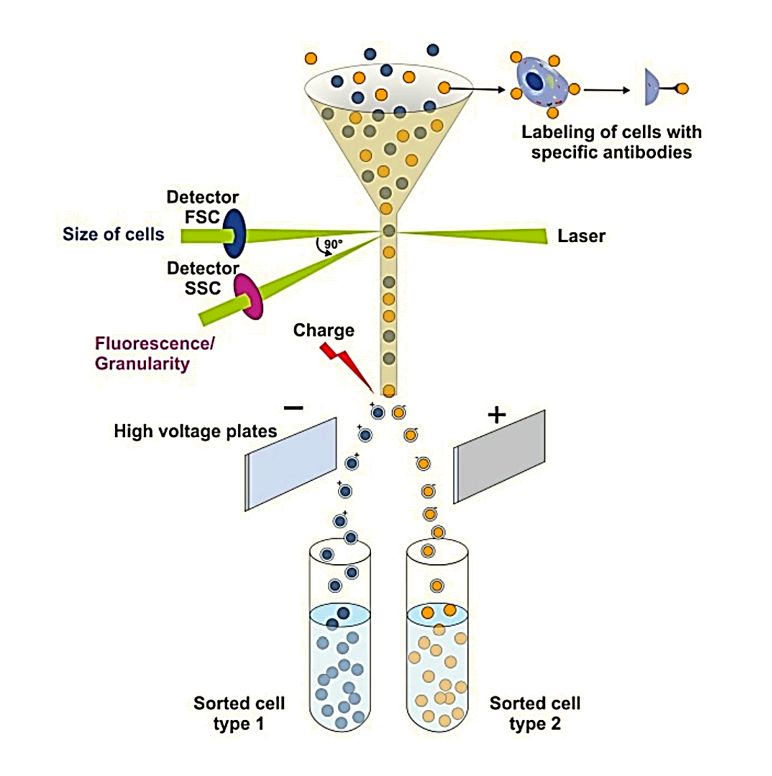
Exosome Identification Services
Exosome preparations are heterogeneous and often contain co-isolates, so reliable identification requires a multi-platform evidence chain. At Creative Biostructure, we follow MISEV2023 end to end, linking morphology, size distribution, positive and negative markers, and purity checks to deliver robust, publication-ready and submission-ready results with full method transparency. Whether your goal is biomarker discovery, functional studies, or quality control of exosome therapeutics, our cross-validated workflow provides data you can trust.
Why Exosome Identification Matters
Accurate exosome identification prevents data bias from co-isolated particles and is the first checkpoint for credible extracellular vesicle (EV) research. It validates downstream readouts in biomarker discovery, functional assays, and exosome-based drug delivery quality control. Exosome identity is confirmed by converging evidence: morphology (TEM or cryo-EM), size distribution (NTA, TRPS, or NanoFCM), positive markers such as CD9, CD63, and CD81, negative markers such as Calnexin or GM130, and matrix-aware purity assessment. Cross-platform verification reduces false positives and increases reproducibility, enabling peer review, meta-analysis, and regulatory acceptance. In short, identification answers "Is it an exosome?" and protects every subsequent decision in your study design.
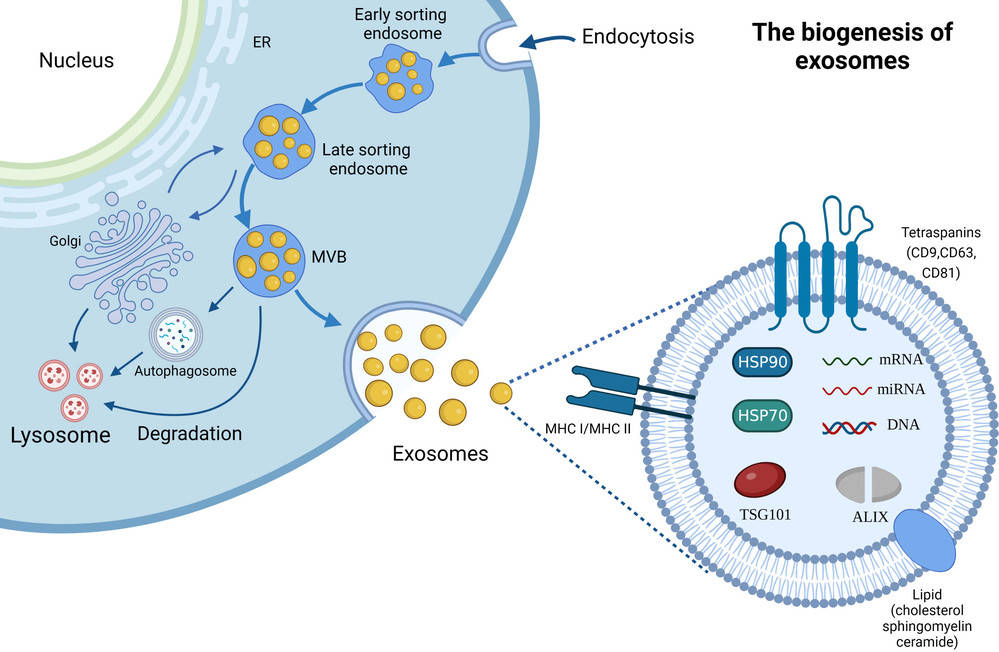
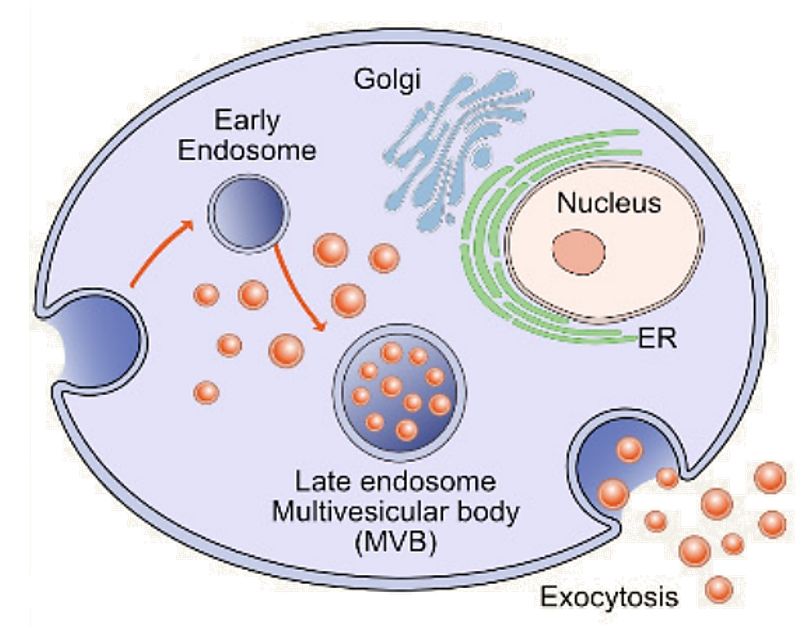
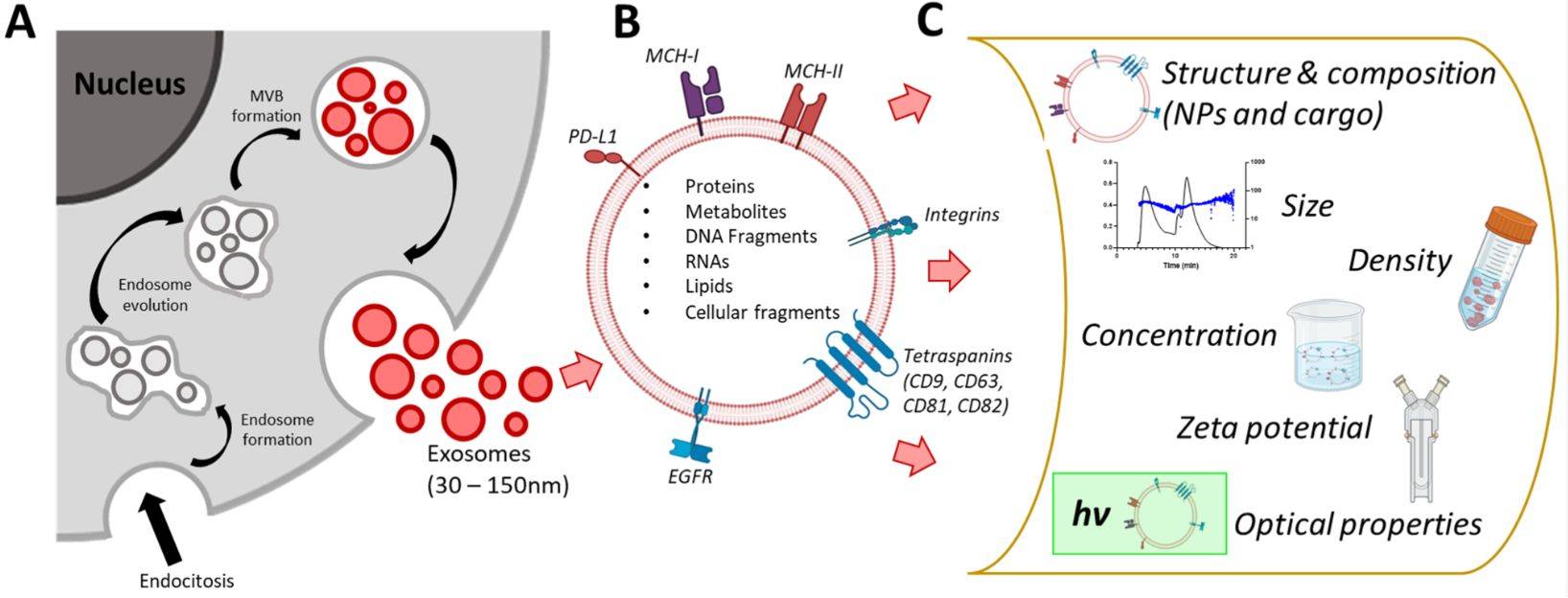
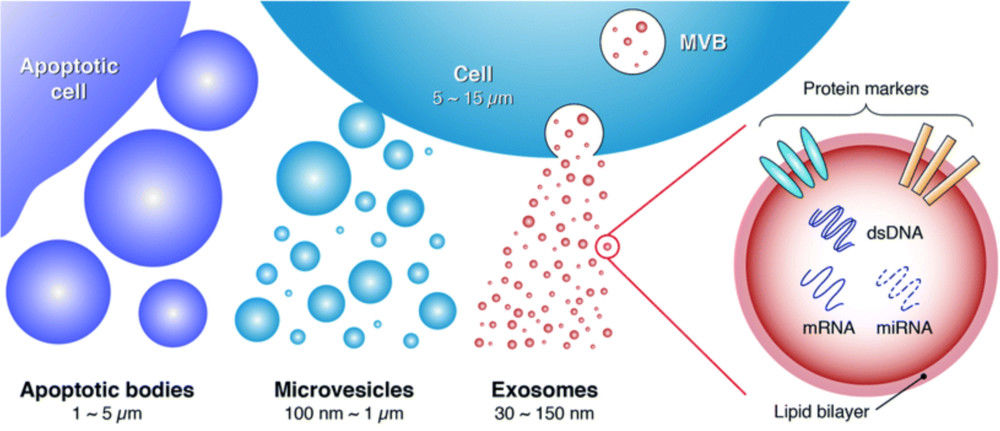 Figure 1. Biogenesis, Size, and Signaling Roles of Exosomes. (Contreras-Naranjo J C, et al., 2017)
Figure 1. Biogenesis, Size, and Signaling Roles of Exosomes. (Contreras-Naranjo J C, et al., 2017)
Our MISEV-Compliant Exosome Identification Services
Robust exosome identification cannot be achieved with a single technique. Our workflow integrates orthogonal, state-of-the-art methods to build an undeniable case for the identity and purity of your sample, providing you with the highest degree of confidence.
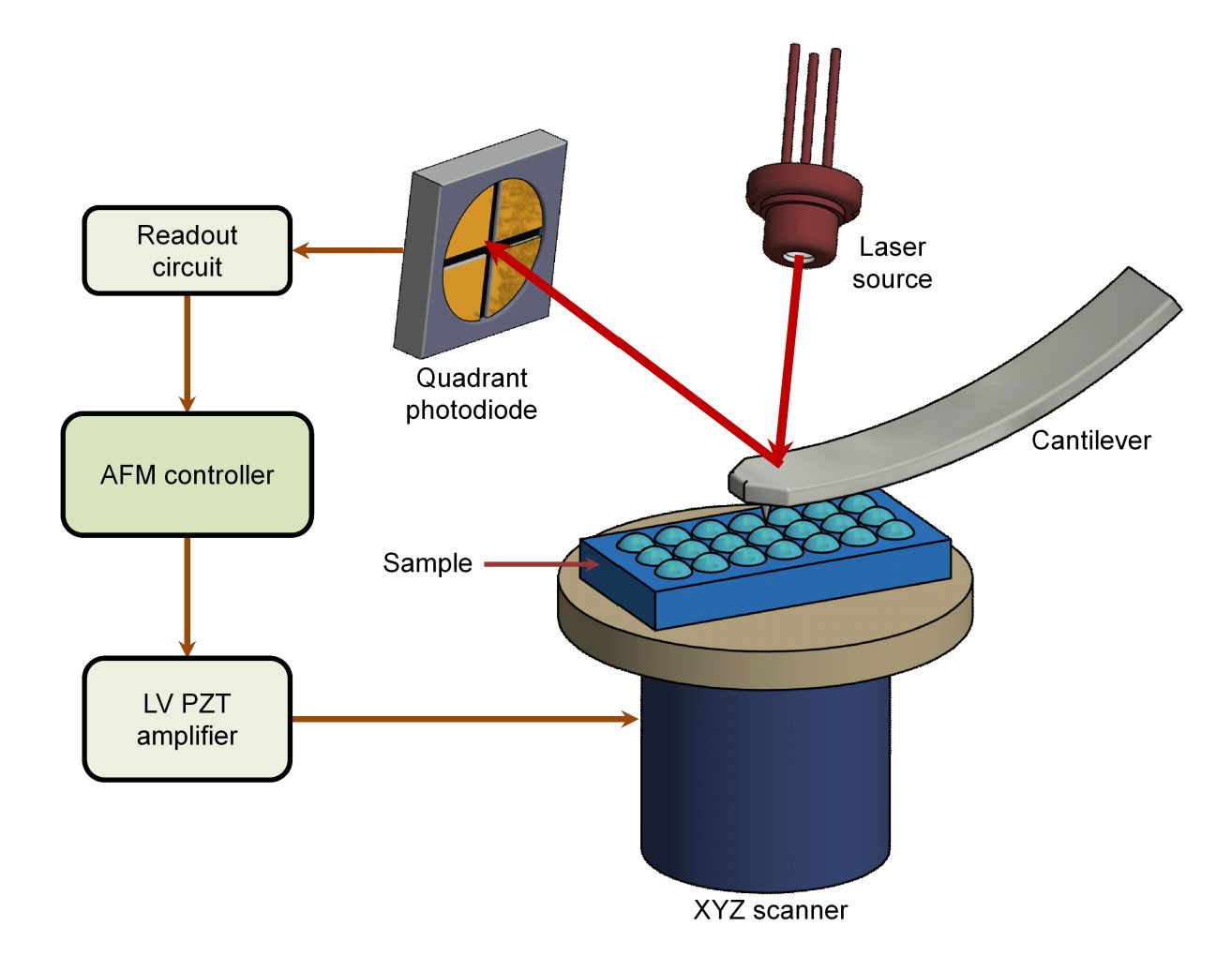
Visualizing Exosome Morphology and Structure
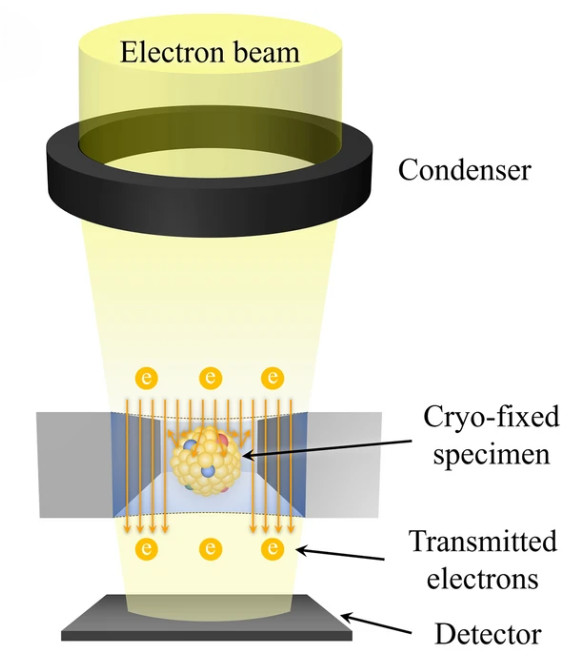
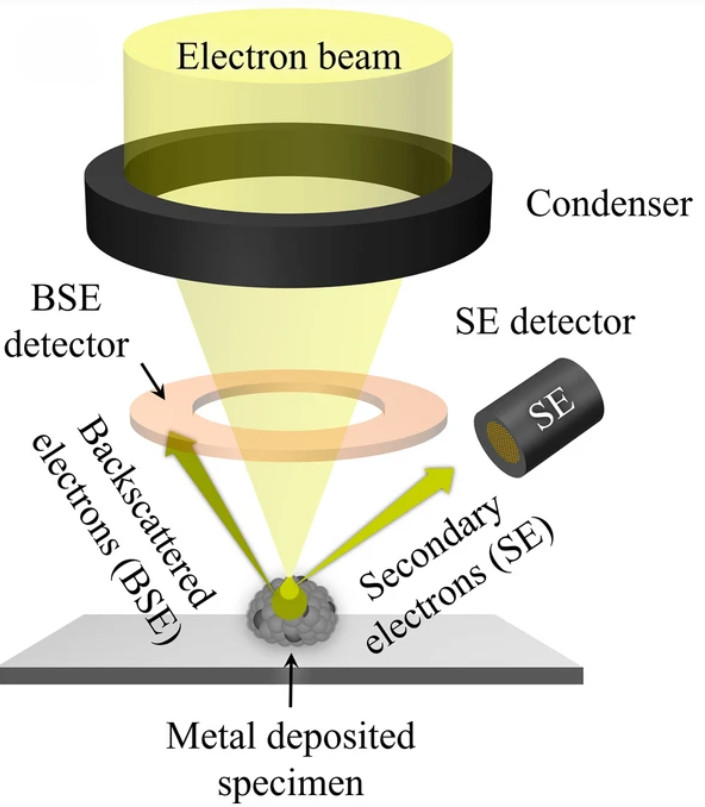
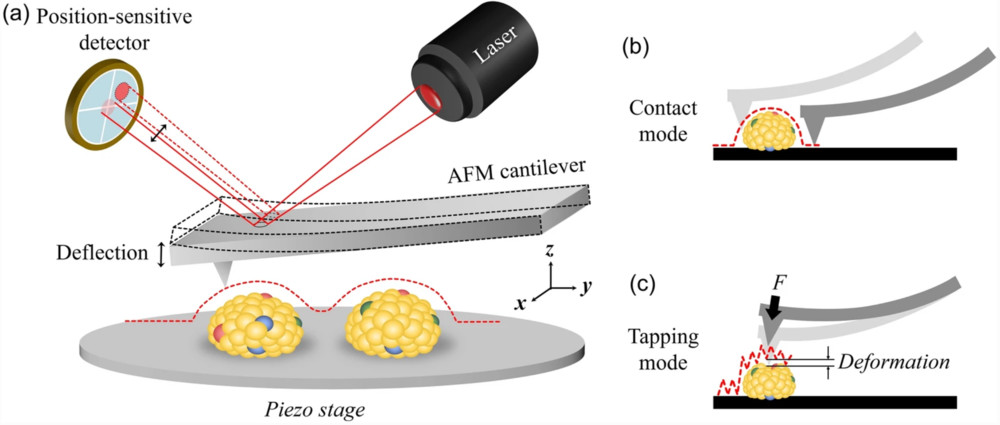
The first pillar of evidence is direct visualization. We employ high-resolution imaging to confirm the presence of intact, membrane-enclosed vesicles and assess the overall purity of the preparation.
| Method | Primary Purpose | Deliverables |
|---|---|---|
| TEM | Visualize lipid bilayer and confirm vesicle integrity | Annotated micrographs with scale bars, artifact notes, image acquisition parameters |
| Cryo-EM | Visualize native bilayer without fixation or staining | |
| AFM | Map surface topography and height distribution | |
| Super-Resolution Microscopy (STED/STORM) | Assess nanoscale protein clustering on vesicles |
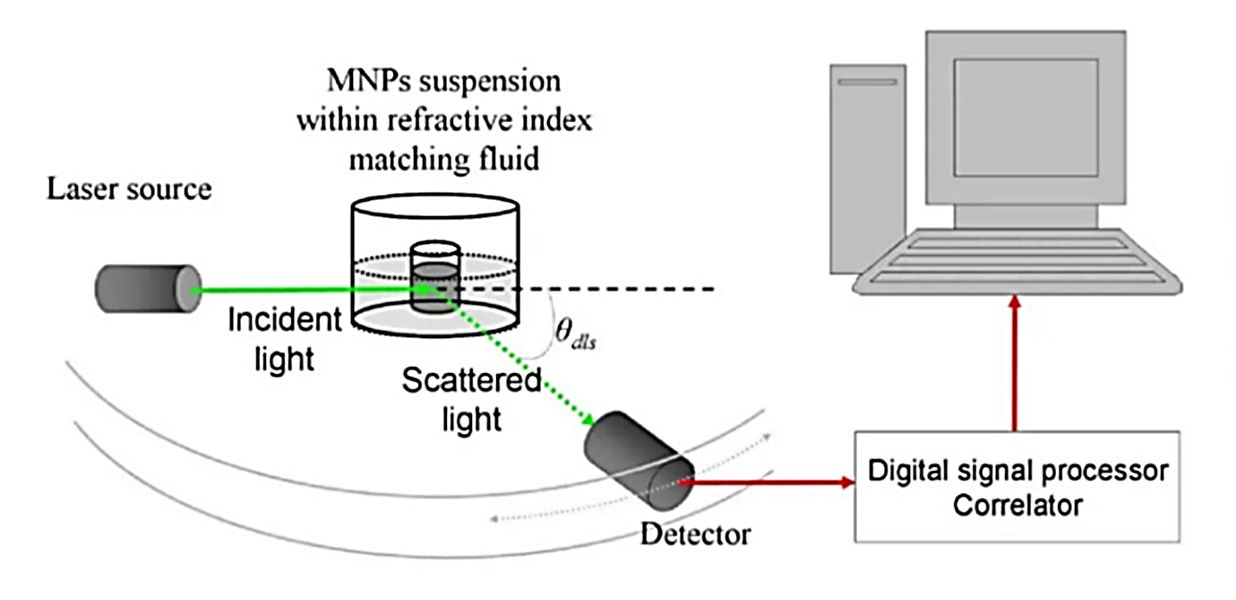
Exosome Particle Size and Distribution Analysis
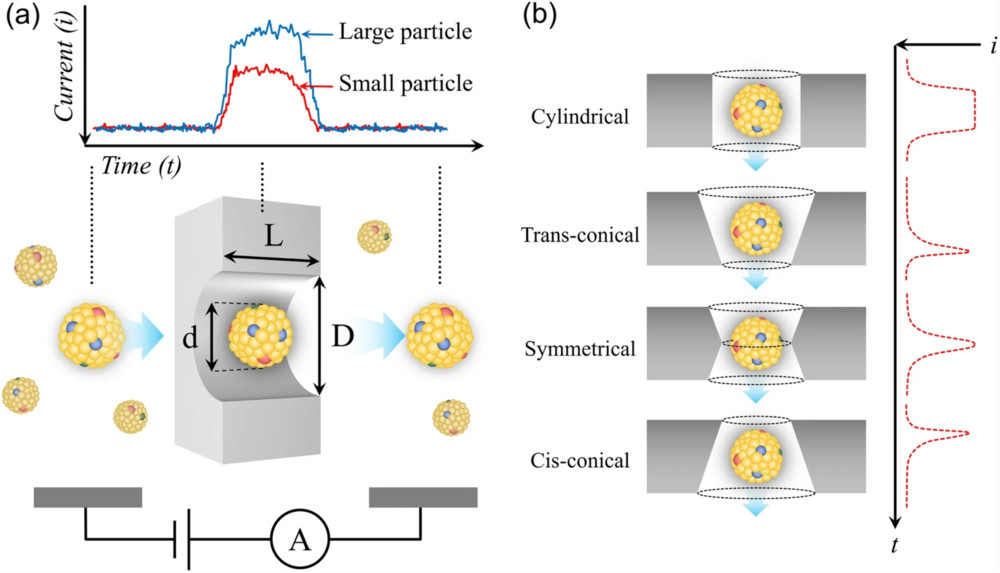
The second pillar is confirming that the particle population fits the established biophysical profile of exosomes. We analyze your sample to ensure the size distribution is within the expected range.
| Platform | Measurement Principle | Typical Outputs |
|---|---|---|
| NTA | Tracks Brownian motion of individual particles under light scattering | Size distribution plot, mode/median size, concentration estimate |
| TRPS | Resistive pulse sensing through a tunable nanopore | Size histogram, particle rate, concentration |
| NanoFCM | Flow cytometry adapted for nanoscale particles with reference beads | Size distribution, particle count, fluorescence intensity plots |
| ExoView | Antibody-based immunocapture with per-particle interferometric sizing | Per-particle size map, marker positivity rates, distribution metrics |
This analysis confirms the characteristic size profile for identification. For precise yield measurement and comparative studies, please see our Exosome Quantification Services.
Exosome Marker Profiling for Identity and Purity
The final and most critical pillar is biochemical verification. We provide definitive evidence of exosome identity by confirming the enrichment of canonical exosomal proteins and, just as importantly, the absence of contaminants from other cellular compartments.
- Positive markers (typical): CD9, CD63, CD81; cytosolic EV markers such as TSG101/ALIX as applicable
- Negative markers / co-isolates: Calnexin (ER), GM130 (Golgi), ApoA1/Albumin (biofluids), actin/tubulin context-dependent
| Assay | Primary purpose | Deliverables |
|---|---|---|
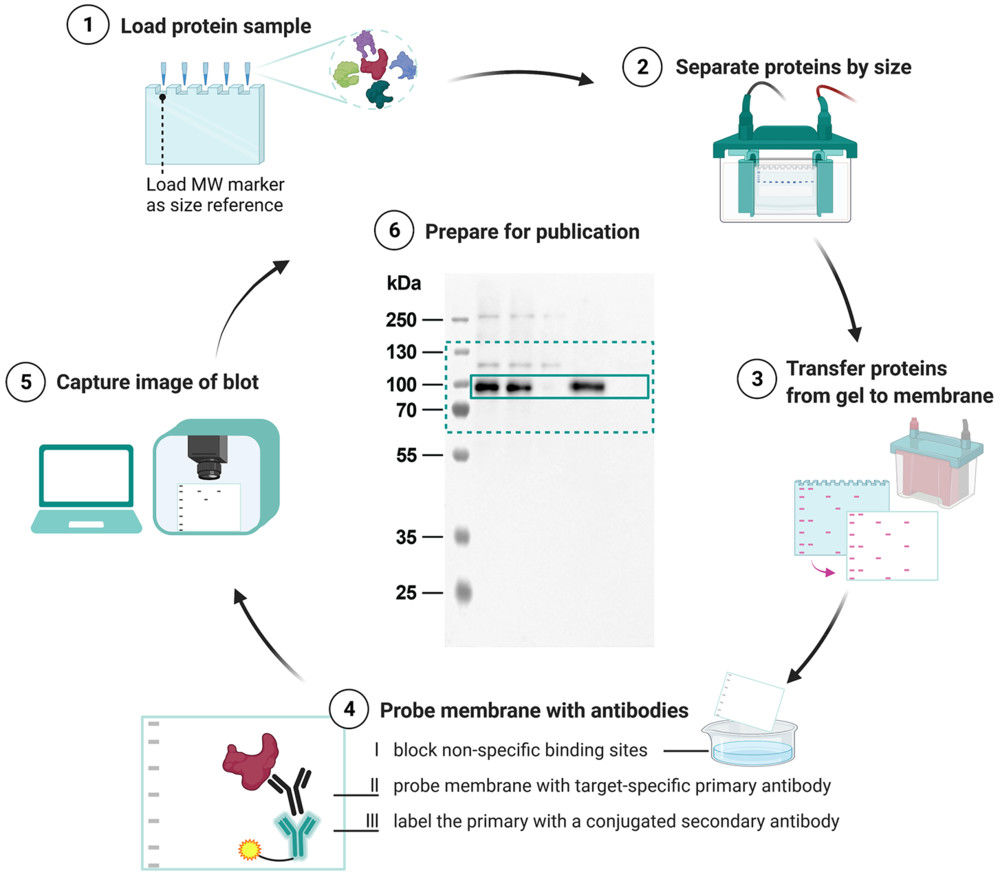
| Western blot | Confirm positive and negative exosome markers | Gel and blot images, marker call for CD9 CD63 CD81 and negatives such as Calnexin, threshold criteria |
| Exosome ELISA | Higher throughput marker screening | Quantitative absorbance values, positivity calls, cutoff definitions |
| Flow cytometry or NanoFCM | Immunophenotyping at single particle or vesicle level | Gating plots, fluorescence intensity distributions, marker positivity rates |
| ExoView | Immunocapture profiling at single particle level | ExoView chip maps, per particle size and marker positivity, distribution metrics |
| LC-MS/MS marker panels | Discovery and verification of protein markers | Identified proteins with confidence scores, quantitative tables, verification summary |
Flexible Service Options Tailored to Your Research Needs
Choose from our curated packages or request individual analyses to meet your specific project goals.
| Feature | Basic Identification (MISEV Essentials) | Advanced Characterization (Publication Grade) | Comprehensive Profiling (Deep Discovery) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Morphology (TEM) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Size Distribution (NTA) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Positive Marker Western Blot (≥3) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Negative Marker Western Blot | ✅ | ✅ | |
| High-Resolution Flow Cytometry | ✅ | ✅ |
Modular Services, such as Western Blot or TEM analysis only, are also available. Contact us to design a custom project.
Standard Workflow & Timelines
- Consultation & study design (matrix, intended use, journals/regulators)
- Isolation (optional) or verification of client-isolated EVs
- Identification panel execution (modules above)
- Cross-validation & QC review (replicates, controls, acceptance criteria)
- Reporting & expert consult (interpretation vs. MISEV2023; raw data access)
Typical timelines: Module-dependent; expedited options available with transparent scheduling.
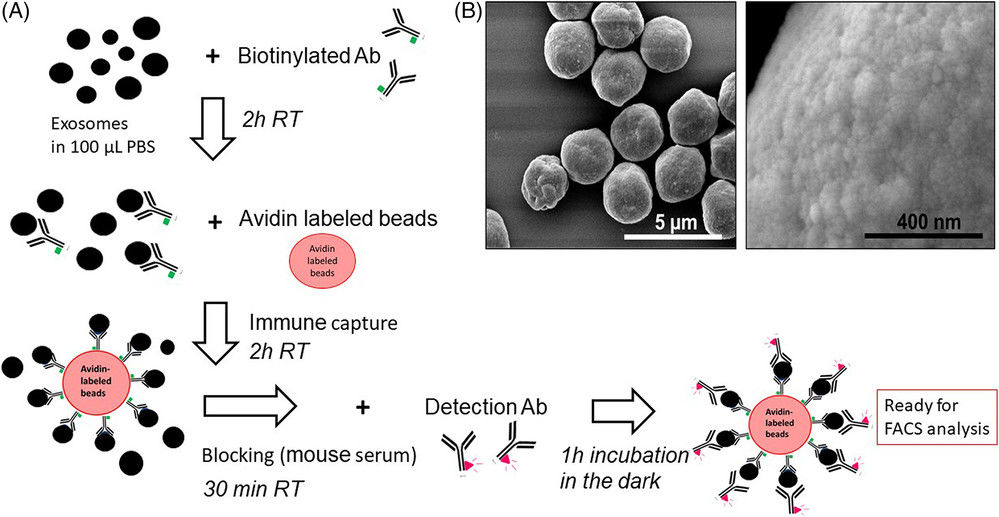
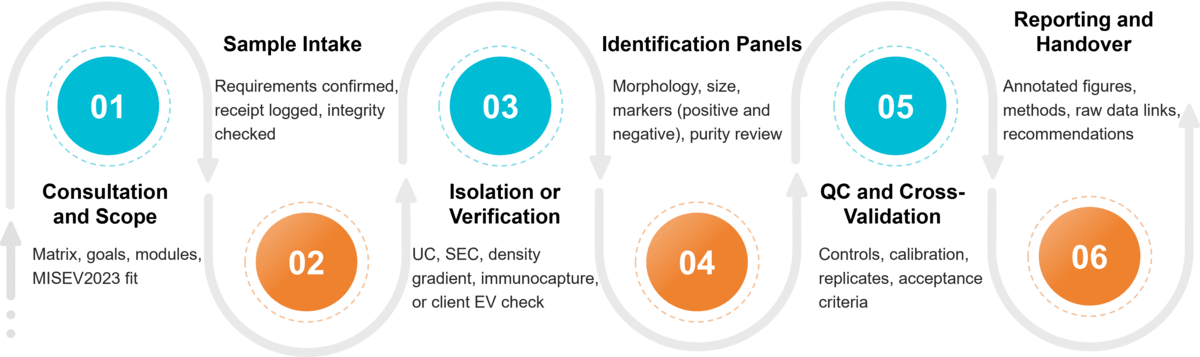 Figure 2. Project Workflow for Exosome Identification. (Creative Biostructure)
Figure 2. Project Workflow for Exosome Identification. (Creative Biostructure)
Sample Requirements
Please prepare samples according to these guidelines to ensure optimal results. If you need to purify exosomes from a raw sample, please inquire about our exosome isolation services.
| Sample Type | Recommended Volume | Preparation & Storage |
|---|---|---|
| Purified Exosomes | > 100 µL (> 50 µg protein) | In filtered PBS; Store at -80°C; Ship on dry ice. |
| Cell Culture Supernatant | > 30 mL | Pre-cleared of cells/debris; Store at -80°C. |
| Biological Fluids | > 2 mL | Use appropriate collection tubes (e.g., EDTA for plasma); Store at -80°C. |
Reporting & Deliverables (Publication-Ready)
- Annotated micrographs, size distribution plots, WB/ELISA/Flow/NanoFCM/ExoView outputs
- Positive/negative marker call with thresholds and rationale
- Purity/co-isolate assessment and mitigation recommendations
- Method parameters (sample handling, instrument settings, controls, statistics)
- Raw data files and journal-style figure panels on request
- Optional COA-style summary for product lots or regulatory packages
Supporting a Broad Spectrum of Exosome Research
Our services provide the foundational data required for a wide range of applications:
- Biomarker Discovery
- Functional Biology Assays
- Therapeutic Carrier Development
- Quality Control for Exosome-based Products
- Mechanism of Action Studies
Why Choose Creative Biostructure
- Unyielding Scientific Rigor: Our strict adherence to MISEV2023 guidelines ensures your results withstand the scrutiny of peer review and regulatory bodies.
- True Orthogonal Validation: We integrate data from morphology, biophysics, and biochemistry to provide a holistic and unambiguous characterization of your samples.
- Expert-Led Analysis: Your project is managed by Ph.D.-level scientists with deep experience in EV research. We don't just provide data; we deliver actionable insights.
- State-of-the-Art Technology: Our facility is equipped with advanced instrumentation, including high-resolution electron microscopes and Orbitrap mass spectrometers, for maximum sensitivity and accuracy.
- Transparent Reporting: SOP library, data integrity policy, privacy & security controls; GLP-like documentation available on request.
Case Study
Case: OSCC Exosomal lncRNA Profiling Emphasizes Identification First
Background
Exosomes from CAL-27 OSCC cells vs. primary oral epithelial controls were profiled to discover lncRNA biomarkers. Identity confirmation preceded cargo analysis to avoid co-isolate bias.
Methods
- Identification: TEM confirmed intact vesicles; EV markers (e.g., ALIX, TSG101) enriched; negative markers absent/reduced.
- Cargo profiling: Sequencing followed by RT-qPCR validation with stringent stats (e.g., P < 0.001).
Results
- Multiple lncRNAs showed strong differential expression in CAL-27 exosomes (order-of-magnitude upregulation for top candidates).
- RT-qPCR validated sequencing trends with high significance (P < 0.001), supporting robustness of signals.
Conclusion
Rigorous identification (morphology + markers) enabled credible lncRNA readouts. The case underscores why exosome identity must be verified before omics analysis to ensure reproducibility and translational value.
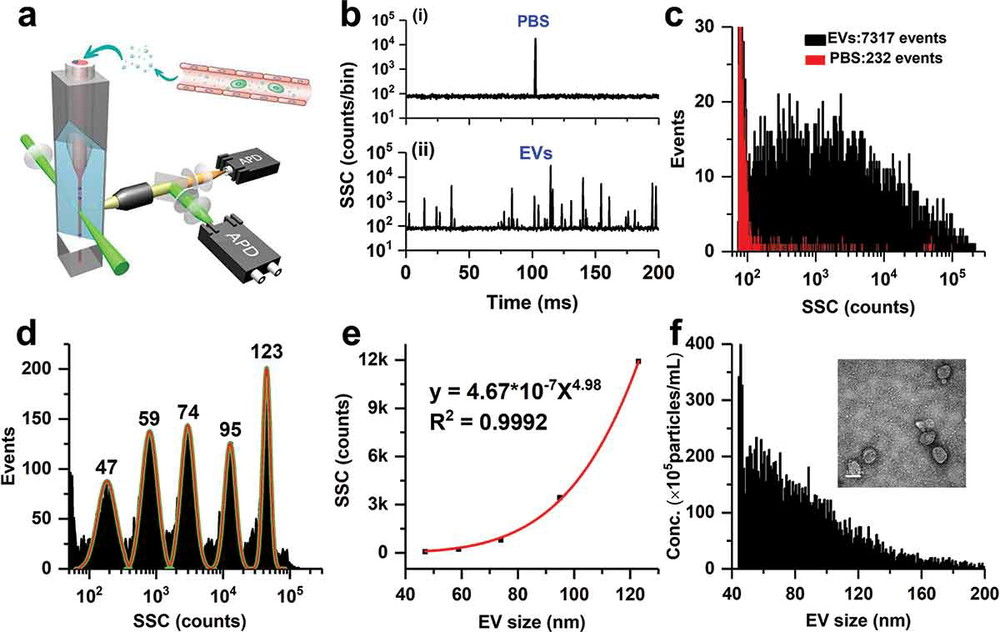
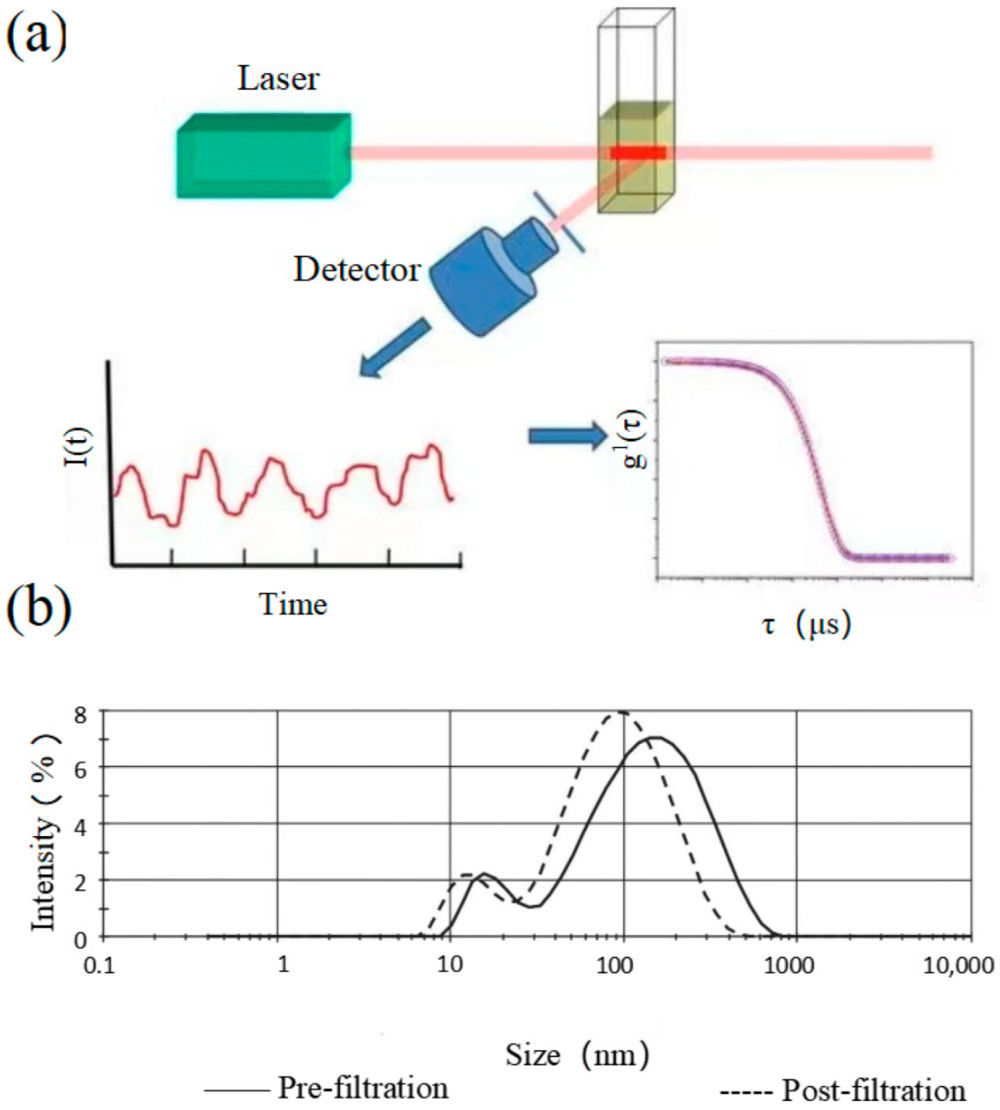
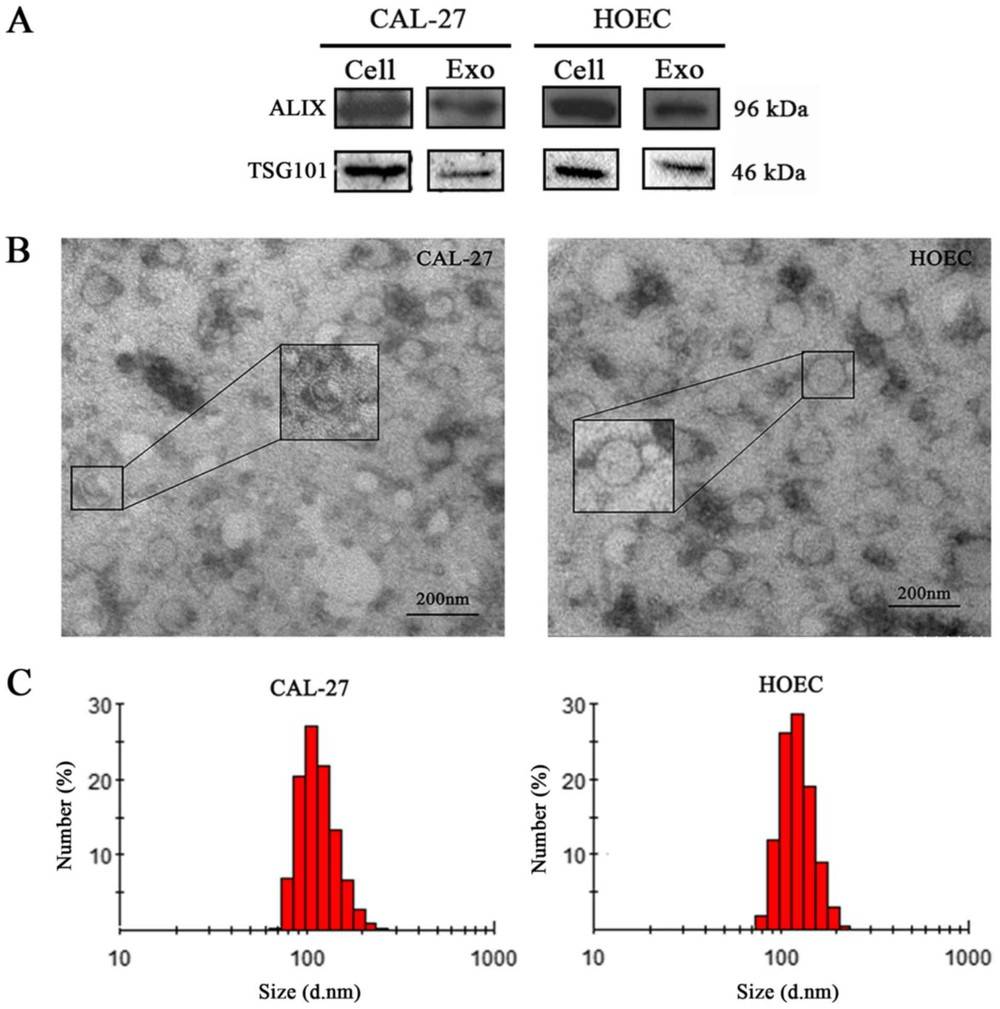 Figure 3. Exosome Identification by WB, TEM, and Zetasizer. (Jin J, et al., 2020)
Figure 3. Exosome Identification by WB, TEM, and Zetasizer. (Jin J, et al., 2020)
Ready to confirm exosome identity with confidence? Our MISEV2023 aligned workflow links morphology, size distribution, positive and negative markers, and purity assessment into a clear evidence chain. At Creative Biostructure, we tailor modules to your matrix and study goals and deliver publication ready reports with full method transparency. Contact us to design your panel and get a fast, accurate quotation.
References
- Contreras-Naranjo J C, Wu H J, Ugaz V M. Microfluidics for exosome isolation and analysis: enabling liquid biopsy for personalized medicine. Lab on a Chip. 2017, 17(21): 3558-3577.
- Jin J, Huang Z, Lu X, et al. Bioinformatics analysis of aberrantly expressed exosomal lncRNAs in oral squamous cell carcinoma (CAL-27 vs. oral epithelial) cells. Oncology Letters. 2020, 20(3): 2378-2386.
- Welsh J A, Goberdhan D C I, O'Driscoll L, et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles (MISEV2023): From basic to advanced approaches. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles. 2024, 13(2): e12404.
Frequently Asked Questions
For any inquiries, our support team is ready to help you get technical support for your research and maximize your experience with Creative Biostructure.