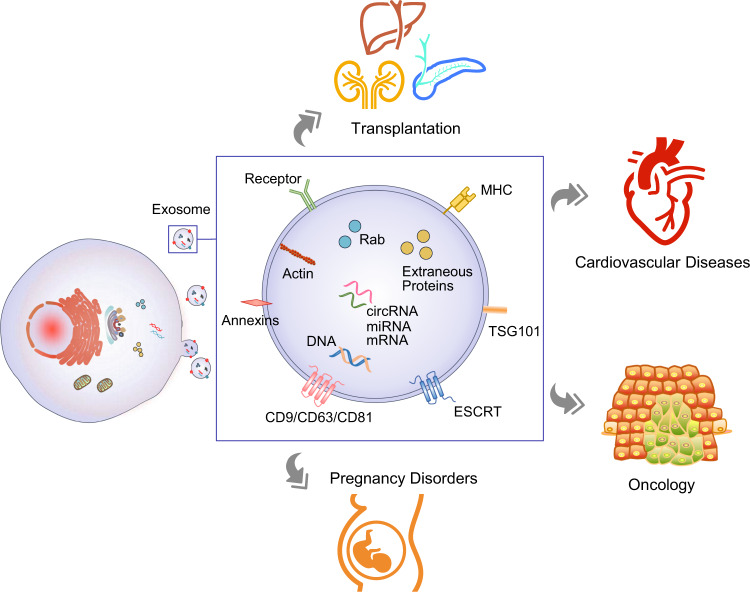
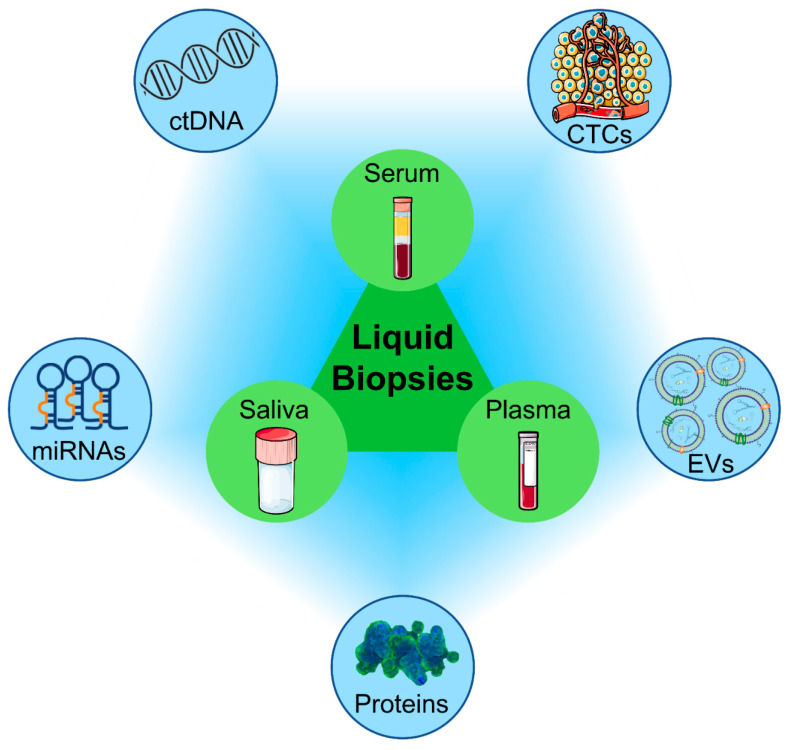
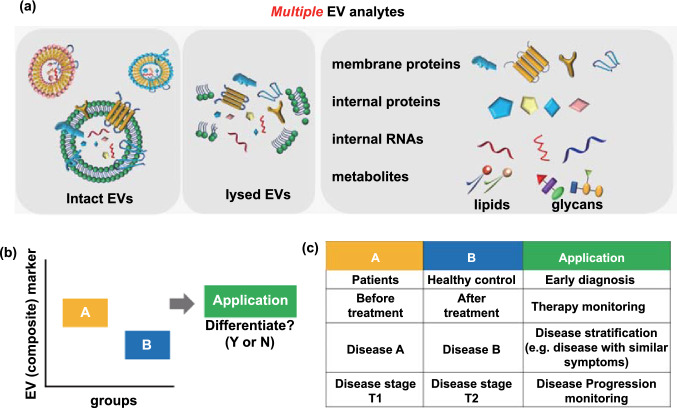
Extracellular Vesicle Biomarker Discovery
The promise of liquid biopsy lies in detecting disease before it becomes clinically visible. While cell-free DNA (cfDNA) offers genetic insight, it fails to capture the dynamic proteomic and transcriptomic state of the tissue. Extracellular Vesicles (EVs) fill this gap.
We provide comprehensive EV biomarker discovery services. Unlike targeted assays that look for what you already know, our unbiased multi-omics platform (NGS & Proteomics) allows you to discover de novo biomarkers—novel miRNAs, proteins, or lipids—hidden within complex biofluids. Accelerate your transition from discovery to clinical validation with our optimized "sample-to-signature" workflow.
The Discovery Challenge
Identifying a reliable biomarker in plasma or urine is a technical hurdle. The target vesicles are rare, and the background noise is high.
- High Dynamic Range: Blood proteins (albumin, immunoglobulins) exist at concentrations millions of times higher than EV biomarkers, masking the signal in Mass Spectrometry.
- Low RNA Input: EVs carry limited RNA cargo. Standard sequencing protocols often fail to generate sufficient library complexity from low-volume clinical samples.
- Heterogeneity: A "bulk" isolation might mix tumor-derived EVs with healthy host EVs, diluting the disease-specific signature.
Our platform addresses these specific bottlenecks to ensure high-sensitivity discovery.
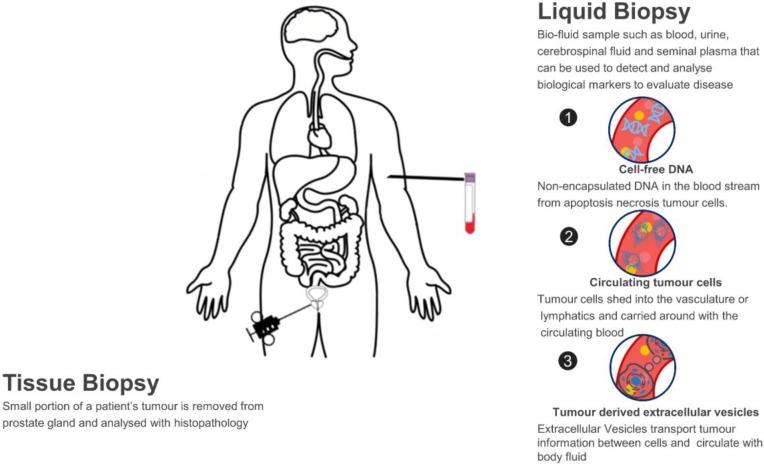 Figure 1. Liquid Biopsy for Prostate Cancer (PCa) Diagnosis: A non-invasive method utilizing bio-fluid samples to detect and analyze cell-free DNA, circulating tumor cells, and tumor-derived extracellular vesicles as biological markers for disease evaluation. (Pang B, et al., 2020)
Figure 1. Liquid Biopsy for Prostate Cancer (PCa) Diagnosis: A non-invasive method utilizing bio-fluid samples to detect and analyze cell-free DNA, circulating tumor cells, and tumor-derived extracellular vesicles as biological markers for disease evaluation. (Pang B, et al., 2020)
Our Biomarker Discovery Workflow
We offer a streamlined "Sample-to-Data" pipeline designed specifically for clinical biofluids.
| Discovery Phase | Our Specialized Approach & Solution | Key Services Applied |
|---|---|---|
| Sample Prep & Enrichment | Depletion & Enrichment: We use optimized Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC) or Immunoaffinity Capture to remove high-abundance plasma proteins (like albumin) and lipoproteins. This enrichment step is critical for improving the depth of coverage in downstream Omics analysis. | Biofluid Exosome Isolation, Exosome Purification by Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC), Exosome Isolation by Immunoaffinity Capture |
| Transcriptomic Discovery | Small RNA-Seq & Long RNA-Seq: We utilize specialized library prep kits optimized for low-input samples. We comprehensively profile exosomal miRNAs, lncRNAs, and circRNAs, which are often more stable and specific biomarkers than linear mRNAs in biofluids. | Exosomal Small RNA and miRNA Sequencing, Exosomal lncRNA Sequencing, Exosomal circRNA Sequencing |
| Proteomic Discovery | Deep Profiling: We employ Label-Free or TMT-labeled Quantitative Proteomics. By digesting proteins from purified EVs, we can identify thousands of proteins, including membrane-bound markers and cytosolic cargo, to find unique disease signatures. | Exosome Quantitative Proteomics, Exosome Biomarker Protein Screening |
| Bioinformatics & Selection | Statistical Selection: Raw data is not a result. Our bioinformatics pipeline performs normalization, differential expression analysis, and ROC curve analysis to rank candidates based on diagnostic power (Sensitivity/Specificity). | Exosome Multi-Omics Integration, Custom Exosome Panels for Disease Biomarkers |
Core Technologies for Your Discovery Program
We deploy specific technologies to maximize the breadth and depth of your screening.
Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) for EVs
Unbiased RNA Profiling: We don't just use arrays; we sequence. This allows for the discovery of novel miRNAs or distinct isoforms that are unique to the disease state. Our pipeline is optimized to handle the short read lengths and specific adapter ligation requirements of exosomal small RNAs, ensuring we capture the full transcriptomic landscape.
High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS)
Global Protein Quantification: We utilize high-resolution instruments (e.g., Orbitrap) to perform shotgun proteomics on your EV samples. This technology is essential for discovering surface protein markers that can later be developed into practical immunoassays (ELISA) or flow cytometry panels for clinical use.
Multi-Omics Integration
Combined Power: The strongest biomarkers are often combinatorial. We integrate RNA and Protein datasets from the same sample to identify multi-analyte signatures. For example, correlating the upregulation of a specific miRNA with the downregulation of its target protein within the EV cargo provides stronger biological validation.
Application Spotlight: The First Glioblastoma RNA Biomarker
This analysis highlights the foundational study that established EVs as a source for tumor-specific genetic mutations in biofluids.
Featured Technologies:
- Serum EV Isolation
- RNA Analysis (RT-PCR/Seq)
Literature Interpretation:
This seminal paper launched the field of exosome diagnostics by addressing the difficulty of monitoring Glioblastoma (GBM) without invasive surgery. The researchers isolated EVs (microvesicles) from the serum of GBM patients and analyzed their RNA content. They successfully detected the EGFRvIII mutation—a specific tumor marker—within these serum EVs, finding it to be identical to the mutation present in the tumor tissue. This breakthrough proved that serum EVs provide a reliable "genetic snapshot" of the tumor, validating our service model of using biofluid EV screening to discover specific mutation-bearing RNA biomarkers.
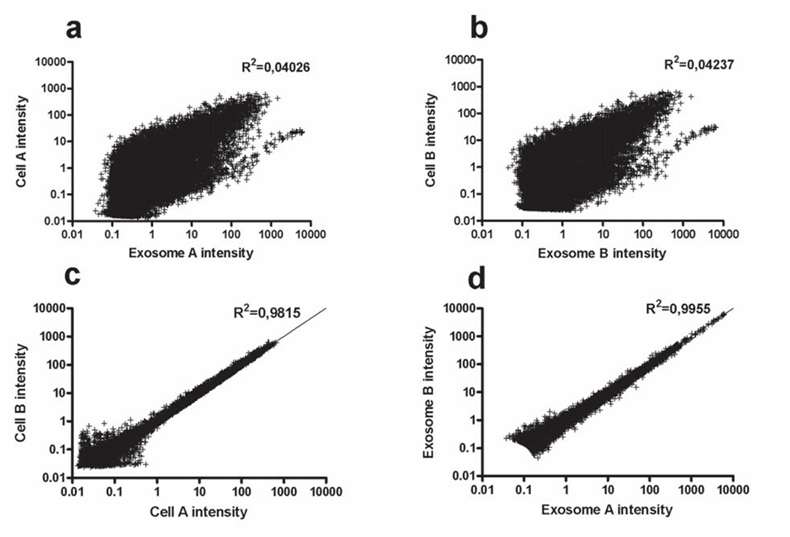 Figure 2. Analysis of microvesicle RNA expression patterns: (a, b) Scatterplots demonstrate a lack of correlation between mRNA levels in microvesicles and donor cells across two experiments. (c, d) In contrast, mRNA intensities within the same cell type or between different microvesicle preparations show a strong correlation. (Skog J, et al., 2008)
Figure 2. Analysis of microvesicle RNA expression patterns: (a, b) Scatterplots demonstrate a lack of correlation between mRNA levels in microvesicles and donor cells across two experiments. (c, d) In contrast, mRNA intensities within the same cell type or between different microvesicle preparations show a strong correlation. (Skog J, et al., 2008)
Start Your Discovery Project
We make getting started straightforward. Our process is designed to be collaborative and transparent.
How It Works: Our Project Pathway
 Figure 3. Our unbiased discovery pipeline for identifying de novo biomarkers from clinical biofluids. (Creative Biostructure)
Figure 3. Our unbiased discovery pipeline for identifying de novo biomarkers from clinical biofluids. (Creative Biostructure)
Ready to find the needle in the haystack? Our scientific team is available for a free consultation to discuss your biomarker discovery strategy. Contact us today to discuss your project.
References
- Pang B, Zhu Y, Ni J, et al. Extracellular vesicles: the next generation of biomarkers for liquid biopsy-based prostate cancer diagnosis. Theranostics. 2020 Jan 16;10(5):2309-2326.
- Skog J, Würdinger T, van Rijn S, et al. Glioblastoma microvesicles transport RNA and proteins that promote tumour growth and provide diagnostic biomarkers Nat Cell Biol. 2008 Dec;10(12):1470-6.