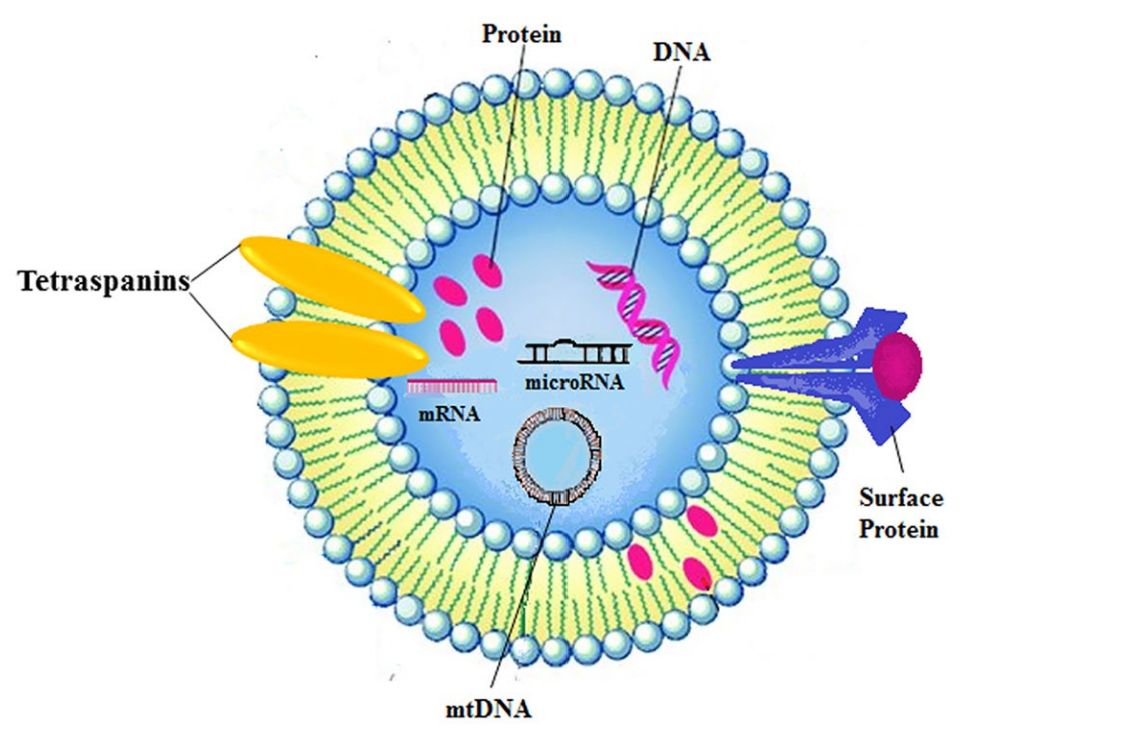
Exosome Immunomodulation and Inflammation Assays
Exosome immunomodulation and inflammation assays are methods used to quantify how exosome treatment functionally alters an immune response. These assays measure specific outcomes, such as macrophage polarization, T-cell activation, or inflammatory cytokine release, to determine an exosome's pro- or anti-inflammatory properties.
Why Test Exosome Immune Function?
Characterizing your exosome's size and cargo is only the first step. To understand their true biological impact, you must provide functional data. Our platform is designed to provide this critical evidence.
- Validate Therapeutic Efficacy: For developing exosome therapy for inflammation, you must provide quantitative data demonstrating a potent anti-inflammatory or immune-resolving effect.
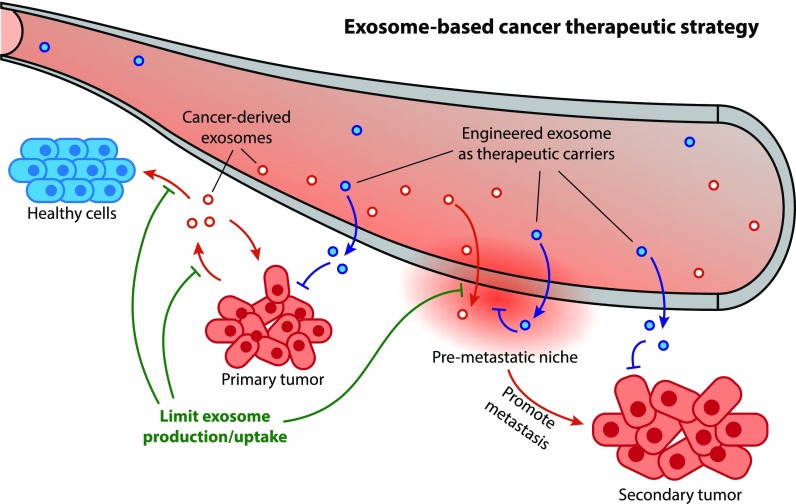
- Elucidate Disease Mechanisms: In oncology and autoimmune disease, the link between exosomes and inflammation is critical. Tumor-derived exosomes can "educate" macrophages, creating a pro-tumor microenvironment. Our assays help you uncover these mechanisms.
- De-risk Therapeutic Candidates: Before advancing to in vivo studies, it is vital to screen your exosome-based therapeutics for potential off-target immune activation, such as a "cytokine storm."
- Move Beyond Characterization: Our platform provides the direct functional data needed to validate your exosome's impact on the immune system, moving your research from "what it is" to "what it does."
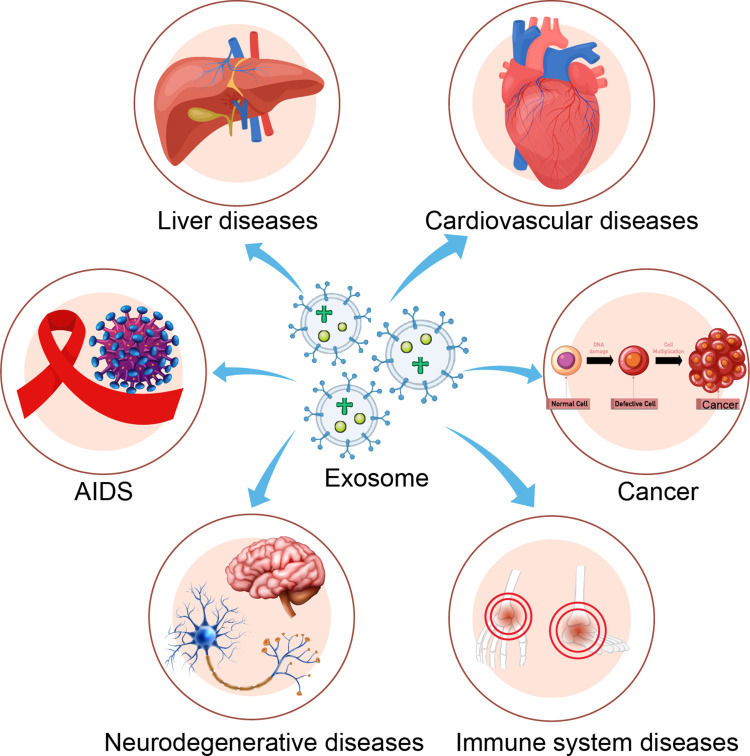
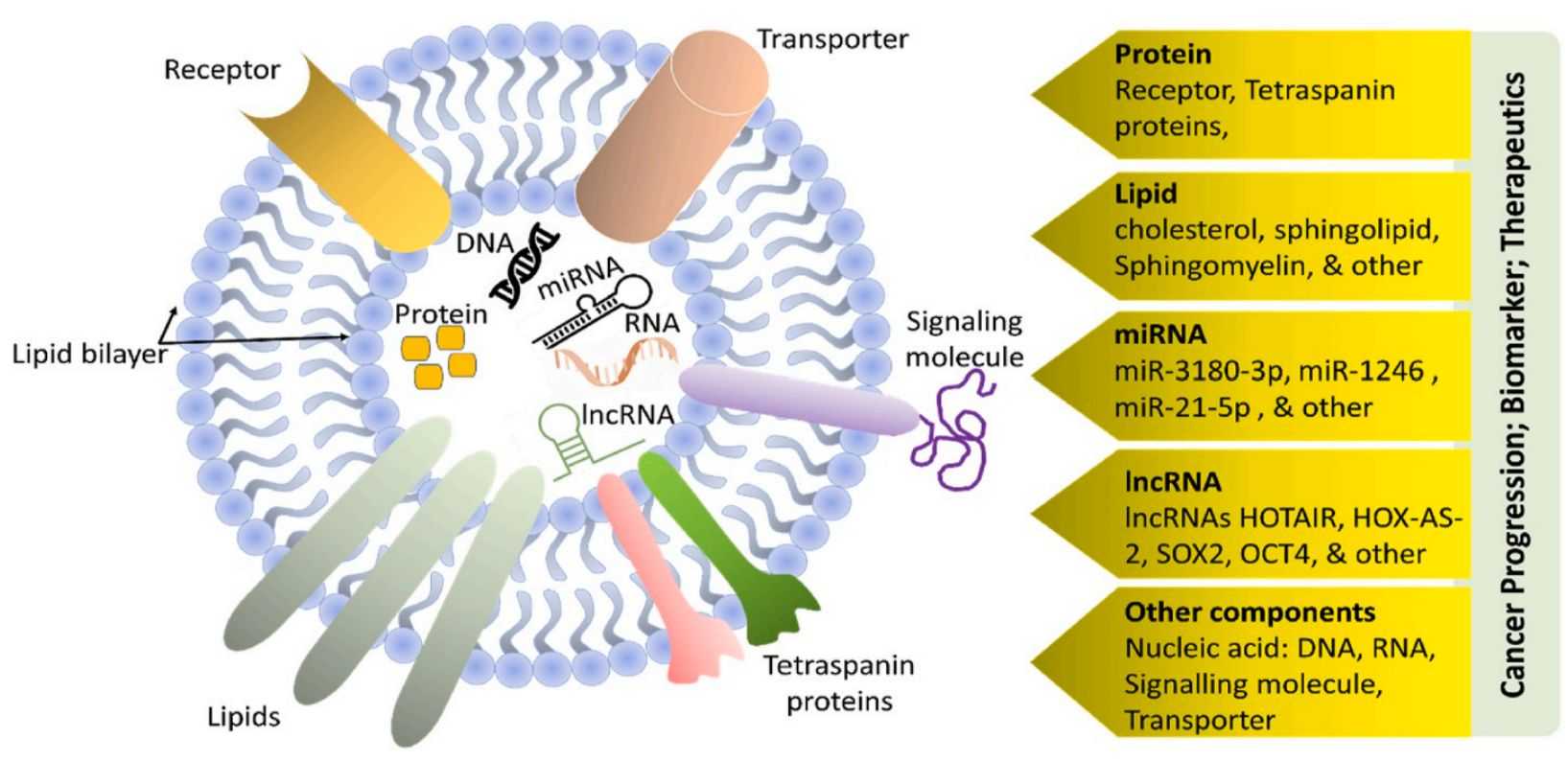
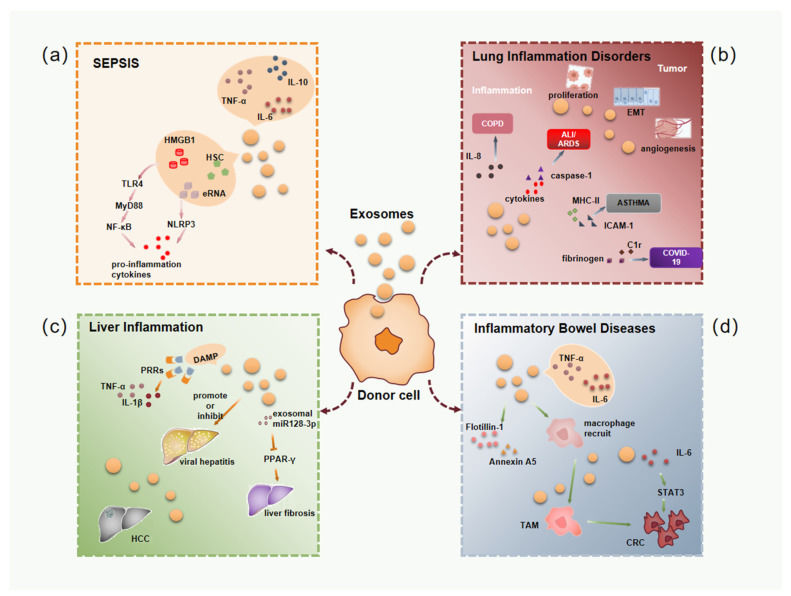 Figure 1. Exosomes in inflammatory diseases and tumor-related inflammation. (a) Sepsis. (b) Pulmonary diseases. (c) Liver conditions. (d) Intestinal inflammation. (Tian Y, et al., 2022)
Figure 1. Exosomes in inflammatory diseases and tumor-related inflammation. (a) Sepsis. (b) Pulmonary diseases. (c) Liver conditions. (d) Intestinal inflammation. (Tian Y, et al., 2022)
Our Exosome Immunomodulation and Inflammation Service Portfolio
We provide a focused suite of assays to dissect the precise immunomodulatory function of your exosome preparations.
Macrophage Polarization and Function Assays
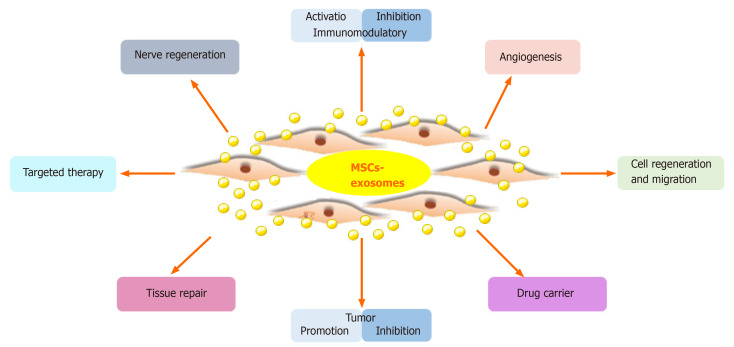
Macrophages are highly plastic and central to the inflammatory response. We assess the ability of your exosomes to polarize M0 macrophages toward either a pro-inflammatory (M1) or an anti-inflammatory/pro-resolving (M2) phenotype. This is a critical assay for researchers targeting macrophage immunomodulation by exosomes.
- Key Readouts:
- Phenotypic Analysis (Flow Cytometry): Quantification of M1 surface markers (e.g., CD80, CD86) and M2 markers (e.g., CD206, CD163).
- Gene Expression (RT-qPCR): Measurement of M1-related genes (e.g., TNF-α, iNOS) and M2-related genes (e.g., Arg1, IL-10).
- Functional Analysis: Phagocytosis assays to determine the functional capacity of polarized macrophages.
T-Cell Activation and Proliferation Assays
We evaluate the direct impact of your exosomes on T-cell function, a cornerstone of the adaptive immune response.
- Key Readouts:
- Proliferation Assays (e.g., CFSE): We measure the rate of T-cell division in response to exosome treatment.
- Activation Markers (Flow Cytometry): Quantification of early (e.g., CD69) and late (e.g., CD25) activation markers on CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell subsets.
- Exhaustion Markers: Analysis of PD-1, TIM-3, and Lag-3 expression for oncology or chronic inflammation models.
Cytokine Release Assays (Inflammation Panel)
This service provides a broad or focused snapshot of the soluble factors secreted by immune cells (like PBMCs or macrophages) after exosome stimulation. We can detect and quantify dozens of cytokines, chemokines, and growth factors simultaneously.
- Key Applications:
- Detecting pro-inflammatory exosomes inflammation profiles (e.g., IL-6, TNF-α, IL-1β).
- Identifying anti-inflammatory or regenerative profiles (e.g., IL-10, TGF-β).
- Screening for potential "cytokine storm" risks in therapeutic candidates.
- Technology: Multiplex platforms (e.g., Luminex) or targeted ELISA.
Neutrophil Function Assays
Beyond macrophages, we offer specialized assays for neutrophils. We can measure the ability of your exosomes to induce or inhibit the formation of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps (NETs), a critical process in acute inflammation and autoimmune disease.
- Key Readouts: Quantification of extracellular DNA (e.g., Sytox Green) or specific NET-associated proteins (e.g., Citrullinated Histone H3) via fluorescence microscopy or plate-based assays.
Advanced iPSC-Derived Immune Cell Models
For highly relevant, patient-specific data, we support human ipsc exosome in vitro study. We can differentiate iPSCs into various immune cell types, providing a renewable and physiologically relevant alternative to primary cells.
- Available Models:
- iPSC-derived Macrophages (iPSC-M)
- iPSC-derived Microglia (iPSC-MG)
- iPSC-derived T-Cells
Preclinical Research Support (In Vivo Next Steps)
To validate the immunomodulatory effects observed in your in vitro assays, the next crucial step is demonstrating functional efficacy in preclinical animal models. Confirm whether your exosomes can effectively reduce inflammation (e.g., lower pro-inflammatory cytokines in sepsis models) or modulate immune cell responses (e.g., alter macrophage polarization in inflamed tissues) in vivo.
For detailed in vivo study designs, models, and functional readouts, please see our dedicated In Vivo Exosome Functional Assays.
Our End-to-End Project Workflow
We manage every step of your project, from initial design to final data interpretation, ensuring a transparent and collaborative process.
Key Service Steps
Our standard workflow includes the following key steps, ensuring robust and reproducible data:
Advanced Cell Model Selection
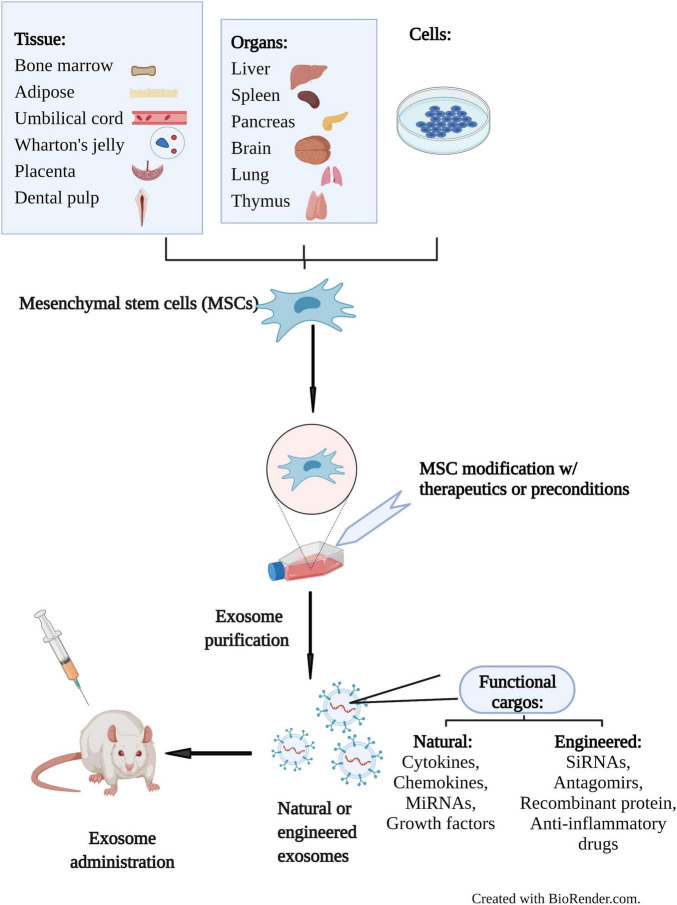
This is a critical step. Our experts consult with you to select the right model, whether it's primary human monocytes, BMDMs, or advanced human iPSC exosome in vitro study models.
Multi-Parametric Assay Execution
We don't just look at one marker. We combine key readouts, such as co-culturing your exosomes and then analyzing macrophage M1/M2 markers by flow cytometry while simultaneously quantifying the cytokine profile from the supernatant via Luminex.
In-Depth Data Interpretation
A final report isn't just a data table. We provide a full scientific interpretation, connecting the phenotypic (flow) data with the functional (cytokine) data to give you a complete picture of your exosome's immunomodulatory profile.
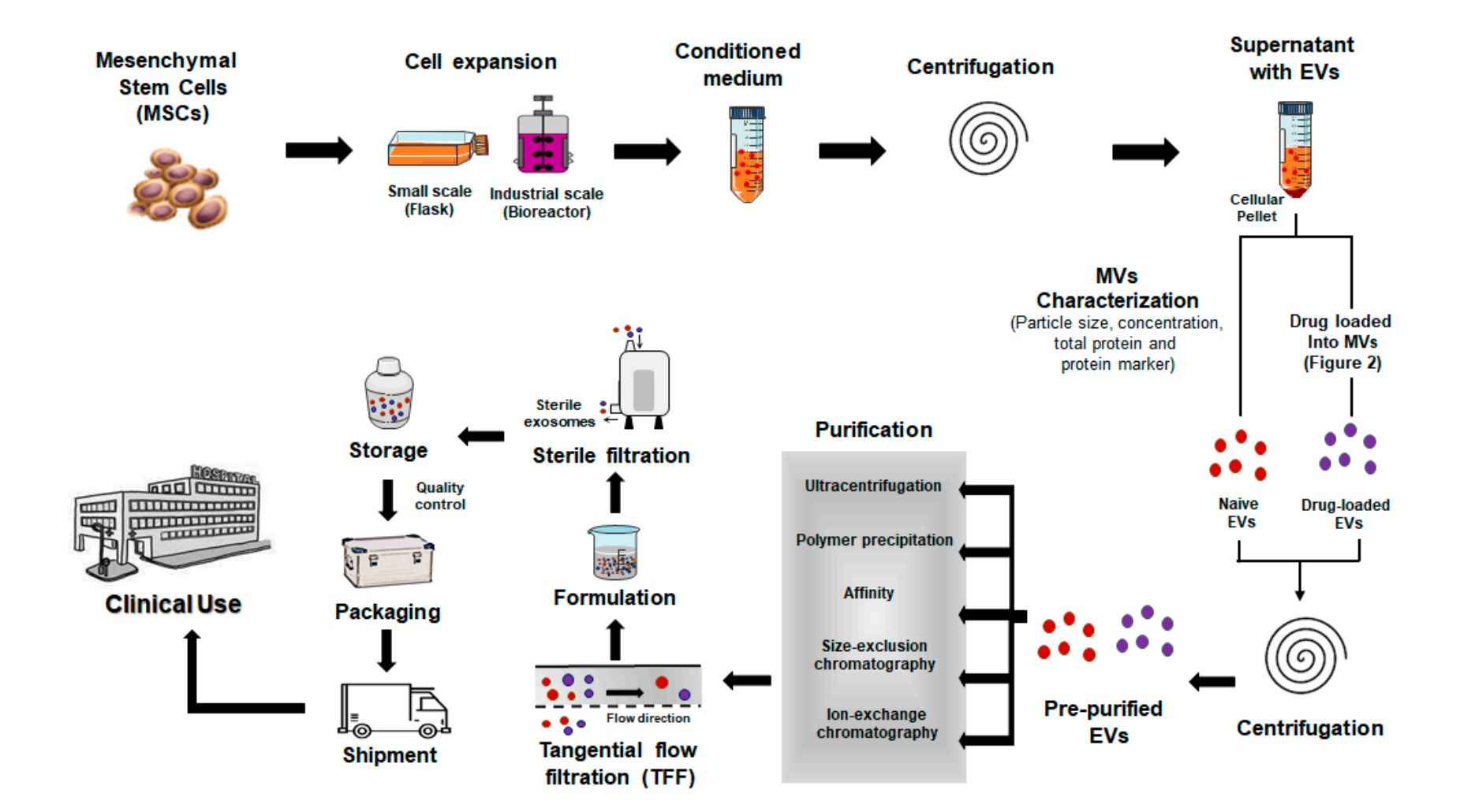
Project Workflow
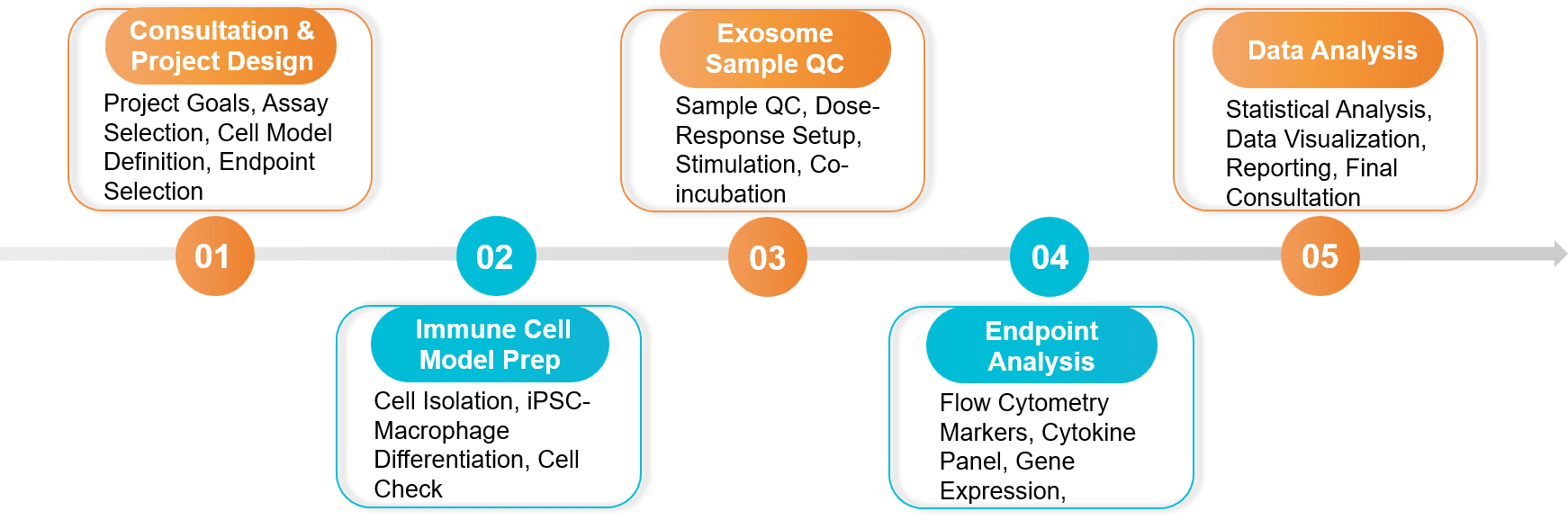 Figure 2. Immunomodulation and Inflammation Assay Project Workflow. (Creative Biostructure)
Figure 2. Immunomodulation and Inflammation Assay Project Workflow. (Creative Biostructure)
Sample Requirements
- Client-Provided Exosomes:
- Quantity: ≥ 1x10¹⁰ particles (assay-dependent, please inquire).
- Purity: Purified exosomes (e.g., by SEC, UC) are required. We strongly recommend providing characterization data (NTA, WB).
- Buffer: Suspended in sterile PBS or a compatible culture-grade buffer.
- Test Articles: If testing small molecule inhibitors or other controls, please provide concentration and solvent details.
Standard Deliverables
- A comprehensive project report detailing the experimental design, protocols, and results.
- Raw and analyzed data (e.g., flow cytometry .fcs files, Luminex multiplex data, qPCR Cq values).
- Publication-ready figures (e.g., histograms, bar graphs, heatmaps).
- A final consultation call to discuss the data and future steps.
Case Study
Case: Exosomes from Breast Cancer Cells Drive Pro-Tumor Macrophage Polarization
Background: Researchers investigated how breast cancer derived exosomes influence the tumor microenvironment. A key hypothesis was that these exosomes could "educate" macrophages, converting them into a pro-tumor (M2) phenotype, which aids in tumor progression and metastasis.
Methodology: To test this in vitro, researchers isolated exosomes from triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cell lines. These exosomes were co-cultured with M0-type macrophages.
Key Findings:
- Phenotypic Change: The in vitro assay demonstrated that TNBC-derived exosomes successfully induced macrophage polarization.
- M2-Marker Upregulation: Using flow cytometry and histological analysis, the researchers confirmed that the "educated" macrophages showed significantly increased expression of CD206, a classic M2-type marker.
- Functional Consequence: This M2 polarization created favorable conditions for tumor cell migration and lymph node metastasis.
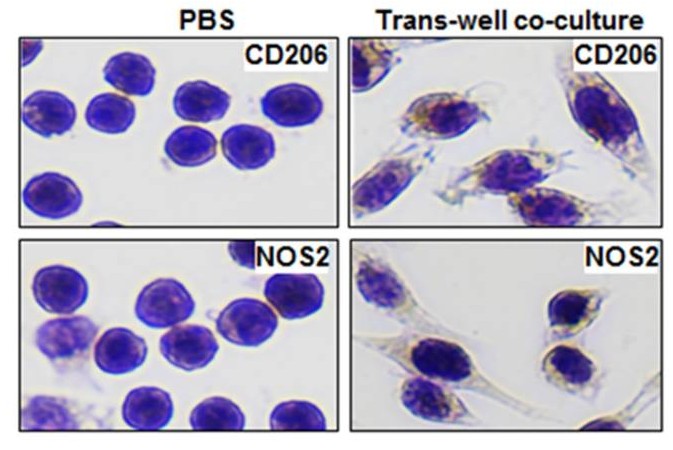 Figure 3. CD206 and NOS2 staining in RAW264.7 cells after 24 h co-culture with MDA-MB-231/CD63-RFP cell-derived exosomes, indicating M2 polarization. (Piao YJ, et al., 2017)
Figure 3. CD206 and NOS2 staining in RAW264.7 cells after 24 h co-culture with MDA-MB-231/CD63-RFP cell-derived exosomes, indicating M2 polarization. (Piao YJ, et al., 2017)
Conclusion: This study used an in vitro macrophage polarization assay to provide direct evidence that breast cancer-derived exosomes induce a pro-tumor M2 phenotype, identified by the CD206 marker.
Ready to quantify how your exosomes shape immune responses? Our team will design the right macrophage, T-cell, cytokine, and neutrophil assays and deliver clear, quantitative readouts. Contact us for a free consultation and an assay plan tailored to your model and goals.
References
- Piao YJ, Kim HS, Hwang EH, et al. Breast cancer cell-derived exosomes and macrophage polarization are associated with lymph node metastasis. Oncotarget. 2017 Dec 13;9(7):7398-7410.
- Tian Y, Cheng C, Wei Y, et al. The Role of Exosomes in Inflammatory Diseases and Tumor-Related Inflammation. Cells. 2022 Mar 16;11(6):1005.
Frequently Asked Questions
For any inquiries, our support team is ready to help you get technical support for your research and maximize your experience with Creative Biostructure.