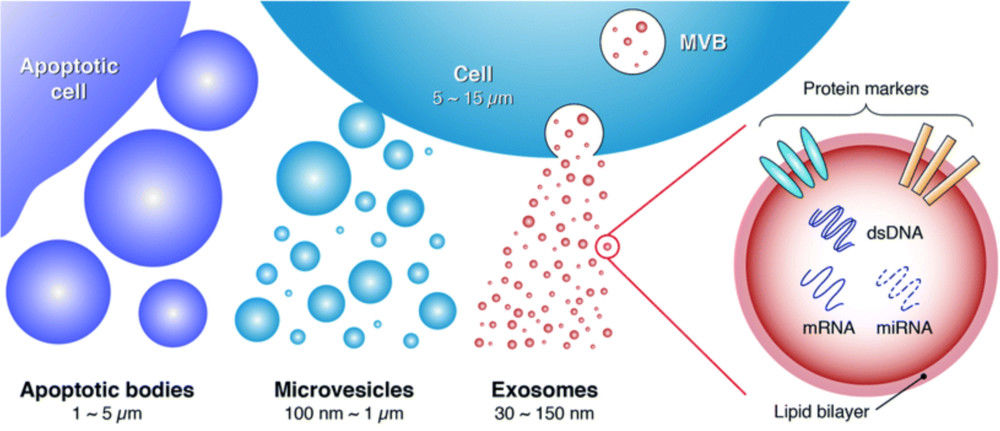
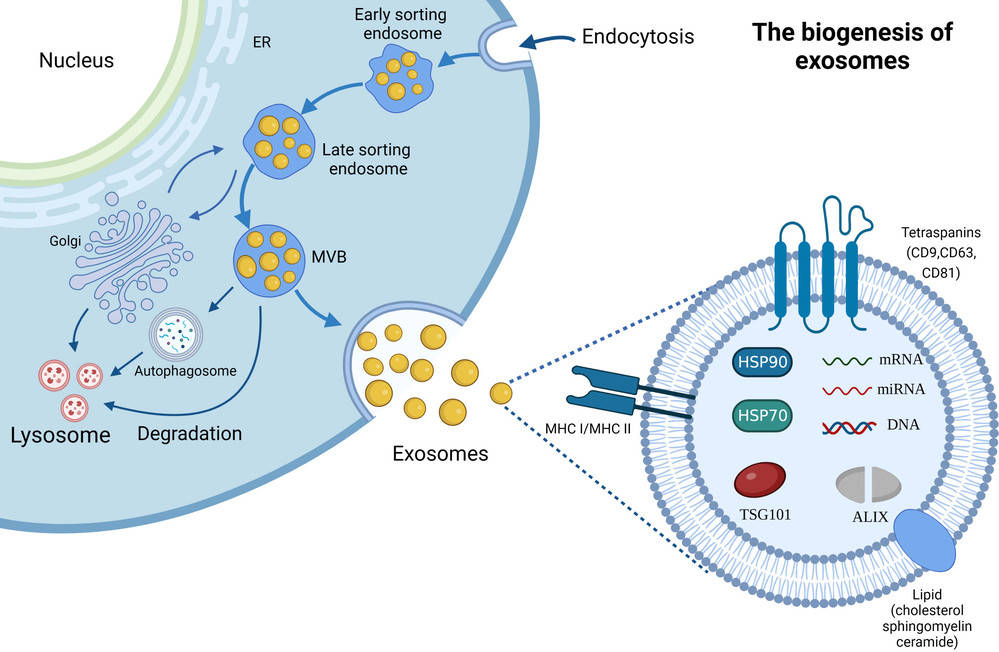
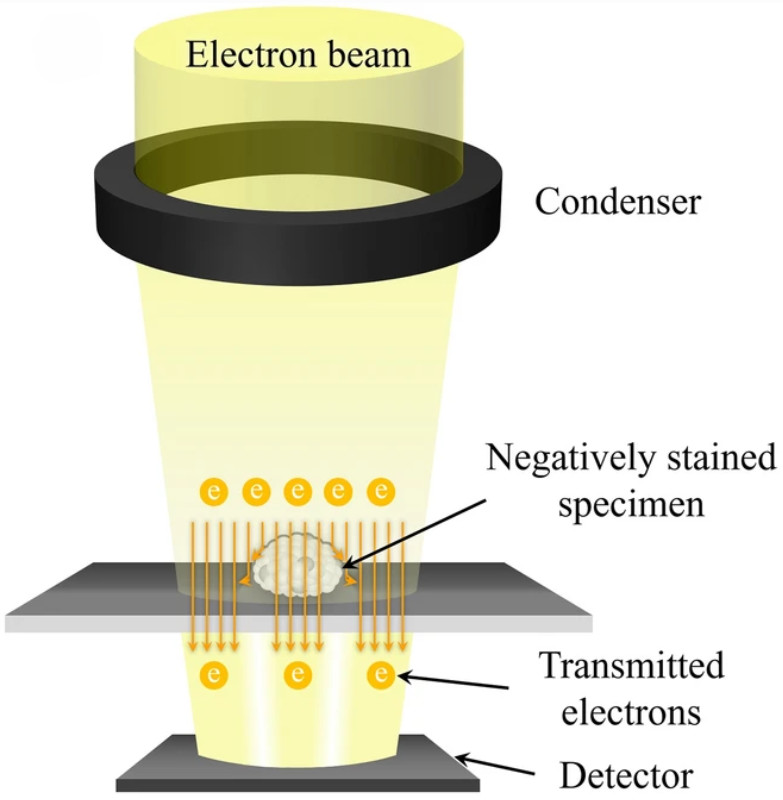
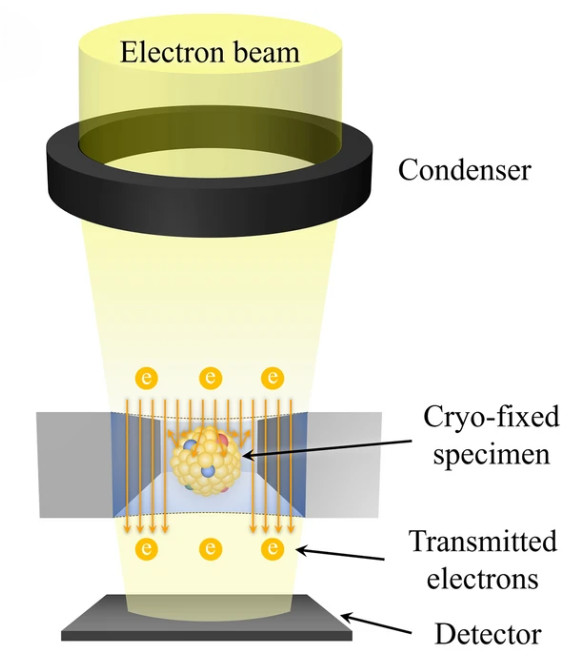
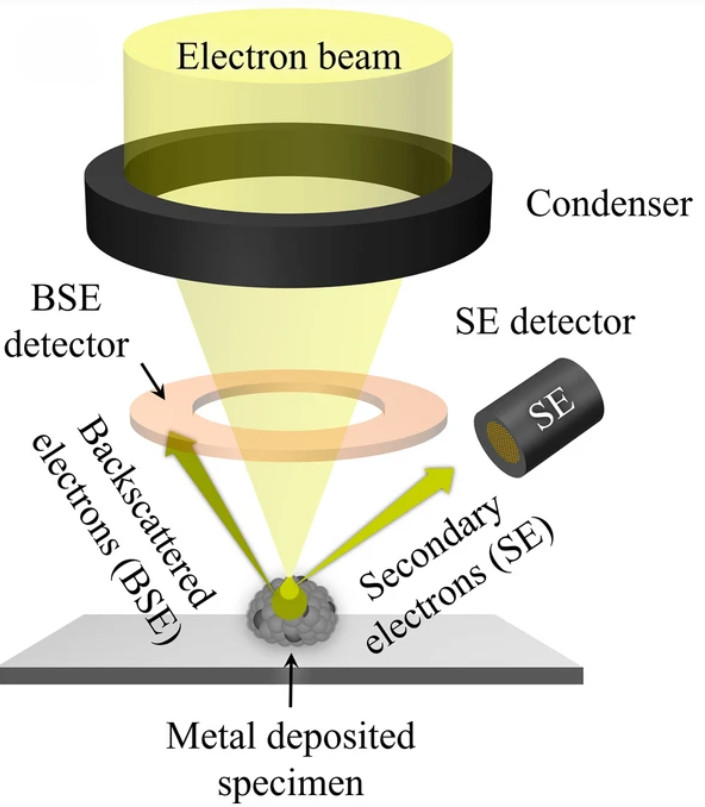
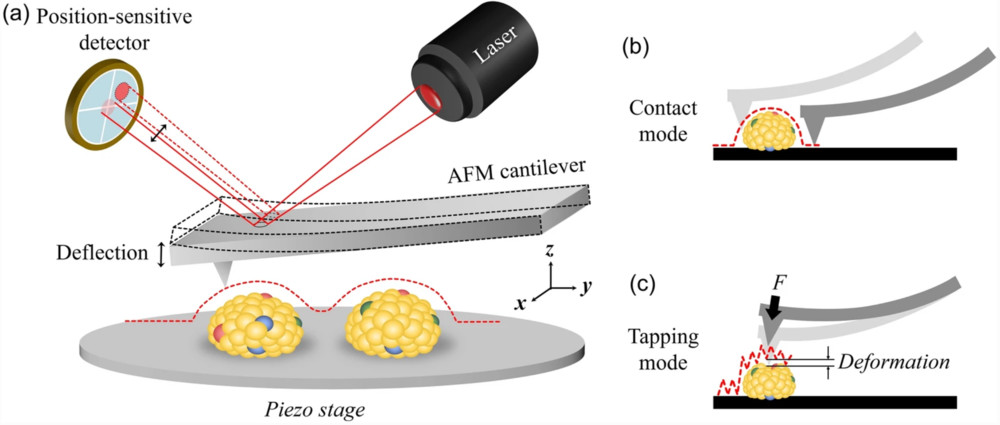
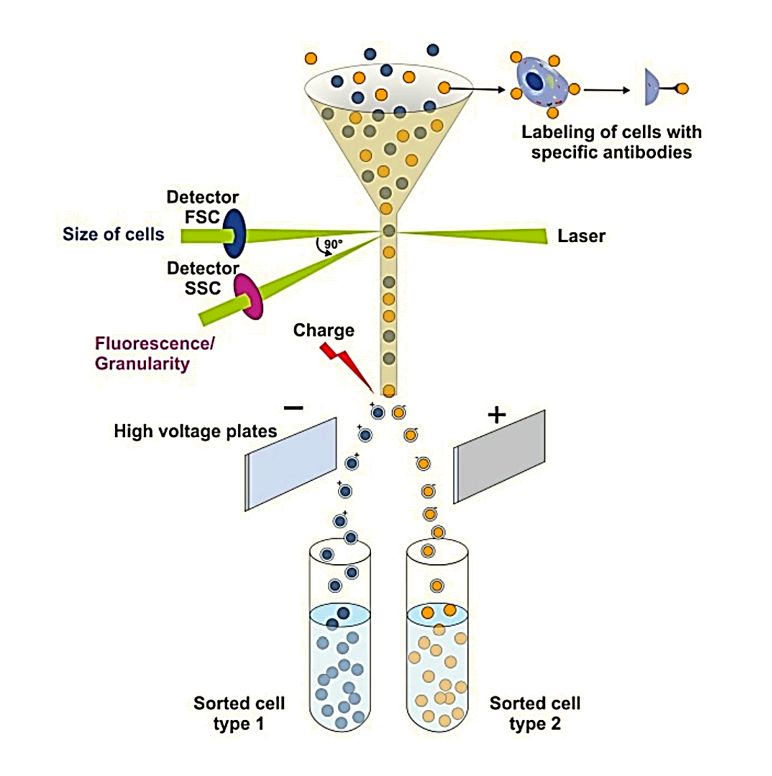
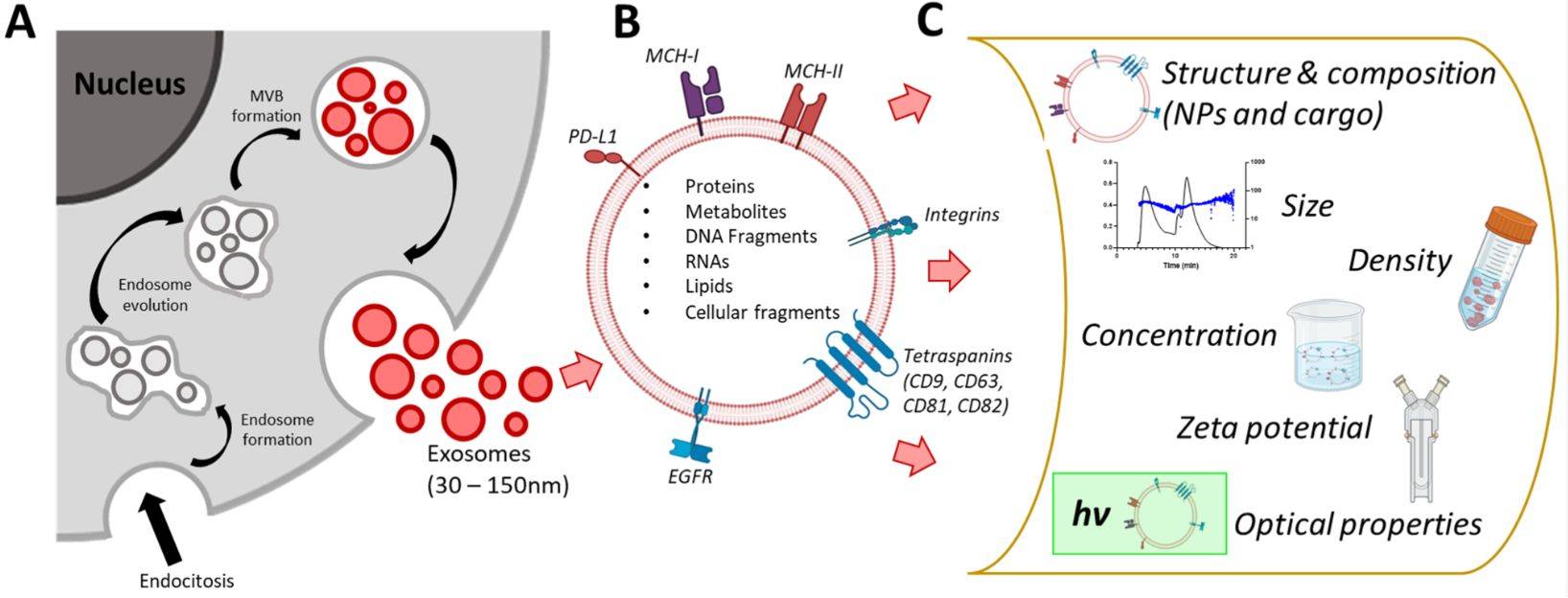
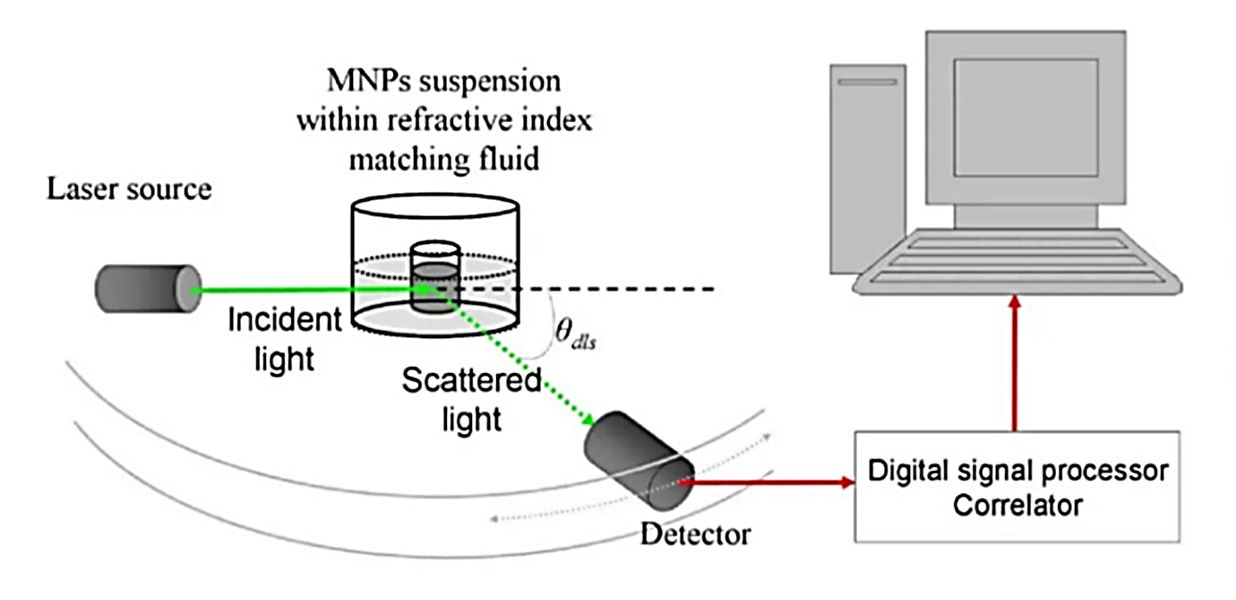
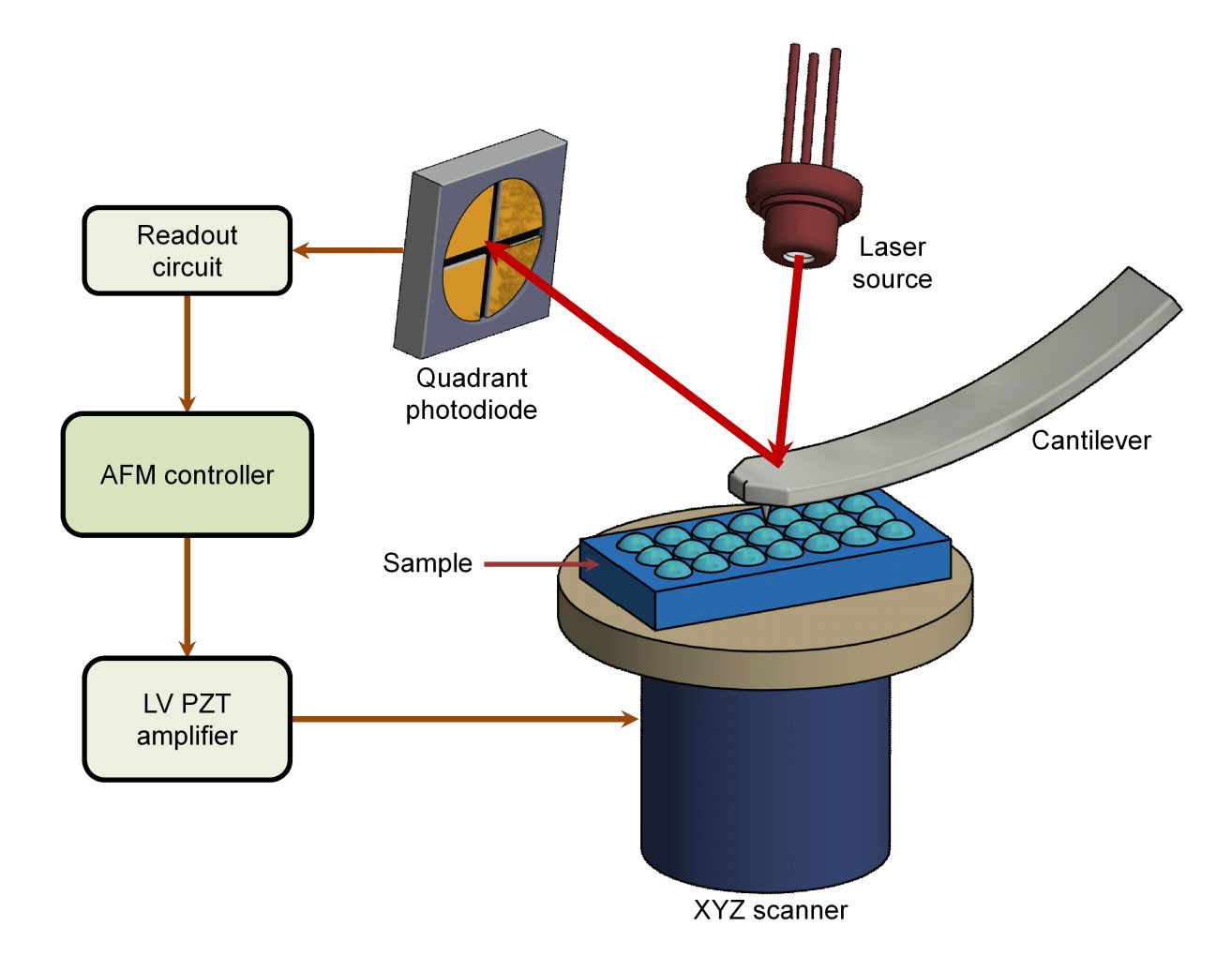
Raman Spectroscopy-Based Exosome Characterization Service
Raman spectroscopy (RS) has emerged as a powerful, label-free, and non-destructive analytical technique for probing the chemical composition of exosomes. At Creative Biostructure, we provide Raman Spectroscopy-Based Exosome Characterization Service to deliver reliable molecular fingerprints of exosomes, enabling comprehensive analysis of their biochemical heterogeneity in compliance with MISEV2023 guidelines.
How Raman Spectroscopy Differentiates and Characterizes Exosomes
Raman spectroscopy measures the vibrational modes of molecules when irradiated by a focused laser. While most light scatters elastically, a small fraction undergoes energy shifts (the Raman effect), which are specific to molecular bonds. The resulting Raman spectrum serves as a biochemical fingerprint of the exosome population.
A major advancement in this field is Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS). By using metallic nanostructures, SERS amplifies weak Raman signals by several orders of magnitude, dramatically improving sensitivity for low-abundance exosomal biomarkers.
With this spectrum, we can:
- Differentiate exosome populations by cell origin (e.g., healthy vs. cancer-derived vesicles).
- Assess purity and heterogeneity, detecting co-isolated vesicles or contaminants.
- Monitor dynamic changes in exosome cargo under disease progression or therapeutic intervention.
- Perform comprehensive cargo analysis, profiling lipids, proteins, nucleic acids, and metabolites simultaneously.
This holistic view provides a level of insight unmatched by many conventional exosome characterization techniques.
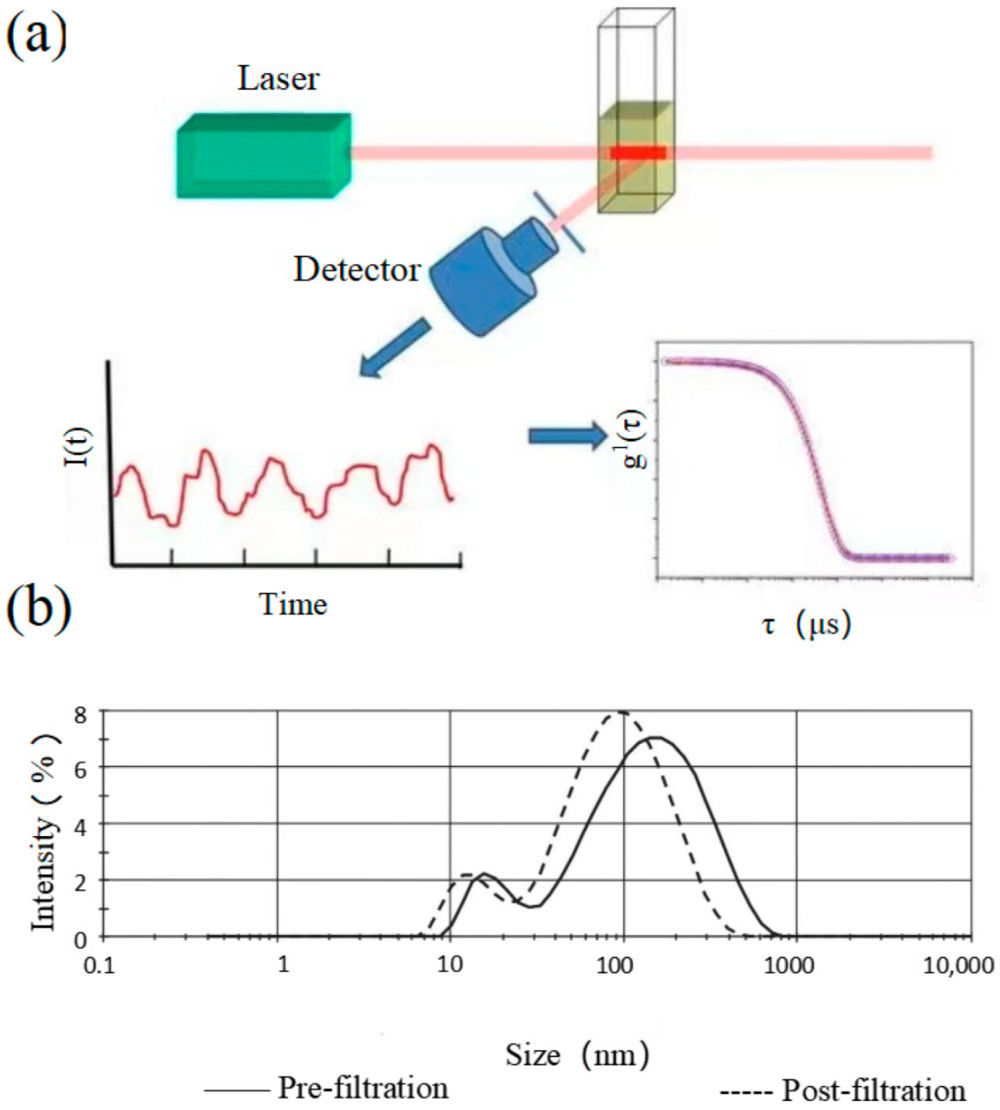
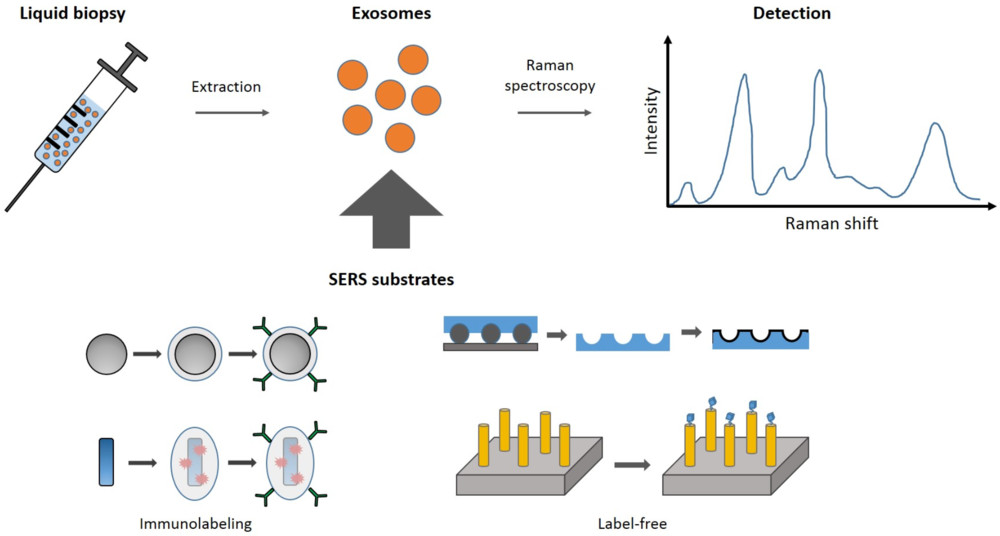 Figure 1. Principle of Exosome Identification by Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy (SERS). (Merdalimova A, et al., 2019)
Figure 1. Principle of Exosome Identification by Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy (SERS). (Merdalimova A, et al., 2019)
Raman vs. Other Exosome Characterization Techniques
| Method | Key Features | How Raman Adds Value |
|---|---|---|
| NTA | Particle size distribution and concentration | Adds chemical composition profiling |
| TEM/SEM | High-resolution vesicle morphology | Complements with biochemical fingerprints |
| Flow Cytometry | Surface marker detection | Provides holistic molecular-level analysis |
| Western Blot | Protein marker confirmation | Expands to simultaneous detection of multiple biomolecule types |
When combined with Raman, these complementary techniques provide a comprehensive view of exosome structure, cargo, and function.
Raman Spectroscopy Platforms for Exosome Analysis
| Platform | Key Advantages |
|---|---|
| High-Sensitivity Raman Spectroscopy |
|
| Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy (SERS) |
|
All Raman platforms are routinely calibrated to ensure reproducibility and follow MISEV2023 guidelines for transparency and data integrity. By combining both platforms, Creative Biostructure can flexibly adapt to different project requirements.
Our Raman Exosome Characterization Workflow
Project Consultation & Strategic Design
We begin by defining the research objectives and then select the most suitable platform, either spontaneous Raman or SERS, tailoring the acquisition strategy to meet specific project requirements.
Sample Submission & Preparation
Accept pre-purified exosomes or raw materials for in-house isolation. Prepare either suspension samples (SERS probes) or dried samples (substrates). Document buffer conditions, concentration, and handling steps.
Spectral Acquisition
Raman spectra are recorded using high-resolution systems with strict control of laser wavelength, power, acquisition time, and spot size, and multiple spectra are collected from each sample to account for EV heterogeneity.
Data Processing & Bioinformatic Analysis
Data processing includes baseline correction, normalization, and background subtraction, followed by advanced statistical and machine learning analyses such as PCA, clustering, and classification to compare exosome populations and reveal biochemical differences.
Comprehensive Reporting
We provide raw and processed spectral data along with publication-ready figures and tables, and offer expert consultation to support data interpretation and manuscript preparation.
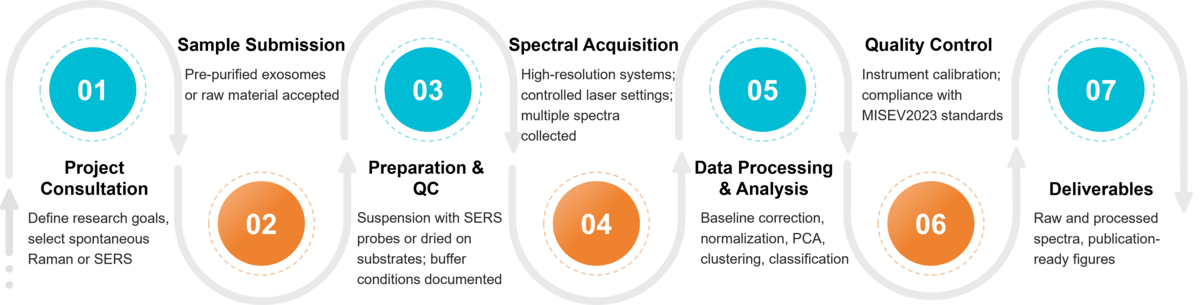 Figure 2. Project Workflow for Exosome Characterization by Raman Spectroscopy. (Creative Biostructure)
Figure 2. Project Workflow for Exosome Characterization by Raman Spectroscopy. (Creative Biostructure)
Sample Requirements for Raman Analysis
| Requirement | Description |
|---|---|
| Sample Type | Pre-purified exosomes or raw material (e.g., cell culture supernatant, biofluid) |
| Purity | Free of large debris, apoptotic bodies, or protein aggregates |
| Concentration | ≥10-20 µg protein or ≥109 particles/mL recommended (SERS allows lower inputs) |
| Volume | 50-100 µL recommended |
| Buffer Conditions | Preferably PBS or physiological buffer; avoid detergents and strong salts |
| Storage & Shipping | Fresh or frozen (-80 °C), shipped on dry ice |
What Deliverables Will You Receive
- Raw and processed Raman/SERS spectra
- Multivariate statistical analyses (PCA plots, cluster analyses)
- High-resolution spectral fingerprints of exosomes
- Publication-ready figures and full methodological documentation
- Comprehensive technical report with expert interpretation
Applications of Raman-Based Exosome Characterization
Our service supports multiple research and translational domains:
- Cancer Research: Identify exosome-based spectral biomarkers for early detection.
- Neuroscience: Characterize brain-derived exosomes linked to neurodegenerative disorders.
- Immunology: Profile immune-cell-derived EVs to study their role in immune modulation.
- Drug Delivery & QC: Verify engineered exosome cargo and batch consistency.
- Biomarker Discovery: Identify unique Raman spectral peaks as diagnostic signatures.
Why Choose Creative Biostructure?
- Extensive expertise in EV biology and vibrational spectroscopy
- Cutting-edge Raman and SERS instrumentation
- Strict adherence to MISEV2023 standards for reproducibility
- Integrated service portfolio (NTA, TEM, FACS, proteomics, lipidomics)
- Trusted CRO partner for leading universities and biotech firms worldwide
Case Study
Case: Label-Free Characterization of Plasma-Derived EV Subpopulations Using Raman Spectroscopy
Background
Plasma-derived EV subpopulations, including exomeres (<50 nm) and exosomes (50-80 nm), were isolated to test whether Raman spectroscopy could distinguish EVs from contaminants and among subtypes.
Methods
Raman spectra were collected in fingerprint and C-H regions and analyzed with PCA, LDA, and SVM. Complementary GC×GC-TOFMS assessed fatty acid compositions.
Results
Raman spectroscopy separated EVs from apoB-100 lipoproteins and discriminated platelet-derived CD61+ EVs from CD9+/CD63+/CD81+ subsets, achieving up to 90% classification accuracy. Distinct spectral bands indicated differences in protein and lipid composition, supported by fatty acid profiling.
Conclusion
Raman spectroscopy proved to be a rapid, label-free method for EV purity assessment and subtype discrimination, offering valuable biochemical fingerprints for biomarker discovery and translational studies.
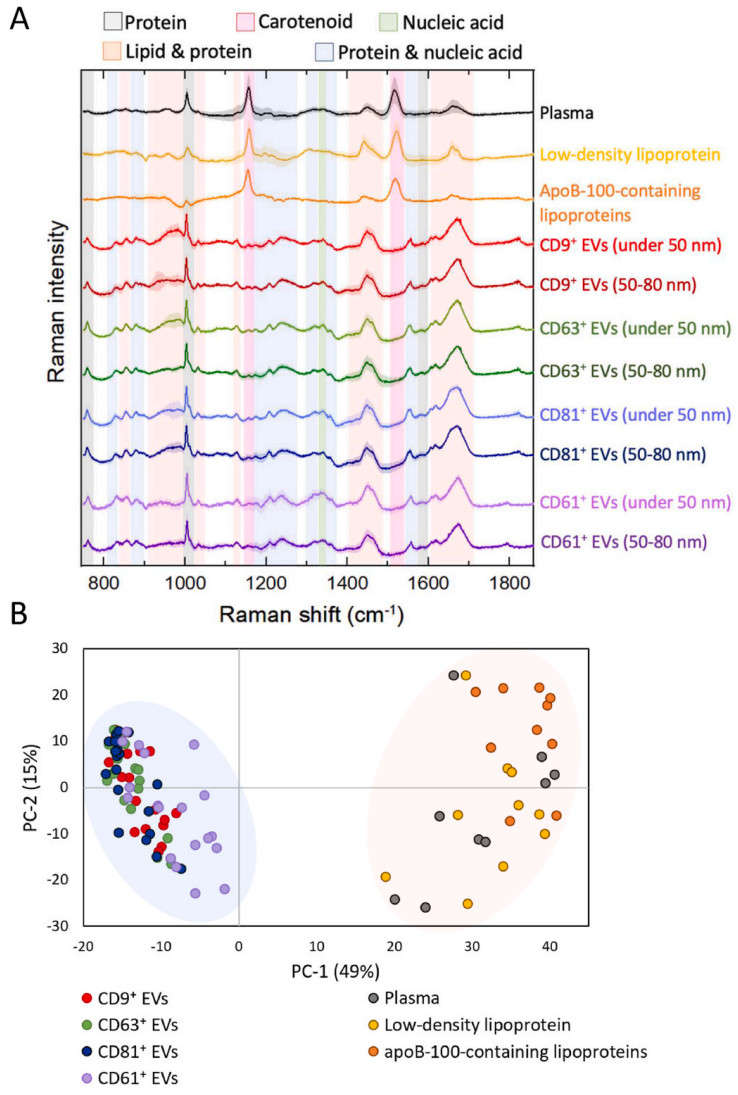 Figure 3. Raman spectroscopy-based analysis of biological samples. (A) Average baseline-corrected and SNV-normalized Raman spectra from plasma, LDL isolated by ultracentrifugation, apoB-100 lipoproteins isolated via IAC-AsFlFFF, and EV subpopulations in the fingerprint region.
Figure 3. Raman spectroscopy-based analysis of biological samples. (A) Average baseline-corrected and SNV-normalized Raman spectra from plasma, LDL isolated by ultracentrifugation, apoB-100 lipoproteins isolated via IAC-AsFlFFF, and EV subpopulations in the fingerprint region.
(B) Principal component analysis (PCA) scatter plot of measured spectra (with outliers removed). EV subpopulations were classified according to immunoaffinity ligands used in the isolation process. (Liangsupree T, et al., 2022)
Creative Biostructure provides state-of-the-art Raman and SERS platforms for comprehensive exosome characterization. Contact us to discuss your project needs and learn how we can support your research.
References
- Merdalimova A, Chernyshev V, Nozdriukhin D, et al. Identification and analysis of exosomes by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Applied Sciences. 2019, 9(6): 1135.
- Liangsupree T, Multia E, Saarinen J, et al. Raman spectroscopy combined with comprehensive gas chromatography for label-free characterization of plasma-derived extracellular vesicle subpopulations. Analytical Biochemistry. 2022, 647: 114672.
- Welsh J A, Goberdhan D C I, O'Driscoll L, et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles (MISEV2023): From basic to advanced approaches. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles. 2024, 13(2): e12404.
Frequently Asked Questions
For any inquiries, our support team is ready to help you get technical support for your research and maximize your experience with Creative Biostructure.