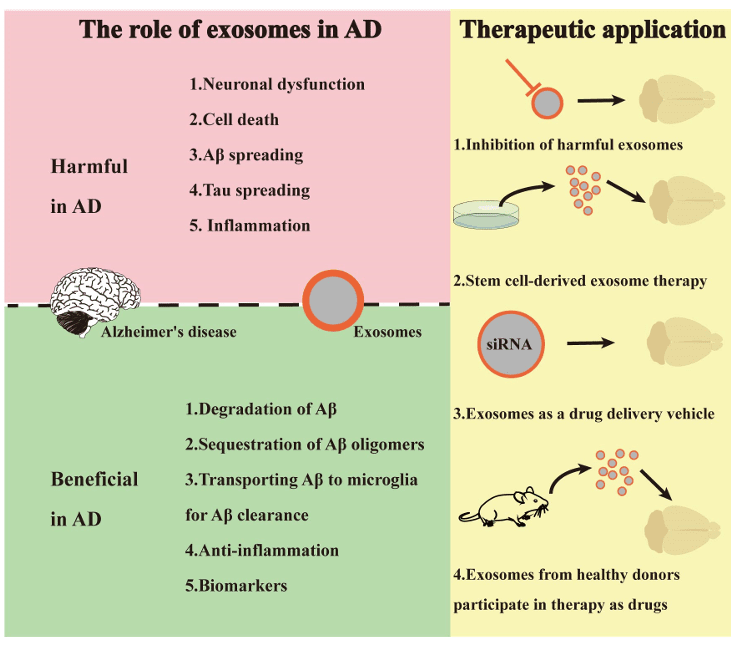
Huntington Disease Exosome Research Services
Huntington's Disease (HD) is a devastating genetic disorder caused by a CAG repeat expansion, leading to the accumulation of toxic mutant Huntingtin (mHTT) protein. Developing effective therapies requires two critical capabilities: the ability to track mHTT levels in the brain non-invasively, and the ability to deliver gene-silencing drugs (like ASOs) across the Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB).
We provide a holistic Huntington Disease Exosome Research Solution. We combine L1CAM-targeted enrichment with Quantitative Proteomics to measure trace mHTT levels in plasma as a pharmacodynamic biomarker. Simultaneously, our Therapeutic Development platform enables you to engineer exosomes for targeted ASO Delivery or utilize Stem Cell Exosomes to rescue synaptic dysfunction, accelerating the path to clinical trials.
Critical Frontiers in HD Research
Huntington's Disease poses unique challenges as a monogenic disorder with systemic manifestations.
- Pharmacodynamic Monitoring: Clinical trials for huntingtin-lowering therapies (ASOs) need a way to measure mutant Huntingtin (mHTT) levels in the brain without invasive sampling. CSF and plasma exosomes are the primary candidates.
- Blood-Brain Barrier Delivery: While the genetic target is known, delivering silencing agents (ASOs/siRNA) to the striatum remains the biggest hurdle. Biological vehicles like exosomes are being explored to overcome BBB restrictions.
- Mitochondrial Defects: mHTT impairs energy metabolism. Investigating the release of mitochondrial components via exosomes provides insights into the metabolic health of neurons.
- Extra-Neural Pathology: HD affects muscle and metabolism, not just the brain. Research is expanding to look at skeletal muscle exosomes to understand systemic wasting.
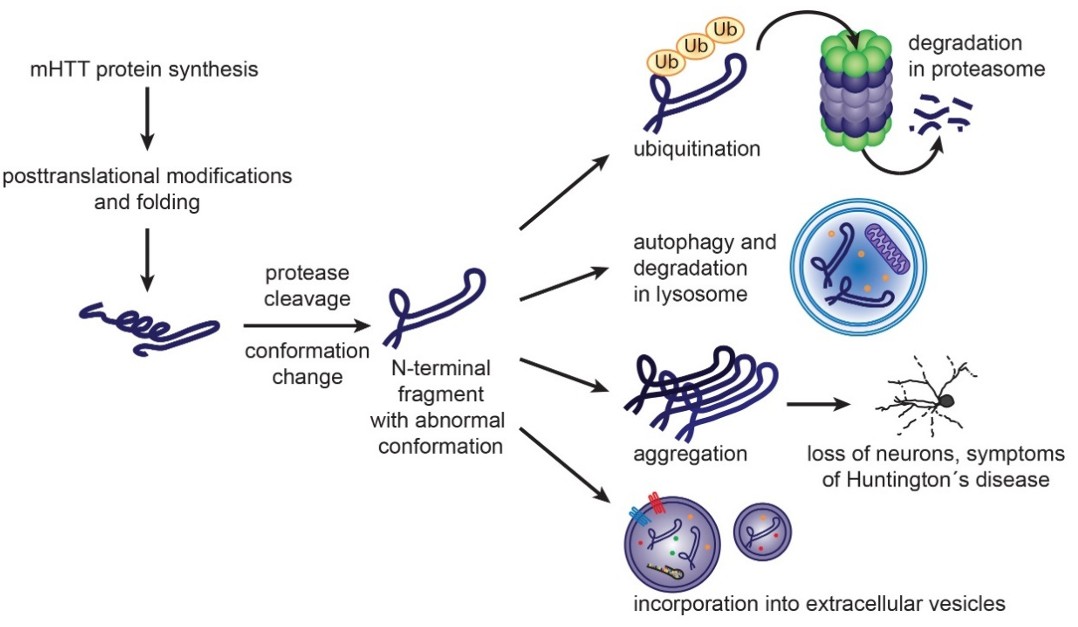 Figure 1. Formation and cellular handling of mHTT toxic species, including misfolding, aggregation, and clearance mechanisms. (Ananbeh H, et al., 2021)
Figure 1. Formation and cellular handling of mHTT toxic species, including misfolding, aggregation, and clearance mechanisms. (Ananbeh H, et al., 2021)
Comprehensive Service Portfolio for HD
We offer an integrated matrix of services tailored to your specific research focus, covering biomarkers, mechanism, and therapy.
| Research Phase | Our Specialized Approach & Solution | Key Services Applied |
|---|---|---|
| Biomarker Discovery (Diagnosis) | Brain-Derived mHTT Detection: We enrich L1CAM+ exosomes from plasma and use Quantitative Proteomics to detect femtomolar levels of mHTT, correlating cargo with CAG repeat length. | Exosome Surface Marker Analysis |
| Pathological Mechanism (Cellular) | Mitochondrial & Synaptic Assays: We use HD iPSC-derived neurons to assess mitochondrial respiration (Seahorse) and synaptic density. We test if exosomes transfer mHTT seeds or toxic RNAs. | Exosome Cellular Functional Assays |
| Therapeutic Development (Therapy) | Gene Silencing & Neuroprotection: We offer two tracks: Exosome ASO Delivery (loading siHTT) for gene knockdown, and MSC-Derived Exosome Therapy for neurotrophic support and repair. | Exosome ASO Delivery |
| In Vivo Validation (Animal Models) | Efficacy Testing in R6/2 Mice: We administer exosomes systemically to HD transgenic mice (e.g., R6/2 or YAC128). We evaluate motor function (Rotarod) and striatal mHTT aggregates via IHC. | In Vivo Exosome Functional Assays |
Core Technologies for Huntington's Disease
We deploy specific technologies designed to handle the "undruggable" targets of HD.
L1CAM Neural Exosome Isolation
The Liquid Biopsy Key: Mutant Huntingtin is abundant in the brain but scarce in blood. Standard isolation fails to capture enough signal. By using Immuno-Affinity Capture for L1CAM (CD171), we selectively concentrate exosomes released by neurons. This allows researchers to track brain mHTT levels via a simple blood draw, a game-changer for monitoring clinical trials.
Exosome Quantitative Proteomics (mHTT)
Measuring the Toxin: Quantifying mHTT requires extreme sensitivity. Our Exosome Quantitative Proteomics service employs advanced immunoassays (like Simoa or MSD) capable of detecting femtomolar concentrations of polyglutamine-expanded proteins. This provides a precise readout of the toxic burden in patient biofluids.
Exosome ASO Delivery
Crossing the Barrier: Antisense Oligonucleotides (ASOs) are the leading therapeutic strategy for HD, but delivery is the bottleneck. Our Exosome ASO Delivery service encapsulates these genetic medicines into exosomes. We optimize loading efficiency and surface engineering (e.g., Rabies Virus Glycoprotein peptides) to ensure the payload reaches the striatum and cortex after systemic administration.
Application Spotlight: Stem Cell Exosomes Restore Neuronal Function
This analysis highlights the therapeutic potential of stem cell-derived exosomes in rescuing synaptic deficits in patient-derived neuronal models.
Featured Technologies:
- MSC and Stem Cell Derived Exosome Therapy
- Exosome Cellular Functional Assays
Literature Interpretation:
The loss of GABAergic neurons in the striatum is a hallmark of Huntington's disease (HD). Researchers investigated whether extracellular vesicles (EVs) derived from adipose stem cells (ASCs) could rescue this neuronal dysfunction. Using HD patient-specific iPSC-derived neurons, the study demonstrated that treatment with ASC-EVs significantly improved mitochondrial respiration and reduced oxidative stress. Most critically, electrophysiological analysis revealed that these exosomes restored GABAergic synaptic transmission, effectively reversing the neuronal firing deficits caused by the HTT mutation. This study validates the neuroprotective capacity of stem cell exosomes and underscores the importance of using advanced iPSC-based functional assays to screen potential therapeutics.
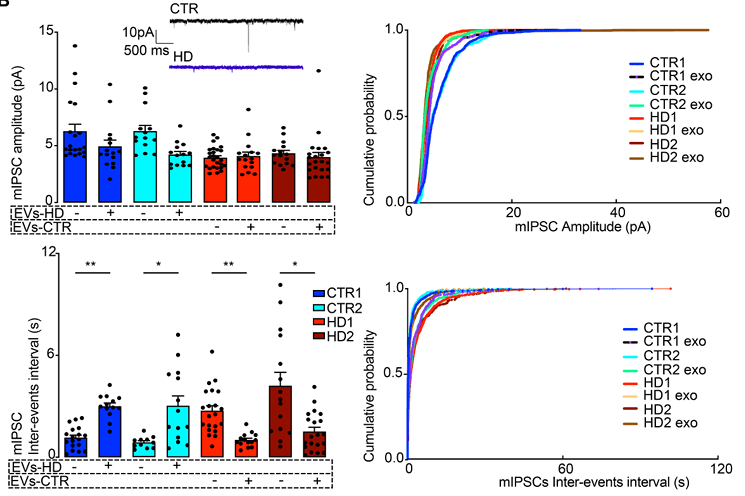 Figure 2. mIPSC amplitude and frequency changes in HD-derived neurons treated with control (CTR-EVs) and HD-derived exosomes (HD-EVs), showing synaptic recovery and impairment effects, respectively. (Beatriz M, et al., 2023)
Figure 2. mIPSC amplitude and frequency changes in HD-derived neurons treated with control (CTR-EVs) and HD-derived exosomes (HD-EVs), showing synaptic recovery and impairment effects, respectively. (Beatriz M, et al., 2023)
Start Your HD Research Project
Advance your therapeutic or diagnostic program with our specialized neuro-platform.
How It Works: Our Project Pathway
 Figure 3. Workflow for isolating neural exosomes, quantifying mutant Huntingtin (mHTT), and validating ASO-mediated gene silencing. (Creative Biostructure)
Figure 3. Workflow for isolating neural exosomes, quantifying mutant Huntingtin (mHTT), and validating ASO-mediated gene silencing. (Creative Biostructure)
Ready to track mHTT or deliver gene-silencing therapies? Our neuroscience experts are available to discuss your HD research strategy. Contact us today to discuss your project.
References
- Ananbeh H, Vodicka P, Kupcova Skalnikova H. Emerging Roles of Exosomes in Huntington's Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 15;22(8):4085.
- Beatriz M, Rodrigues RJ, Vilaça R, et al. Extracellular vesicles improve GABAergic transmission in Huntington's disease iPSC-derived neurons. Theranostics. 2023 Jun 26;13(11):3707-3724.