Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)-Based Exosome Characterization Service
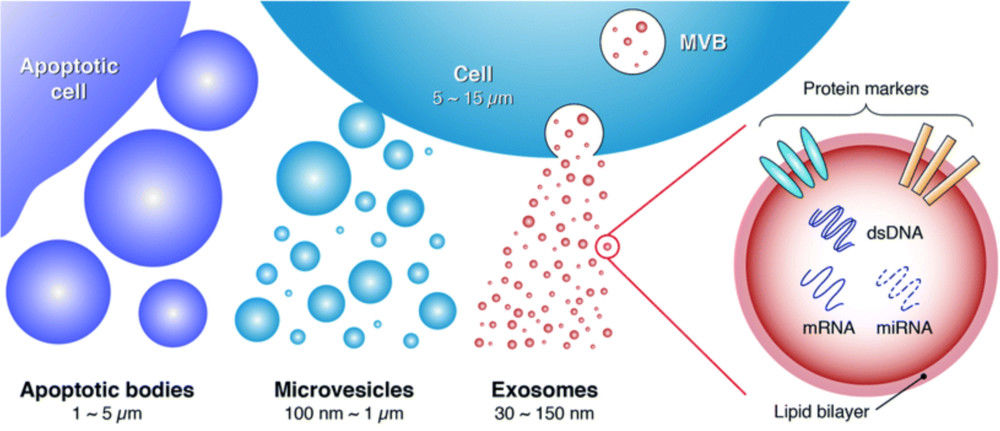
Exosomes are minute extracellular vesicles (EVs) released by diverse cell types and recognized as important mediators of cellular communication and disease mechanisms. For both basic and applied research, a reliable assessment of their structural features is essential to confirm vesicle authenticity, evaluate preparation quality, and support downstream functional studies.
Electron microscopy (EM) has become a cornerstone technology in this field, offering resolution well beyond the limits of light microscopy. In line with the MISEV2023 recommendations, EM provides high-definition visualization of vesicle morphology and enables researchers to distinguish true exosomes from co-isolated nanoparticles or other extracellular components.
What is SEM Analysis of Exosomes?
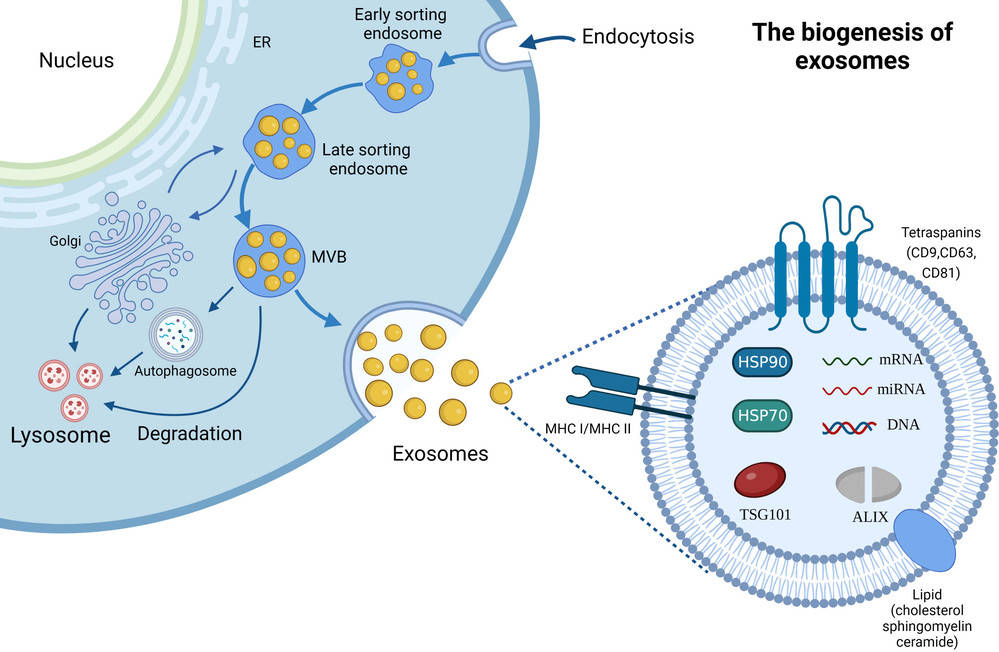
Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) is a powerful method for studying the surface morphology of exosomes at nanometer resolution. Unlike transmission electron microscopy (TEM), which provides internal structural details, SEM captures high-contrast images of the vesicle exterior using backscattered and secondary electron signals.
Because exosomes are non-conductive, they are typically coated with a thin conductive film before SEM imaging. This preparation allows for clear visualization of vesicle surfaces, although it can sometimes alter fine structures. Despite this limitation, SEM is a valuable approach for identifying particle topology, detecting contaminants, and comparing exosomes across isolation methods.
Key Advantages of SEM in Exosome Research:
- High-resolution imaging of vesicle surface architecture.
- Broad applicability across different exosome size ranges.
- Ability to reveal heterogeneity and aggregation states.
- Provides complementary insights alongside TEM, cryo-EM, and nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA).
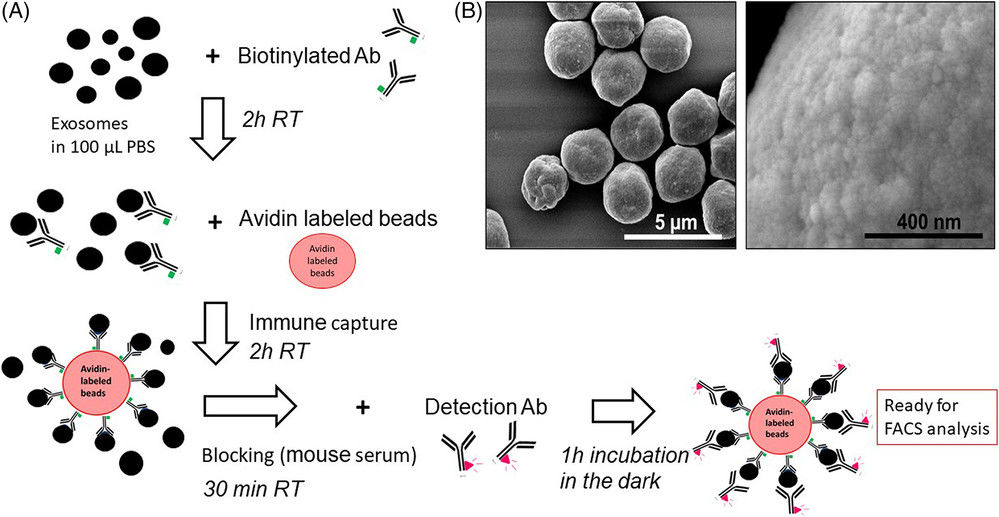
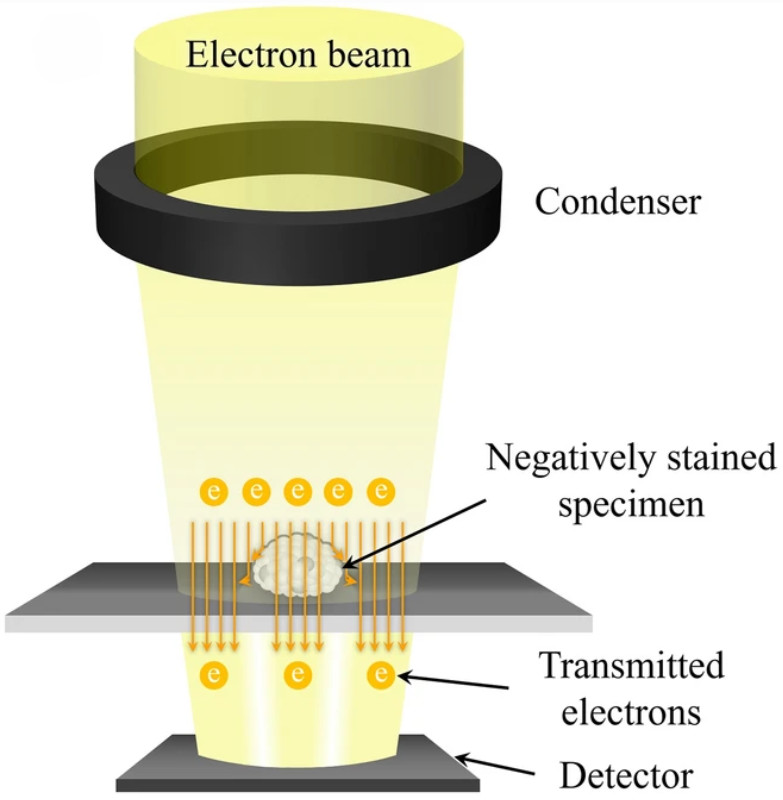
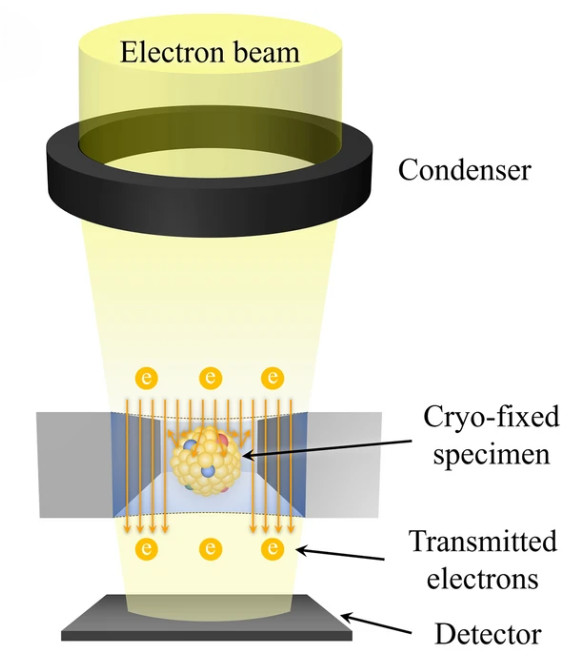
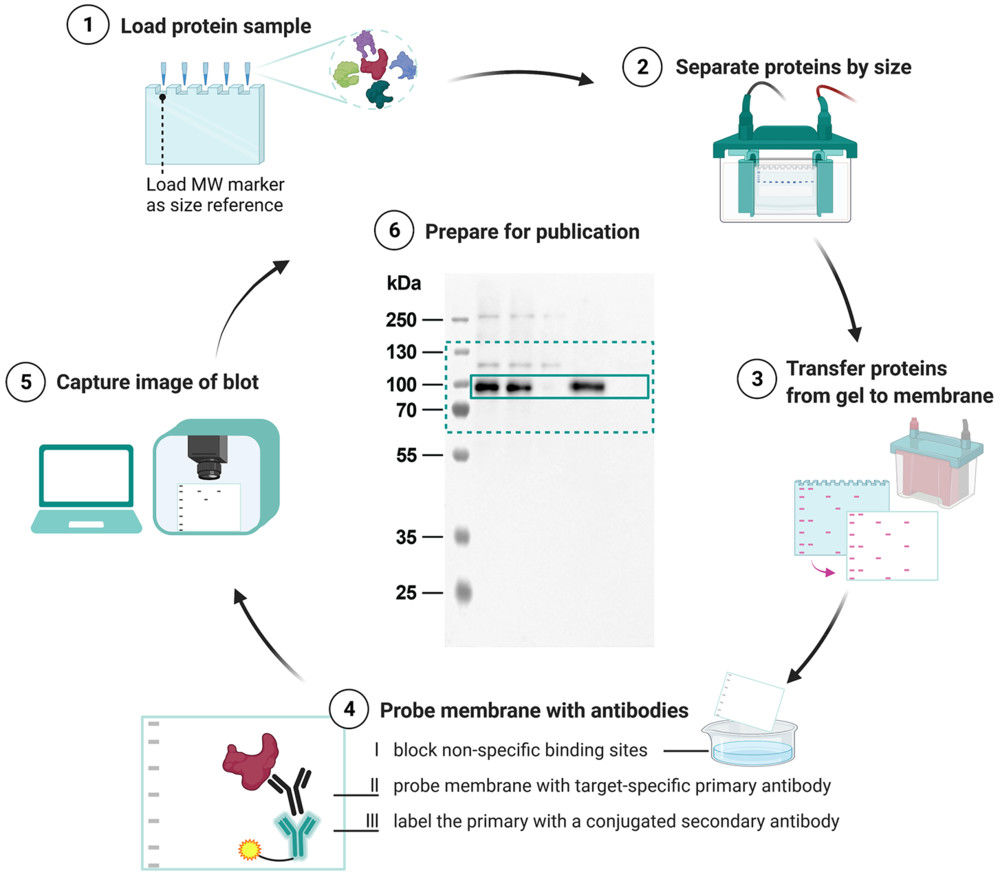
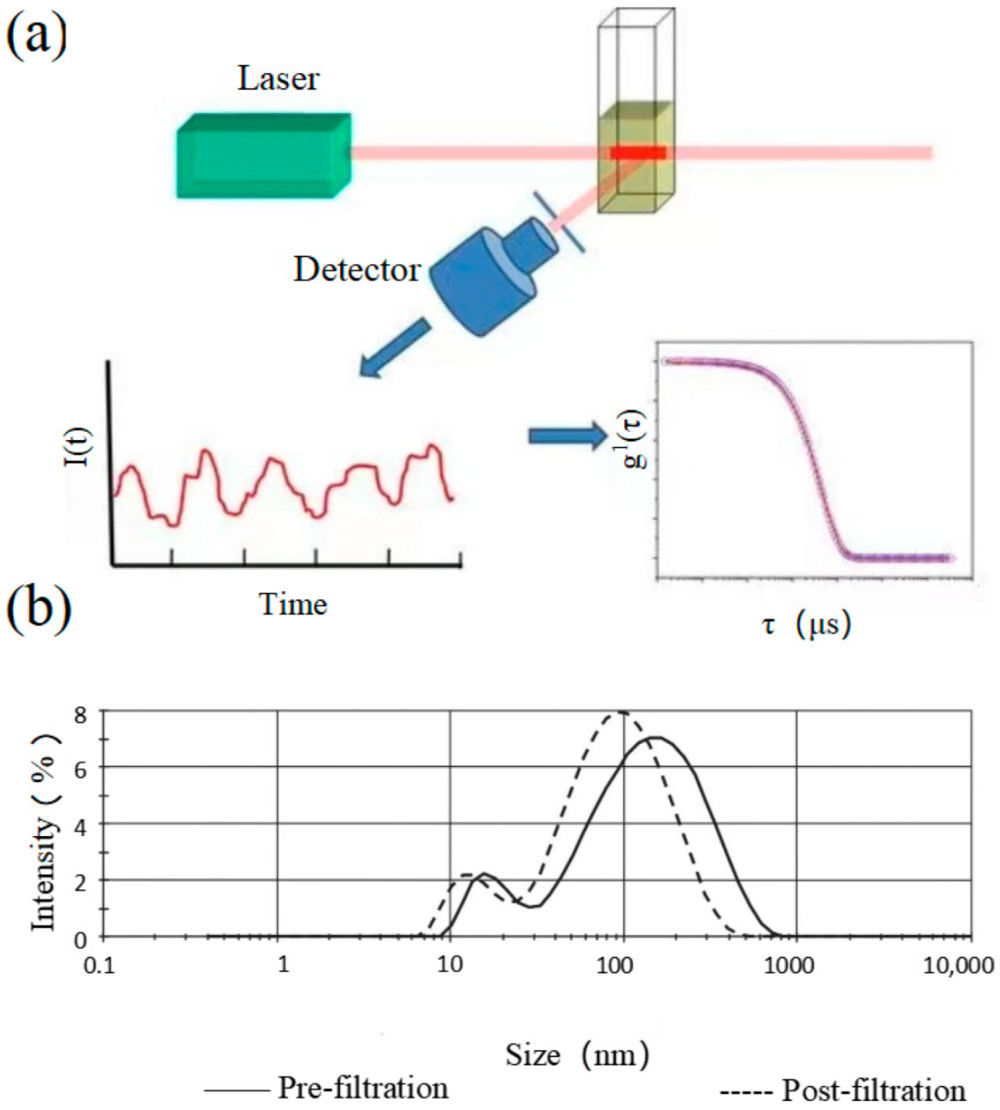
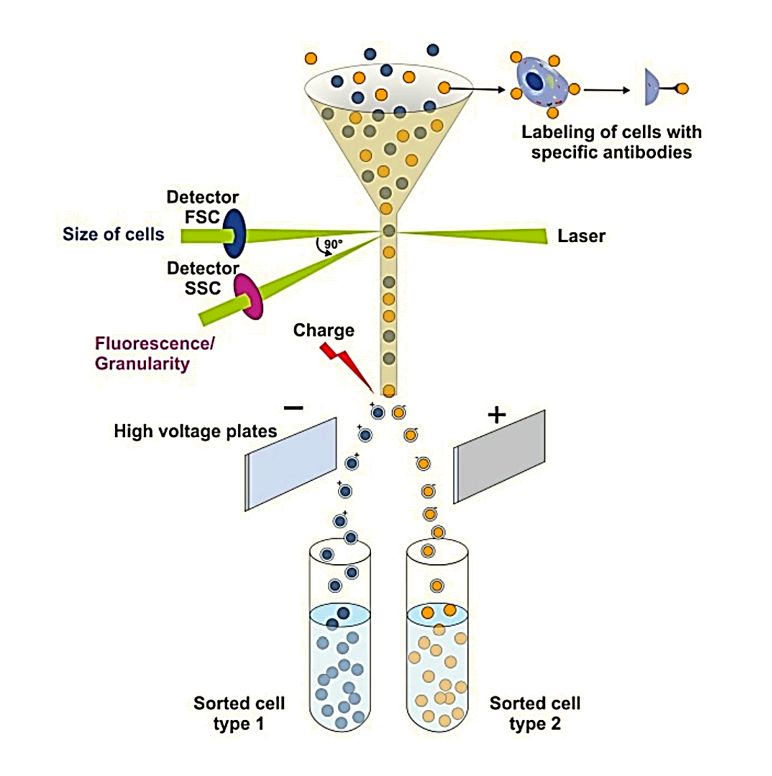
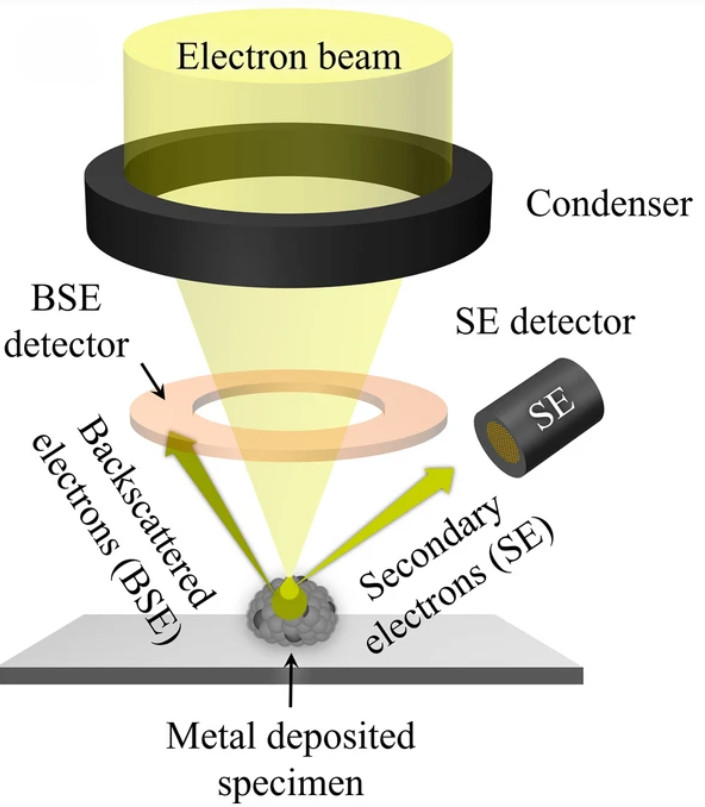 Figure 1. Principle of SEM for EV Characterization. (Kwon Y, et al., 2022)
Figure 1. Principle of SEM for EV Characterization. (Kwon Y, et al., 2022)
SEM vs. TEM and Cryo-TEM for Exosome Characterization
Different electron microscopy approaches provide complementary insights into exosome morphology. While all achieve nanometer-scale resolution, each technique has unique strengths and limitations depending on whether surface features, internal structures, or native states are the focus of analysis.
| Technique | Key Features | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| SEM | Detects backscattered & secondary electrons from coated samples | Excellent for surface morphology, 3D-like imaging, broad size range | Requires metal coating; cannot visualize internal bilayer |
| TEM | Uses transmitted electrons through negatively stained samples | High-resolution images of vesicle interior; widely used standard | Dehydration can distort shape (cup-like artefacts); staining required |
| Cryo-TEM | Imaging of rapidly frozen vesicles in hydrated state | Preserves natural spherical morphology; resolves lipid bilayer; ~2 nm resolution | Technically demanding, lower throughput, costly instrumentation |
Our SEM Exosome Characterization Workflow
Project Consultation & Experimental Planning
Each project starts with a consultation to define research goals and sample background. We then suggest the most suitable imaging strategy and provide guidance on sample submission and storage to maintain vesicle integrity.
Sample Submission & Preparation
Clients may submit pre-purified exosome samples for SEM analysis, or rely on Creative Biostructure's isolation and purification services to obtain high-quality vesicles. Samples are then gently fixed to preserve morphology, coated with a thin conductive layer for compatibility, and carefully adsorbed onto selected substrates to achieve uniform distribution for imaging.
SEM Imaging Process
• High-performance SEM instruments with adjustable accelerating voltages for optimized resolution.
• Multi-scale magnification to capture both fine nanoscale surface details and broader field views.
• Inclusion of calibration standards and control imaging for reproducibility and data accuracy.
Data Processing & Quantitative Analysis
• Generation of both high- and low-magnification SEM images.
• Morphological assessment, including vesicle size distribution, surface roughness, and aggregation states.
• Comparison with isolation controls or reference standards when applicable.
Reporting & Delivery
We deliver a complete report with SEM images, quantitative analysis, and interpretation, fully documented under MISEV2023 guidelines. Data can be provided in formats suitable for publication or internal use, and follow-up consultations are available to support the next steps in exosome research.
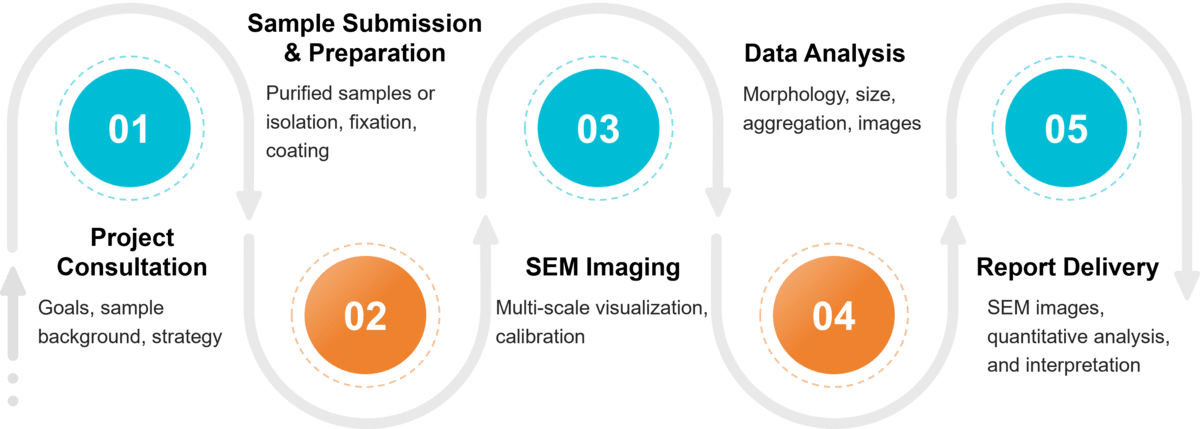 Figure 2. Project Workflow for Exosome Morphology Analysis by Scanning Electron Microscopy. (Creative Biostructure)
Figure 2. Project Workflow for Exosome Morphology Analysis by Scanning Electron Microscopy. (Creative Biostructure)
Sample Requirements for SEM Imaging
To ensure high-quality imaging results, Creative Biostructure provides flexible options for sample submission. Clients may provide pre-purified exosomes or request our exosome isolation service. The following table outlines recommended sample requirements:
| Requirement | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Sample Type | Pre-purified exosomes or biological fluids (e.g., serum, plasma, cell culture supernatant) | Isolation can be performed upon request |
| Minimum Volume | 100–200 µL (for purified exosomes) | Larger volumes may be required for isolation |
| Concentration | ≥1 × 109 particles/mL | Higher concentration improves image clarity |
| Buffer | PBS or other physiologically compatible buffer | Avoid detergents or high salt conditions |
| Storage & Transport | 4 °C short term; -80 °C for long-term storage | Ship samples on dry ice if frozen |
What Deliverables Will You Receive
- High-resolution SEM images at multiple magnifications
- Quantitative analysis of exosome morphology and size distribution
- Documentation of experimental parameters following MISEV2023 guidelines
- Tailored data formats: publication-ready figures, supplementary datasets, or internal QC reports
Applications of SEM in Exosome Research
SEM is widely applied across basic and translational research fields, including:
- Morphological characterization: Confirmation of vesicle shape, size, and surface features.
- Quality control: Assessment of exosome preparations for contaminants such as non-vesicular extracellular particles (NVEPs).
- Comparative isolation studies: Evaluating vesicles obtained from ultracentrifugation, filtration, or chromatography.
- Biomedical research: Supporting oncology, neurology, and immunology studies by validating vesicle integrity before downstream assays.
Why Choose Creative Biostructure?
- Extensive EM Expertise: Our team has years of experience applying SEM, TEM, cryo-EM, and AFM to nanoscale vesicle research.
- Comprehensive Characterization: We integrate SEM with complementary techniques such as TEM exosome imaging and NTA exosomes analysis to provide a complete morphological profile.
- Quality and Reproducibility: All experiments follow internationally recognized standards for reliable, publication-ready data.
- Tailored Solutions: Customized workflows for academic and industrial projects, ranging from exploratory research to translational applications.
Case Study
Case: Improved Isolation and Characterization of NSCLC-Derived Exosomes
Background
Exosome isolation from NSCLC (NCI-1975) cells is often limited by low purity and structural artefacts. This study optimized methods to enhance vesicle integrity for diagnostic applications.
Methods
Exosomes were isolated using combined ultracentrifugation, ultrafiltration, and cryopreservation. Morphology was evaluated by TEM and SEM, and surface markers (CD9, CD63, CD81) were confirmed by Western blot. Statistical analysis compared exosomes with apoptotic vesicles and necrotic bodies.
Results
SEM provided clear surface imaging, complementing TEM data and confirming consistent vesicle size (~64 nm). Exosomes were distinct from apoptotic vesicles (~450 nm) and necrotic bodies (~280 nm). No significant differences were found between SEM and TEM measurements.
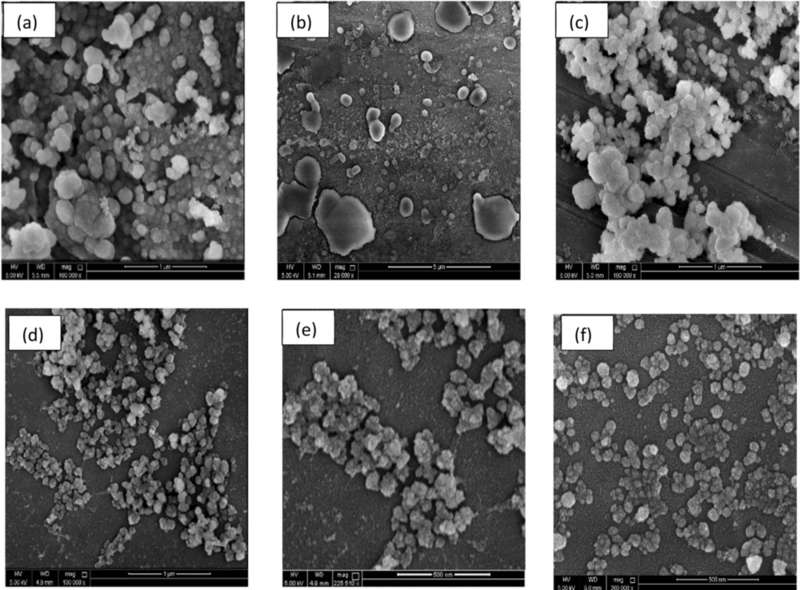 Figure 3. SEM Characterization of Circulating Exosomes and EVs from NSCLC Cells. (a-c) Visualization of apoptotic vesicles (AV) and necrotic bodies (NCB) with diameters ranging from 300-500 nm. (d-e) Exosomes isolated using ultrafiltration. (f) Exosomes purified via ultracentrifugation. (Mahgoub E O, et al., 2023)
Figure 3. SEM Characterization of Circulating Exosomes and EVs from NSCLC Cells. (a-c) Visualization of apoptotic vesicles (AV) and necrotic bodies (NCB) with diameters ranging from 300-500 nm. (d-e) Exosomes isolated using ultrafiltration. (f) Exosomes purified via ultracentrifugation. (Mahgoub E O, et al., 2023)
Conclusion
The integration of ultracentrifugation, ultrafiltration, and cryopreservation improved exosome purity and stability. SEM was critical in validating surface morphology and distinguishing exosomes from other extracellular vesicles, supporting their use in NSCLC research and biomarker development.
At Creative Biostructure, we are dedicated to delivering reliable and reproducible exosome characterization using advanced SEM technology. With strict adherence to MISEV2023 guidelines, our team ensures high-quality data suitable for both academic and industrial applications. Contact us to discuss your project and learn how our SEM services can accelerate your research.
References
- Kwon Y, Park J. Methods to analyze extracellular vesicles at single particle level. Micro and Nano Systems Letters. 2022, 10(1): 14.
- Mahgoub E O, Abdella G M. Improved exosome isolation methods from non-small lung cancer cells (NC1975) and their characterization using morphological and surface protein biomarker methods. Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology. 2023, 149(10): 7505-7514.
- Welsh J A, Goberdhan D C I, O'Driscoll L, et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles (MISEV2023): From basic to advanced approaches. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles. 2024, 13(2): e12404.
Frequently Asked Questions
For any inquiries, our support team is ready to help you get technical support for your research and maximize your experience with Creative Biostructure.