Animal Tissue Exosome Isolation Service
At Creative Biostructure, we offer a professional exosome isolation service from animal tissues to support cutting-edge research in intercellular communication, disease progression, and biomarker discovery. Compared to exosomes derived from cell culture or body fluids, tissue-derived exosomes preserve the molecular signatures of the native tissue microenvironment, offering unique biological insights with higher specificity.
Why Tissue-Derived Exosomes Matter
Body fluids like blood and urine contain a mixture of exosomes originating from multiple organs, which can dilute or obscure the signal from a specific tissue. In contrast, exosomes isolated directly from tissue interstitial spaces more accurately reflect localized cellular states, making them ideal for:
- Disease mechanism studies
- Diagnostic biomarker screening
- Functional exosome profiling
- Preclinical drug evaluation
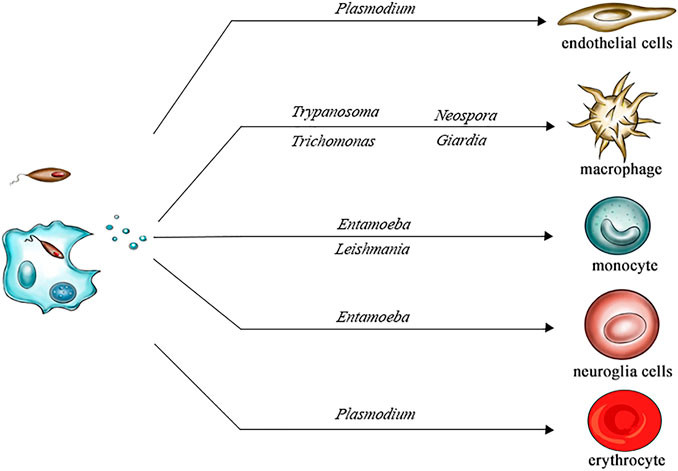
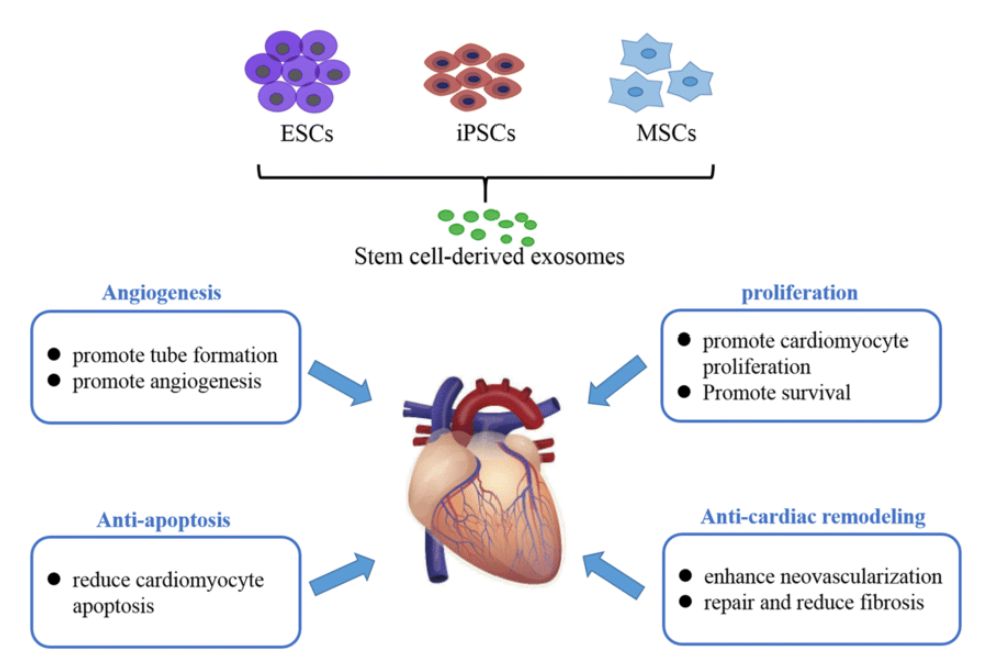
Numerous studies have confirmed the physiological and pathological relevance of exosomes from adipose, brain, liver, and other tissues. Adipose tissue-derived exosomes (AT-exosomes), for instance, have shown involvement in metabolic regulation, neuroregeneration, and tumorigenesis.
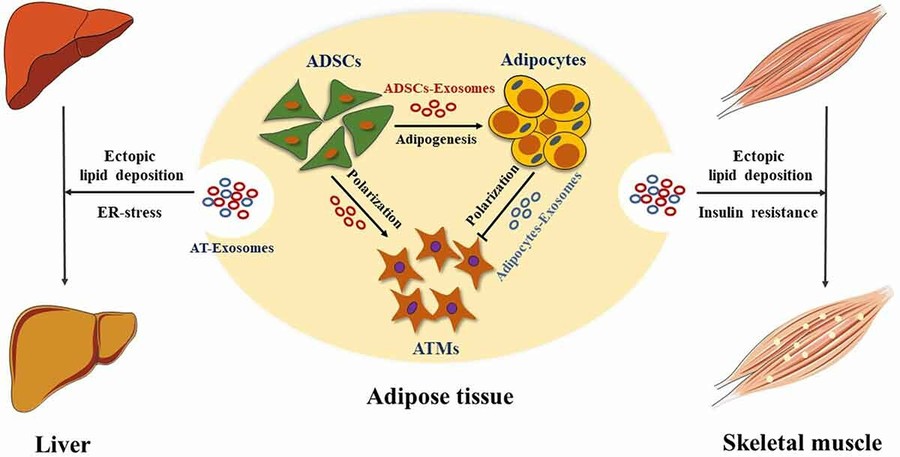
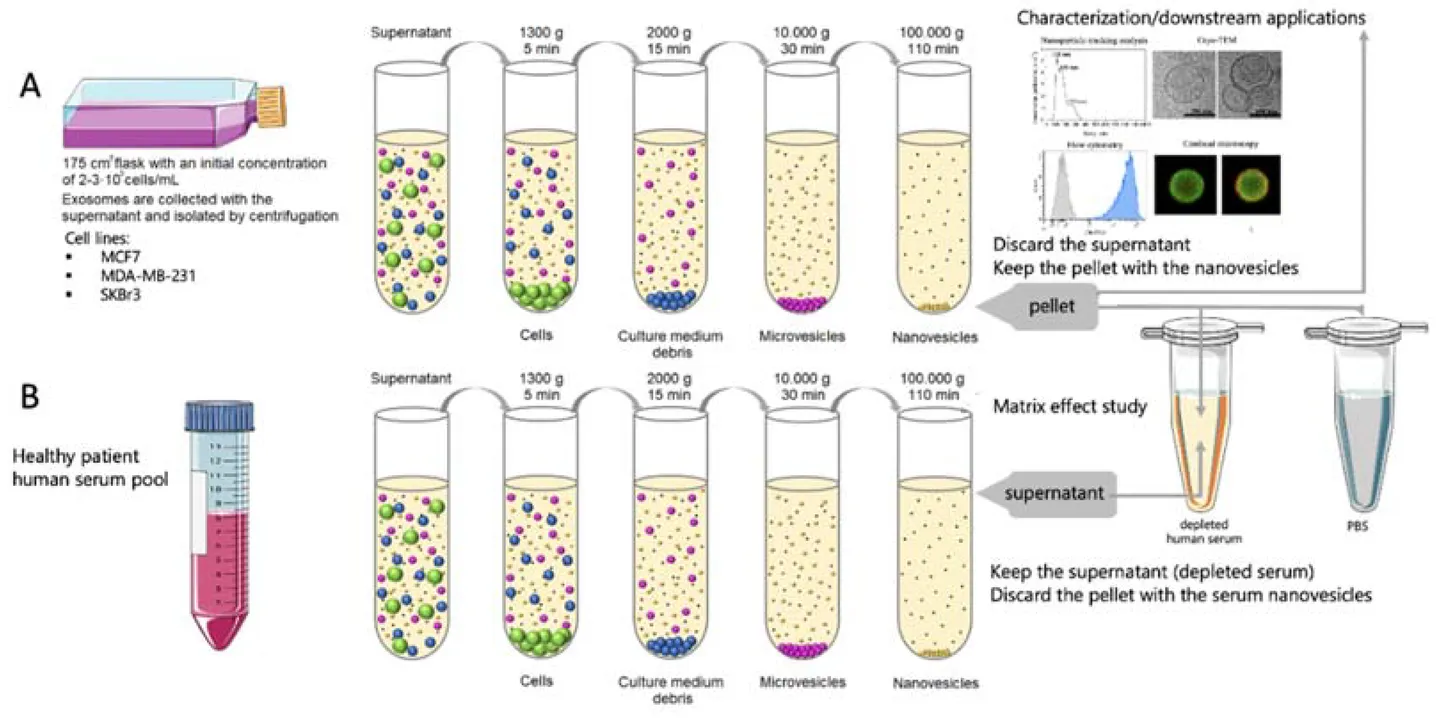
Figure 1. Role of Adipose Tissue-Derived Exosomes in Metabolic Regulation. (Zhao R, et al., 2021)
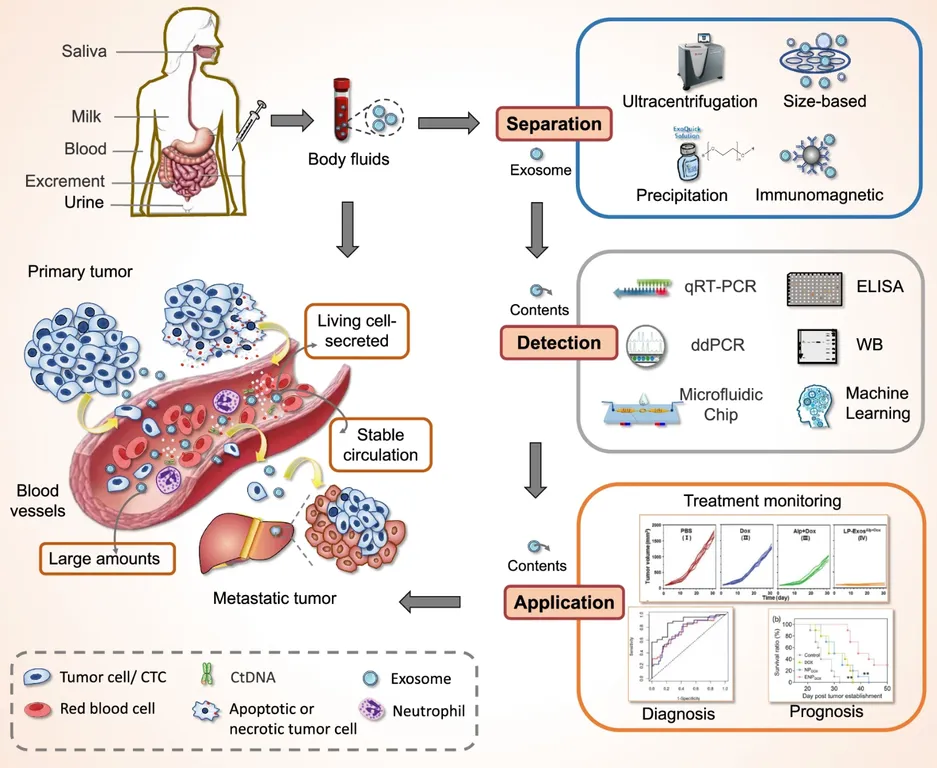
Our Exosome Isolation Techniques
Creative Biostructure employs a range of advanced exosome isolation techniques to accommodate different sample types, purity requirements, and downstream applications. The table below summarizes the core technologies we use, along with their descriptions and suitable research contexts:
| Technique | Description | Recommended Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Differential Ultracentrifugation | Sequential high-speed spins to isolate exosomes based on size and density. | Standard for high-throughput isolation from tissue homogenates and culture media. |
| Density Gradient Ultracentrifugation | Uses sucrose or iodixanol layers to achieve high-purity separation. | Best for functional assays, electron microscopy, and omics analysis. |
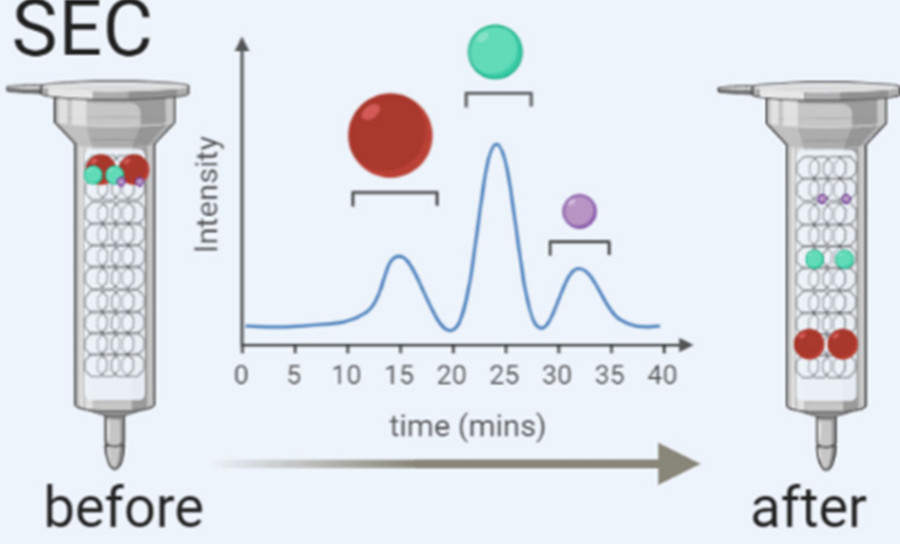
| Size-Exclusion Chromatography (SEC) | Separates vesicles by size through a porous column, preserving vesicle integrity. | Ideal for downstream RNA sequencing, proteomics, and functional exosome research. |
| Ultrafiltration (UF) | Uses membranes with specific molecular weight cut-offs to concentrate exosomes. | Suitable for rapid sample concentration and pre-purification prior to SEC or affinity. |
| Polymer-Based Precipitation | Uses hydrophilic polymers to precipitate exosomes from biological fluids. | Convenient for high-yield recovery from large sample volumes; suitable for screening. |
| Immunoaffinity Capture | Uses antibodies targeting surface markers (e.g., CD63, CD81) for specific capture. | High-specificity isolation for biomarker studies and targeted subpopulation analysis. |
We also offer integrated isolation workflows that combine multiple techniques to optimize yield, purity, and functional integrity based on your specific research needs.
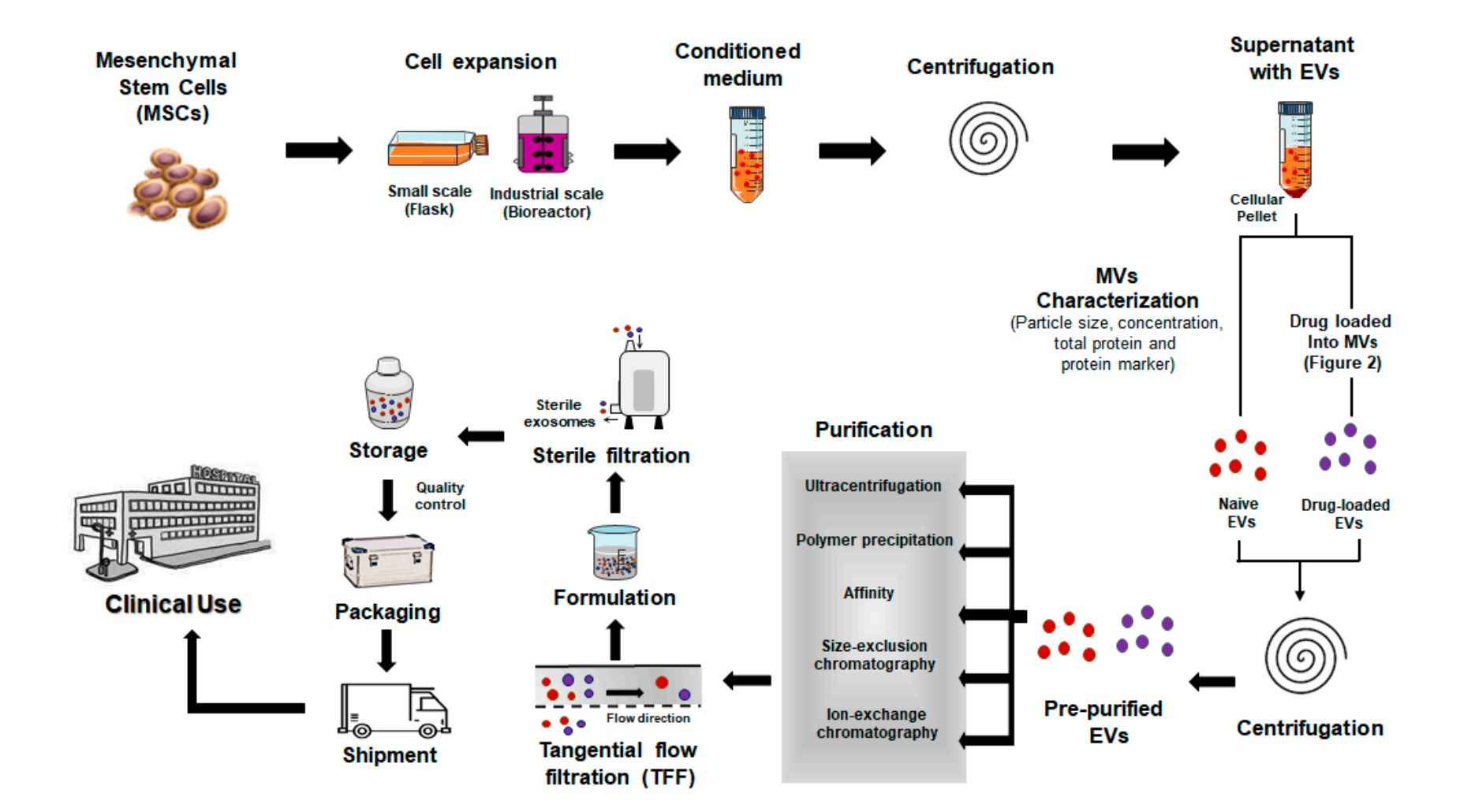
Our Tissue Exosome Isolation Workflow
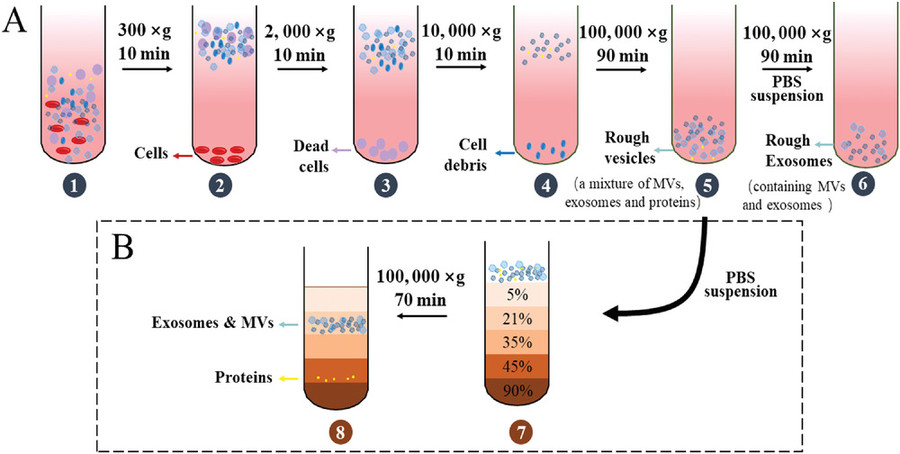
Isolating exosomes from animal tissues requires careful handling to preserve vesicle integrity while eliminating contaminants. At Creative Biostructure, we have established a robust and customizable workflow optimized for various tissue types and downstream applications. The key steps include:
Tissue Dissection & Preprocessing
Animal tissues are finely minced or sectioned to maximize surface area. Depending on tissue type, optional perfusion or enzymatic softening is applied to improve exosome release.
Tissue Digestion & Conditioned Media Preparation
Samples are incubated with specialized enzyme cocktails (e.g., collagenase, DNase) in exosome-compatible medium to facilitate exosome diffusion from the interstitial space into the supernatant.
Preliminary Clarification
Sequential centrifugation at low to medium speeds (e.g., 300 ×g, 2,000 ×g, 10,000 ×g) removes cells, debris, apoptotic bodies, and larger vesicles.
Exosome Enrichment
We apply advanced isolation methods such as ultracentrifugation, size-exclusion chromatography (SEC), or immunoaffinity capture to selectively enrich for exosomes while preserving their biological activity.
Buffer Exchange & Concentration
Final concentration and buffer exchange are performed using ultrafiltration or dialysis to prepare exosomes for intended downstream assays (e.g., proteomics, sequencing, cell-based assays).
This modular workflow can be adapted based on tissue source, project goals, and preferred analytical endpoints. Additionally, we offer combined technology strategies to enhance both recovery and specificity, especially for low-yield or complex tissues.
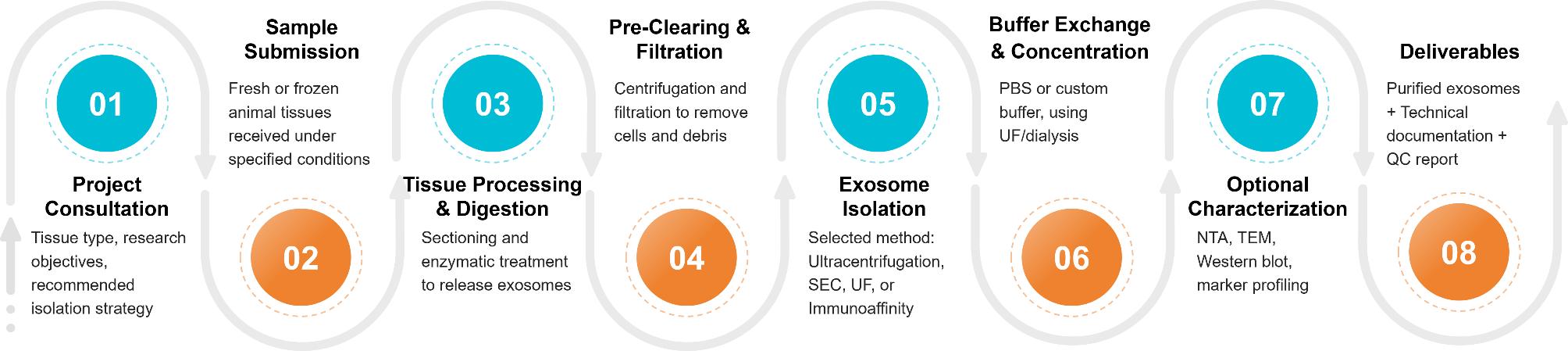
Figure 2. Tissue Exosome Isolation Project Workflow. (Creative Biostructure)
Supported Sample Types
We accept both fresh and frozen tissue specimens from multiple species, including:
- Mouse (liver, brain, adipose, spleen)
- Rat (kidney, skeletal muscle)
- Bovine and porcine tissues
- Other custom sources upon request
For optimal yield and QC performance, we recommend ≥2 grams of tissue per sample. Contact us for guidance on your specific tissue type.
Quality Control and Deliverables
Every exosome batch undergoes comprehensive quality testing, including:
- Particle Size and Concentration by Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA)
- Morphology via Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
- Exosomal Marker Validation (CD9, CD63, TSG101, Alix) using Western Blot or ELISA
- Optional: RNA profiling, proteomics, and lipidomics upon request
You will receive:
- Purified tissue-derived exosomes (lyophilized or in solution)
- Technical documentation (detailed protocols, reagent information, sample handling notes, and storage guidelines)
- Comprehensive QC report (NTA graphs, TEM images, marker validation data, and recommended downstream applications)
- Optional omics datasets and functional assay results
Optional Add-On Services
To help you extract maximum biological insight from your exosome samples, Creative Biostructure offers a suite of optional downstream services tailored to diverse research goals. These add-on services can be bundled with our tissue exosome isolation workflow or requested independently.
| Advanced Omics Analysis | Functional & Validation Assays | Customization & Engineering |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Each optional service is backed by expert consultation to ensure methodological compatibility and data reproducibility across platforms.
Frequently Asked Questions
For any inquiries, our support team is ready to help you get technical support for your research and maximize your experience with Creative Biostructure.
Case Study
Case: Tissue-Derived Exosome Isolation Enables Biomarker Discovery in Esophageal Cancer
Background
To identify novel biomarkers for esophageal cancer (EC), researchers developed a workflow for isolating exosomes directly from tumor and adjacent tissues, offering a more localized and disease-relevant vesicle population than fluid-derived exosomes.
Methods
- Tissue samples (8 tumor/paracancer pairs) were digested enzymatically and processed using differential centrifugation, 0.22 µm filtration, and ultracentrifugation (110,000 × g).
- Further purification was achieved via size-exclusion chromatography and ultrafiltration (100 kDa).
- Exosomes were characterized by:
- Nano-flow cytometry: size range 50–200 nm
- TEM: classic cup-shaped morphology (~120 nm)
- Western blot: expression of CD9, CD63, TSG101; absence of non-exosomal marker GM130
Conclusion
This study demonstrates a reproducible method for isolating high-purity exosomes from solid tissue samples. The approach enabled subsequent proteomic profiling and highlighted the utility of tissue-derived exosomes as a reliable source for cancer biomarker discovery.
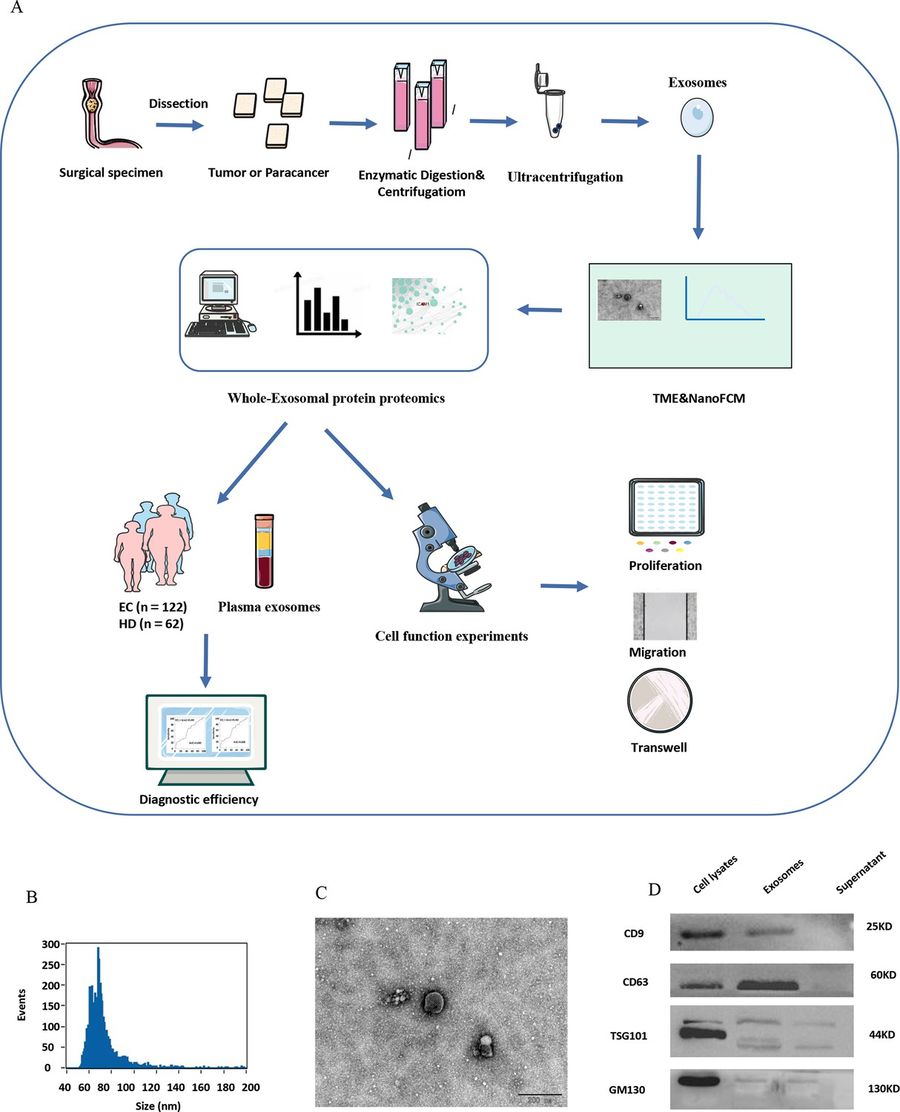
Figure 3. Exosome Identification and Characterization. (A) Overview of the experimental workflow. (B) NanoFCM confirms particle size distribution of isolated exosomes (50–200 nm). (C) TEM image reveals round exosome morphology (~120 nm); scale bar: 100 μm. (D) Western blot analysis detects exosomal markers CD9, CD63, TSG101, and absence of GM130 as a negative control. (Rao D, et al., 2023)
At Creative Biostructure, we are committed to helping you unlock the full potential of tissue-derived exosomes. Contact us to discuss your project needs or request a quote, and our experts are ready to support your research from isolation to in-depth functional analysis.
References
- Zhao R, Zhao T, He Z, et al. Composition, isolation, identification and function of adipose tissue-derived exosomes. Adipocyte. 2021, 10(1): 587-604.
- Rao D, Lu H, Wang X, et al. Tissue-derived exosome proteomics identifies promising diagnostic biomarkers for esophageal cancer. Elife. 2023, 12: e86209.