Exosome-Based Companion Diagnostics
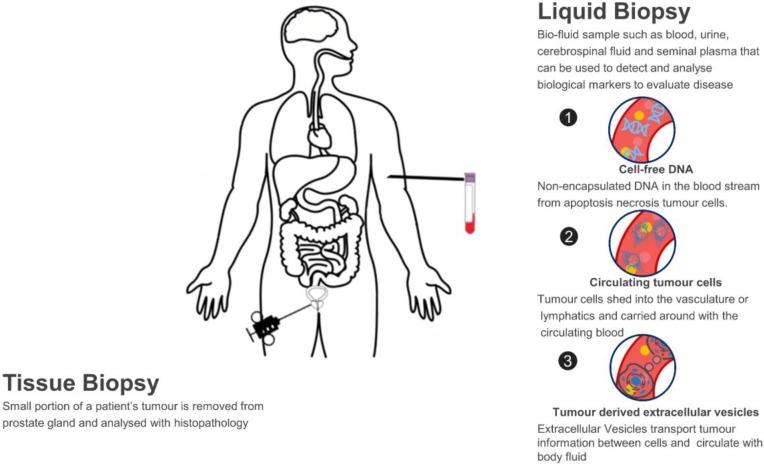
The success of targeted therapies and immunotherapies depends on selecting the right patient. However, traditional tissue biopsies are static, invasive, and often fail to capture the spatial and temporal heterogeneity of the tumor. Relying on archival tissue can lead to misdiagnosis of the current molecular status.
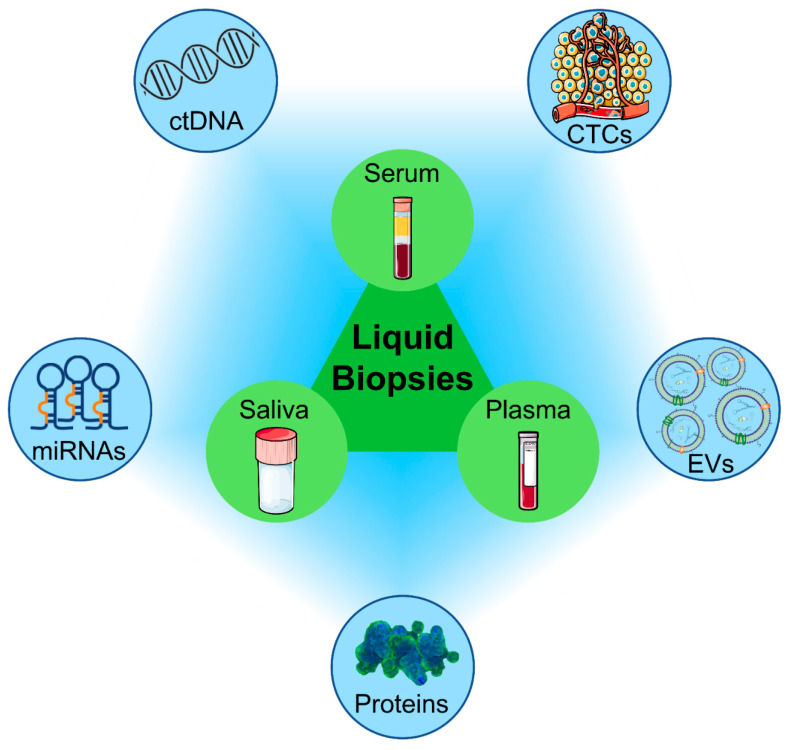
We provide specialized Exosome-Based Companion (CDx) Diagnostics solutions. By analyzing circulating exosomes—which carry the real-time expression levels of drug targets (e.g., PD-L1, HER2, EGFR) from the tumor—we help pharmaceutical partners develop robust liquid biopsy assays. These assays stratify patients, predict treatment response, and monitor the emergence of resistance mechanisms dynamically.
Why Exosomes are the Future of CDx?
Exosomes solve the "sampling error" of tissue biopsies. They provide a systemic view of the tumor burden and drug target availability.
- Real-Time Target Profiling: Exosomes reflect the current protein/RNA expression of the tumor. For example, exosomal PD-L1 levels often correlate better with immunotherapy response than PD-L1 levels in old tissue blocks.
- Overcoming Heterogeneity: A single blood draw captures exosomes released from both primary tumors and multiple metastatic sites, providing a comprehensive molecular profile that a single-site needle biopsy cannot match.
- Non-Invasive Monitoring: You can test patients serially (e.g., every cycle) to track dynamic changes in the drug target or detect the emergence of resistance mutations (e.g., T790M) weeks before radiological progression.
- Preserved Integrity: Exosomes protect RNA targets from degradation, enabling the detection of complex fusion genes (e.g., ALK, ROS1) in plasma with higher sensitivity than cfDNA alone.
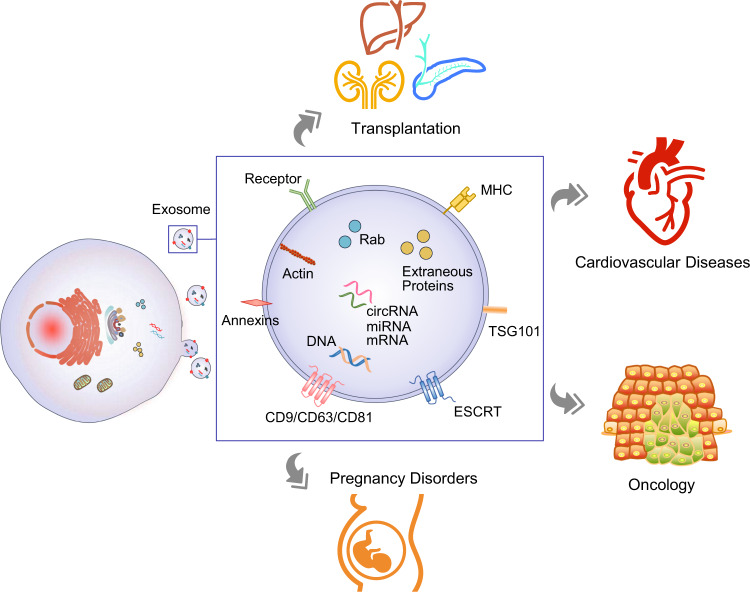 Figure 1. Overview of exosome biogenesis, secretion, composition, and clinical applications in liquid biopsy. Exosomes, derived from multivesicular bodies, carry molecular cargo from parent cells and are valuable in diagnosing various diseases. (Zhou B, et al., 2020)
Figure 1. Overview of exosome biogenesis, secretion, composition, and clinical applications in liquid biopsy. Exosomes, derived from multivesicular bodies, carry molecular cargo from parent cells and are valuable in diagnosing various diseases. (Zhou B, et al., 2020)
Our CDx Development Workflow
We offer a phased approach to co-develop diagnostic assays alongside your therapeutic pipeline, from biomarker verification to clinical validation.
| Development Phase | Our Specialized Approach & Solution | Key Services Applied |
|---|---|---|
| Target Feasibility Study | Proof of Concept: We isolate exosomes from patient plasma or cell line models to verify that your specific drug target (e.g., a surface receptor or kinase) is present and detectable on/in exosomes using high-sensitivity ELISA or FACS. | Exosome Surface Marker Analysis, Exosome Characterization by NanoFCM |
| Assay Prototype Design | Method Development: We optimize a robust, scalable assay (e.g., dPCR for mutations or Simoa/ELISA for proteins) suitable for clinical use. We establish the Limit of Detection (LOD) and verify linearity in surrogate matrices. | Liquid Biopsy via Exosomal miRNA/Protein, Custom Exosome Panels for Disease Biomarkers |
| Clinical Verification | Retrospective Testing: We screen a cohort of banked patient samples (responders vs. non-responders) to correlate exosomal marker levels with clinical outcomes (PFS/OS), establishing preliminary cut-off values for patient selection. | Exosome Multi-Omics Integration, In Vivo Exosome Functional Assays |
| Analytical Validation | Robustness Testing: We rigorously test the assay for reproducibility, precision, and stability (freeze-thaw cycles) to ensure it meets the stringent quality standards required for regulatory submission. | Exosome Purity Analysis, Exosome Quality Control |
Core Technologies for CDx Programs
We focus on the specific biomarkers that drive decision-making in oncology and autoimmunity.
Exosomal Immuno-Oncology (IO) Markers
Predicting Checkpoint Inhibitor Response: Circulating exosomal PD-L1 has emerged as a critical predictor of response to anti-PD-1 therapy. We utilize high-sensitivity immunoassays to quantify PD-L1 on the surface of exosomes, helping you identify non-responders who might have "cold" tumors despite positive tissue staining.
Mutation-Based Stratification (EGFR/KRAS)
Tracking Resistance: For targeted therapies (e.g., TKIs), we develop dPCR or NGS assays to detect resistance mutations (like EGFR T790M or KRAS G12C) carried in exosomal RNA/DNA. This allows for the timely switch to second- or third-line therapies.
Multi-Analyte Panels
Complex Signatures: Response often depends on multiple factors. We integrate exosomal RNA and protein data to build multi-analyte classifiers (e.g., Tumor Mutational Burden + Interferon Signature) that offer superior predictive power compared to single biomarkers.
Application Spotlight: Exosomal PD-L1 Predicts Immunotherapy Outcome
This analysis highlights how exosomal proteins serve as superior predictive biomarkers for patient stratification in immunotherapy.
Featured Technologies:
- Exosomal Protein Quantification
- Clinical Correlation Analysis
Literature Interpretation:
This landmark study addressed the failure of tissue biopsies to accurately predict responses to anti-PD-1 therapy in metastatic melanoma. The researchers discovered that PD-L1 is not just on the tumor cell surface but is actively released on exosomes into the circulation. By isolating and quantifying circulating exosomal PD-L1, they found that patients with high pre-treatment levels of exosomal PD-L1 were less likely to respond to pembrolizumab (Keytruda), and changes during treatment correlated with tumor burden. This finding demonstrates that circulating exosomal proteins can serve as a real-time "liquid biopsy" to stratify patients and monitor therapeutic efficacy.
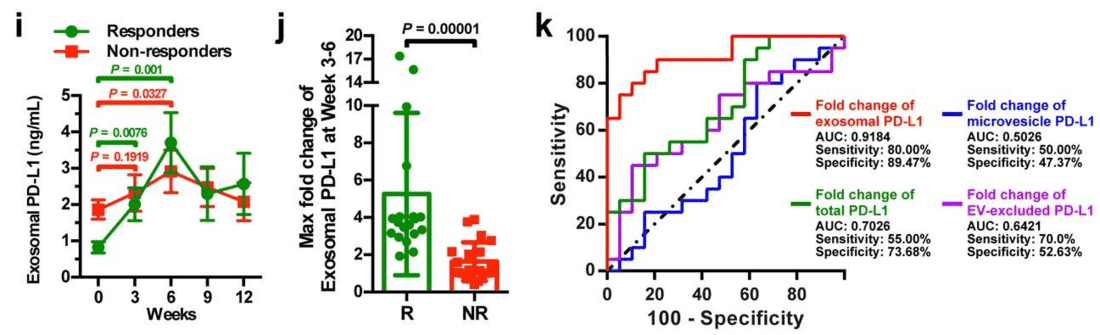 Figure 2. Analysis of circulating exosomal PD-L1 levels to differentiate clinical responders from non-responders to pembrolizumab treatment. (i) Shows PD-L1 levels in responders and non-responders over time; (j) compares the maximum fold change in PD-L1 levels between groups; (k) presents an ROC curve for the predictive value of PD-L1 changes. (Chen G, et al., 2018)
Figure 2. Analysis of circulating exosomal PD-L1 levels to differentiate clinical responders from non-responders to pembrolizumab treatment. (i) Shows PD-L1 levels in responders and non-responders over time; (j) compares the maximum fold change in PD-L1 levels between groups; (k) presents an ROC curve for the predictive value of PD-L1 changes. (Chen G, et al., 2018)
Start Your CDx Partnership
We make getting started straightforward. Our process is designed to be collaborative and transparent.
How It Works: Our Project Pathway
 Figure 3. Our phased approach for developing liquid biopsy assays to predict and monitor therapeutic response. (Creative Biostructure)
Figure 3. Our phased approach for developing liquid biopsy assays to predict and monitor therapeutic response. (Creative Biostructure)
Ready to improve your clinical trial success rate? Our scientific team is available for a free consultation to discuss your companion diagnostic strategy. Contact us today to discuss your project.
References
- Zhou B, Xu K, Zheng X, et al. Application of exosomes as liquid biopsy in clinical diagnosis. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020 Aug 3;5(1):144.
- Chen G, Huang AC, Zhang W, et al. Exosomal PD-L1 contributes to immunosuppression and is associated with anti-PD-1 response. Nature. 2018 Aug;560(7718):382-386.