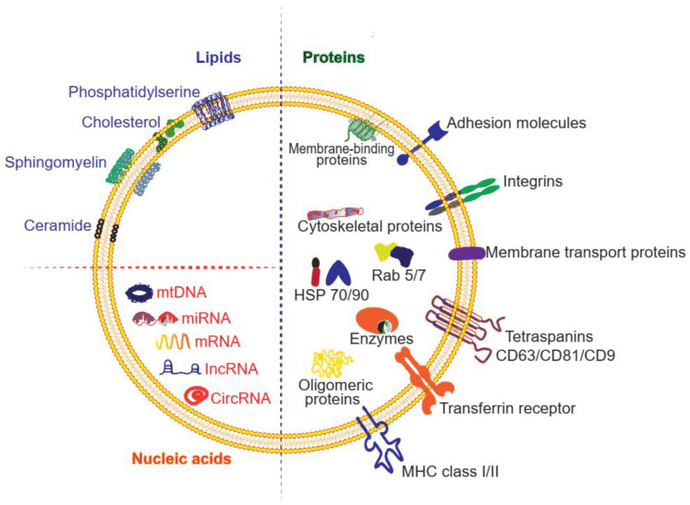
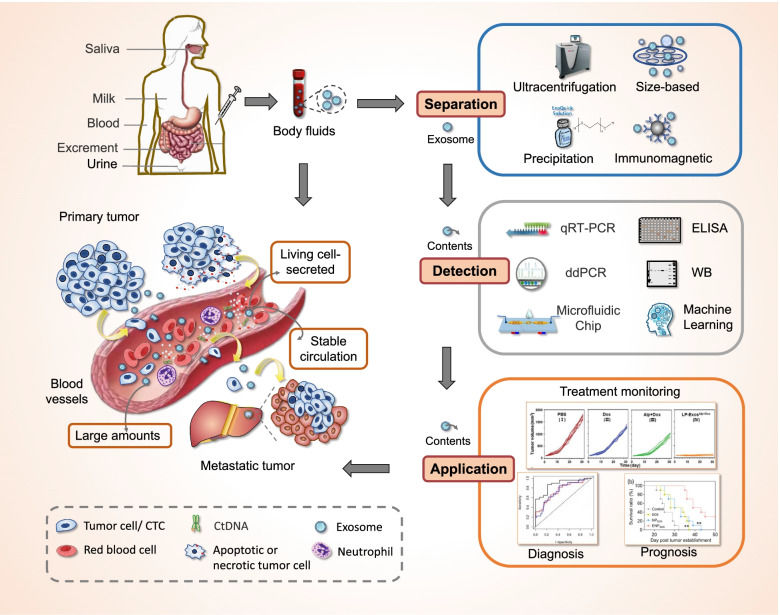
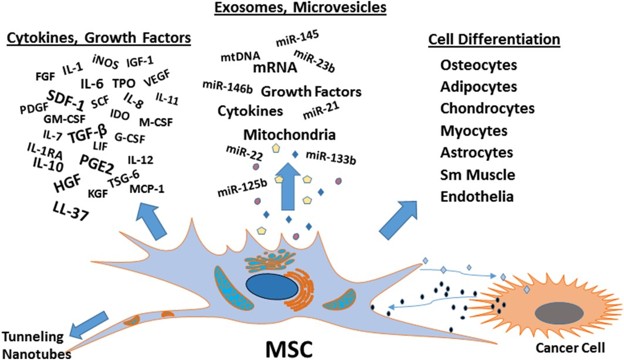
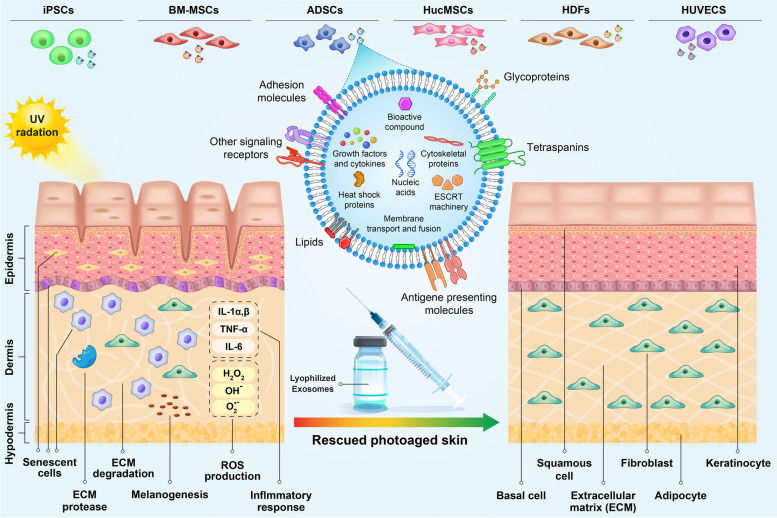
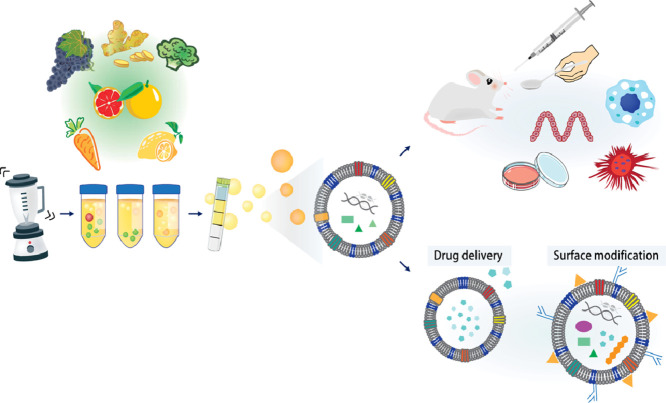
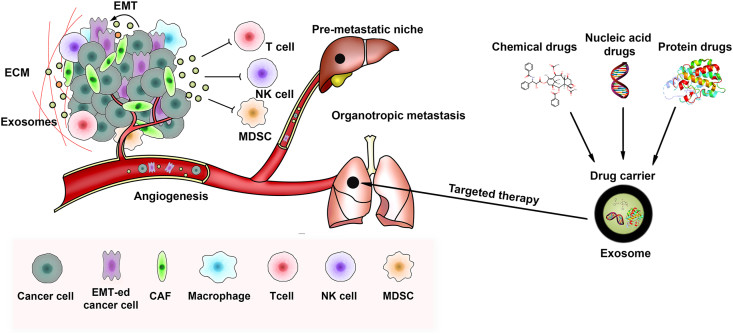
Cardiovascular and Metabolic Disease Exosome Solutions
Cardiovascular disease and metabolic disorders (like Diabetes) are not isolated events. They are driven by complex, systemic communication networks. Exosomes are the critical messengers in this crosstalk, carrying signals from adipose tissue to the heart, or from blood vessels to the liver.
We provide end-to-end cardiovascular and metabolic exosome solutions. Whether you are investigating how circulating exosomes in cardiovascular diseases regulate vascular inflammation, or developing Mesenchymal Stem Cell exosomes to repair heart tissue after a myocardial infarction, our platform offers the specific isolation tools, functional assays, and pathway analysis needed to decipher these mechanisms.
The Role of Exosomes in Circulatory and Metabolic Health
Why is exosome research vital? These vesicles are the "Wi-Fi" signals of the body, orchestrating systemic responses in health and pathology.
- Inter-Organ Communication: In metabolic syndrome, fat cells release obesity-associated exosomal miRNAs that travel to the liver, modulating glucose and lipid metabolism. Mapping this traffic is key to understanding insulin resistance.
- Myocardial Repair & Sepsis: Exosome and its roles in cardiovascular diseases extend to acute injury. We support research into how stem cell exosomes promote angiogenesis after infarction, and how pathogen-induced exosomes drive exosomes sepsis cardiovascular pathology (septic cardiomyopathy).
- Exercise & Metabolism: Recent studies highlight the potential of endurance exercise-derived exosomes to treat metabolic diseases. Muscles release exosomes during exercise that improve systemic metabolism; we help you isolate and characterize these "exerkines."
- Vascular Health: Endothelial exosomes regulate blood pressure and plaque formation. We analyze their content to find metabolic enzymes in exosomes that may serve as therapeutic targets.
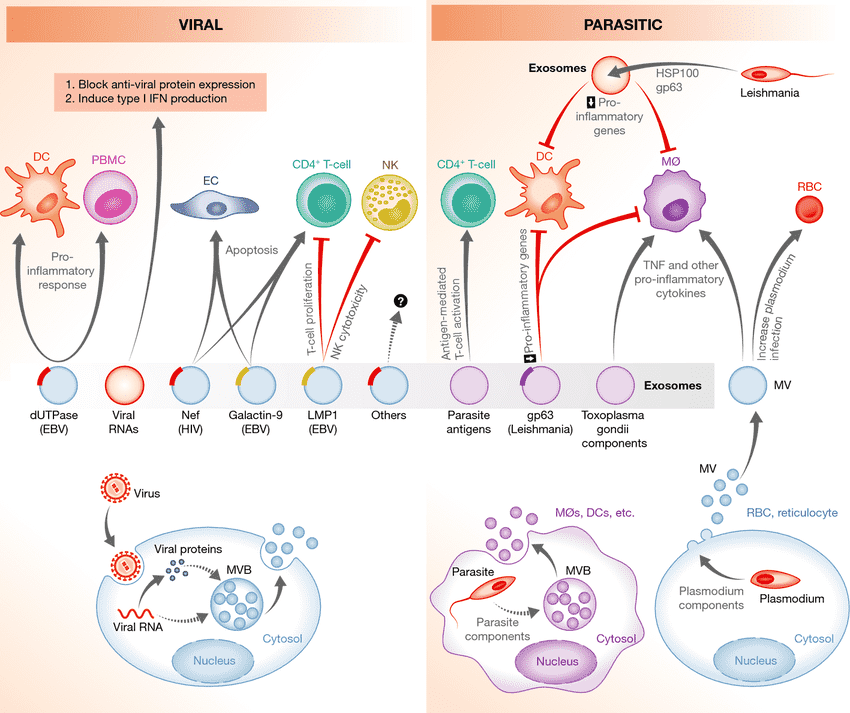
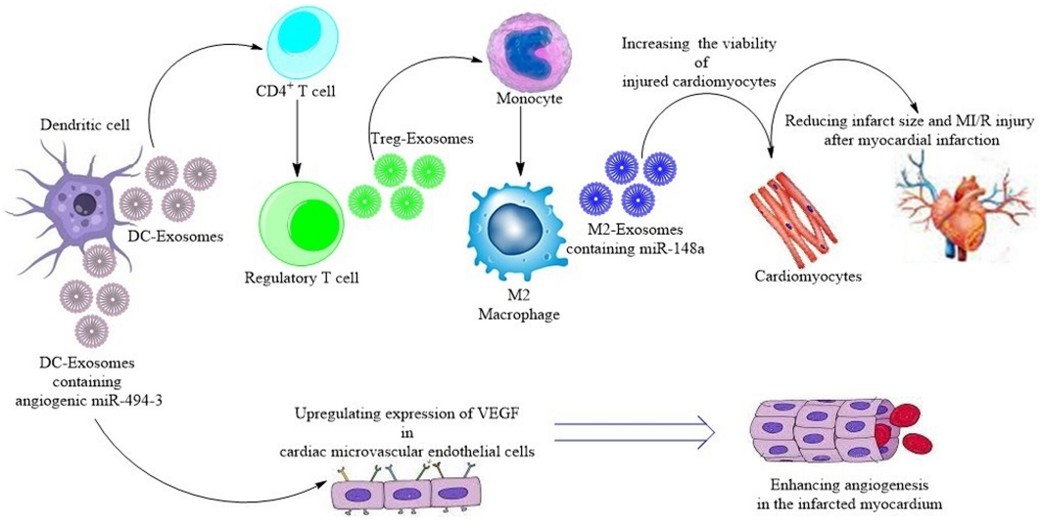 Figure 1. Exosome-mediated crosstalk between cardioprotective immune cells and cardiac cells. (Wen H, et al., 2021)
Figure 1. Exosome-mediated crosstalk between cardioprotective immune cells and cardiac cells. (Wen H, et al., 2021)
Our Integrated Cardio-Metabolic Workflow
We utilize specialized models to simulate the stress conditions found in diabetic and cardiac patients, bridging the gap between basic biology and clinical application.
| Service Pillar | Key Services & Technologies We Provide |
|---|---|
| Tissue & Biofluid Isolation | Source Specificity: We isolate exosomes from adipose tissue, cardiac progenitor cells, or lipid-rich plasma. We use gentle techniques to preserve vesicle integrity and key structures like lipid rafts from degradation. |
| Metabolic Cargo Profiling | Pathway Discovery: We profile cargo linked to exosome metabolism. This includes Lipidomics to analyze exosome lipid raft metabolism and Sequencing to find miRNAs targeting insulin signaling (e.g., AKT/mTOR). We also identify functional metabolic enzymes within the vesicle. |
| Functional Disease Models | Simulating Pathology: We test exosomes in relevant in vitro models: Cardiomyocytes subjected to hypoxia, or Hepatocytes treated with high glucose to mimic exosomes change metabolism in diabetes. |
| Therapeutic Validation | Repair & Regeneration: For therapeutic projects, we validate efficacy using angiogenesis assays (Tube Formation) and in vivo models of myocardial infarction or diet-induced obesity. |
Applications We Support
Our platform is tailored to investigate the two major pillars of chronic disease: Heart Disease and Metabolism.
Atherosclerosis and Myocardial Injury Exosome Services
We focus on the mechanisms of heart failure and vessel damage. We help you profile circulating exosomes in cardiovascular diseases released during ischemia-reperfusion injury to identify damage markers. On the therapeutic side, we test the potential of Mesenchymal Stem Cell exosomes to reduce infarct size and prevent cardiac fibrosis (scarring) in post-infarction models.
Diabetes Related Exosome Pathway Analysis
Diabetes is a disease of signaling. We trace how exosomes from adipose tissue (fat) or the pancreas modulate insulin sensitivity in peripheral tissues. Our services include identifying exosomal microRNAs that act as biomarkers for pre-diabetes or diabetic complications (like diabetic cardiomyopathy and nephropathy).
Adipose Tissue & Exercise Metabolism Research
Beyond pathology, we support lifestyle medicine research. We provide profiling of exercise-derived exosomes to understand their protective effects against metabolic disease. We also offer deep lipidomic profiling of white vs. brown adipose tissue exosomes to reveal their role in systemic energy balance.
Advantages of Our Cardio-Metabolic Platform
Cardiovascular and metabolic research presents unique challenges, particularly regarding sample quality and functional validation. We have optimized our platform to address these specific hurdles.
Lipid-Rich Sample Optimization
Solving the Lipoprotein Problem: Isolating exosomes from the plasma of diabetic or obese patients is notoriously difficult because high levels of lipoproteins (HDL/LDL) co-isolate with exosomes. We utilize optimized Size Exclusion Chromatography workflows. Unlike precipitation methods, SEC effectively separates exosomes from lipoproteins based on size, ensuring that your downstream RNA or protein data reflects the exosome cargo, not plasma contaminants.
Standardized Angiogenesis Assays
Validating Vascular Repair: Vascular health is central to cardiovascular disease. We do not rely on visual estimation. We provide standardized, quantitative HUVEC tube formation assays and cell migration assays. We use image analysis software to precisely measure total tube length and branching points, providing rigorous statistical data to support your claims of vascular regeneration.
Integrated Metabolic Pathway Mapping
Contextualizing the Data: Metabolic diseases involve complex pathways. Our bioinformatics team maps your cargo to specific metabolic signaling pathways (e.g., Insulin, AMPK), helping you understand exactly how exosomes change metabolism at the cellular level.
Application Spotlight: Adipose Exosomes Regulate Whole-Body Metabolism
This analysis highlights the critical role of circulating exosomes as signaling molecules in metabolic diseases like diabetes and obesity, validating the "Endocrine Exosome" concept.
Featured Technologies:
- Circulating Exosome Isolation
- miRNA Analysis & Knockdown
Literature Interpretation:
This landmark study fundamentally changed how we view fat tissue. It asked: How does body fat talk to the liver? The researchers demonstrated that adipose tissue releases exosomes containing specific microRNAs (like miRNA-99b) into the circulation. These exosomes travel to the liver and regulate gene expression. When the researchers blocked the release of these exosomes in mice, the animals developed metabolic dysfunction. Restoring the exosomes reversed the effect. This proves that circulating exosomes in cardiovascular diseases and metabolic disorders are essential regulators of health.
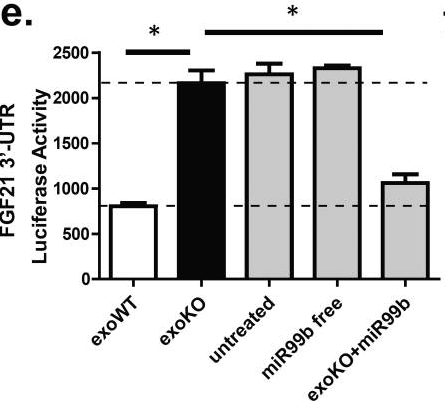 Figure 2. Exosomal miRNAs regulate hepatic FGF21. FGF21-3'UTR luciferase activity in AML-12 cells treated with exosomes from Lox (exoWT), ADicerKO (exoKO), free miR-99b, or exoKO+miR-99b (n=3/group). (Thomou T, et al., 2017)
Figure 2. Exosomal miRNAs regulate hepatic FGF21. FGF21-3'UTR luciferase activity in AML-12 cells treated with exosomes from Lox (exoWT), ADicerKO (exoKO), free miR-99b, or exoKO+miR-99b (n=3/group). (Thomou T, et al., 2017)
Start Your Cardiovascular & Metabolic Project
We make getting started straightforward. Our process is designed to be collaborative and transparent, ensuring your project goals are met at every stage.
How It Works: Our Project Pathway
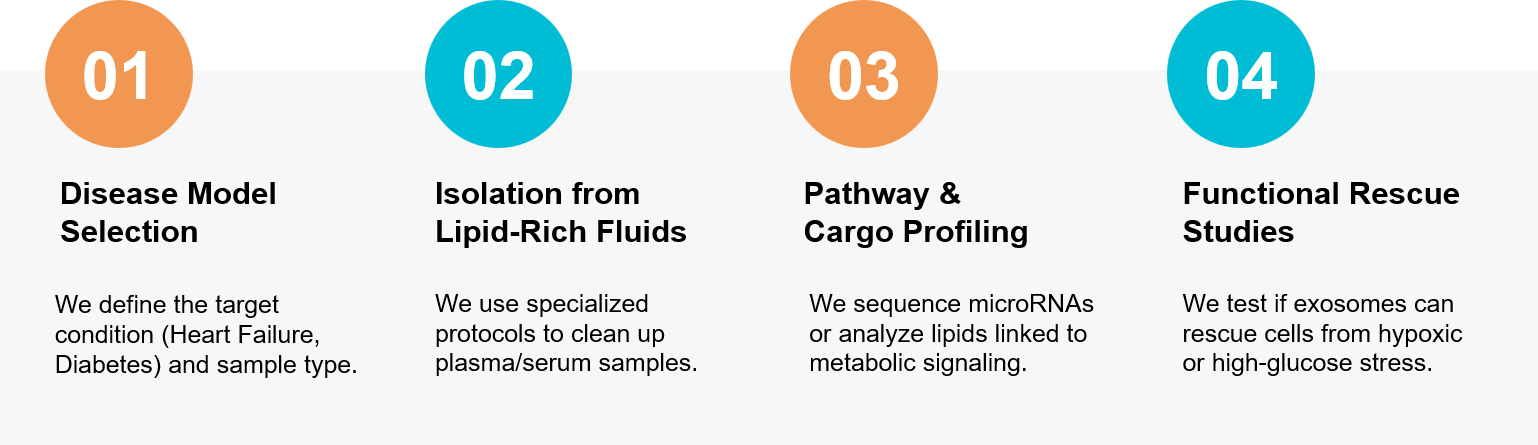 Figure 3. Our workflow for investigating systemic metabolic signaling and cardiac repair mechanisms via exosomes. (Creative Biostructure)
Figure 3. Our workflow for investigating systemic metabolic signaling and cardiac repair mechanisms via exosomes. (Creative Biostructure)
Ready to uncover the mechanisms of chronic disease? Our scientific team is available for a free consultation to discuss your cardio-metabolic research strategy.
References
- Wen H, Peng L, Chen Y. The effect of immune cell-derived exosomes in the cardiac tissue repair after myocardial infarction: Molecular mechanisms and pre-clinical evidence. J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Jul;25(14):6500-6510.
- Thomou T, Mori MA, Dreyfuss JM, et al. Adipose-derived circulating miRNAs regulate gene expression in other tissues. Nature. 2017 Feb 23;542(7642):450-455.