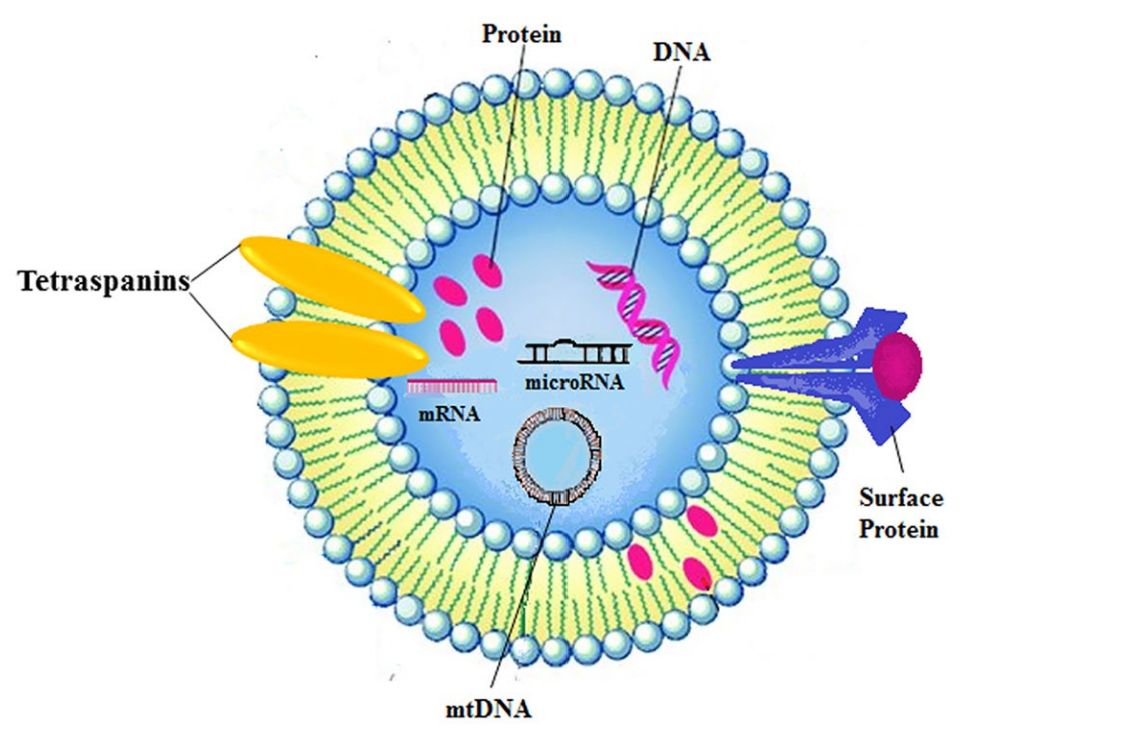
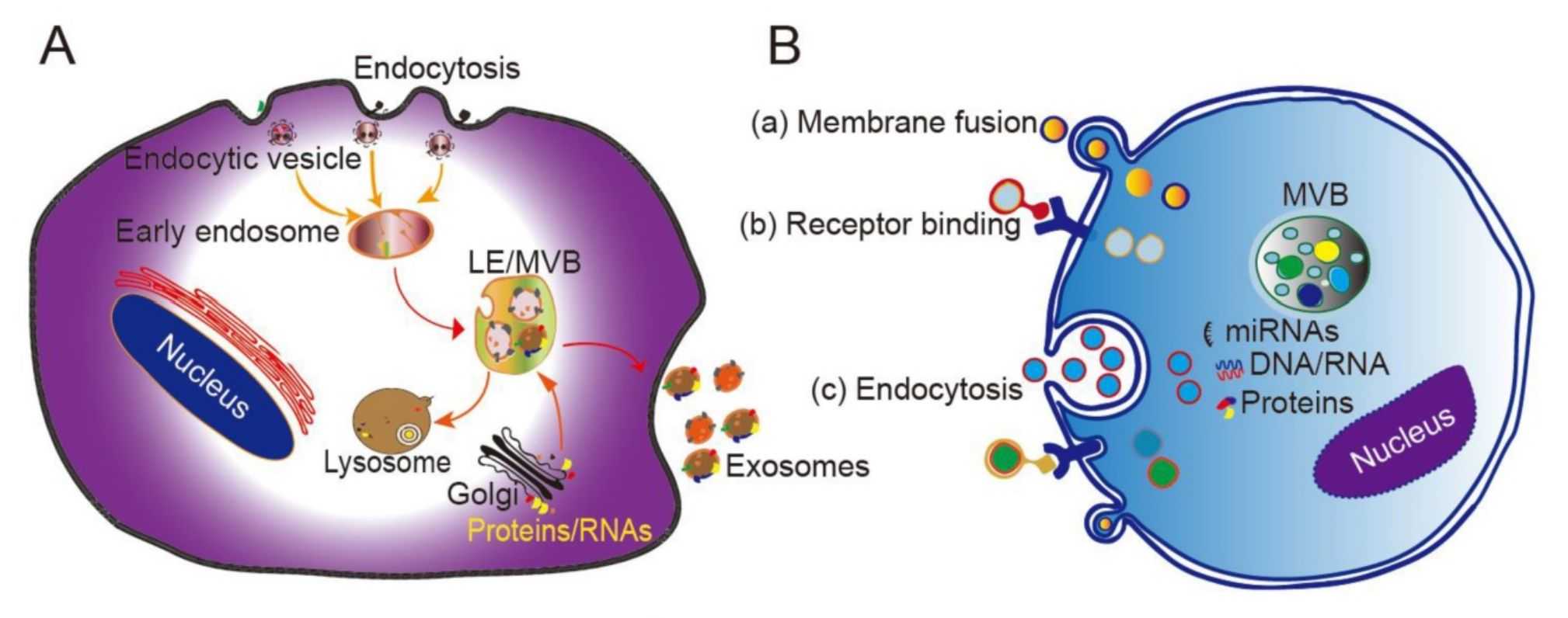
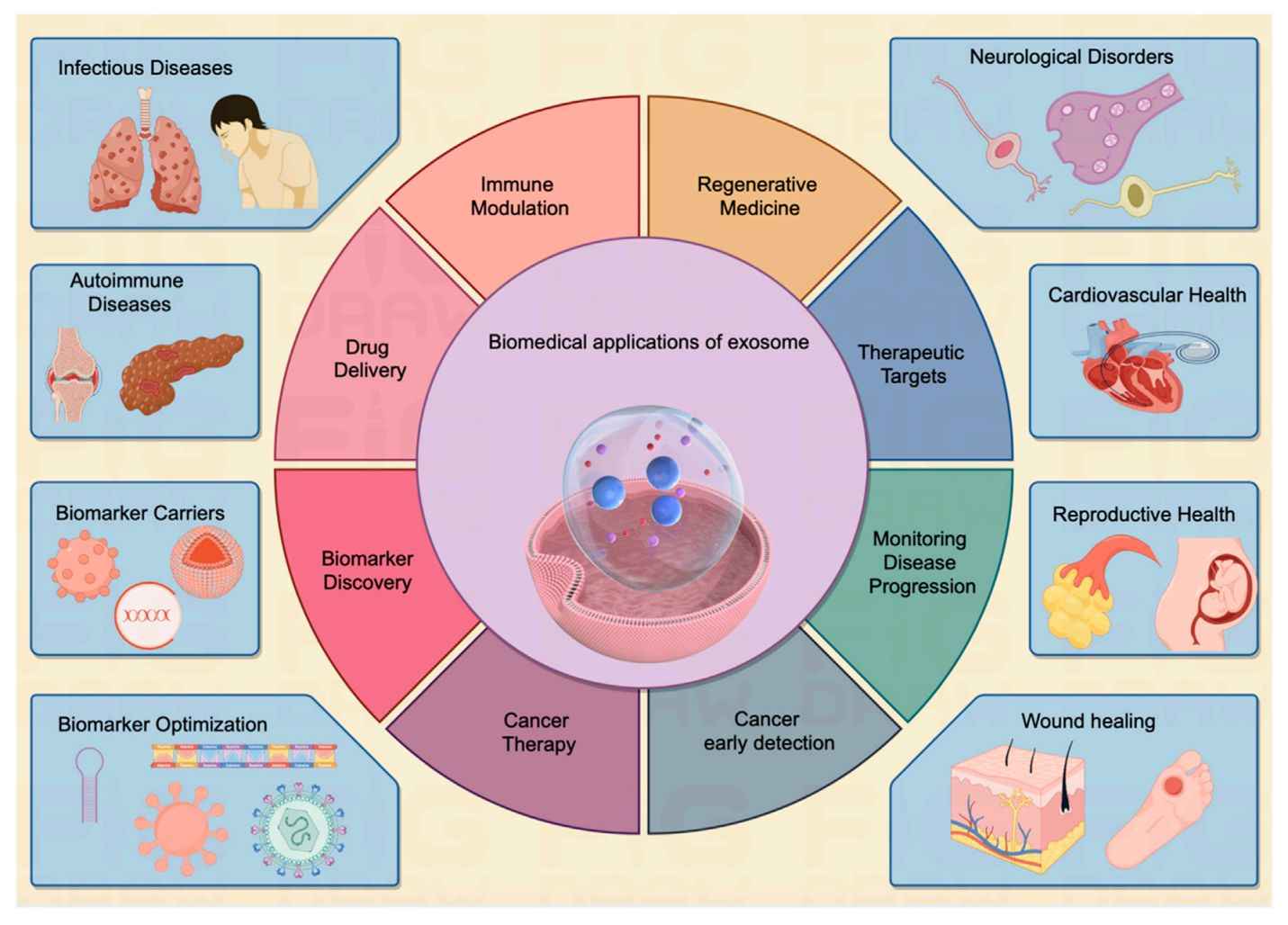
Exosome Drug Delivery and Bioactivity Validation Services
Exosome bioactivity validation is a critical experimental process used to confirm that a therapeutic "cargo" (like siRNA, drugs, or proteins) delivered via an exosome drug delivery system remains active and functional after it reaches the target cell. It measures the intended biological effect, such as gene knockdown or cell killing, to prove the exosome-based drug delivery is effective.
Why Validate Cargo Bioactivity and Targeting?
Validating that your exosomes can release cargo (as covered in our Exosome Drug Release and Transcytosis Assays) is only the first step. The ultimate question for any exosome drug delivery therapeutic is: Does the drug still work?
The complex processes of Exosome Cargo Loading and cellular uptake can damage sensitive cargo like siRNA or proteins. You must prove that your cargo is not only delivered but delivered in an active state.
Our platform is designed to provide this essential proof of efficacy. We help you answer:
- Is the Cargo Active? Does the delivered siRNA still knock down its target gene? Does the delivered chemotherapy drug still kill cancer cells?
- Is Targeting Functional? Does your engineering exosomes for targeted drug delivery strategy result in greater uptake by target cells versus control cells?
- Is it Superior? Does your exosome drug delivery platform show a better therapeutic index (e.g., higher potency, lower toxicity) than the "free drug" alone?
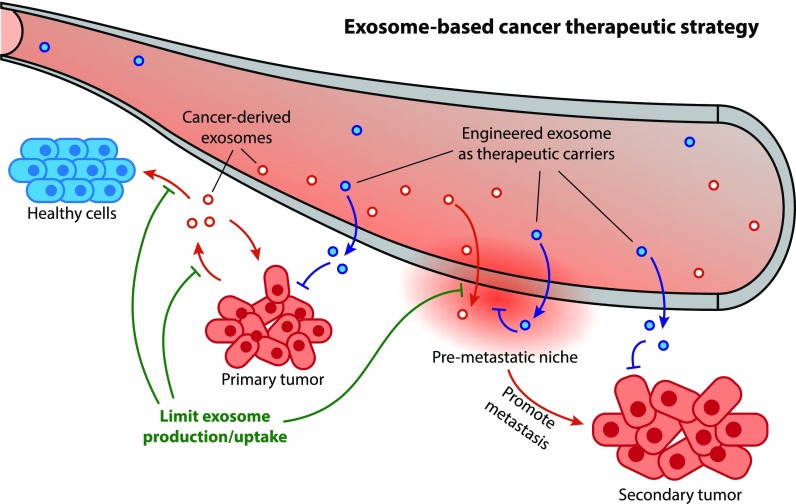
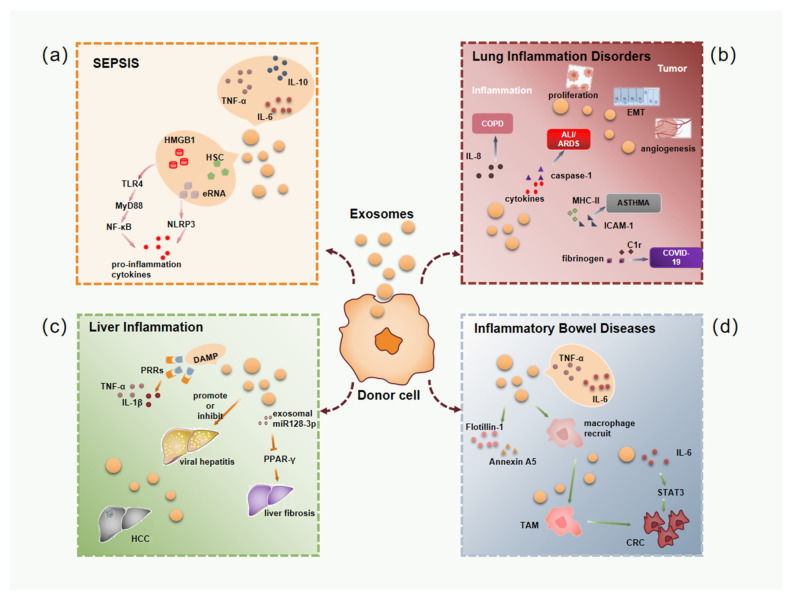
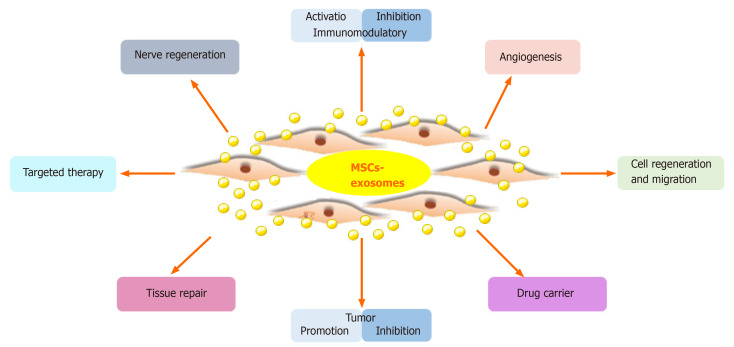
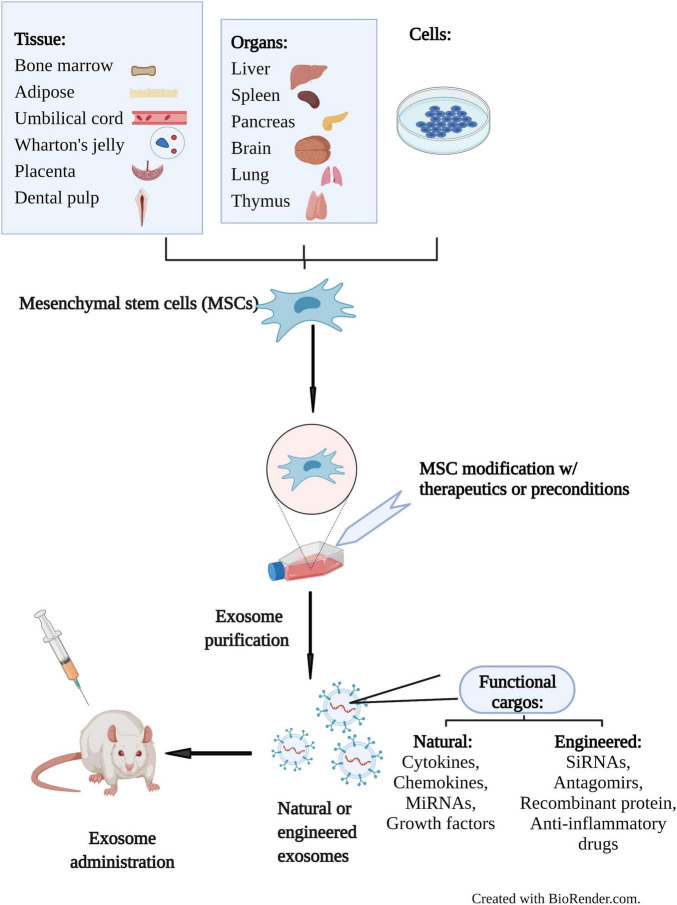
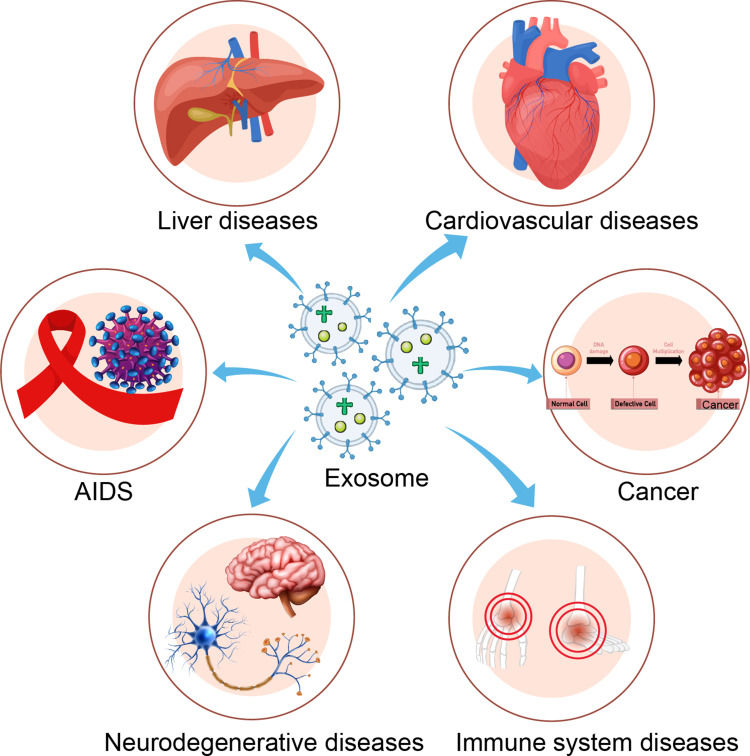 Figure 1. Clinical applications of drug-loaded exosomes. Engineered exosomes deliver drugs or nucleic acids to target cells/tissues for therapeutic effects, tested in various diseases. (Tian J, et al., 2023)
Figure 1. Clinical applications of drug-loaded exosomes. Engineered exosomes deliver drugs or nucleic acids to target cells/tissues for therapeutic effects, tested in various diseases. (Tian J, et al., 2023)
Our Exosome Bioactivity & Targeting Validation Portfolio
Our services are designed to validate the functional performance (Pharmacodynamics) of your exosome drug delivery system, serving as the critical link between Exosome Engineering and in vivo efficacy.
Cargo Bioactivity Validation (In Vitro)
This service package confirms that your exosomal cargo is delivered in a functionally active state to the recipient cell's cytoplasm.
- siRNA/miRNA Cargo Knockdown Assay
- Service: While our Exosome Drug Release Services confirm siRNA transport, this assay confirms its function. We co-culture your siRNA-loaded exosomes with target cells and measure the subsequent knockdown of the target gene.
- Key Readouts: Target gene mRNA downregulation (measured by RT-qPCR) or functional protein knockdown (measured by Western Blot or ELISA). We also link to the Reporter Gene Assay for gold-standard validation.
- Small Molecule / Drug Potency Assay (Cytotoxicity)
- Service: We evaluate the potency of your exosome-delivered small molecule drug (e.g., for exosome drug delivery cancer models). We treat target cancer cells with your drug-loaded exosomes and measure cell viability.
- Key Readouts: We calculate the IC50 value of your exosome formulation and compare it directly to the IC50 of the "free drug" to prove superior or equivalent potency.
- Protein/Peptide Cargo Functional Assay
- Service: We validate the function of delivered therapeutic proteins. This is critical for exosomes as drug delivery vehicles for Parkinson's disease therapy, where cargo might include functional enzymes or neurotrophic factors.
- Key Readouts: Varies by cargo (e.g., enzymatic activity assays, anti-apoptotic assays, or downstream pathway signaling analysis via Western Blot).
Targeted Delivery Validation (In Vitro)
This package validates the efficacy of your Exosome Surface Modification by confirming enhanced and specific targeting.
- Receptor-Mediated Uptake Assay
- Service: We perform comparative and competitive uptake assays. Your engineered, ligand-displaying exosomes are co-cultured with two cell populations: target cells (high receptor expression) and control cells (low receptor expression).
- Key Readouts: Quantitative comparison of exosome uptake (via flow cytometry or imaging) between the target and non-target cells.
- Stimuli-Responsive Bioactivity Assay
- Service: For pH-responsive exosomes designed for the tumor microenvironment. We test the bioactivity (e.g., IC50 of cargo) of your exosome formulation under acidic conditions (e.g., pH 6.5) versus physiological conditions (pH 7.4).
- Key Readouts: A measurable increase in potency (lower IC50) at the target pH, proving your delivery system is "smart."
Preclinical Validation (In Vivo Next Steps)
To validate that your in vitro cargo bioactivity translates into effective treatment in a living system, the next crucial step is demonstrating therapeutic efficacy in preclinical animal models. Confirm whether your exosome drug delivery system can successfully suppress disease progression (e.g., inhibit tumor growth or provide neuroprotection) and achieve functional targeted delivery in vivo.
For detailed in vivo study designs, disease models, and therapeutic efficacy readouts, please see our dedicated In Vivo Exosome Functional Assays.
Our End-to-End Project Workflow
We manage every step of your project, from initial design to final data interpretation, ensuring transparency and collaboration.
Key Service Steps
Consultation & Assay Design
Our scientists consult with you to select the right bioactivity assay and cell model (e.g., a specific cancer cell line, primary neurons for Parkinson's models) to validate your cargo.
Control Establishment
We establish baseline data for your "free drug" (e.g., IC50) and "empty exosome" controls, which are essential for proving the added value of your exosome drug delivery system.
Bioactivity Assay Execution
We perform the definitive experiment, treating target cells with your cargo-loaded exosomes and measuring the specific functional outcome (e.g., gene knockdown, cytotoxicity, or target phosphorylation).
Project Workflow
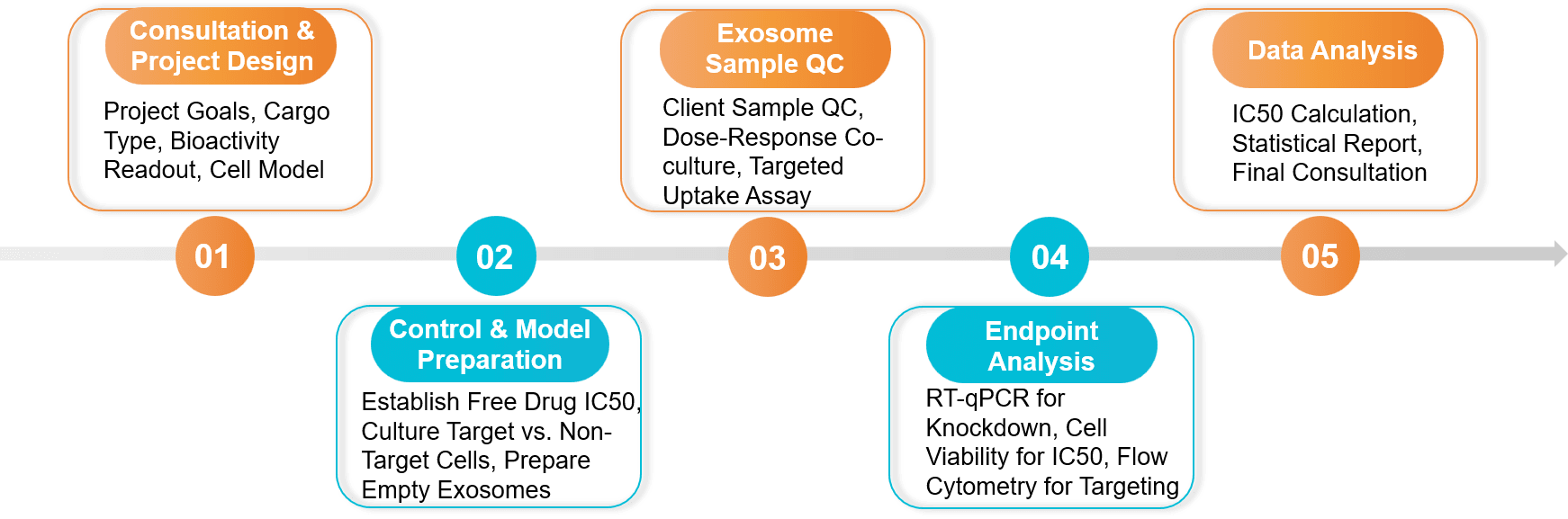 Figure 2. Drug Delivery and Bioactivity Validation Project Workflow. (Creative Biostructure)
Figure 2. Drug Delivery and Bioactivity Validation Project Workflow. (Creative Biostructure)
Sample Requirements
To ensure a successful bioactivity validation, a complete set of controls is critical.
- Client-Provided Formulations:
- Test Article: Purified exosomes loaded with your specific cargo (e.g., drug, protein, siRNA).
- Required Controls: We strongly recommend providing:
1. A sample of the "free" (non-encapsulated) cargo.
2. A sample of "empty" (unloaded) exosomes from the same source. - Quantity: ≥ 1x10¹¹ particles (assay-dependent, please inquire).
- Buffer: Suspended in sterile PBS or a compatible culture-grade buffer.
- Cargo Information (Essential):
- The identity of the cargo and its mechanism of action (e.g., "siRNA for KRAS", "Doxorubicin").
- A validated method or standard for its quantification (e.g., qPCR primers for siRNA, drug standard for HPLC).
Standard Deliverables
Our deliverables are focused on providing a direct comparison of your exosome formulation against its controls.
- A Comprehensive Project Report: Details the experimental design, cell models used, protocols, and a full scientific interpretation of the results.
- Raw and Analyzed Data: Includes all raw data files (e.g., plate reader outputs, flow cytometry .fcs files, gene expression Cq values).
- Publication-Ready Figures:
- For Cargo Bioactivity Assays: Comparative IC50 curves (Exosome Formulation vs. Free Drug) or bar graphs showing % gene/protein knockdown.
- For Targeted Delivery Assays: Comparative uptake graphs (e.g., fluorescence intensity in target cells vs. non-target cells).
- For In Vivo Studies: Tumor growth curves, animal survival plots, and representative IVIS biodistribution images.
- Scientific Consultation: A final meeting with our technical team to discuss the results and how they validate your delivery platform.
Case Study
Case: Targeted Exosome Delivery of siRNA Validates Anti-Tumor Bioactivity
Background: Glioblastoma (GBM) is notoriously difficult to treat, often developing drug resistance. Researchers aimed to develop a targeted exosome-based drug delivery system to co-deliver siRNA and other drugs specifically to GBM cells to overcome this resistance.
Methodology & Findings: The researchers developed a targeted exosome-based delivery system loaded with a specific siRNA. The core of their study was bioactivity validation:
1. In Vitro Bioactivity: They first proved the cargo was active in vitro. Treatment of GBM cells with the exosome-siRNA formulation successfully inhibited the RAS signaling pathway, which in turn suppressed the proliferation and invasion of the tumor cells.
 Figure 3. Targeted Exos delivery system encapsulating drugs and siRNAs. IF images show Cy5.5 accumulation in tumor vs. normal brain regions. (Zhao J, et al., 2024)
Figure 3. Targeted Exos delivery system encapsulating drugs and siRNAs. IF images show Cy5.5 accumulation in tumor vs. normal brain regions. (Zhao J, et al., 2024)
2. In Vivo Efficacy: They then tested this bioactivity in vivo. The targeted exosome delivery system encapsulating the drugs and siRNA together showed a powerful therapeutic effect and significantly reduced tumor burden in the animal model.
Conclusion: This study demonstrates the essential link between in vitro bioactivity validation and in vivo efficacy. By first confirming that the exosome-delivered siRNA was functional in vitro (suppressing RAS signaling and proliferation), the researchers could confidently attribute their in vivo anti-tumor effects to the successful exosome drug delivery of the active cargo.
Ready to confirm your exosome cargo is active and precisely targeted? Our scientists design fit for purpose bioactivity and targeting studies, establish the right controls, and deliver quantitative readouts such as knockdown, IC50, and uptake. Contact us for a free consultation and a tailored assay plan.
References
- Tian J, Han Z, Song D, et al. Engineered Exosome for Drug Delivery: Recent Development and Clinical Applications. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023 Dec 23;18:7923-7940.
- Zhao J, Cui X, Zhan Q, et al. CRISPR-Cas9 library screening combined with an exosome-targeted delivery system addresses tumorigenesis/TMZ resistance in the mesenchymal subtype of glioblastoma Theranostics. 2024 Apr 29;14(7):2835-2855.
Frequently Asked Questions
For any inquiries, our support team is ready to help you get technical support for your research and maximize your experience with Creative Biostructure.