Human Exosome Lipidomics Analysis Service
As an important medium for intercellular communication, the lipid information carried by exosomes is crucial for understanding the physiological state of cells, the mechanism of disease development, and the search for potential biomarkers. Creative Biostructure's Human Exosome Lipidomics Analysis Service delivers a comprehensive solution for in-depth exploration of lipid profiles in human exosomes. Leveraging advanced mass spectrometry platforms and rigorous workflows, we provide high-quality quantitative data for hundreds of lipids, empowering researchers to pioneer novel discoveries across diverse fields.
Why Is Exosomal Lipidomics Important in Disease Research?
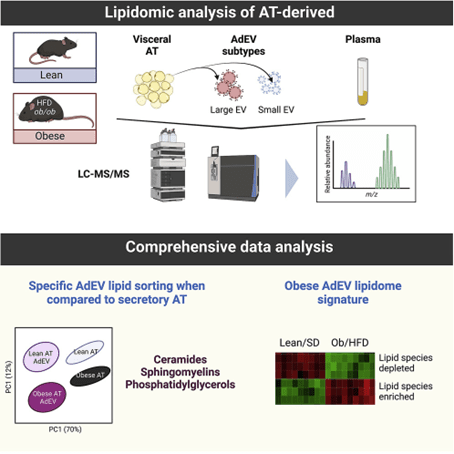
Lipids are not only involved in the biogenesis and structural maintenance of exosomes, but changes in their types and contents are also closely related to the onset and development of many diseases. For example, in tumor research, exosomal lipid profiles of tumor cell origin may provide new biomarkers for early diagnosis and therapeutic monitoring of tumors. In neurological disease research, exosomal lipids are closely associated with the progression of neurodegenerative diseases. With the deepening of research, the need for systematic analysis of exosomal lipidomics has become increasingly urgent. The analysis of exosomal lipidomics can not only identify novel diagnostic markers, but also has a guiding significance for basic research, such as the assessment of exosomal drug-carrying capacity and bioactivity analysis.
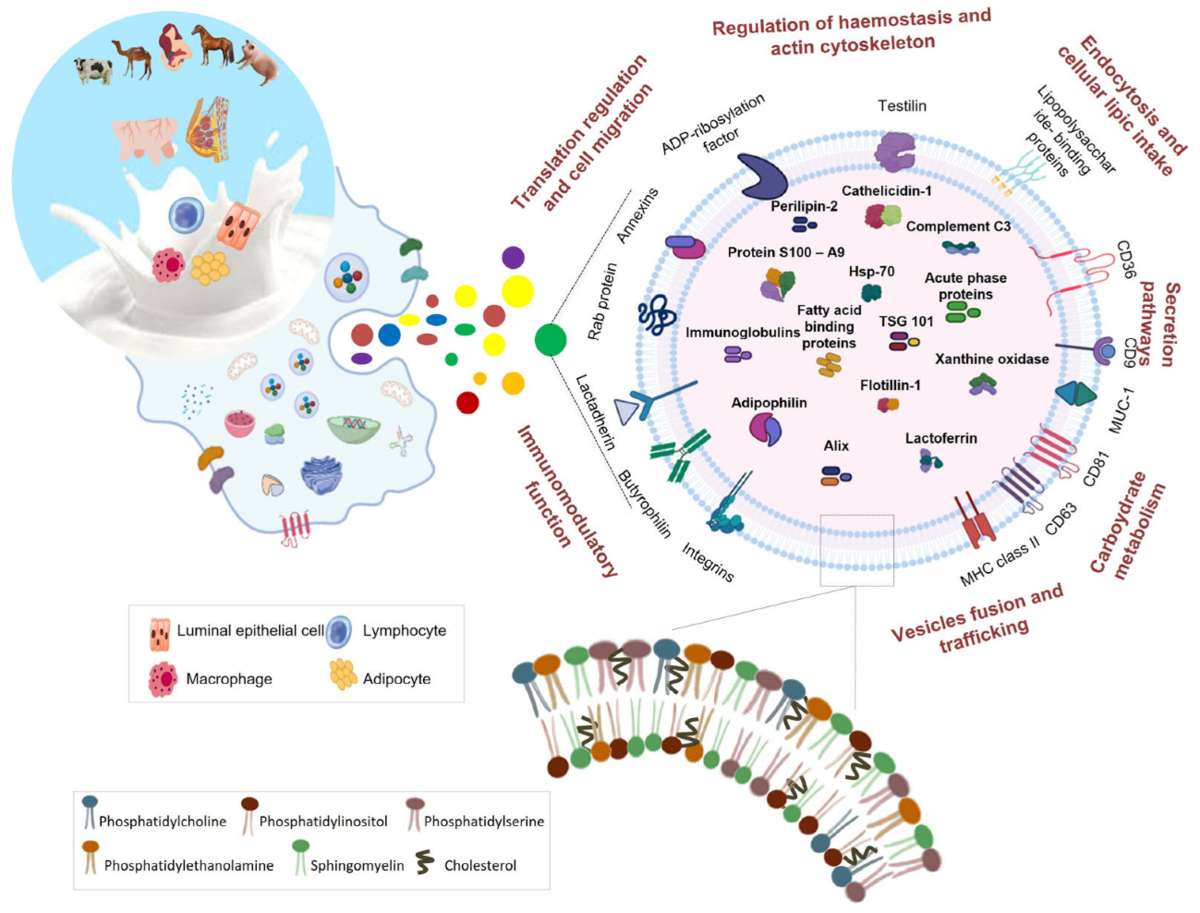
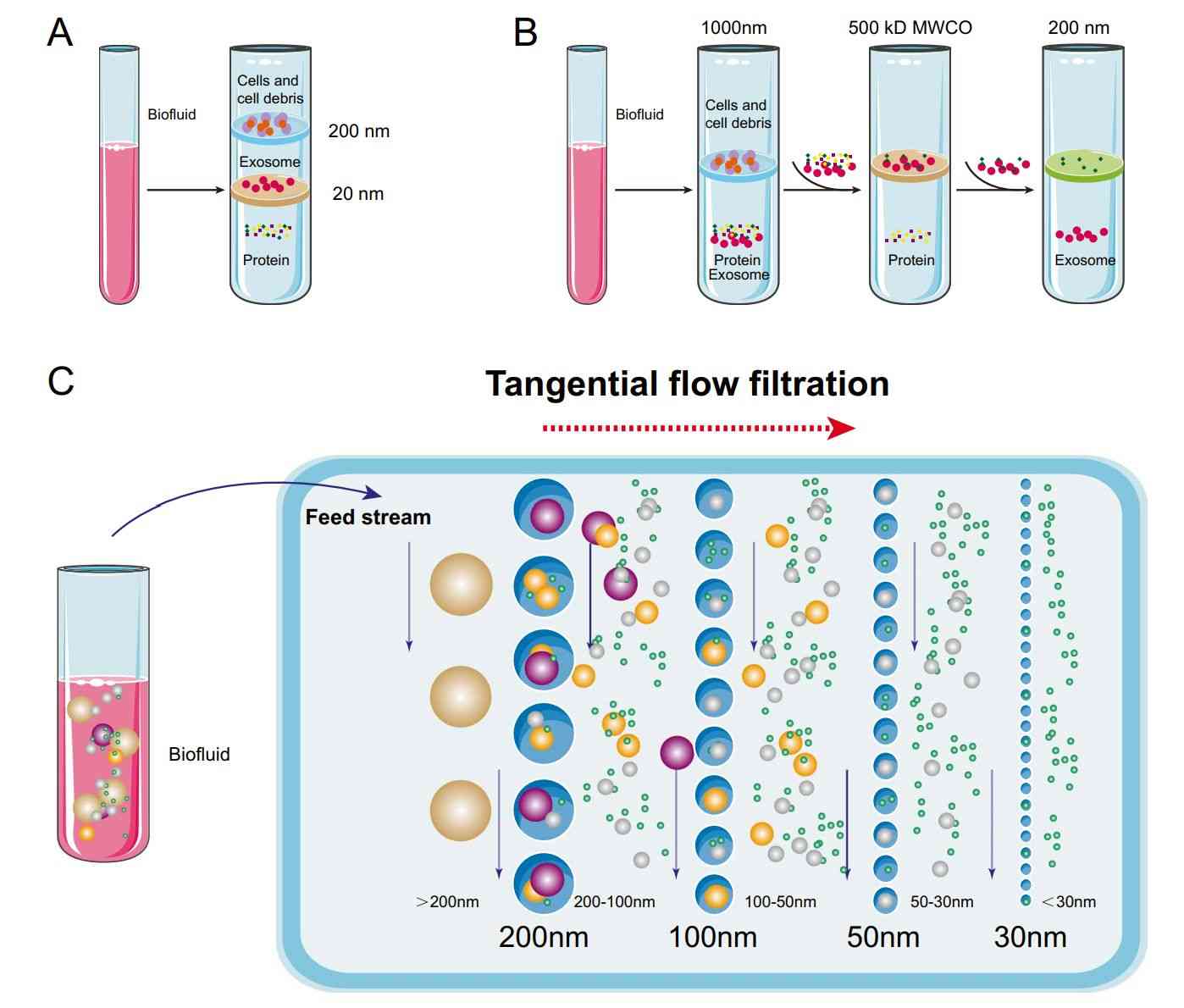
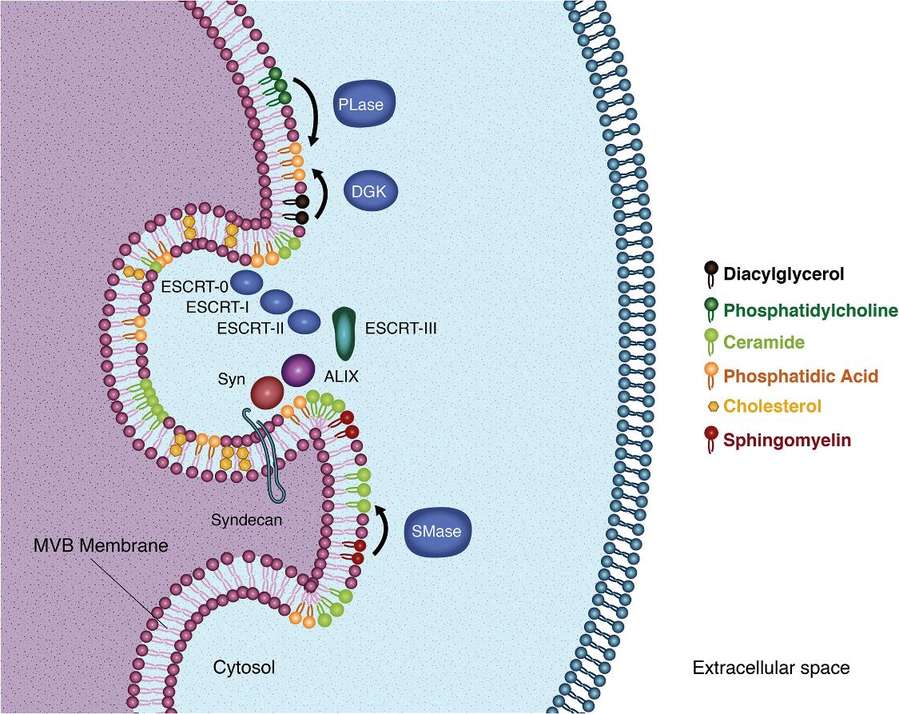 Figure 1. Lipids in exosome biogenesis. (Donoso‐Quezada J, et al., 2021)
Figure 1. Lipids in exosome biogenesis. (Donoso‐Quezada J, et al., 2021)
Our Human Exosome Lipidomics Analysis Service
We utilize an advanced liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) technology platform, which is characterized by high resolution, high sensitivity and high accuracy. Through optimized chromatographic separation conditions and mass spectrometry detection parameters, we are able to accurately identify and quantify various lipid molecules in exosomes, covering glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids, sterolipids and other different lipid classes. Meanwhile, the combination of data processing software and professional lipid database ensures the reliability and reproducibility of analysis results.
| Lipid Types | Number of Detections |
|---|---|
| Phosphatidylcholine (PC) | 122 |
| Ether-linked Phosphatidylethanolamin (POE) | 49 |
| Diacylglycerol (DAG) | 40 |
| Phosphatidylinositol (PI) | 32 |
| Free Fatty Acids (FFA) | 27 |
| Ceramide (Cer) | 24 |
| Lyso-phosphatidylethanolamine (LPE) | 24 |
| Sphingomyelin (SM) | 24 |
| Hexosylceramide (HexCer) | 23 |
| Lyso-phosphatidylcholine (LPC) | 22 |
| Phosphatidate (PA) | 20 |
| Phosphatidylglycerol (PG) | 20 |
| Triacylglycerol (TAG) | 20 |
| Phosphatidylcholin (PS) | 18 |
| Cholesteryl Ester (CE) | 10 |
| Monoacylglycerol (MAG) | 7 |
| Lyso-phosphatidylinositol (LPI) | 6 |
| Lyso-phosphatidate (LPA) | 5 |
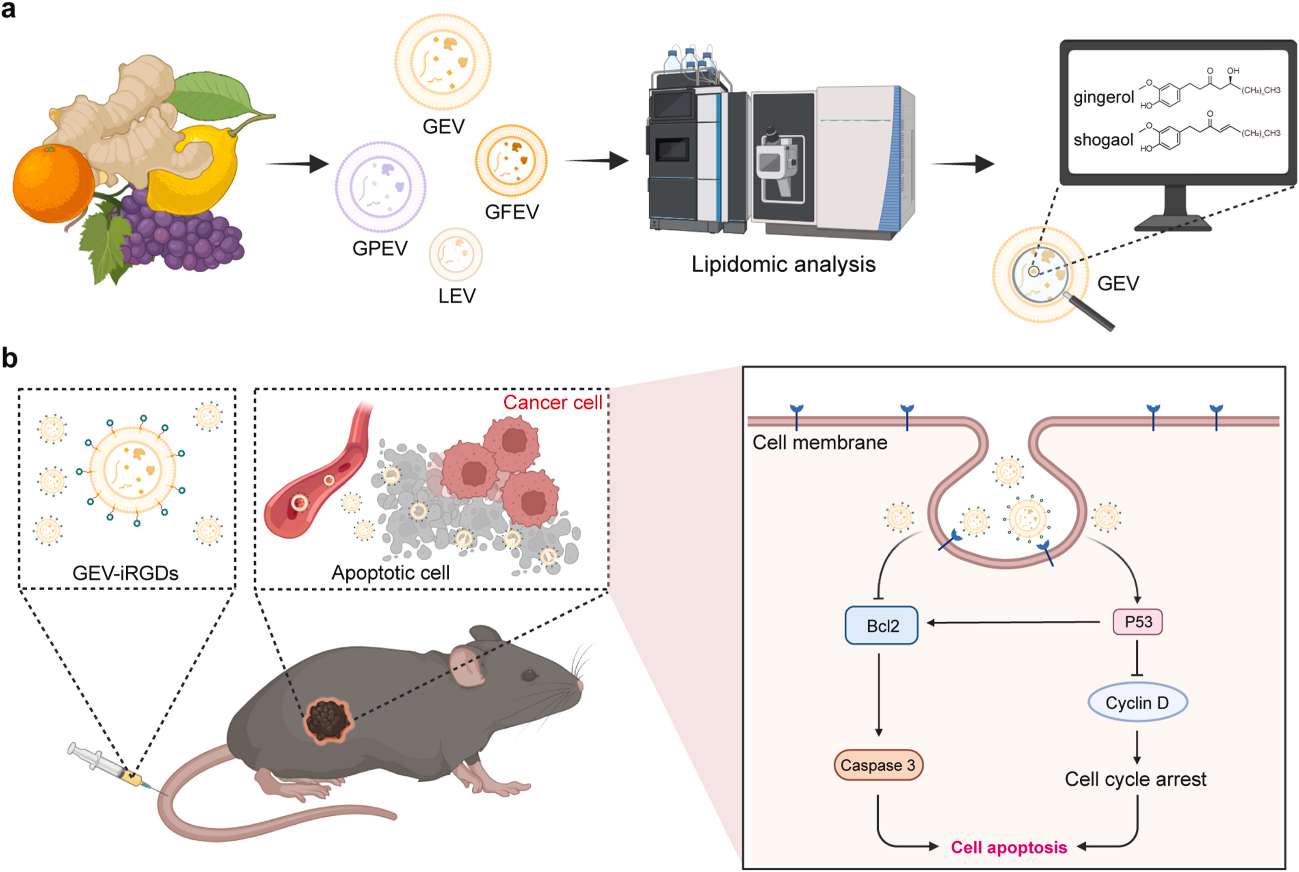
Human Exosome Lipidomics Service Workflow
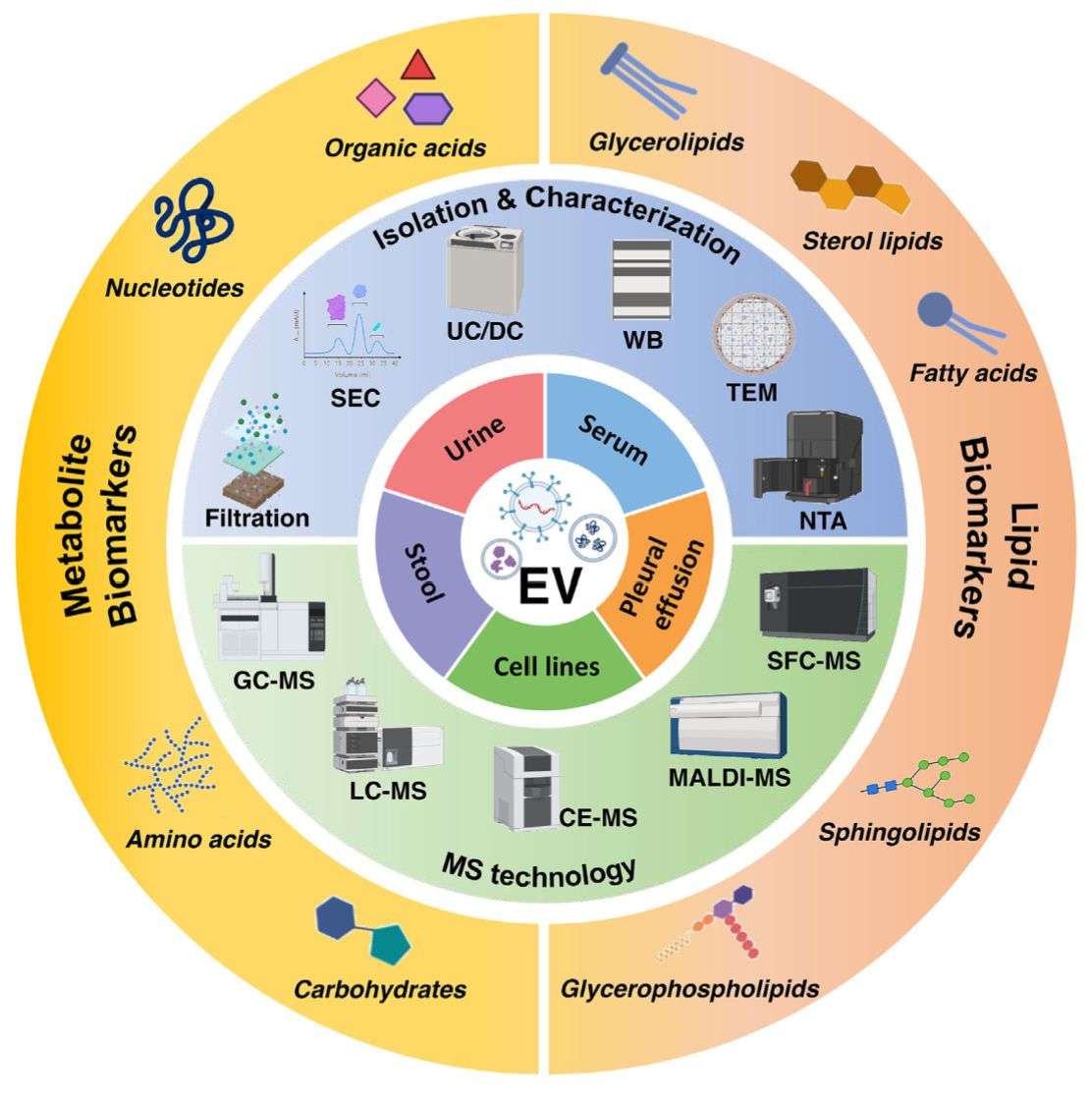
To obtain higher-quality exosomal lipidomics data, Creative Biostructure has developed proprietary exosome preparation technology ensuring high sample purity prior to detection. Concurrently, we have established an untargeted metabolomics platform for comprehensive lipid profiling that delivers broad coverage while maintaining robust qualitative and quantitative accuracy.
The workflow includes the following key steps:
Sample Receipt and Pretreatment
Receive exosome samples or biological fluid samples (such as plasma, serum, urine, etc.) provided by clients. For biological fluid samples, methods such as differential centrifugation, density gradient centrifugation, and immunomagnetic bead capture are first used for the separation and enrichment of exosomes. Subsequently, the quality and concentration of the extracted exosomes are tested to ensure that the samples meet the requirements for subsequent analysis.
Lipid Extraction
An efficient lipid extraction method is used to extract total lipids from exosomes. This method can maximize the preservation of lipid integrity and diversity, and reduce lipid loss and degradation.
LC-MS Analysis
The extracted lipid samples are injected into the LC-MS system. Different lipid components are separated by liquid chromatography, and then mass spectrometry is used for accurate mass analysis and structural identification of the separated lipids. During the analysis process, instrument parameters are monitored and adjusted in real-time to ensure the accuracy and stability of the data.
Data Processing and Analysis
Professional data processing software is used to screen, integrate, and quantitatively analyze the large amount of data generated by LC-MS. By comparing with lipid databases, the types and contents of lipids are determined, and statistical analysis is performed to explore the differences in lipid composition between different samples and potential biomarkers.
Report Generation
Based on the results of data analysis, a detailed analysis report is generated, which includes an overview of exosomal lipid composition, analysis of differential lipids, prediction of biomarkers, etc., and provides professional interpretations and suggestions.
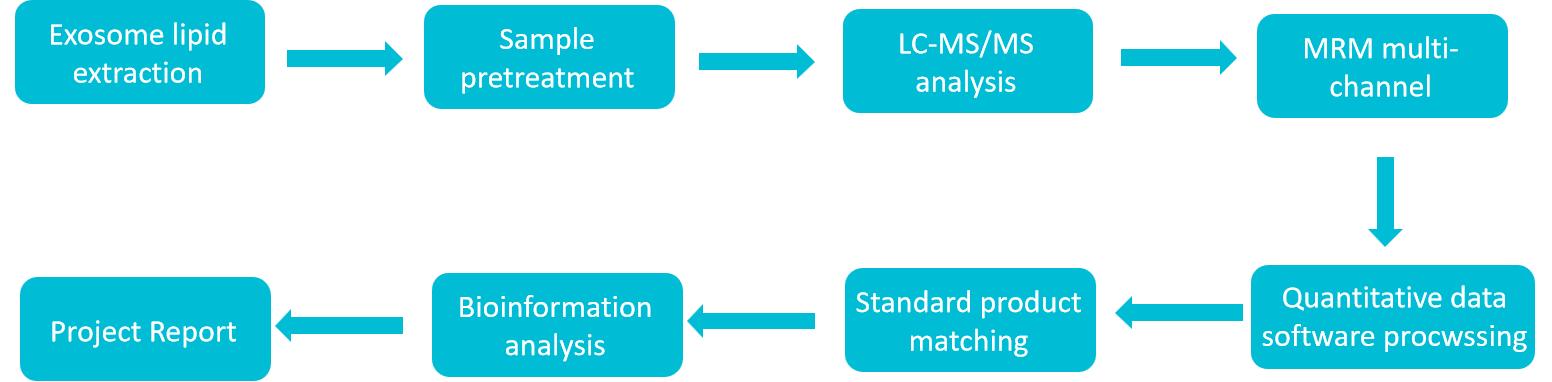 Figure 2. Human exosome lipidomics analysis service workflow. (Creative Biostructure)
Figure 2. Human exosome lipidomics analysis service workflow. (Creative Biostructure)
Sample Requirements
We support the analysis of exosome samples from multiple sources, including but not limited to:
- Human biological fluids: such as plasma, serum, urine, saliva, cerebrospinal fluid, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, etc. Exosomes in these biological fluids can reflect the physiological and pathological states of different tissues and organs in the body.
- Cell culture supernatants: supernatants from various cell lines (such as tumor cell lines, normal cell lines, etc.) can be used to study the lipid characteristics of exosomes secreted by cells and the mechanisms of intercellular communication.
Guidelines for Sample Submission
- Sample Collection: When collecting biological fluid samples, aseptic operation principles must be followed. Appropriate anticoagulants should be used (e.g., EDTA for plasma collection), and the samples should be processed or frozen for storage as soon as possible. Cell culture supernatant samples should be collected when cells are in the logarithmic growth phase to ensure the yield and quality of exosomes.
- Sample Storage and Transportation: All samples should be stored frozen at -80℃, and repeated freeze-thaw cycles should be avoided. Dry ice must be used during transportation to ensure that the samples are always kept at a low temperature, so as to maintain the integrity of exosomes and the stability of lipids.
- Sample Quantity Requirements: For biological fluid samples, it is recommended to provide at least 1 mL; for cell culture supernatant samples, it is recommended to provide 5-10 mL. If the sample quantity is insufficient, please communicate with us in advance, and we will evaluate whether the analysis can be performed.
Deliverables
- Detailed Analysis Report
The report includes detailed information on exosomal lipid composition, such as the types, contents, and relative abundances of various lipids; results of differential lipid analysis between different sample groups; and potential biomarkers predicted through bioinformatics analysis along with their related functional annotations.
- Raw Data
The raw data files generated from LC-MS analysis are provided to facilitate your further in-depth analysis and verification.
- Data Visualization Files
The results of exosomal lipidomics analysis are intuitively presented in the form of charts (such as bar charts, heatmaps, volcano plots, etc.) to help you understand the data more clearly.
Applications of Human Exosome Lipidomics Analysis Service
Disease Diagnosis and Prognosis Assessment
Exosomal lipidome analysis reveals disease-specific biomarkers for early diagnosis, monitoring, and prognosis. For example, in cardiovascular disease, these lipid profiles can signal atherosclerosis progression and cardiovascular event risk.
Drug Development
The lipid changes in exosomes secreted by cells after drug treatment are studied to understand the mechanism of drug action and cellular responses; meanwhile, exosomal lipidomic analysis can be used to screen potential drug targets and evaluate drug efficacy.
Cellular Communication Research
Studying exosome-mediated lipid transfer deepens our understanding of how cellular communication networks function in both health and disease.
Regenerative Medicine and Tissue Engineering
Analyzing the lipid composition of exosomes derived from stem cells and studying their role in tissue repair and regeneration processes provides a theoretical basis for the development of exosome-based regenerative medicine therapies.
Advantages of Our Human Exosome Lipidomics Analysis Service
- Expert Team: Our team comprises experienced lipidomics specialists, bioinformaticians, and technicians, offering professional support and customized experimental design in exosome and lipidomics research.
- Advanced Platform: We utilize a cutting-edge LC-MS platform with optimized protocols to ensure accurate and comprehensive exosomal lipidomics analysis.
- Customized Services: Tailored experimental and data analysis strategies are provided to meet specific research needs and sample types.
- Quality Assurance: Adherence to strict SOPs, along with internal QC and external validation, guarantees reliable and reproducible results.
- Fast Turnaround: We deliver high-quality results promptly to help accelerate your research progress.
Case Study
Case: Identification of Potential Biomarkers in Melanoma Cell-Derived Exosomes Using Lipidomics Approaches
Background
Melanoma is a highly malignant skin cancer with a propensity for bone metastasis. Studies show melanoma cells exhibit varying attractions to bone tissue, mediated by exosomes that regulate this osteotropism. This study investigates the lipid profiles of LCP and SK-Mel28 melanoma cells and their exosomes to identify lipid biomarkers associated with differential migratory and invasive behavior.
Methods
- Isolation and characterization of exosomes from melanoma cell supernatants by ultracentrifugation.
- Total lipids of LCP and SK-Mel28 cells and exosomes were extracted by the Bligh and Dyer method.
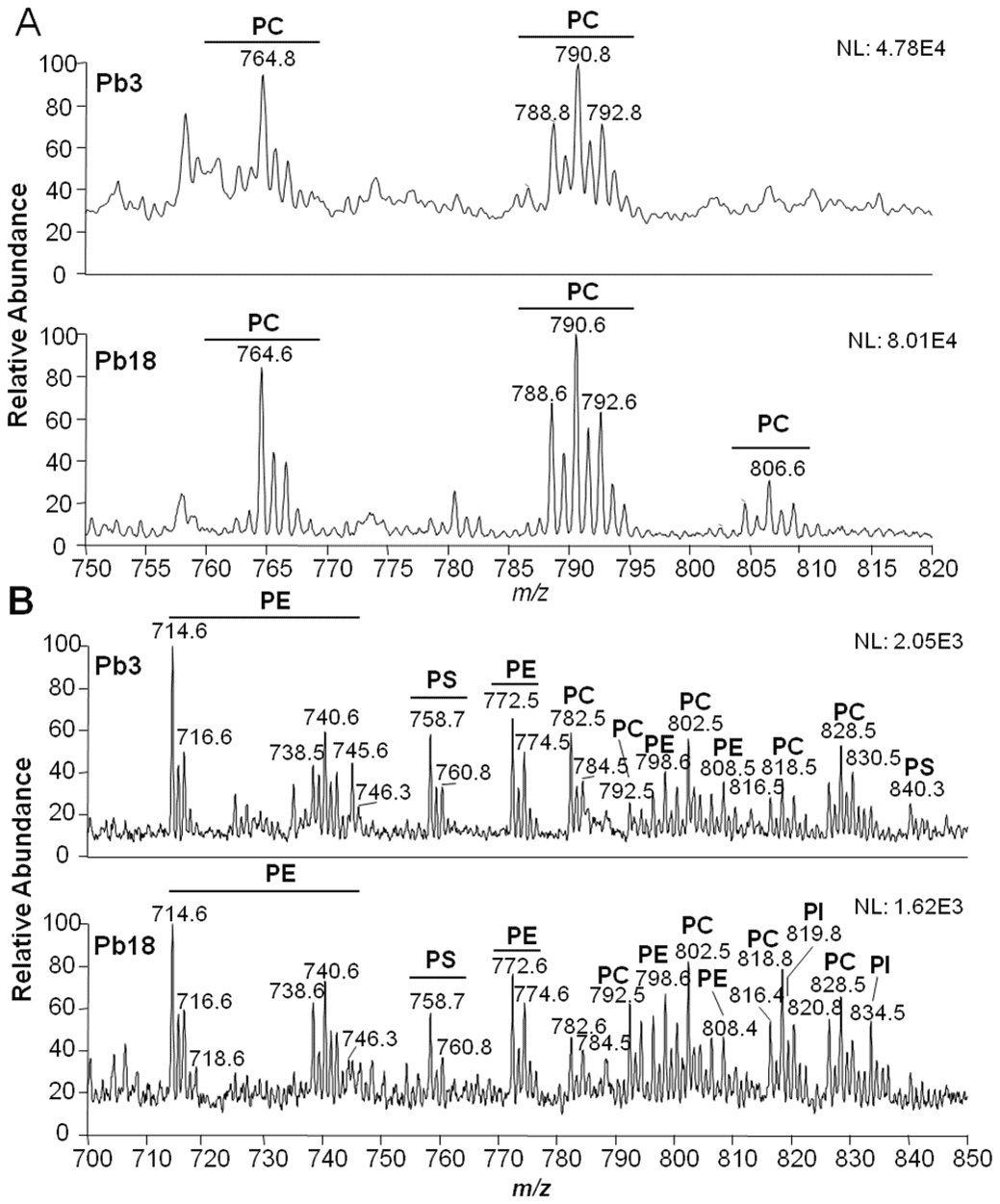
- Total lipid extracts were analyzed by thin-layer chromatography analyses (TLC).
- Comparing the lipid content of whole melanoma cells and exosomes by direct matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time-of-flight/mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF/MS) lipid analysis of intact membranes.
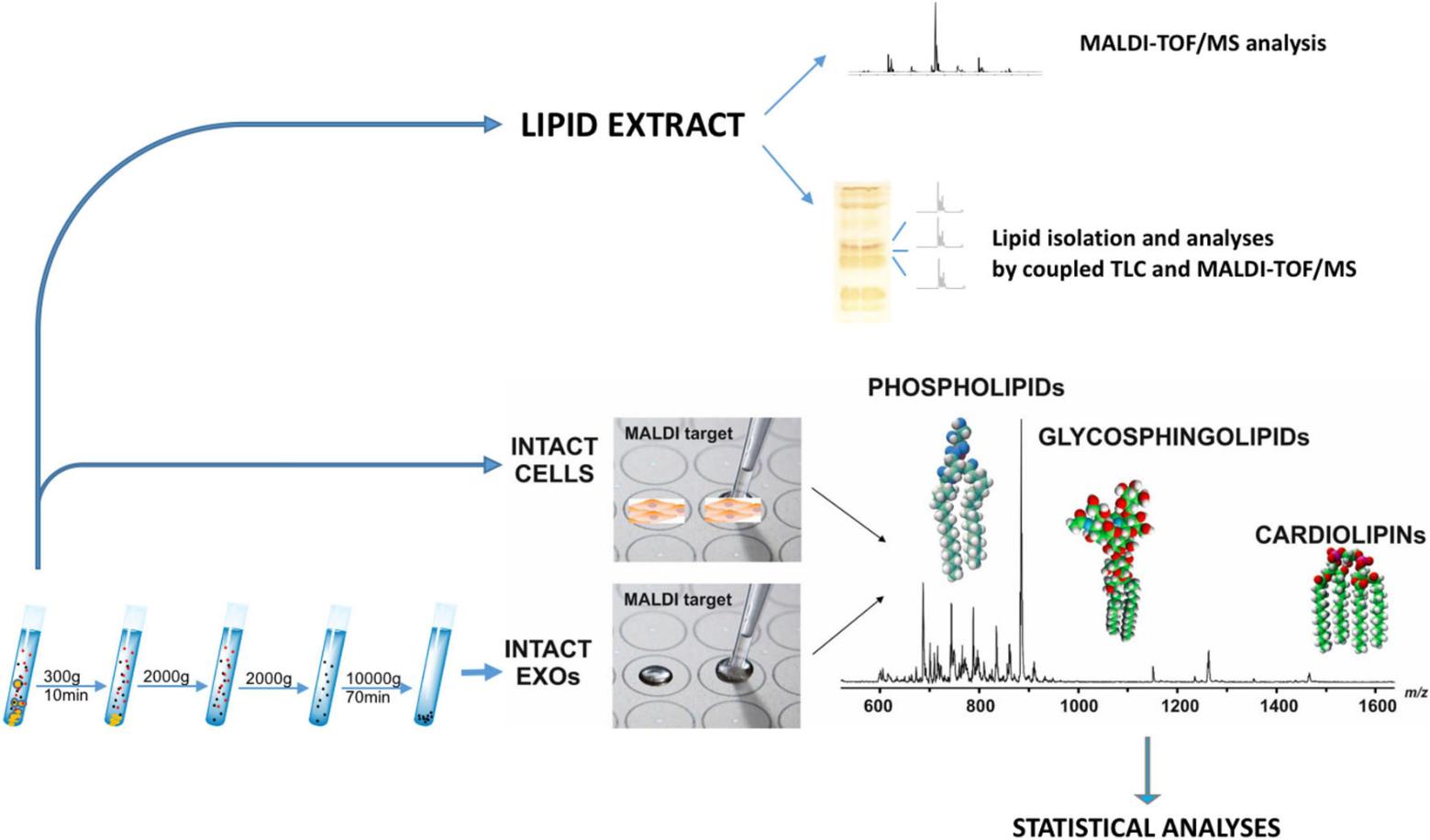 Figure 3. Lipidomics workflow for melanoma cells and exosomes. (Lobasso S, et al., 2021)
Figure 3. Lipidomics workflow for melanoma cells and exosomes. (Lobasso S, et al., 2021)
Conclusion
- Poorly metastatic (LCP) cells contain more saturated and shorter fatty acid chains, especially certain species of phosphatidylinositol compared to highly metastatic (SK-Mel28) cells.
- Sphingomyelin, lysophosphatidylcholine, and phosphatidic acid were enriched in exosome membranes compared to parental cells.
- Identified a peculiar phospholipid bis(monoacylglycero)phosphate as a specific lipid marker of exosomes.
Creative Biostructure, relying on our advanced LC-MS technology platform, professional scientific research team and perfect workflow, can provide accurate, reliable and efficient data analysis support for customers' exosome lipidomics research. We are committed to helping clients make breakthroughs in multiple fields such as disease diagnosis, drug research and development, and cell communication. If you want to learn more details about our service, such as specific technical parameters, formulation of customized schemes, in-depth analysis of past successful cases, etc., please feel free to contact us at any time.
References
- Donoso‐Quezada J, Ayala‐Mar S, González‐Valdez J. The role of lipids in exosome biology and intercellular communication: Function, analytics and applications. Traffic, 2021, 22(7): 204-220.
- Lobasso S, Tanzarella P, Mannavola F, et al. A lipidomic approach to identify potential biomarkers in exosomes from melanoma cells with different metastatic potential. Frontiers in physiology, 2021, 12: 748895.
Frequently Asked Questions
For any inquiries, our support team is ready to help you get technical support for your research and maximize your experience with Creative Biostructure.