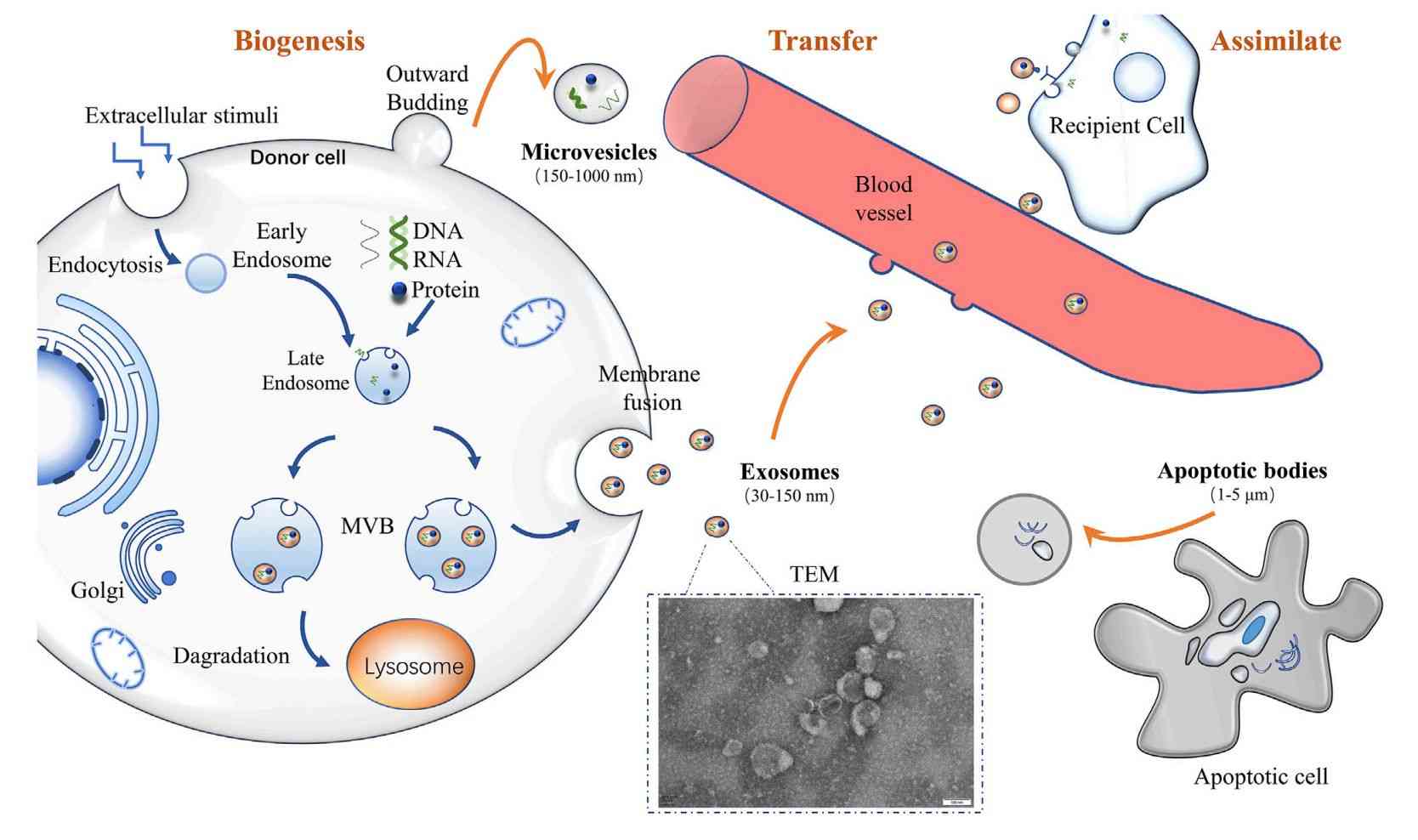
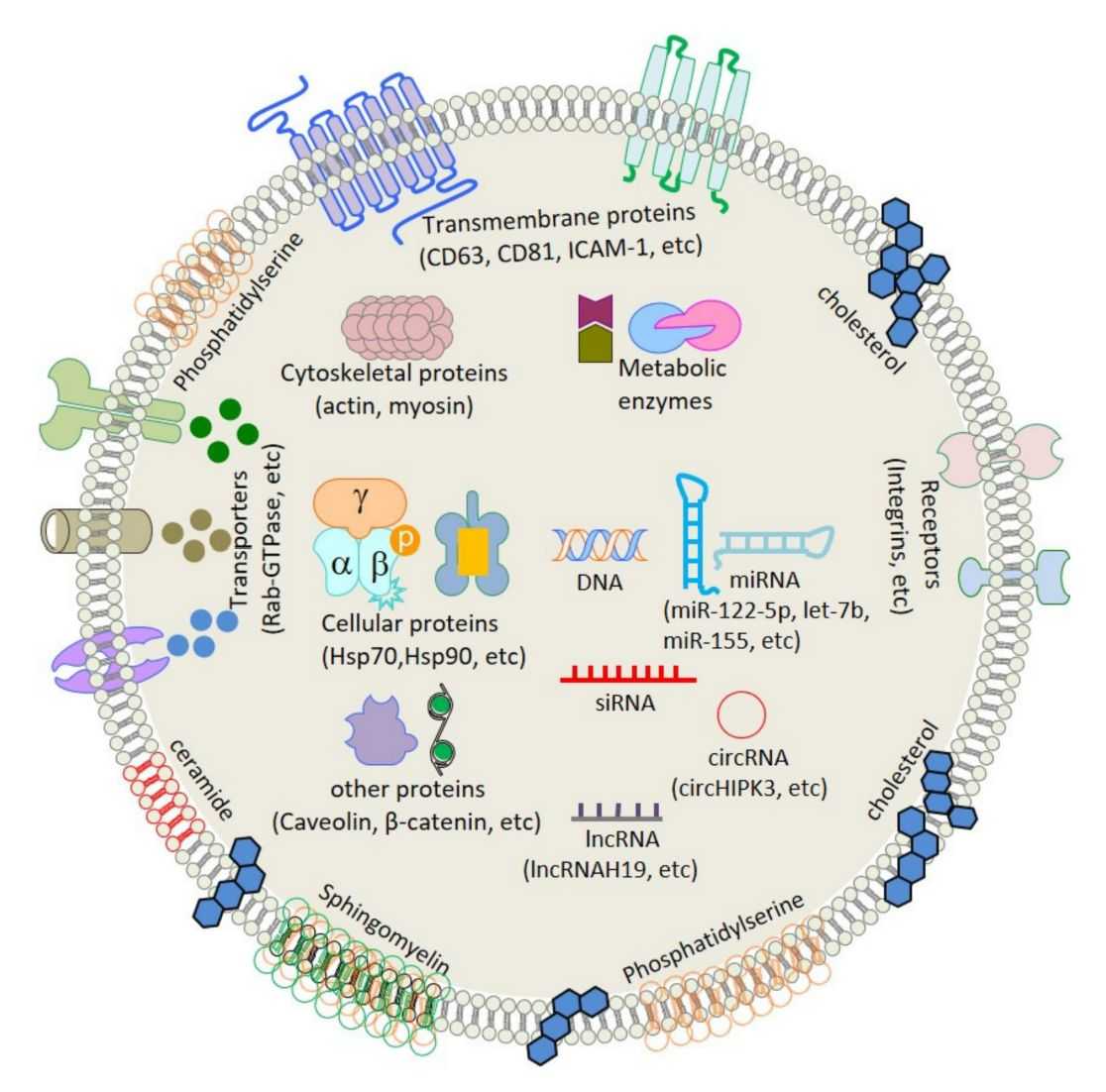
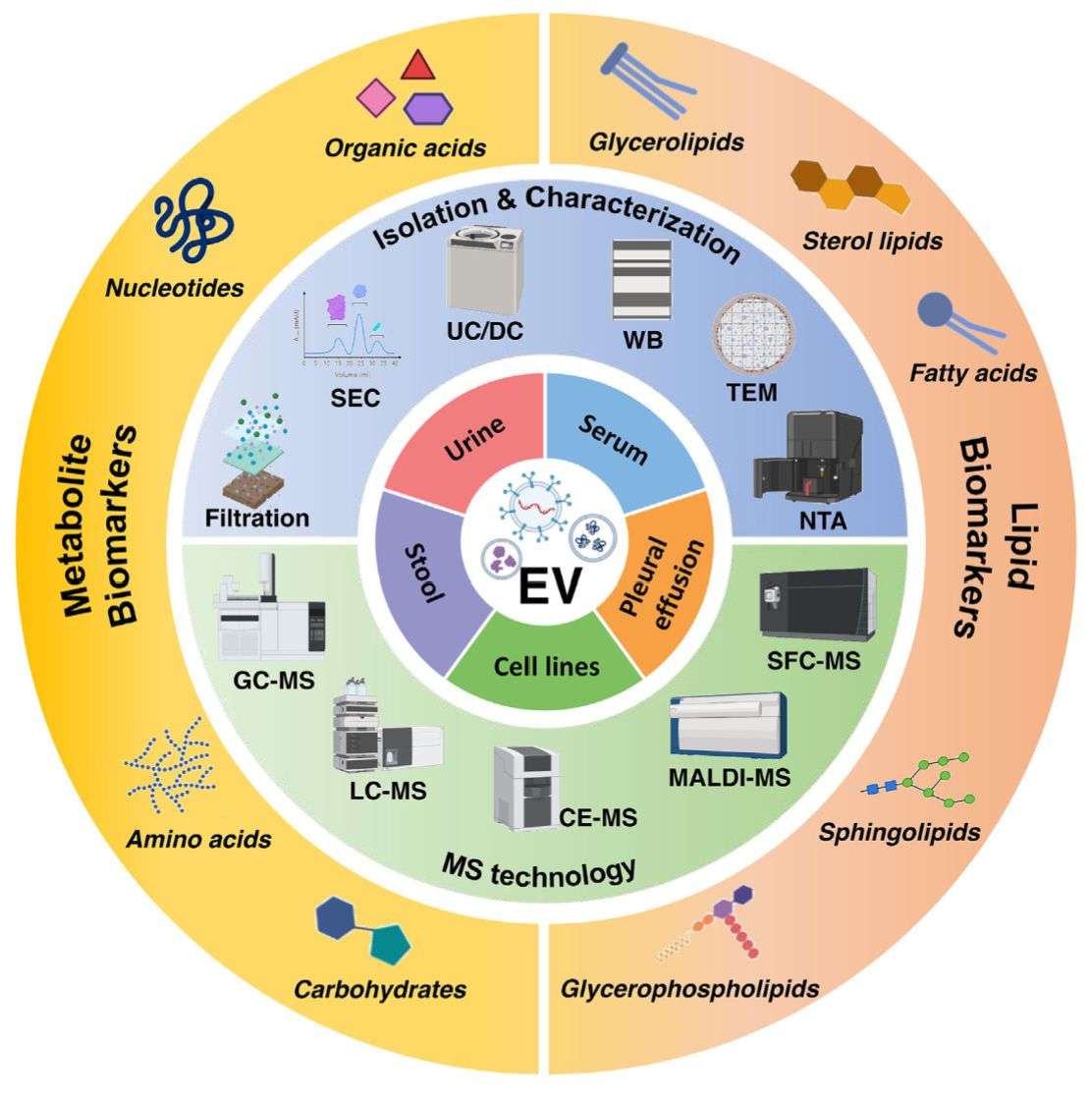
Plant Exosome Lipidomics Analysis Service
Plant exosomes represent a new frontier for understanding intercellular signaling and plant-microbe interactions. As natural nanocarriers, their lipid composition determines structural integrity and biological functionality. Creative Biostructure offers meticulously designed exosome lipidomics analysis solutions specifically tailored for plant-derived exosome samples. Our standardized workflow enables comprehensive exploration of the exosome lipidome, empowering clients to advance research in intercellular communication, signaling pathways, and plant-microbe interactions within agricultural and bioscience fields.
Why Analyze the Lipidome of Plant Exosomes?
Analyzing the lipidome of plant exosomes is central to unlocking key mechanisms underlying vital processes such as intercellular communication, stress responses, and symbiotic relationships in plants. The lipid bilayer of plant exosomes not only forms their structural foundation but also carries out intricate biological functions including signal recognition, membrane fusion, and targeted delivery. Systematic elucidation of their lipid composition reveals proactive defense strategies in plants responding to biotic/abiotic stresses, clarifies the molecular basis of plant-microbe interactions, and provides revolutionary research insights and data support for crop stress-tolerant breeding, green agricultural formulation development, and the design of plant-derived drug delivery systems.
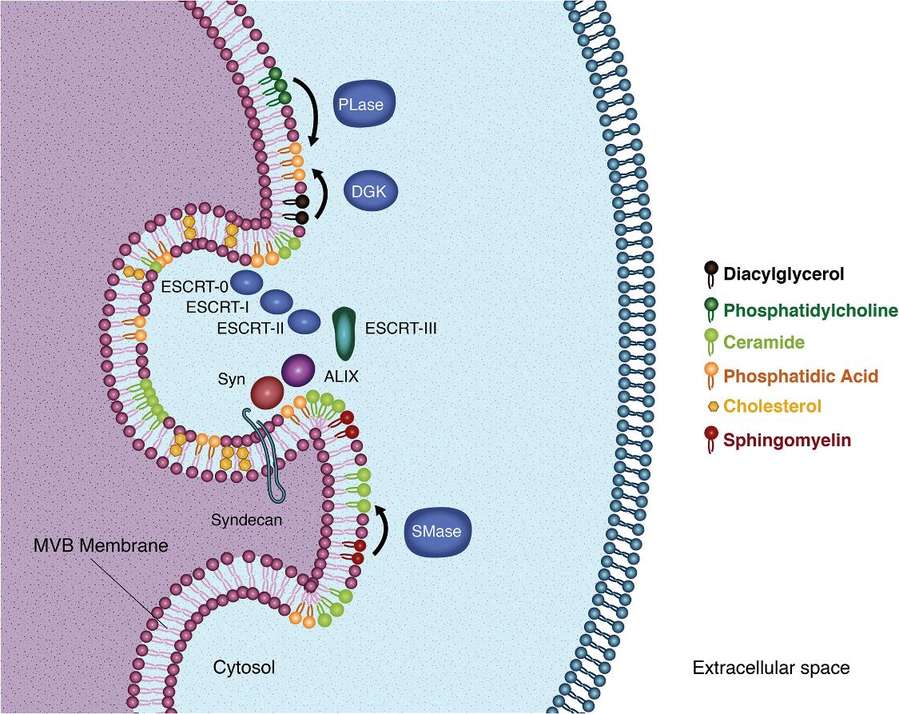
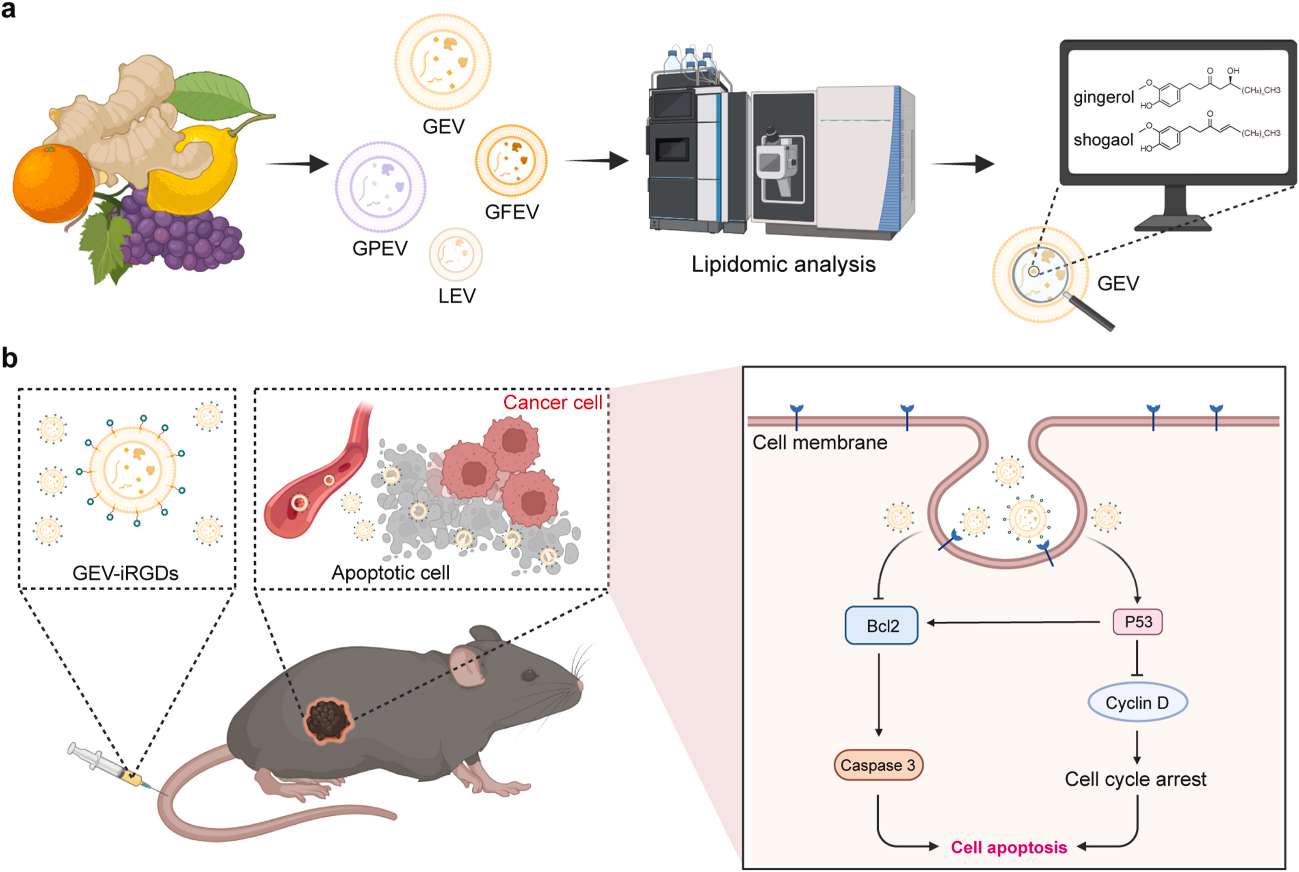 Figure 1. Schematic illustration of lipidomics of PEVs for potential anti-cancer therapy. (Wang, F. et al., 2025)
Figure 1. Schematic illustration of lipidomics of PEVs for potential anti-cancer therapy. (Wang, F. et al., 2025)
Our Plant Exosome Lipidomics Analysis Service
Creative Biostructure provides professional plant exosome lipidomics analysis services, utilizing high-resolution mass spectrometry to comprehensively profile multiple lipid classes through a complete workflow from sample pretreatment and lipid extraction to data processing. Employing optimized plant exosome isolation protocols combined with stringent QC standards, this service enables precise identification of key functional lipids such as phospholipids and glycerolipids. It helps reveal the molecular mechanisms underlying intercellular communication, stress response, and symbiotic interactions in plants, delivering precise lipidomics data support for crop improvement and natural drug development.
Our Plant Exosome Lipidomics Analysis Workflow
To translate commitments into actionable scientific insights, we have established rigorously standardized operating procedures. The comprehensive workflow below ensures traceability and reproducibility at every stage, from sample to report, laying a solid foundation for our clients' research discoveries.
Sample Receipt and Quality Control
Upon receipt of plant tissue or secretion samples, we immediately perform tests for pH, microbial load, and hemolysis indicators to ensure compliance with analytical standards.
Exosome Isolation and Validation
We employ ultracentrifugation combined with density gradient centrifugation to efficiently isolate plant exosomes. The particle size distribution is determined by nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA), and exosomal marker proteins (e.g., HSP70, TSG101) are validated by Western blot to ensure the purity and integrity of the extracted products.
Lipid Extraction and Preparation
Lipid extraction was performed using a modified Bligh-Dyer method to optimize phospholipid recovery. The extracts were then concentrated to volume under a nitrogen stream, with all procedures conducted under antioxidant conditions to maintain lipid stability.
Lipidomics Analysis
Employing a UHPLC-MS/MS platform equipped with C18 reverse-phase columns for lipid separation and utilizing a high-resolution mass spectrometer for data acquisition, this method covers 24 classes of lipid molecules unique to plants, including sterol glycosides and sulfoesters.
Data Analysis and Visualization
Lipid identification and relative quantification were performed using software such as LipidSearch, followed by pathway enrichment analysis with KEGG/GO databases. Visualization plots including heatmaps and volcano plots were generated using Python to reveal characteristics of the lipid metabolic network.
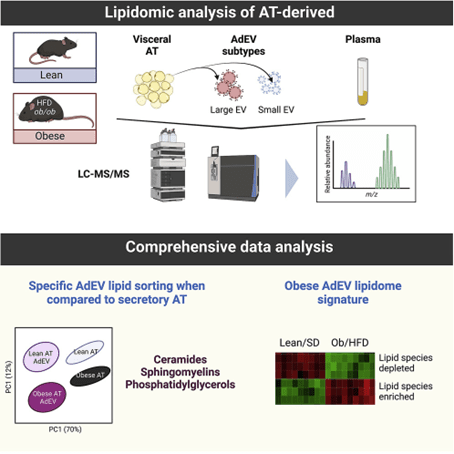
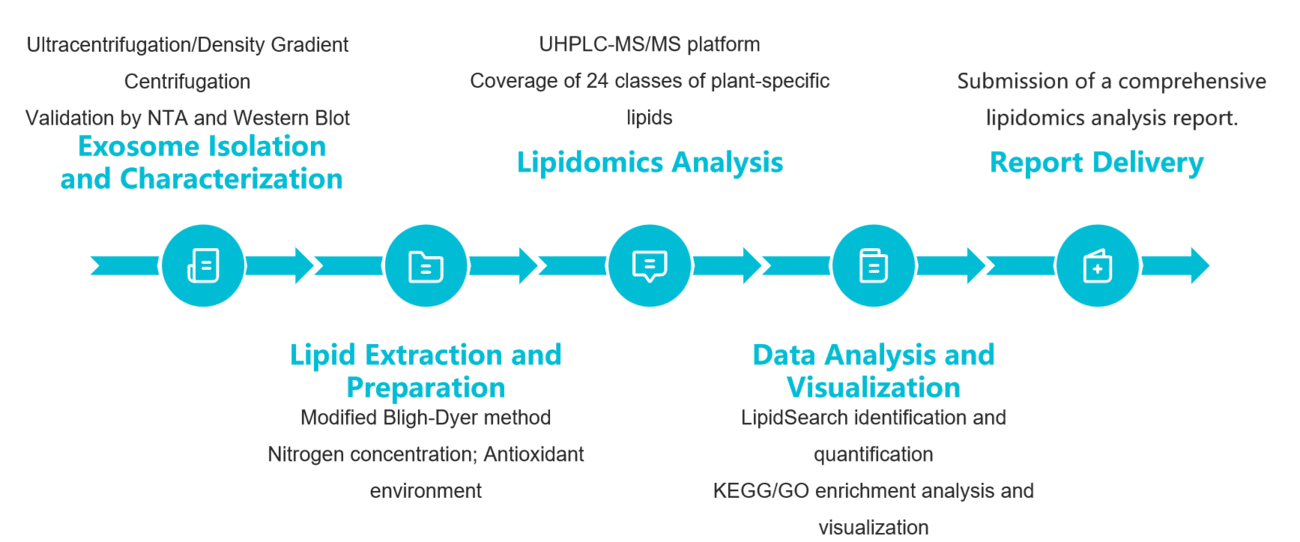 Figure 2. Plant exosome lipidomics analysis pipeline. (Creative Biostructure)
Figure 2. Plant exosome lipidomics analysis pipeline. (Creative Biostructure)
Sample Types & Requirements
| Sample Categories | Specific Types | Minimum Quantity | Storage Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plant Solid Tissue | Leaves (Arabidopsis, rice, tobacco), roots, fruits, seeds | 2 g (fresh weight) | -80 °C freezing, vacuum-sealed to prevent browning |
| Plant Liquid Samples | Suspension cell culture medium, plant sap, nectar | 50 mL | 4°C refrigeration, ship within 24 hours |
| Processed Samples | Plant exosome crude extract, plant-derived health supplements | 20 mL/10 g | -80 °C freezing, avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles |
Final Delivery
- Raw data: UPLC-MS/MS raw files (.raw), lipid identification log.
- Analysis report: PDF version (includes sample pretreatment records, QC data, differential lipid list, KEGG plant pathway diagrams.
- Visualization files: Excel data tables (lipid ID, concentration, fold change), interactive heatmaps (filterable for tissue-specific lipids), radar charts showing lipid category proportions.
Applications of Our Plant Exosome Lipidomics Analysis Service
Plant stress response mechanisms
Analyzing lipid changes in plant exosomes under salt/drought stress (e.g., increased phosphatidylinositol in Arabidopsis root exosomes mediating stress signaling).
Secondary metabolism research
Correlating lipids with flavonoid/alkaloid transport (e.g., association between sphingolipid content in tea leaf exosomes and tea polyphenol accumulation).
Developmental Biology
Tracking lipid dynamics during seed germination (e.g., degradation patterns of triglycerides in rice seed exosomes).
Agri-Tech Breeding
Screening stress-resistant lipid biomarkers (e.g., maize varieties with elevated PC 34:2 expression in exosomes exhibit 20% improved drought tolerance).
Plant-based health supplement development
Quantifying functional lipids (e.g., ceramide content in ginseng exosomes to guide supplement dosage design).
Case Study
Case: Lipidomic Analysis of Plant-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Guiding Anti-cancer Therapy
Background
Plant-derived extracellular vesicles (PEVs) have been regarded as a superior source for nanomedicine and drug delivery systems. This study conducts a comprehensive compositional analysis of four commonly used PEVs to fully understand their functional lipid contents and assess their potential therapeutic applications.
Research Highlights
- The lipidomic analysis revealed the presence of cytotoxic gingerols and shogaols in ginger-derived EVs (GEVs).
- In vitro and in vivo investigations substantiated the remarkable tumor cell inhibitory and tumor growth suppression efficacy of GEVs.
- The transcriptomic analysis indicated that GEVs regulate the cell cycle and p53 signaling pathways, thereby inducing cancer cell apoptosis.
Conclusion
These findings highlight the value of multi-omics analyses in elucidating the potential therapeutic effects of PEVs and in advancing the development of PEV-based therapies.
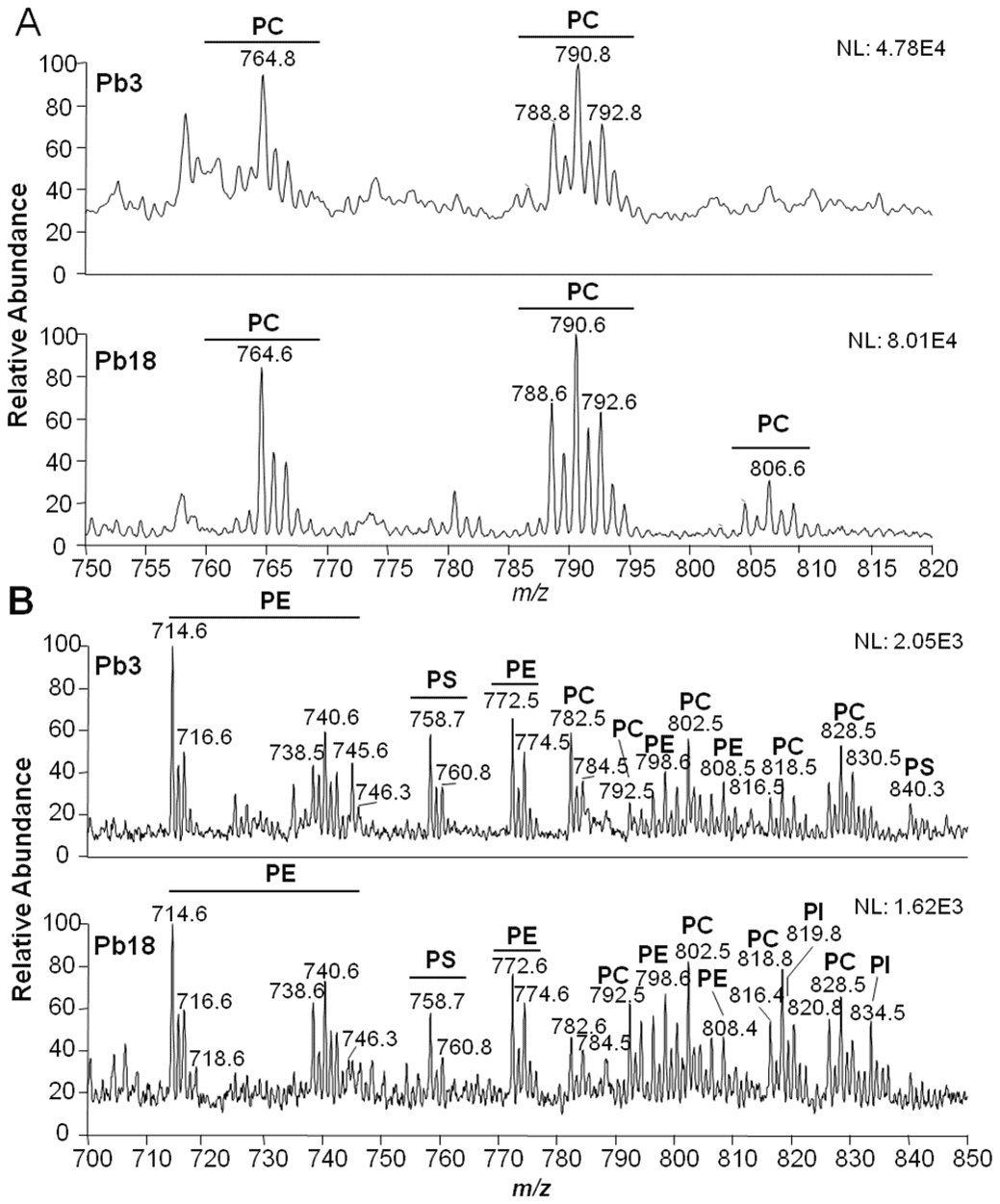
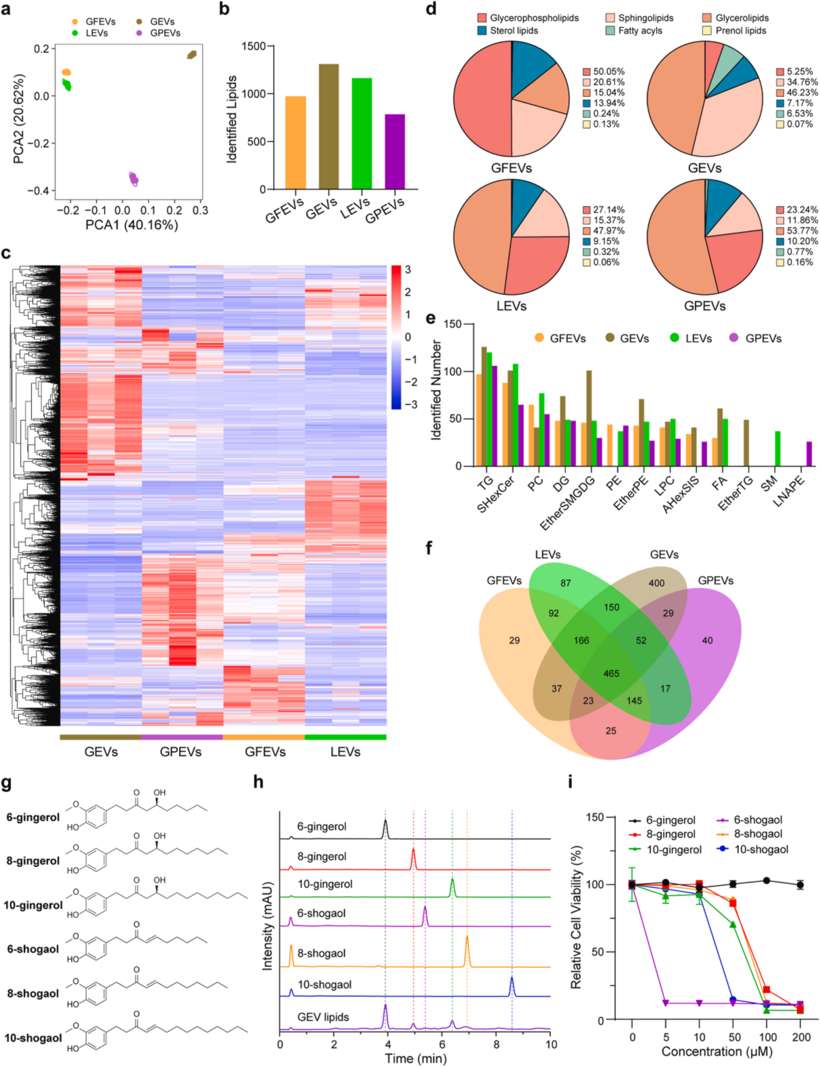 Figure 3. Comparative lipidomic analyses of PEVs. (Wang, F. et al., 2025)
Figure 3. Comparative lipidomic analyses of PEVs. (Wang, F. et al., 2025)
Creative Biostructure's plant exosome lipidomics analysis service delivers precise and comprehensive lipid profiling to uncover the functional potential of plant-derived exosomes, empowering clients in botanical research, agricultural biotechnology, and natural active substance development. Leverage our cutting-edge mass spectrometry platforms, expert data interpretation, and tailored workflows to accelerate discoveries. Contact us and our experienced team of experts will provide you with customized solutions.
Reference
- Wang, F., et al. Lipidomic analysis of plant-derived extracellular vesicles for guidance of potential anti-cancer therapy. Bioactive Materials. 46 (2025): 82-96.
Frequently Asked Questions
For any inquiries, our support team is ready to help you get technical support for your research and maximize your experience with Creative Biostructure.