Breast Cancer Exosome Research Services
Breast cancer is not a single disease; it is a complex spectrum ranging from Luminal A/B to HER2-positive and Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC). Exosomes act as the communication hub within this spectrum, facilitating the horizontal transfer of drug resistance (e.g., Trastuzumab or Tamoxifen resistance) and preparing the lethal pre-metastatic niche in the bone, lung, and brain.
We provide a holistic Breast Cancer Exosome Research Solution. Unlike generalist services, our platform is tailored to the specific molecular landscapes of breast malignancy. Whether you are developing Liquid Biopsy panels to distinguish TNBC subtypes, mapping the Phosphoproteomic networks driving kinase inhibitor resistance, or validating Brain Metastasis mechanisms in vivo, we offer an integrated portfolio to accelerate your translational research.
Critical Frontiers in Breast Oncology
Breast cancer research has moved beyond simple receptor status to understanding dynamic resistance and metastasis mechanisms.
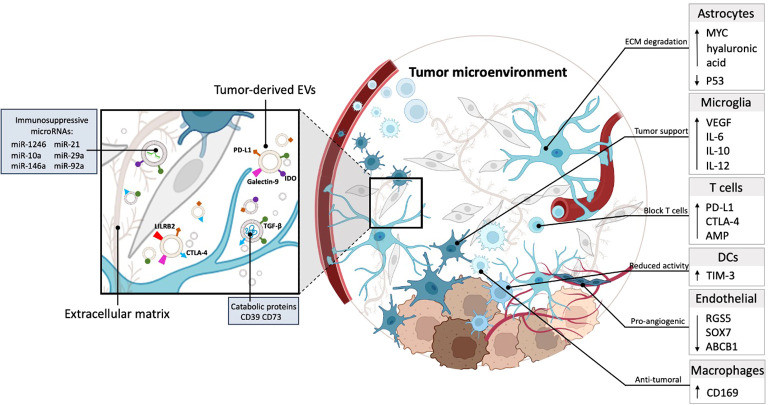
- Mechanisms of Brain Metastasis: The blood-brain barrier (BBB) makes the brain a sanctuary site for breast cancer cells. Deciphering how exosomes breach the BBB to seed metastases is a top priority for HER2+ and TNBC research.
- Therapeutic Resistance: A major hurdle is the acquisition of resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors and anti-HER2 therapies. Investigating the transfer of non-coding RNAs or phosphorylated kinases via exosomes offers insights into these adaptive mechanisms.
- Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC): Lacking targeted therapies, TNBC relies on understanding the immune microenvironment. Research focuses on how exosomes modulate the "immune desert" phenotype to identify new immunotherapeutic targets.
- Dormancy and Recurrence: Breast cancer can recur decades later. Understanding how exosomes signal disseminated tumor cells (DTCs) to wake from dormancy is critical for long-term survival.
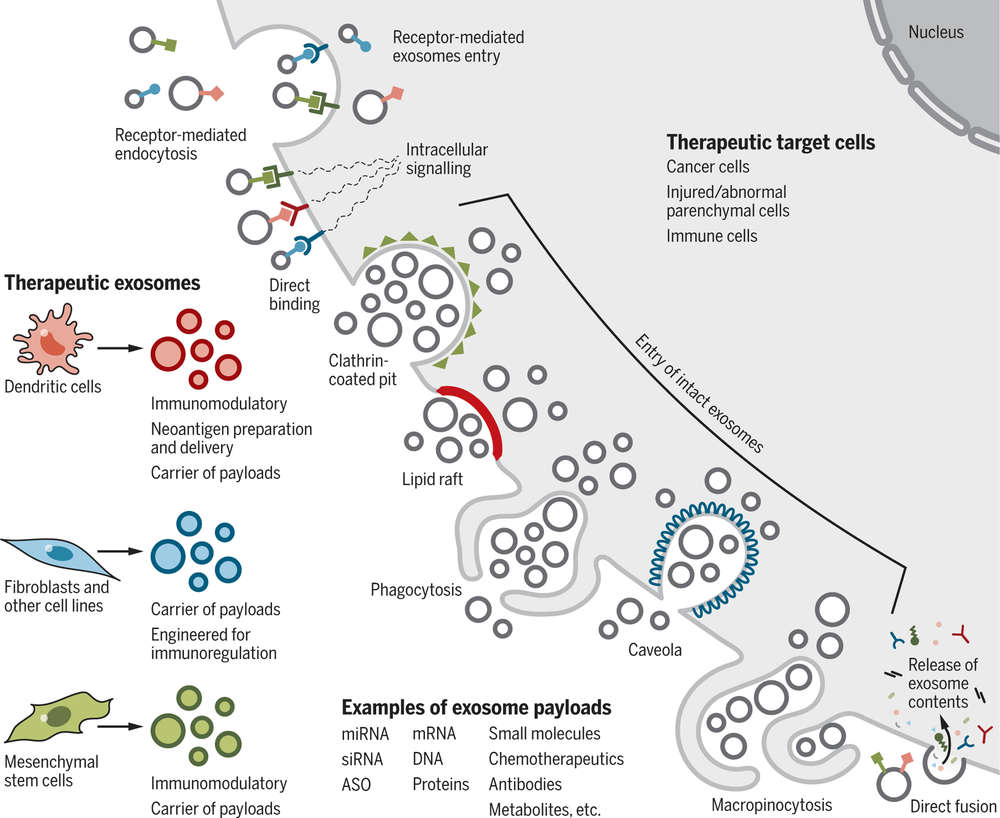
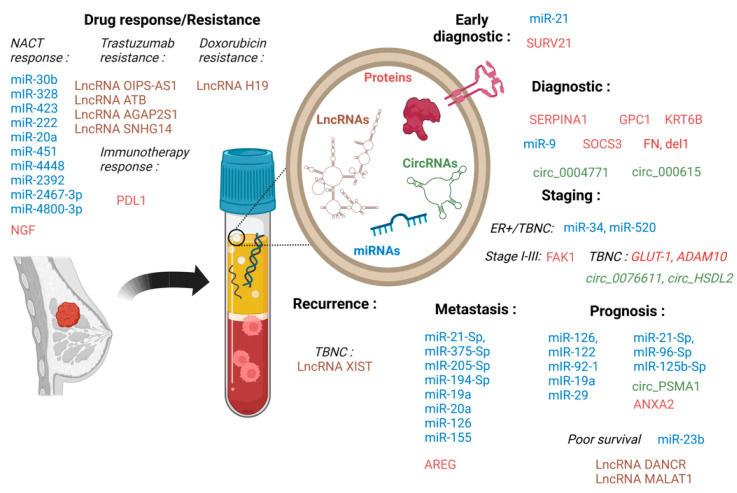 Figure 1. SEVs cargo as biomarkers for breast cancer, including differential expression of miRNAs, LncRNAs, CirRNAs, and proteins. (Loric S, et al., 2023)
Figure 1. SEVs cargo as biomarkers for breast cancer, including differential expression of miRNAs, LncRNAs, CirRNAs, and proteins. (Loric S, et al., 2023)
Comprehensive Service Portfolio for Breast Cancer
We offer an integrated matrix of services tailored to your specific research focus, covering biomarkers, mechanism, and in vivo validation.
| Research Focus | Our Specialized Approach & Solution | Key Services Applied |
|---|---|---|
| Biomarker Discovery (Diagnosis) | Subtype Enrichment & Profiling: We use Immuno-Affinity Capture (Anti-HER2/EpCAM) to enrich tumor exosomes from plasma, followed by Small RNA-Seq or Proteomics to identify recurrence signatures. | Exosome Isolation by Immunoaffinity Capture, Exosome Quantitative Proteomics |
| Drug Resistance (Mechanism) | Signaling Pathway Analysis: We apply Phosphoproteomics to detect activated kinases (PI3K/Akt/mTOR) in exosomes from resistant cells. We also use Co-culture Assays to test if resistance is transferable. | Exosomal Phosphoproteomics Analysis |
| Metastasis & TME (Function) | Invasion & Bone Remodeling: We utilize 3D Organoid Invasion assays and Osteoclast Differentiation assays (TRAP staining) to validate the role of exosomes in promoting spread and bone lesions. | Exosome Organoid-based Functional Assays, Angiogenesis and Stem Cell Functional Assays |
| In Vivo Validation (Animal Models) | Organotropism Tracking: We inject labeled exosomes intracardially into mice to track homing to the Bone, Lung, or Brain. We also monitor tumor growth in orthotopic mammary fat pad models. | Exosome Tracing and Tracking |
Core Technologies for Breast Oncology
We highlight specialized technologies that address the unique requirements of breast cancer subtypes and metastatic patterns.
HER2/EpCAM Exosome Isolation
Subtype-Specific Capture: Standard isolation methods (like ultracentrifugation) collect all exosomes. To study breast cancer specifically, we utilize magnetic beads coated with Anti-HER2 or Anti-EpCAM antibodies. This allows for the selective pull-down of tumor-derived exosomes from patient serum, significantly improving the signal-to-noise ratio for downstream biomarker discovery.
Phosphoproteomics for Kinase Signaling
Deciphering Resistance: Resistance to targeted therapies (like Lapatinib) often involves compensatory kinase activation. Our Phosphoproteomics service analyzes the phosphorylation status of key signaling proteins packed into exosomes, providing a "liquid biopsy" view of the tumor's intracellular kinase activity without needing a tissue biopsy.
3D Organoid Functional Assays
The Clinical Avatar: 2D cell lines often fail to mimic clinical drug responses. We use Breast Cancer Organoids as recipient models. By adding exosomes to these 3D systems, we can accurately evaluate how TDEs (Tumor-Derived Exosomes) modulate tumor architecture, invasiveness, and resistance to chemotherapy in a physiologically relevant context.
Application Spotlight: Exosomal miR-105 Promotes Metastasis
This analysis highlights a seminal study demonstrating how breast cancer exosomes destroy vascular barriers to facilitate distant spread.
Featured Technologies:
- Small RNA Sequencing
- In Vitro Cellular Functional Assays
Literature Interpretation:
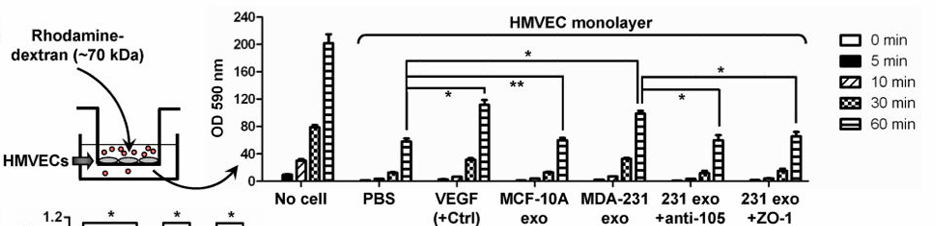 Figure 2. Permeability measurement of HMVEC monolayers treated with VEGF and other conditions, using rhodamine-dextran. (Zhou W, et al., 2014)
Figure 2. Permeability measurement of HMVEC monolayers treated with VEGF and other conditions, using rhodamine-dextran. (Zhou W, et al., 2014)
Metastasis is the leading cause of death in breast cancer. Researchers identified that exosomes secreted by metastatic breast cancer cells contain high levels of miR-105. Upon release, these exosomes are taken up by endothelial cells in distant organs. The study demonstrated that exosomal miR-105 targets and downregulates ZO-1, a tight junction protein. This destruction of the vascular barrier increases vessel permeability, allowing cancer cells to easily extravasate into the lung and brain. This mechanism explains the high metastatic potential of certain breast cancers and validates the importance of functional assays (like permeability testing) in exosome research.
Start Your Breast Cancer Project
Leverage our comprehensive platform to accelerate your discovery, from biomarkers to therapeutic targets.
How It Works: Our Project Pathway
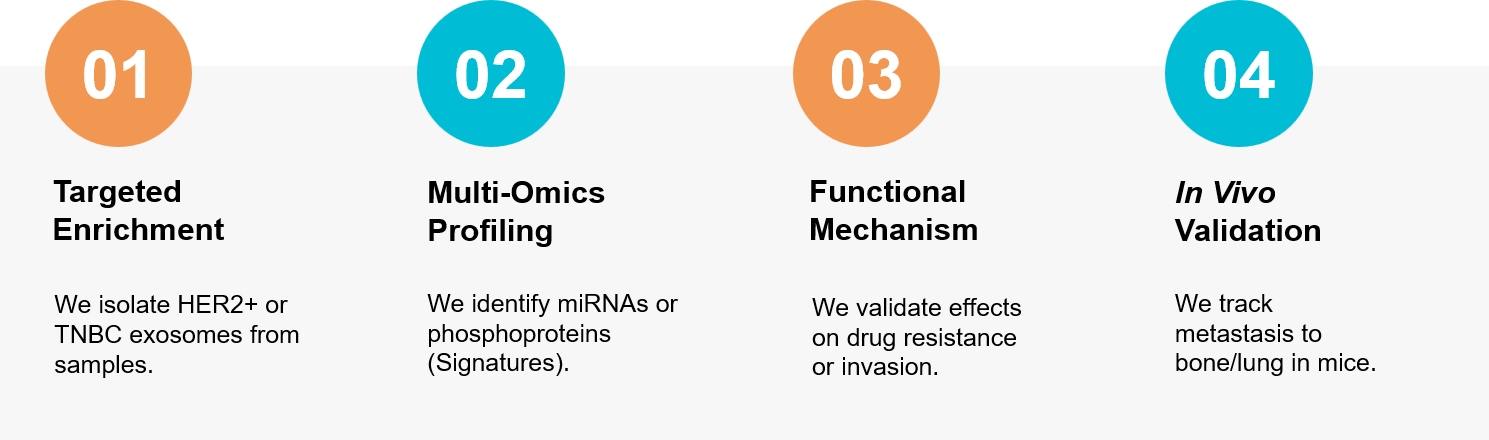 Figure 3. Our integrated workflow for isolating subtype-specific breast cancer exosomes and validating their role in metastasis and therapeutic resistance. (Creative Biostructure)
Figure 3. Our integrated workflow for isolating subtype-specific breast cancer exosomes and validating their role in metastasis and therapeutic resistance. (Creative Biostructure)
Ready to uncover the next breakthrough in breast cancer biomarkers or therapy? Our oncology experts are available to build a custom study plan tailored to your research goals. Contact us today to discuss your project.
References
- Loric S, Denis JA, Desbene C, et al. Extracellular Vesicles in Breast Cancer: From Biology and Function to Clinical Diagnosis and Therapeutic Management. Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 13;24(8):7208.
- Zhou W, Fong MY, Min Y, et al. Cancer-secreted miR-105 destroys vascular endothelial barriers to promote metastasis. Cancer Cell. 2014 Apr 14;25(4):501-15.