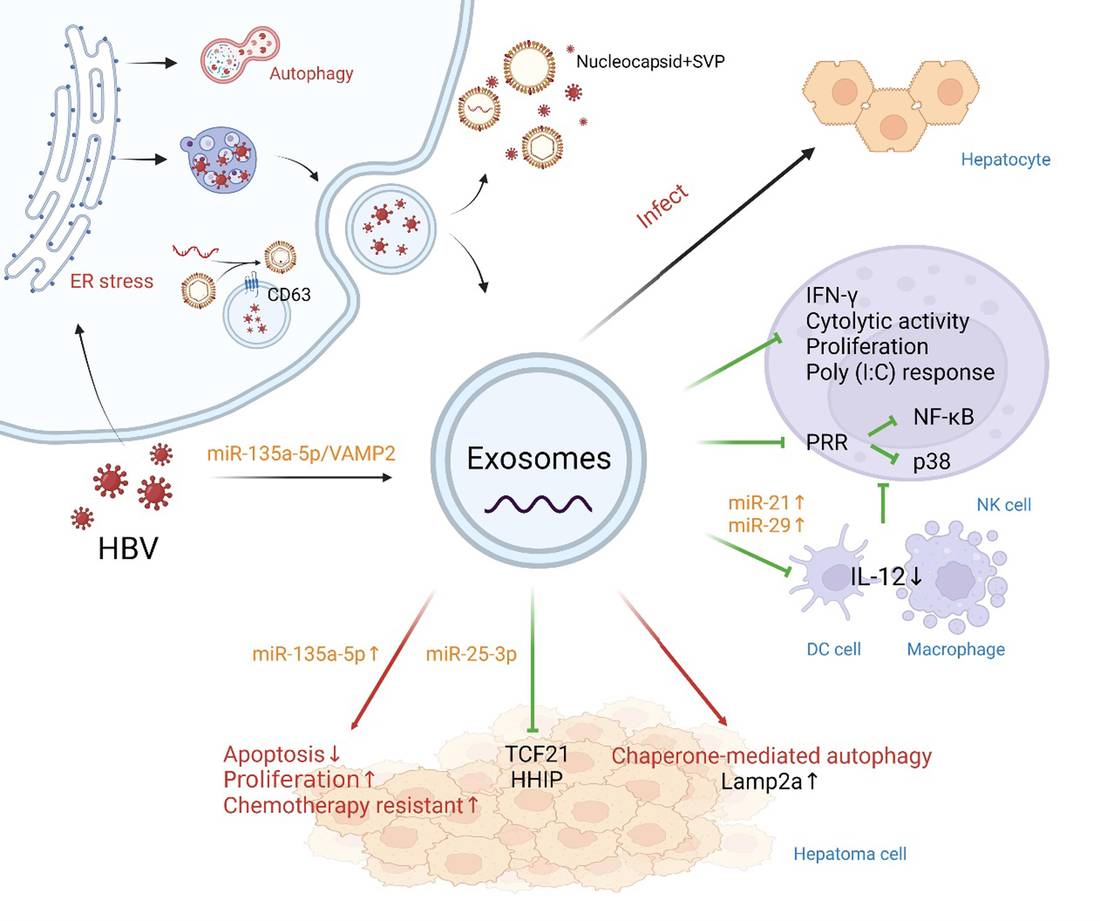
Immune Response Modulation via Exosomes
The immune system utilizes Extracellular Vesicles (EVs) as a sophisticated "wireless" communication network to coordinate host defense. During infection, immune cells (such as Macrophages, Dendritic Cells, and T-cells) release exosomes carrying MHC-peptide complexes, pro-inflammatory cytokines, and regulatory miRNAs. These vesicles can prime T-cells for attack, propagate inflammation (as seen in Sepsis), or conversely, induce immune tolerance to prevent tissue damage.
However, decoding this network is challenging due to the dual nature of exosomes—they can be immunostimulatory or immunosuppressive depending on the context and cellular origin. Furthermore, immunomodulatory cargo (like Interferons or PD-L1) is often present in trace amounts, requiring highly sensitive detection methods beyond standard proteomics. We provide a specialized immunology platform designed to phenotype immune-derived exosomes and validate their functional impact on host defense mechanisms.
Critical Frontiers in Immunology Research
The study of exosome-mediated immunity is reshaping our understanding of infectious diseases and immunotherapy. Key research frontiers include:
- Sepsis & Cytokine Storms: In bacterial sepsis or severe viral infections (e.g., COVID-19), circulating exosomes carry a "storm" of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-6, TNF-α) and DAMPs (HMGB1). Research focuses on blocking these pathogenic exosomes to dampen systemic inflammation.
- Antigen Presentation (Cross-Dressing): Dendritic cells (DCs) release exosomes carrying pre-formed MHC-peptide complexes. These exosomes can fuse with bystander cells, allowing them to present antigens to T-cells without direct infection—a mechanism known as "cross-dressing" that amplifies antiviral immunity.
- Immune Exhaustion & Checkpoints: Chronic pathogens (like HIV or Hepatitis) exploit exosomes to express Checkpoint Inhibitors (e.g., Exosomal PD-L1). These vesicles travel systemically to suppress CD8+ T-cell function, facilitating viral persistence.
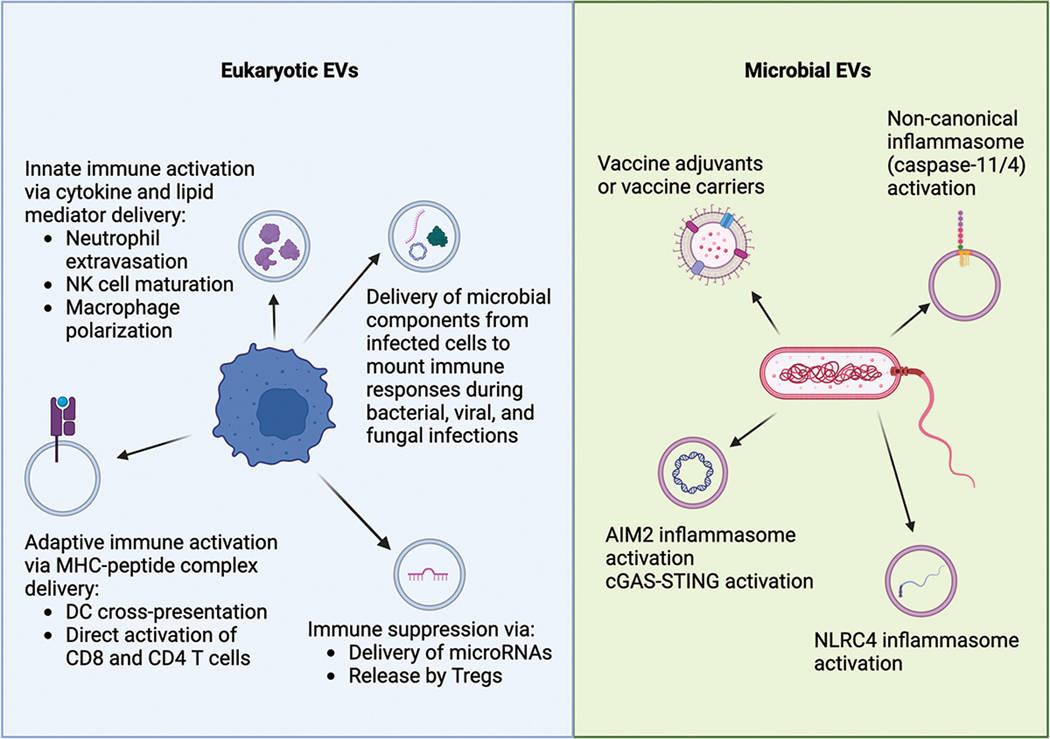 Figure 1. Extracellular vesicles' role in immune response and host defense, including modulation of immune cells and potential as vaccine platforms. (Kumari P, et al., 2024)
Figure 1. Extracellular vesicles' role in immune response and host defense, including modulation of immune cells and potential as vaccine platforms. (Kumari P, et al., 2024)
Accelerating Immunological Discovery with Targeted Solutions
We offer a modular service portfolio to dissect the specific roles of exosomes in innate and adaptive immunity.
| Research Focus | Our Specialized Approach & Solution | Key Services Applied |
|---|---|---|
| Macrophage Polarization Studies | M1/M2 Phenotyping: We isolate exosomes from infected tissues and test their ability to drive naive macrophages towards pro-inflammatory (M1) or anti-inflammatory (M2) states using qPCR (iNOS vs. Arg1) and Flow Cytometry. | Exosome Cellular Functional Assays, Immunomodulation and Inflammation Assays |
| Cytokine Storm Profiling | Multiplex Protein Detection: Using Olink technology, we quantify up to 40+ cytokines directly associated with or encapsulated within exosomes, providing a higher sensitivity than ELISA for low-volume samples. | Exosome Protein Profiling with Olink Proteomics Technology |
| Antigen Presentation Analysis | MHC & T-Cell Activation: We characterize the expression of MHC-I/II molecules on exosomes via NanoFCM and assess their functional capacity to induce T-cell proliferation in mixed lymphocyte reactions (MLR). | Exosome Characterization by NanoFCM, Exosome Surface Marker Analysis |
| Immune Checkpoint (PD-L1) | Exosomal PD-L1 Quantification: We measure the surface density of PD-L1 on circulating exosomes to evaluate immune exhaustion status, serving as a potential biomarker for immunotherapy response. | Exosome Isolation by Immunoaffinity Capture, Exosome Characterization by Western Blotting |
Featured Technologies for Immune Analysis
Multiplex Cytokine Array (Luminex/Olink)
Exosomes often carry cytokines attached to their surface or encapsulated within. Standard ELISA requires large volumes and detects only soluble cytokines. We utilize Multiplex Bead-Based Arrays and Proximity Extension Assays (Olink) optimized for lysed exosome samples. This allows for the simultaneous quantification of dozens of inflammatory mediators (e.g., IL-1β, IL-6, IFN-γ) from minute amounts of exosomal protein, creating a comprehensive "immune signature" of the infection.
Single-Vesicle Immunotyping (NanoFCM)
Bulk analysis often masks rare immunomodulatory exosomes. Our Nano-Flow Cytometry (NanoFCM) platform enables Single-Particle Analysis. By using fluorescent antibodies against immune markers (e.g., CD86 for activated APCs, PD-L1 for suppressive cells, or CD3 for T-cell derived EVs), we can determine exactly what fraction of the circulating exosome pool is contributing to immune modulation.
Immune Cell Co-Culture Models
To validate function, structure alone is insufficient. We have established robust in vitro co-culture systems. For example, we can treat primary human monocytes with client-derived exosomes and monitor their differentiation into Dendritic Cells or Macrophages. These bioassays provide the functional proof-of-concept needed to claim an exosome is "immunomodulatory."
Application Spotlight: Modulating Exosome Machinery to Promote Viral Replication
This case study reveals how specific host trafficking proteins are manipulated to modulate the exosomal pathway and regulate innate immune responses during viral infection.
Featured Technologies:
- Exosome Isolation & Characterization
- Innate Immune Gene Profiling (qPCR)
- Protein-Protein Interaction Analysis
Literature Interpretation:
The intersection of vesicle trafficking and immunity is a new frontier. In this 2024 study, researchers investigated the role of EcSnx27 (Sorting Nexin 27 from Epinephelus coioides) during viral infection. They discovered that EcSnx27 acts as a crucial regulator that bridges the exosomal machinery and the innate immune response. Specifically, EcSnx27 was found to modulate the secretion and cargo sorting of exosomes. By regulating this pathway, EcSnx27 suppressed the host's antiviral immune signaling, thereby facilitating the production of viral products. This study highlights the capability of our platform to dissect complex mechanisms where host trafficking proteins are modulated to alter exosome-mediated immune communication.
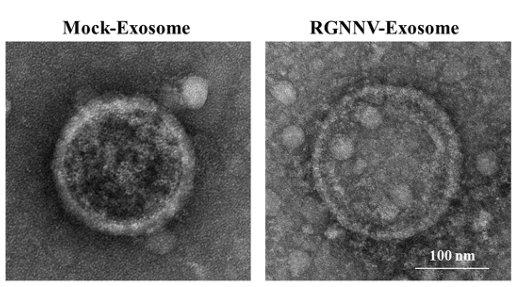 Figure 2. TEM observation of exosomes post-RGNNV infection in GK cells, following cell culture and exosome extraction procedures. (Yu Y, et al., 2024)
Figure 2. TEM observation of exosomes post-RGNNV infection in GK cells, following cell culture and exosome extraction procedures. (Yu Y, et al., 2024)
Start Your Immune Modulation Studies
A standardized pipeline to link exosome cargo to immune function.
How It Works: Our Project Pathway
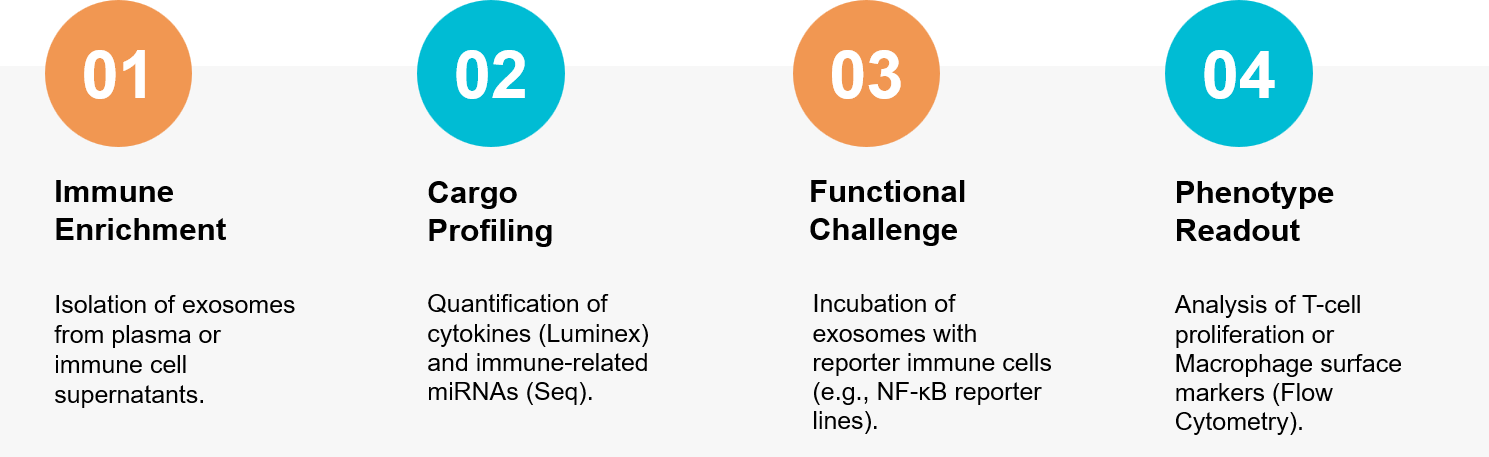 Figure 3. Integrated workflow for profiling immunomodulatory exosomes and validating their function in vitro. (Creative Biostructure)
Figure 3. Integrated workflow for profiling immunomodulatory exosomes and validating their function in vitro. (Creative Biostructure)
Ready to find the next breakthrough in Sepsis Therapy or Viral Immunology? Our immunology experts are available to build a custom study plan tailored to your needs. Contact us today to discuss your project.
References
- Kumari P, Wright SS, Rathinam VA. Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Immunity and Host Defense. Immunol Invest. 2024 Jan;53(1):10-25.
- Yu Y, Liu J, Zhao Z, et al. Fish Snx27 promotes viral products by modulating the innate immune response and exosomal machinery. J Virol. 2024 Dec 17;98(12):e0097424.