed the field of CNS biomarker discovery. The challenge was to diagnose Alzheimer's Disease (AD) at the preclinical stage. Researchers used a specific antibody against L1CAM (a neuronal cell adhesion molecule) to capture neuron-derived exosomes from patient plasma. These enriched exosomes showed significantly elevated levels of p-Tau181 and Aβ42 in AD patients compared to controls—up to 10 years before clinical onset. This validated that selectively isolating neuronal exosomes from blood can provide a "liquid biopsy" of the brain, enabling ultra-early diagnosis.
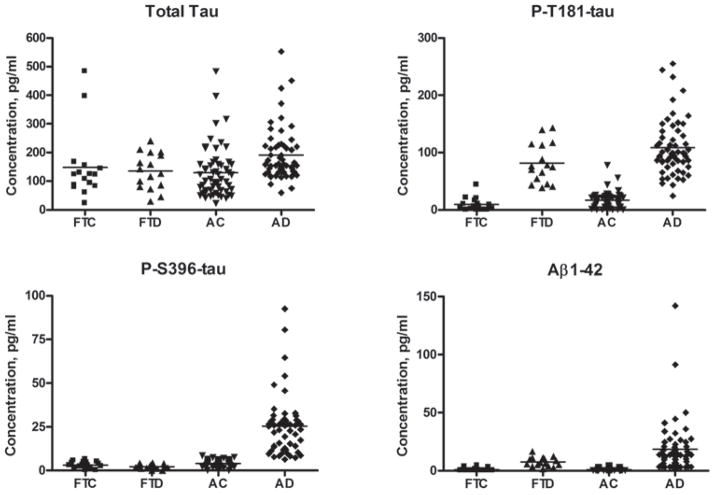 Figure 2. Protein levels in blood exosomes from AD, FTD patients and cognitively normal controls. The horizontal line indicates the mean for each group. (Fiandaca MS, et al., 2015)
Figure 2. Protein levels in blood exosomes from AD, FTD patients and cognitively normal controls. The horizontal line indicates the mean for each group. (Fiandaca MS, et al., 2015)
Start Your Neuroscience Project
We make getting started straightforward. Our process is designed to be collaborative and transparent, ensuring your project goals are met at every stage.
How It Works: Our Project Pathway
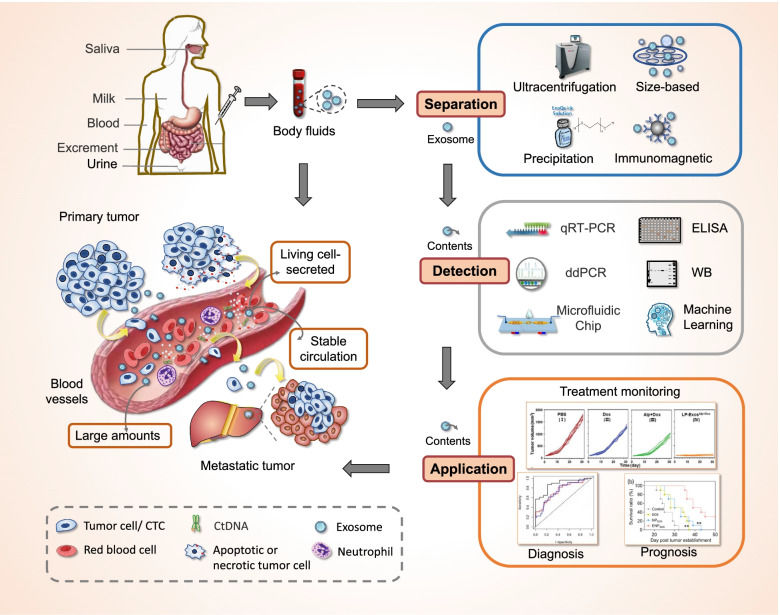
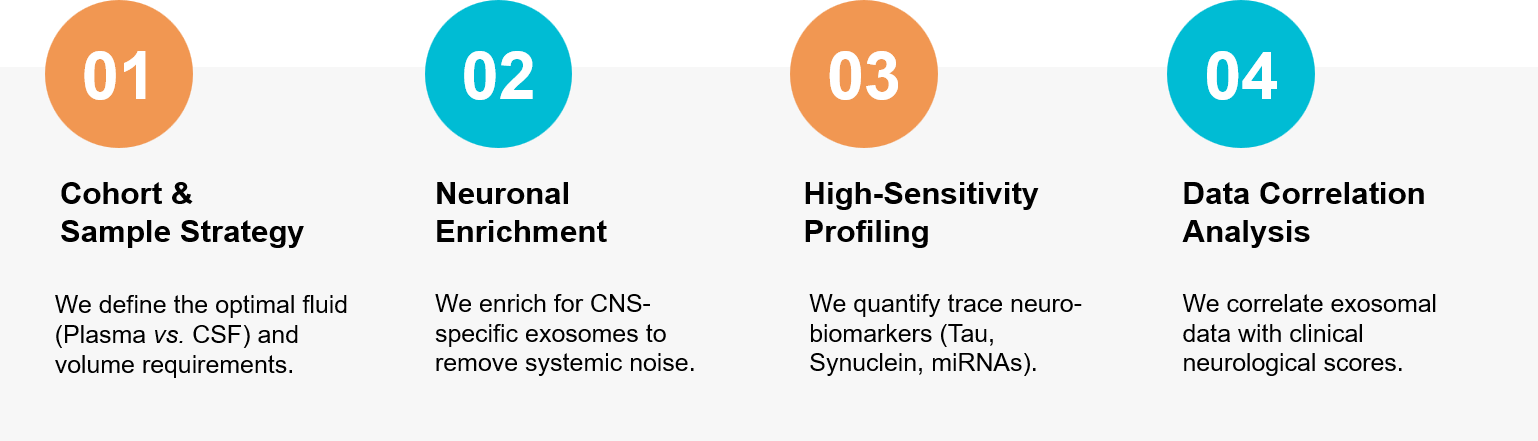 Figure 3. Project workflow for non-invasive CNS research, featuring specific neuronal exosome enrichment from plasma. (Creative Biostructure)
Figure 3. Project workflow for non-invasive CNS research, featuring specific neuronal exosome enrichment from plasma. (Creative Biostructure)
Ready to unlock the mysteries of the brain? Our scientific team is available for a free consultation to discuss your neurological exosome strategy.
References
- Spinelli S, Tripodi D, Corti N, et al. Roles, Functions, and Pathological Implications of Exosomes in the Central Nervous System. Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 5;26(3):1345.
- Fiandaca MS, Kapogiannis D, Mapstone M, et al. Identification of preclinical Alzheimer's disease by a profile of pathogenic proteins in neurally derived blood exosomes: A case-control study. Alzheimers Dement. 2015 Jun;11(6):600-7.e1.