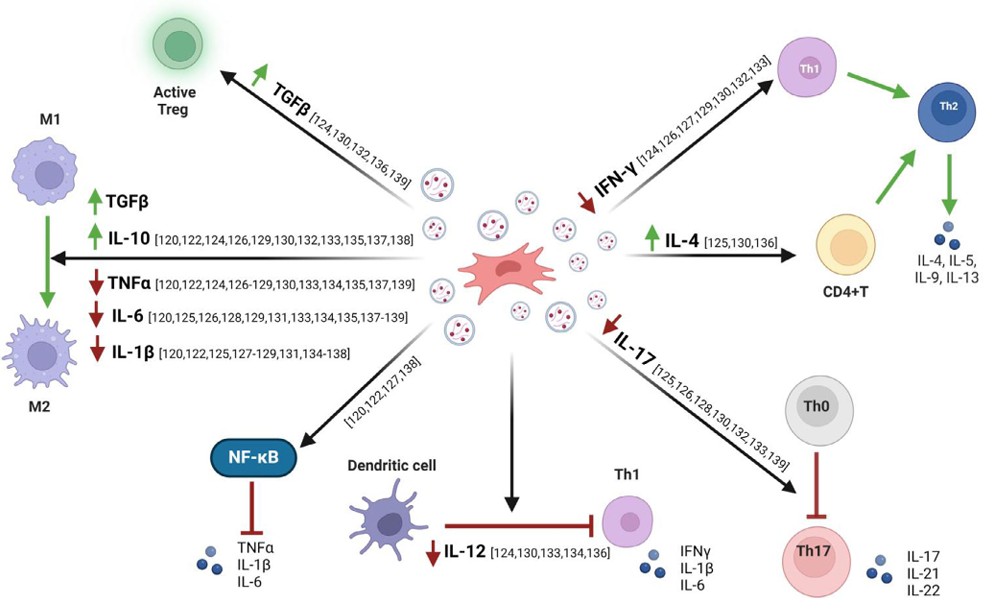
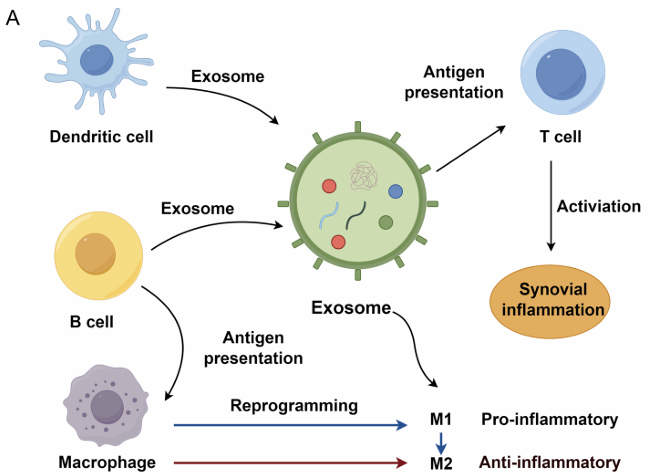
Exosome-Based Vaccine Development
While Lipid Nanoparticles (LNPs) have validated the concept of mRNA vaccines, they often face challenges regarding stability, cold-chain logistics, and inflammatory side effects. Exosomes represent the next evolution in vaccine technology. As nature's own antigen-presenting vehicles, they offer a biocompatible platform to deliver viral antigens or tumor neoepitopes with precision.
We provide end-to-end exosome-based vaccine development solutions. Whether you are developing Dendritic Cell-derived Exosomes (DEX) for cancer immunotherapy or engineering exosomes to display viral spike proteins for infectious disease, our platform covers the entire workflow from antigen design to immunogenicity validation.
The Exosome Vaccine Advantage
Why shift from synthetic carriers to biological exosomes for vaccine delivery? Exosomes mimic the natural mechanisms of the immune system.
- Natural Antigen Presentation: Exosomes derived from antigen-presenting cells (like Dendritic Cells) naturally carry MHC class I and II molecules, allowing them to directly prime CD4+ and CD8+ T cells.
- Self-Adjuvating Properties: The membrane composition of exosomes can stimulate the innate immune system without the need for toxic synthetic adjuvants, enhancing the adaptive response.
- Surface Display: We can genetically engineer exosomes to display viral antigens (e.g., RBD) in their native conformation on the surface, mimicking the structure of a virus to elicit potent neutralizing antibodies.
- Mucosal Immunity: Unlike many synthetic carriers, exosomes are stable in biological fluids and can be engineered for inhalable or oral delivery, inducing critical mucosal immunity (IgA) in the lungs or gut.
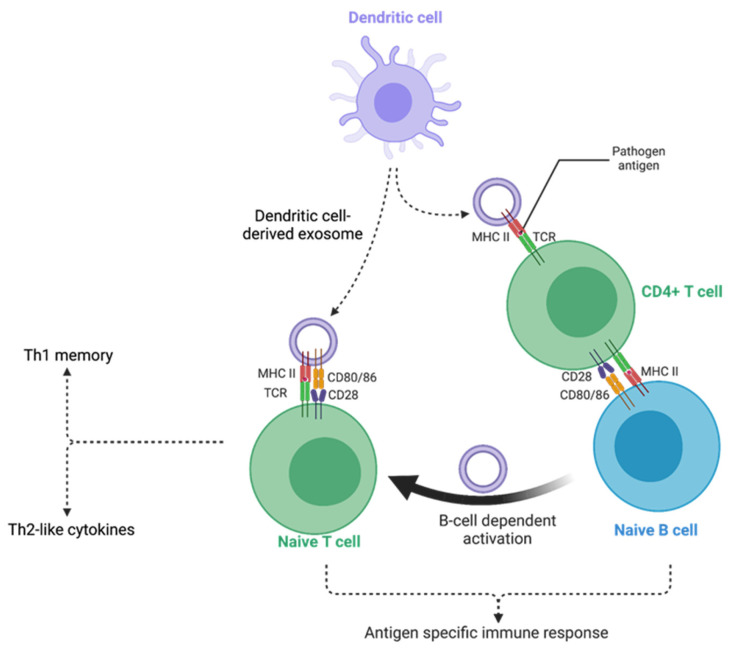 Figure 1. Mechanism of antigen presentation by exosomes leading to immune activation. Exosomes from antigen-primed dendritic cells transfer antigens to naïve dendritic cells, which then present them to T cells, initiating immune responses. (El Safadi D, et al., 2024)
Figure 1. Mechanism of antigen presentation by exosomes leading to immune activation. Exosomes from antigen-primed dendritic cells transfer antigens to naïve dendritic cells, which then present them to T cells, initiating immune responses. (El Safadi D, et al., 2024)
Our Vaccine Development Workflow
We offer a modular pipeline to transform a target antigen into a potent exosome vaccine candidate.
| Development Phase | Our Specialized Approach & Solution | Key Services Applied |
|---|---|---|
| Antigen Engineering | Surface Display Strategy: We construct plasmid vectors to fuse your antigen (Viral Spike or Tumor Neoantigen) to exosomal sorting domains. This ensures the antigen is highly enriched and correctly folded on the exosome surface. | Genetically Engineered Exosome Surface Display, Upstream Process Development (Cell Culture Optimization) |
| Producer Cell Culture | Scalable Bioproduction: We utilize specialized cell lines (e.g., HEK293 or Dendritic Cells) tailored for high-yield exosome secretion. We optimize upstream parameters to maximize the density of the displayed antigen per vesicle. | Exosome Isolation from Cell Culture Supernatants |
| Purification & QC | Vacine-Grade Isolation: Purity is critical for safety. We employ chromatography-based purification to remove host cell proteins and DNA, ensuring the final product meets the stringent quality attributes required for vaccine formulations. | Downstream Purification & Formulation |
| Immunogenicity Testing | In Vivo Validation: We do not just measure particles; we measure immunity. We conduct animal studies to quantify antibody titers (ELISA) and T-cell responses (ELISPOT/Flow Cytometry) following vaccination. | Immunomodulation and Inflammation Assays |
Core Technologies for Vaccine Engineering
We leverage advanced biotechnology to turn exosomes into potent immunological tools.
Genetic Surface Display
To mimic a virus or tumor cell, the immune system must "see" the antigen. We utilize proprietary scaffold proteins (such as the transmembrane domain of PDGFR or Lamp2b) to anchor your target antigen to the outer membrane of the exosome. This high-density surface display allows B-cell receptors to recognize and bind the antigen efficiently, triggering a robust antibody response without the risks associated with live attenuated viruses.
Dendritic Cell Exosome (DEX) Platform
For cancer vaccines, activating T-cells is the goal. We specialize in isolating and culturing exosomes directly from activated Dendritic Cells. These "DEX" vaccines naturally carry the co-stimulatory molecules (CD80, CD86) and MHC complexes needed to present tumor antigens to T-cells, effectively bypassing the need for ex vivo cell manipulation and providing an "off-the-shelf" immunotherapy option.
Adjuvant Co-Loading
To boost the immune response further, we can co-load the exosome lumen with molecular adjuvants, such as STING agonists or TLR ligands. By encapsulating these immune stimulants inside the vesicle, we ensure they are delivered to the same antigen-presenting cell as the antigen, maximizing the immune activation signal while minimizing systemic inflammation.
Application Spotlight: An Inhalable Exosome Vaccine for COVID-19
This analysis demonstrates the potential of engineered exosomes to serve as needle-free, stable vaccines for respiratory viruses.
Featured Technologies:
- Antigen Surface Display
- Immunogenicity Testing
Literature Interpretation:
Addressing the need for stable and mucosal vaccines against SARS-CoV-2, researchers developed a lung-derived exosome platform. They genetically engineered exosomes to display the SARS-CoV-2 Receptor Binding Domain (RBD) on their surface. When administered via inhalation to mice, these RBD-exosomes distributed efficiently into the lung lining and induced potent systemic IgG antibodies as well as mucosal IgA responses. This study confirms that surface-engineered exosomes can serve as robust, shelf-stable vaccine candidates that induce broad immunity in the respiratory tract.
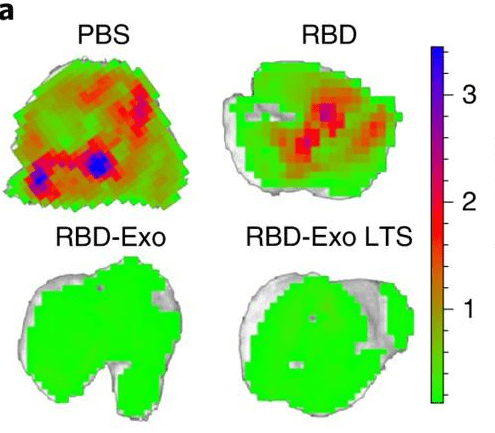 Figure 2. Ex vivo imaging of lung GFP signal after SARS-CoV-2 D614G pseudovirus challenge in immunized mice. RBD-Exo vaccination significantly reduced GFP signal compared to free RBD vaccination. (Wang Z, et al., 2022)
Figure 2. Ex vivo imaging of lung GFP signal after SARS-CoV-2 D614G pseudovirus challenge in immunized mice. RBD-Exo vaccination significantly reduced GFP signal compared to free RBD vaccination. (Wang Z, et al., 2022)
Start Your Vaccine Project
We make getting started straightforward. Our process is designed to be collaborative and transparent.
How It Works: Our Project Pathway
 Figure 3. Our integrated workflow for engineering and validating high-potency exosome-based vaccines. (Creative Biostructure)
Figure 3. Our integrated workflow for engineering and validating high-potency exosome-based vaccines. (Creative Biostructure)
Ready to design a safer, more potent vaccine? Our scientific team is available for a free consultation to discuss your exosome vaccine strategy. Contact us today to discuss your project.
References
- El Safadi D, Mokhtari A, Krejbich M, et al. Exosome-Mediated Antigen Delivery: Unveiling Novel Strategies in Viral Infection Control and Vaccine Design. Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Mar 7;12(3):280.
- Wang Z, Popowski KD, Zhu D, et al. Exosomes decorated with a recombinant SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain as an inhalable COVID-19 vaccine. Nat Biomed Eng. 2022 Jul;6(7):791-805.