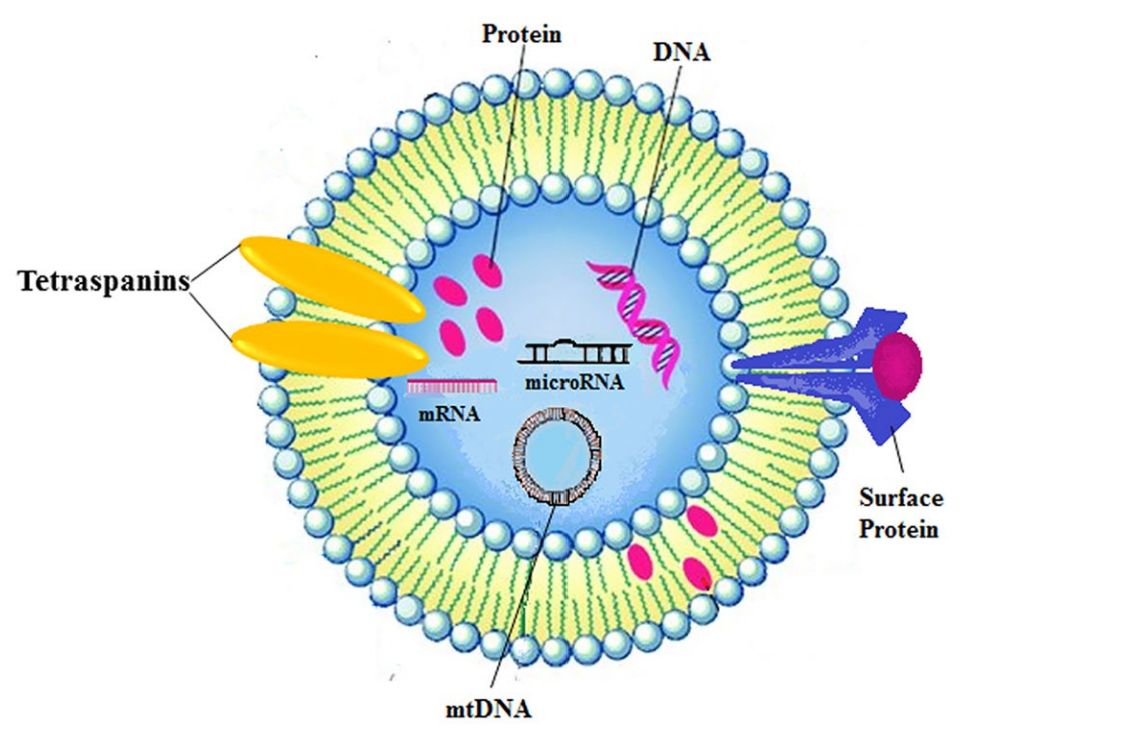
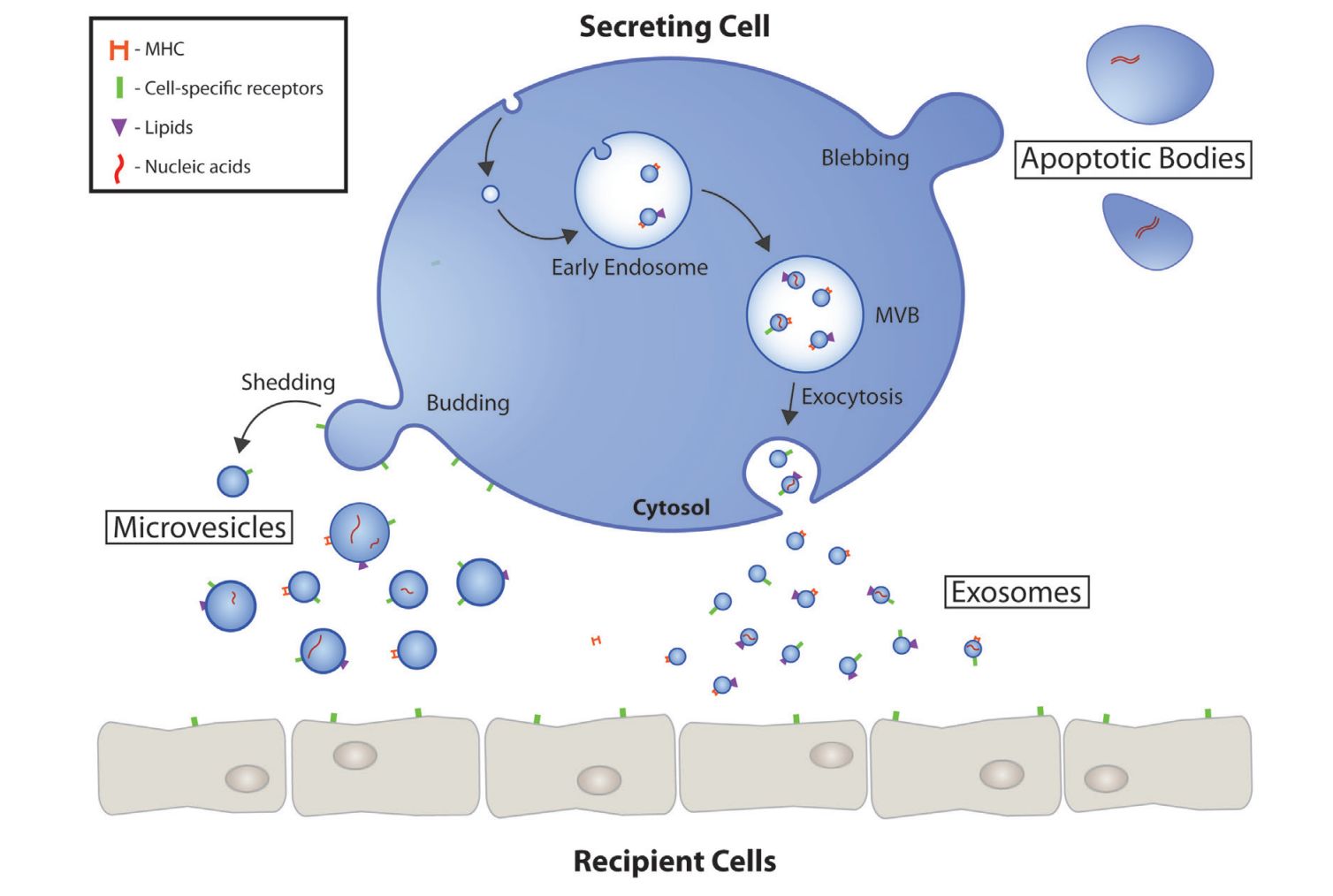
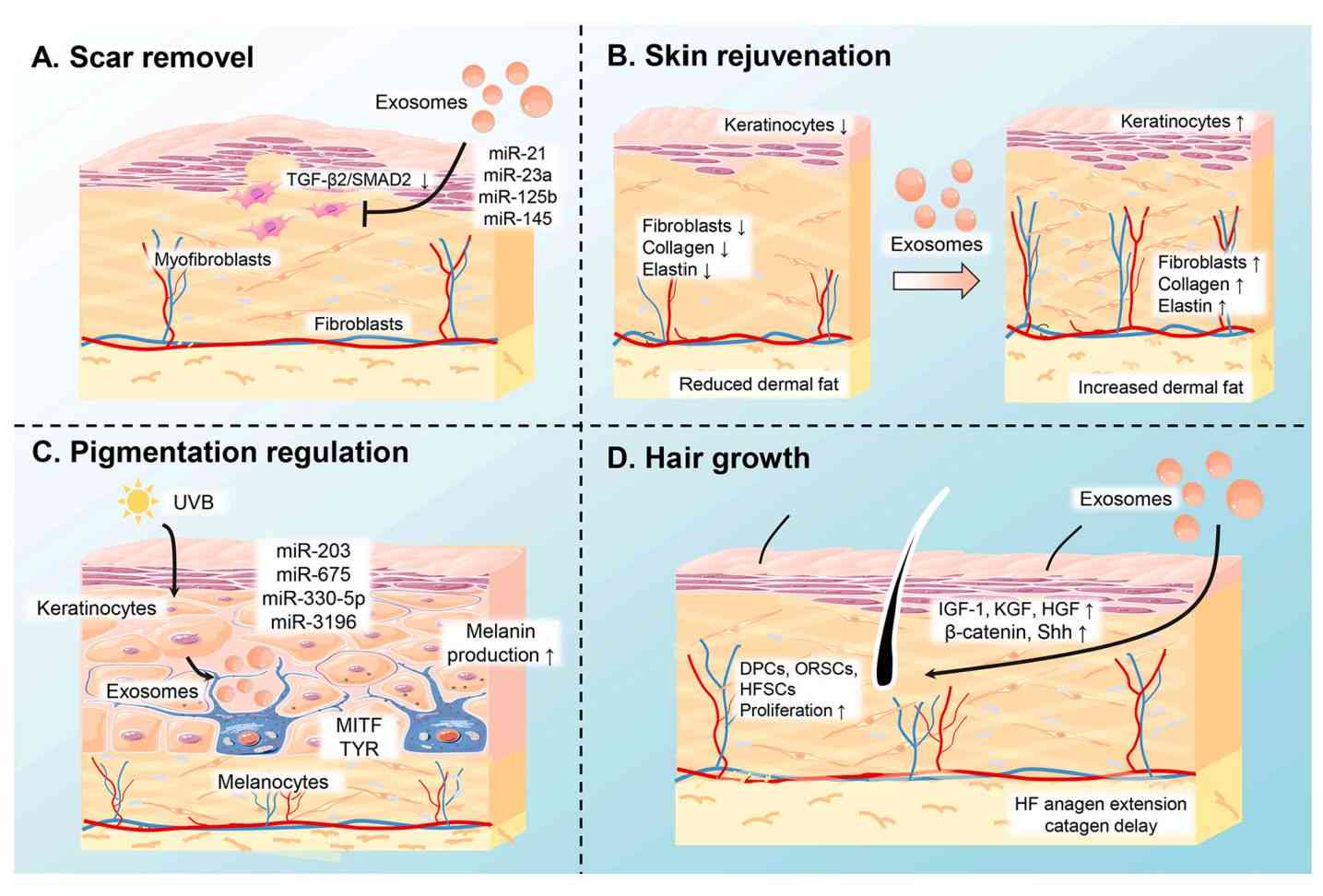
In Vitro Exosome Functional Assays
Exosomes act as natural couriers, facilitating intercellular communication by transferring bioactive cargo like proteins and RNA to recipient cells. To understand their true biological impact, it is essential to move beyond simple characterization and measure their downstream effects. An in vitro exosome functional assay is a crucial experimental tool used to quantify how an in vitro exosome treatment specifically alters the behavior and phenotype of target cells in a controlled setting. These assays provide direct evidence of exosome potency and mechanism of action.
Why Perform In Vitro Exosome Functional Assays?
While characterizing exosomes by size (NTA), morphology (TEM), and protein markers (Western Blot) is a critical first step, it only answers the question of "what they are." It doesn't explain "what they do." For researchers aiming to publish in high-impact journals, secure funding, or develop therapeutic applications, demonstrating biological function is non-negotiable.
- Move Beyond Characterization: Functional data provides direct evidence of your exosomes' biological activity, adding significant depth and impact to your research.
- Validate Therapeutic Efficacy: Directly measure the ability of engineered exosomes to deliver cargo (like siRNA or drugs) and elicit a desired therapeutic response (e.g., inhibit tumor growth).
- Elucidate Mechanisms of Action: Uncover the specific cellular pathways and responses modulated by exosomes, providing critical insights into disease progression and therapeutic targeting.
- Enable Data-Driven Decisions: Use robust in vitro data to de-risk and guide more complex and expensive in vivo animal studies, accelerating the transition from discovery to application.
Our comprehensive platform helps you answer these critical questions by providing robust, quantitative data on exosome function in vitro.
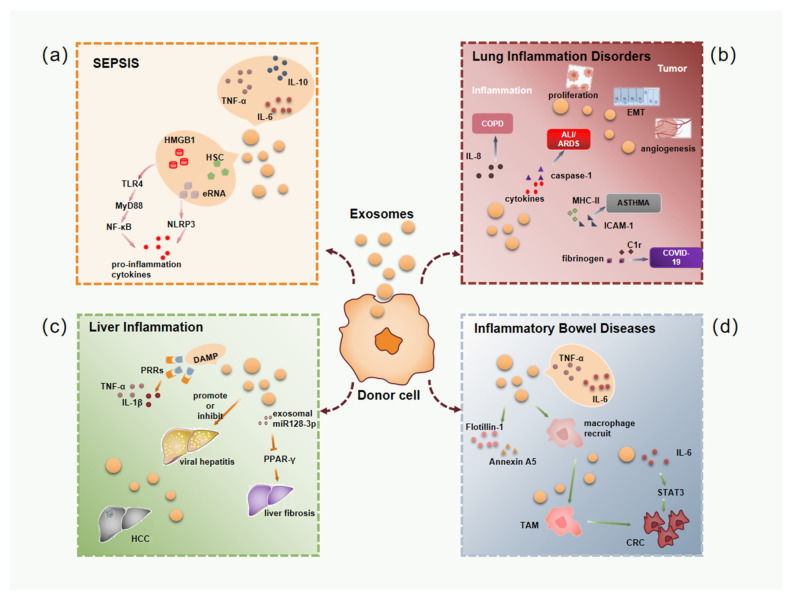
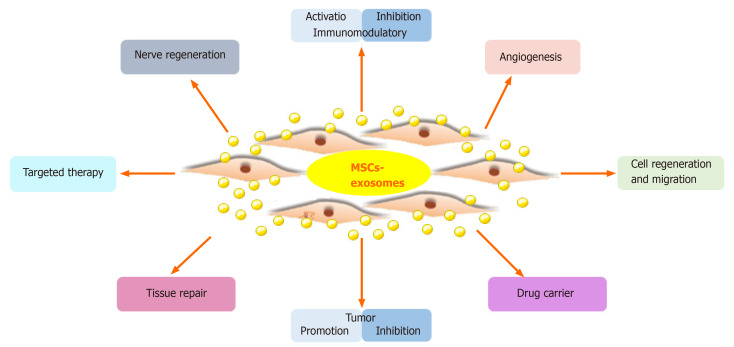
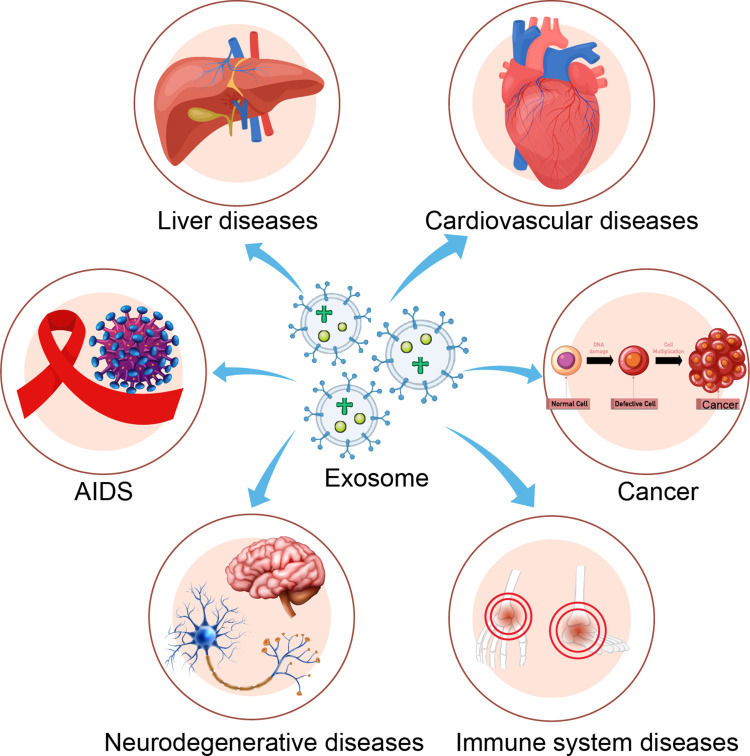
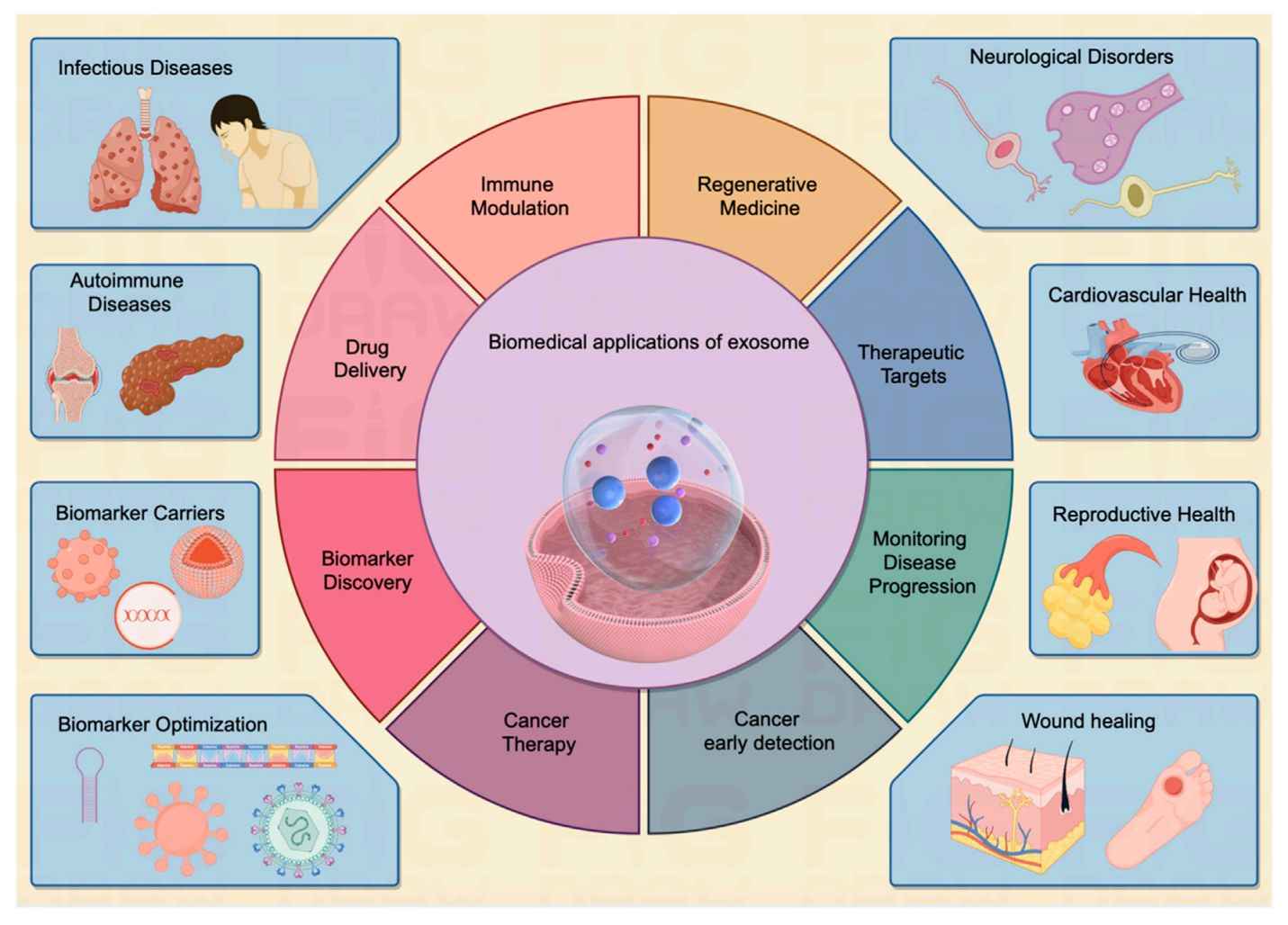
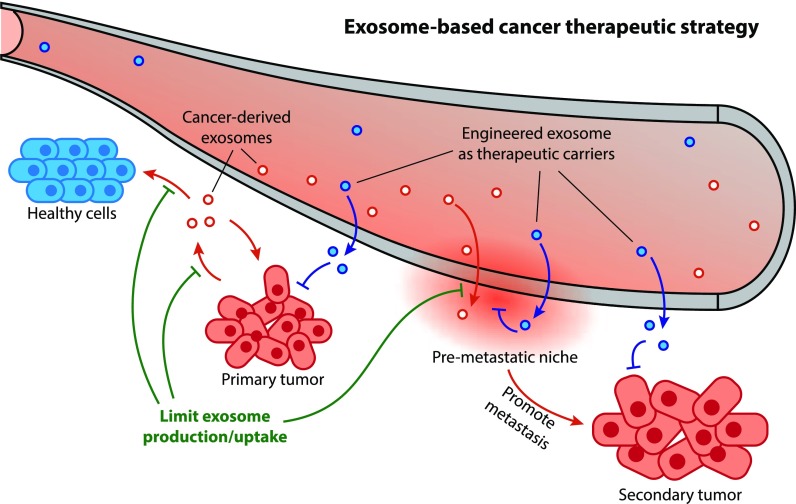 Figure 1. Schematic illustration of exosome's roles in cancer development and therapeutic application. (Li X, et al., 2019)
Figure 1. Schematic illustration of exosome's roles in cancer development and therapeutic application. (Li X, et al., 2019)
In Vitro Exosome Functional Assays Offered
We offer a comprehensive portfolio of in vitro assays, modularly designed to answer your specific biological questions. Our services cover everything from basic cellular responses to complex, organ-specific functional validation.
Core Cellular Functional Assays
This suite of services assesses the most fundamental biological responses of recipient cells upon exosome treatment. We use high-content imaging, flow cytometry, and real-time impedance sensing to provide quantitative data on cell behavior.
- Exosome Uptake Efficiency: We visualize and quantify the internalization of labeled exosomes (e.g., PKH, DiO/DiR) by recipient cells using flow cytometry or confocal microscopy.
- Cell Proliferation & Viability: We measure the effect of exosome treatment on cell growth rates using assays like MTT, WST-1, or real-time monitoring.
- Apoptosis & Cell Cycle Analysis: We determine if exosomes induce or inhibit apoptosis (e.g., Annexin V/PI staining) or cause cell cycle arrest.
- Cell Migration & Invasion: Using scratch/wound-healing assays and Transwell invasion models, we assess the impact of exosomes on cell motility, a critical function in cancer and wound healing.
Exosome Drug Release & Transcytosis Assays
Designed for therapeutic exosome development, these assays evaluate the performance of exosomes as drug delivery vehicles. We assess both payload release and the ability to cross biological barriers.
- Payload Release Kinetics: We monitor the in vitro release of loaded cargo (e.g., small molecules, siRNA) from exosomes over time in a controlled environment.
- Barrier-Crossing Assays (Transcytosis): Using in vitro models of the blood-brain barrier (BBB) or intestinal wall (e.g., Caco-2 monolayers), we quantify the efficiency of exosome transport from the apical to the basolateral side.
Advanced 3D & Organoid-Based Functional Assays
Move beyond traditional 2D monolayers to test exosome function in a more physiologically relevant context. Our 3D models simulate complex in vivo microenvironments, providing more predictive data.
- 3D Skin Model Assays: We utilize reconstructed human epidermis (RhE) models to evaluate the efficacy and safety of exosomes for dermatological or cosmetic applications (e.g., wound healing, anti-aging).
- Organoid-Based Functional Assays: We co-culture your exosomes with patient-derived organoids (PDOs) or iPSC-derived organoids (e.g., tumor, liver, or intestinal organoids) to assess exosome potency and therapeutic effect in a complex, multi-cellular system.
Cargo-Specific Mechanism of Action (MOA) Assays
These assays focus on the specific biomolecular cargo delivered by exosomes and how it interacts with recipient cell pathways.
- Dual-Luciferase Reporter Gene Assay: This is the gold standard for validating exosome-mediated transfer of functional miRNA or siRNA. We measure the suppression of a target gene linked to a luciferase reporter, confirming your nucleic acid cargo is delivered and active.
- Exosome-Protein Interaction Assays: We use techniques like Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) or Bio-Layer Interferometry (BLI) to characterize the binding kinetics of exosome surface proteins to specific cell surface receptors, elucidating the mechanism of targeting and uptake.
Our End-to-End Project Workflow
We follow a transparent, multi-stage workflow to ensure your project's success, integrating rigorous quality control from start to finish. Our process is designed for clarity, collaboration, and the delivery of reliable, publication-ready data.
Integrated Quality Control:
Quality assurance is not a separate step but a core component of our entire workflow. We implement QC checkpoints at every critical stage:
Upstream QC
We verify the quality of your submitted samples and the health of our cell models before any experiment begins.
In-Process QC
Every assay includes appropriate controls to validate the experimental setup and ensure data reliability.
Downstream QC
All data and analyses undergo a final review by our scientific team before the report is delivered to you.
Our Five-Step Project Pathway
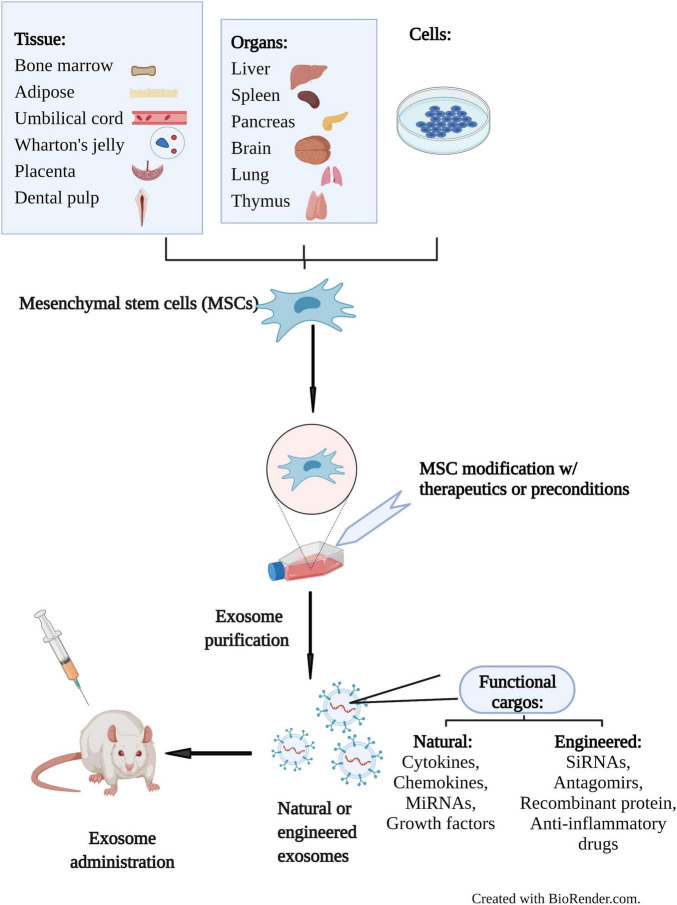
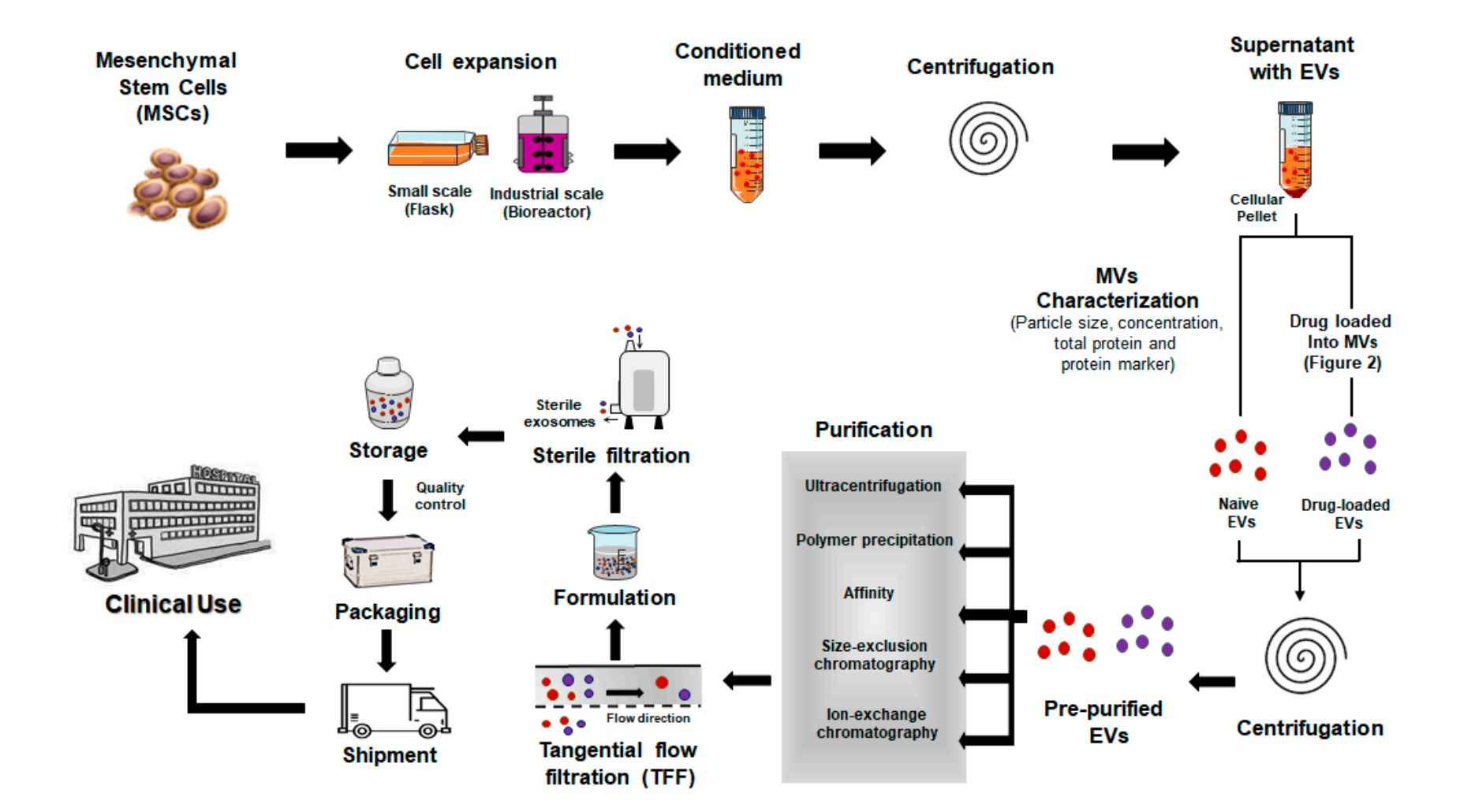
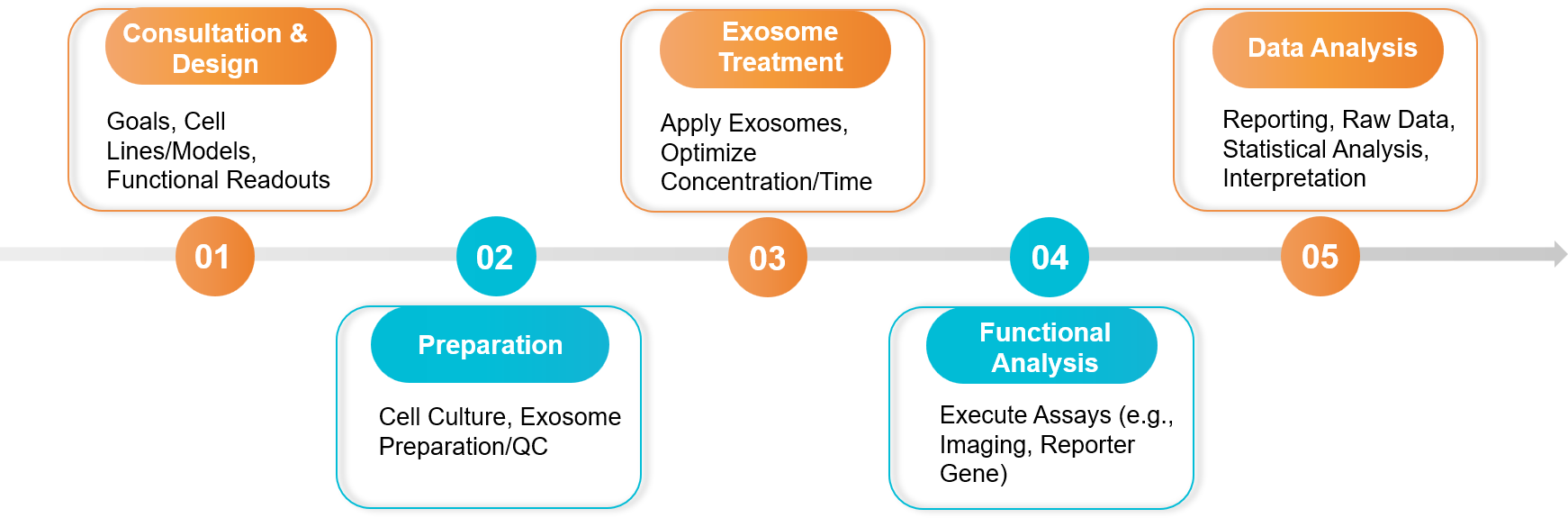 Figure 2. In Vitro Exosome Functional Assay Project Workflow. (Creative Biostructure)
Figure 2. In Vitro Exosome Functional Assay Project Workflow. (Creative Biostructure)
Sample Requirements
- Client-Provided Exosomes:
- Quantity: Typically ≥ 1x10¹⁰ particles (assay-dependent).
- Purity: Purified exosomes (by UC, SEC, affinity, etc.) are required. We strongly recommend providing NTA and Western Blot characterization data.
- Buffer: Suspended in sterile PBS or a compatible culture-grade buffer.
- Recipient Cells:
- Client may provide specific cell lines (e.g., engineered reporter lines).
- Alternatively, we can source and culture standard cell lines (e.g., HUVEC, MCF-7, 3T3) or advanced models (e.g., iPSC-derived neurons).
Standard Deliverables
- A Comprehensive Project Report: Details the experimental design, protocols, and all parameters.
- Raw and Analyzed Data: Includes raw data files (e.g., flow cytometry .fcs files, plate reader outputs) and fully analyzed results.
- High-Quality Figures & Graphs: Publication-ready visualizations of the functional data (e.g., dose-response curves, confocal images, migration plots).
- Scientific Consultation: A final meeting with our technical team to discuss the results and next steps.
Case Study
Case: Validating the Mechanism of UCB-Exosomes in Wound Healing Using In Vitro Functional Assays
Background: Researchers hypothesized that exosomes from human umbilical cord blood (UCB-Exos) could accelerate skin wound healing, but they needed to confirm this and understand how it works before proceeding to complex in vivo models. The goal was to test the in vitro function of UCB-Exos on the key cells involved in wound repair: fibroblasts (for rebuilding tissue) and endothelial cells (for angiogenesis/new blood vessel formation).
Methodology: A comprehensive panel of in vitro functional assays was performed to measure specific cellular responses to UCB-Exo treatment.
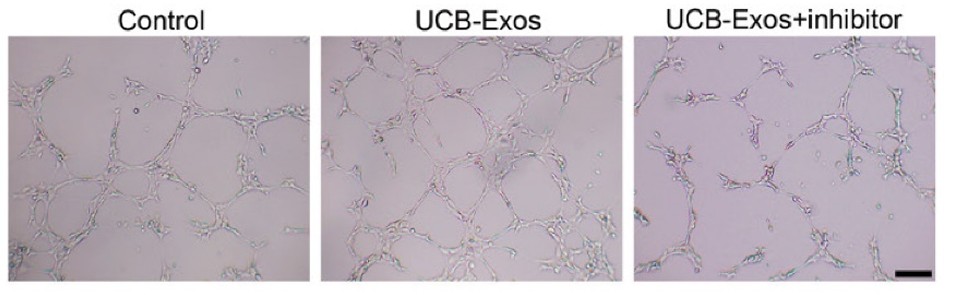 Figure 3. UCB-Exos increased the tube formation ability of HMECs, but this effect was decreased by miR-21-3p inhibition. (Hu Y, et al., 2018)
Figure 3. UCB-Exos increased the tube formation ability of HMECs, but this effect was decreased by miR-21-3p inhibition. (Hu Y, et al., 2018)
1. Core Cellular Functional Assays: Scientists measured cell proliferation (via CCK-8), cell migration (via scratch and Transwell assays), and angiogenesis (via tube formation assay) after UCB-Exo treatment.
2. Mechanism of Action (MOA) Assay: To identify the mechanism, they used RNA inhibitors (siRNA) to block a key exosomal cargo molecule, miR-21-3p, and see if the positive effects disappeared.
Key Findings:
- The in vitro assays confirmed that UCB-Exos treatment significantly promoted fibroblast proliferation and migration, and strongly enhanced endothelial cell tube formation (angiogenesis).
- Critically, when the exosomal cargo miR-21-3p was blocked, these pro-healing effects were significantly reduced. This proved that the exosomes exert their function by successfully delivering active miR-21-3p to the recipient cells.
Conclusion: This study demonstrates the critical value of a multi-assay in vitro platform. By combining assays for proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis, the researchers successfully validated the pro-healing potency of their exosomes. Furthermore, by using an MOA study, they precisely identified the molecular mechanism responsible. This provided a complete and compelling data package that confirmed the exosomes' therapeutic potential before advancing to costly animal studies.
Ready to validate the biological function of your exosomes? Our expert team is here to help you design the perfect study. Contact us today for a free consultation and to discuss how our in vitro functional assays can advance your research.
References
- Li X, Corbett AL, Taatizadeh E, et al. Challenges and opportunities in exosome research-Perspectives from biology, engineering, and cancer therapy. APL Bioeng. 2019 Mar 27;3(1):011503.
- Hu Y, Rao SS, Wang ZX, et al. Exosomes from human umbilical cord blood accelerate cutaneous wound healing through miR-21-3p-mediated promotion of angiogenesis and fibroblast function. Theranostics. 2018 Jan 1;8(1):169-184.
Frequently Asked Questions
For any inquiries, our support team is ready to help you get technical support for your research and maximize your experience with Creative Biostructure.