Diabetes Related Exosome Pathway Analysis
Type 2 Diabetes (T2D) is not just a pancreatic failure; it is a systemic disorder driven by disrupted communication between adipose tissue, liver, and muscle. Exosomes are the key messengers in this metabolic crosstalk. They transport miRNAs from inflamed fat cells to induction Insulin Resistance in peripheral tissues. Conversely, stem cell-derived exosomes offer a breakthrough therapy for managing debilitating complications like Diabetic Foot Ulcers and Nephropathy.
We provide a holistic Diabetes Exosome Research Solution. Whether you are profiling circulating biomarkers for beta-cell stress, investigating the mechanism of Adipose-Liver Crosstalk, or developing MSC-Exosome hydrogels for accelerating wound healing, our platform integrates metabolic assays, specialized tissue isolation, and diabetic animal models to advance your metabolic research.
Critical Frontiers in Diabetes Research
Diabetes research is currently focused on decoding the molecular signals that drive beta-cell failure, systemic insulin resistance, and debilitating complications.
- Beta-Cell Failure & Stress: In both T1D and T2D, the decline of functional beta-cell mass is critical. Identifying exosomal stress signals released by islets before hyperglycemia onset is a key frontier for early intervention and preservation.
- Adipose-Driven Insulin Resistance: In Type 2 Diabetes, inflamed visceral fat releases exosomes that travel to the liver and muscle, blocking insulin signaling. Mapping this "fat-to-tissue" communication is essential for understanding the root cause of hyperglycemia.
- Diabetic Complications (Vascular & Neural): High glucose damages blood vessels and nerves. Research investigates how exosomes mediate the endothelial dysfunction leading to nephropathy, retinopathy, and impaired wound healing (diabetic foot).
- Stem Cell Therapy for Regeneration: For advanced diabetes, restoring islet function or healing chronic ulcers is a major challenge. Investigating the regenerative potential of MSC-derived exosomes as a cell-free alternative to stem cell transplantation is a rapidly growing field.
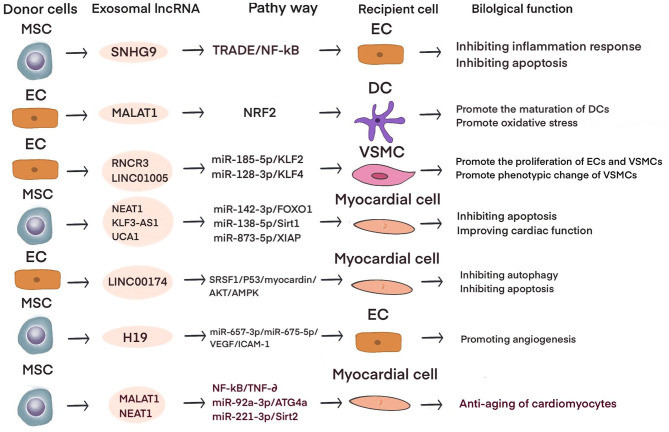
 Figure 1. Molecular mechanisms of mung-bean-sprout-derived PENPs (plant-derived exosome-like nanoparticles) in diabetic hepatic injury improvement. (Yuan Z, et al., 2021)
Figure 1. Molecular mechanisms of mung-bean-sprout-derived PENPs (plant-derived exosome-like nanoparticles) in diabetic hepatic injury improvement. (Yuan Z, et al., 2021)
Comprehensive Service Portfolio for Diabetes
We offer an integrated matrix of services tailored to metabolic research, covering mechanism, diagnosis, and complication management.
| Research Focus | Our Specialized Approach & Solution | Key Services Applied |
|---|---|---|
| Insulin Resistance (Mechanism) | Adipose-Myocyte Crosstalk: We co-culture adipocyte-derived exosomes with muscle cells or hepatocytes. We measure Glucose Uptake (2-NBDG) and insulin signaling pathway activation (p-Akt/p-IRS1). | Exosomal Phosphoproteomics Analysis |
| Diabetic Wound Healing (Therapy) | Wound Closure Models: We utilize db/db mice (diabetic) to create full-thickness skin excision models. We treat wounds with MSC-exosomes (often in hydrogels) and quantify closure rate and angiogenesis. | Exosome Wound Healing and Bone Regeneration |
| Tissue Profiling (Discovery) | Adipose/Pancreas Isolation: Circulating exosomes are a mix. We use specialized protocols to isolate exosomes directly from Adipose Tissue (BAT/WAT) or Pancreatic Islets to profile tissue-specific secretomes. | Animal Tissue Exosome Isolation |
| Biomarker Screening (Diagnosis) | Beta-Cell Stress Markers: We profile plasma exosomes for beta-cell specific miRNAs (e.g., miR-375) or proteins to detect early islet dysfunction. | Exosome Biomarker Protein Screening |
Core Technologies for Metabolic Research
We highlight specialized technologies designed to assess metabolic function and diabetic complications.
Glucose Uptake & Insulin Signaling Assays
Measuring Insulin Sensitivity: To validate if an exosome induces or alleviates insulin resistance, we perform 2-NBDG Glucose Uptake Assays in differentiated adipocytes or myotubes. Combined with Western Blotting for insulin signaling nodes (p-Akt, GLUT4 translocation), this provides a functional readout of metabolic health at the cellular level.
Diabetic Wound Healing Models
Accelerating Regeneration: For diabetic foot ulcer research, simple scratch assays aren't enough. We utilize Type 2 Diabetic (db/db) or STZ-induced mouse models with dorsal skin wounds. We apply exosome-loaded dressings and monitor healing dynamics via digital planimetry and histological analysis (re-epithelialization, collagen deposition), specifically addressing the "chronic wound" environment.
Adipose Tissue Exosome Isolation
Source Matters: Obesity-related diabetes is driven by fat. We offer optimized dissociation protocols to isolate exosomes separately from Brown Adipose Tissue (BAT) and White Adipose Tissue (WAT). This allows researchers to compare the "good" vs. "bad" secretomes and understand how they differentially regulate systemic metabolism.
Application Spotlight: Plant Nanovesicles Treat Diabetic Fatty Liver
This analysis highlights the emerging potential of plant-derived exosome-like nanovesicles (PDNs) as a novel, oral therapeutic strategy for metabolic complications.
Featured Technologies:
- Plant-Derived Exosome Isolation
- In Vivo Metabolic Phenotyping
Literature Interpretation:
Hepatic steatosis (fatty liver) is a common and severe complication of Type 2 Diabetes. Researchers investigated a natural therapeutic approach using Tangerine-peel-derived exosome-like nanovesicles (TNVs). In a diabetic mouse model, oral administration of these tangerine- TNVs significantly reduced liver lipid accumulation and improved insulin sensitivity. The study revealed a dual mechanism: 1) Direct regulation of hepatic lipid metabolism genes (downregulating SREBP-1c/FAS), and 2) Modulation of the Intestinal Microflora, increasing the abundance of beneficial bacteria that suppress inflammation. This study validates that plant-derived nanovesicles can serve as effective metabolic regulators, highlighting our unique capabilities in isolating plant exosomes and validating their function in diabetic models.
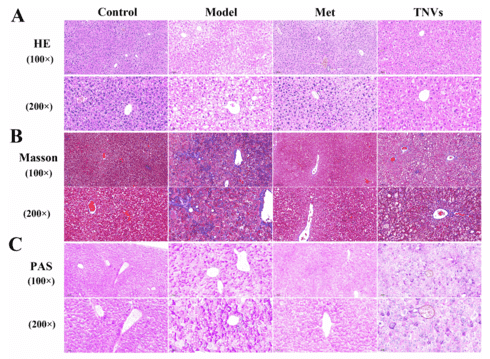 Figure 2. Impact of TNVs on hepatic lipid levels and liver function in db/db mice, as shown by histological staining. (A) H&E staining, (B) Masson staining, and (C) PAS staining reveal reduced lipid droplets, glycogen accumulation, and collagen fiber formation post TNV treatment. (Zou J, et al., 2024)
Figure 2. Impact of TNVs on hepatic lipid levels and liver function in db/db mice, as shown by histological staining. (A) H&E staining, (B) Masson staining, and (C) PAS staining reveal reduced lipid droplets, glycogen accumulation, and collagen fiber formation post TNV treatment. (Zou J, et al., 2024)
Start Your Diabetes Research Project
Leverage our comprehensive platform to accelerate your discovery, from metabolic pathways to complication therapies.
How It Works: Our Project Pathway
 Figure 3. Workflow for studying metabolic crosstalk, screening mechanisms of insulin resistance, and validating exosome therapies for diabetic complications. (Creative Biostructure)
Figure 3. Workflow for studying metabolic crosstalk, screening mechanisms of insulin resistance, and validating exosome therapies for diabetic complications. (Creative Biostructure)
Ready to advance your research on Insulin Resistance or Diabetic Complications? Our metabolic experts are available to build a custom study plan tailored to your needs. Contact us today to discuss your project.
References
- Xiao X, Guo Y, Msomi NZ, et al. Exosome-like Nanoparticles Extracted from Plant Cells for Diabetes Therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Sep 19;26(18):9155.
- Zou J, Song Q, Shaw PC, et al. Tangerine Peel-Derived Exosome-Like Nanovesicles Alleviate Hepatic Steatosis Induced by Type 2 Diabetes: Evidenced by Regulating Lipid Metabolism and Intestinal Microflora. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Sep 30;19:10023-10043.