Pancreatic Cancer Exosome Research Services
Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is lethal primarily due to late diagnosis and rapid resistance to chemotherapy (Gemcitabine). Exosomes offer a beacon of hope. They carry the tumor's mutation signature (e.g., KRAS G12D, GPC1) into the blood long before imaging can detect a mass. Furthermore, they act as messengers within the dense tumor stroma, transferring survival signals from Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts (CAFs) to tumor cells to block cell death.
We provide a holistic Pancreatic Cancer Exosome Research Solution. Unlike generalist providers, our platform is engineered to handle the unique challenges of PDAC. Whether you need to develop ultra-sensitive GPC1-targeted detection assays, unravel the mechanisms of Gemcitabine resistance using 3D organoids, or map the Liver Metastasis niche, we offer an integrated portfolio to accelerate your translational research.
Critical Frontiers in PDAC Research
Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (PDAC) remains one of the most lethal malignancies, presenting unique biological barriers.
- The Diagnostic Gap: Most patients are diagnosed at stage IV. Identifying highly specific biomarkers (like GPC1 or mutant KRAS) that can detect lesions at the PanIN stage (precancerous) is the most urgent clinical need.
- The Desmoplastic Barrier: PDAC is characterized by dense fibrosis (stroma) that blocks drug delivery. Research is investigating how exosomes mediate the crosstalk between tumor cells and stellate cells to drive this fibrosis.
- Metabolic Reprogramming: PDAC causes severe cachexia (muscle wasting). Exosomes are suspected to be the systemic messengers that trigger muscle breakdown and metabolic chaos in distant tissues.
- Immunosuppression: The PDAC microenvironment is notoriously immunosuppressive. Understanding how exosomes exclude effector T-cells is vital for making immunotherapy effective in this disease.
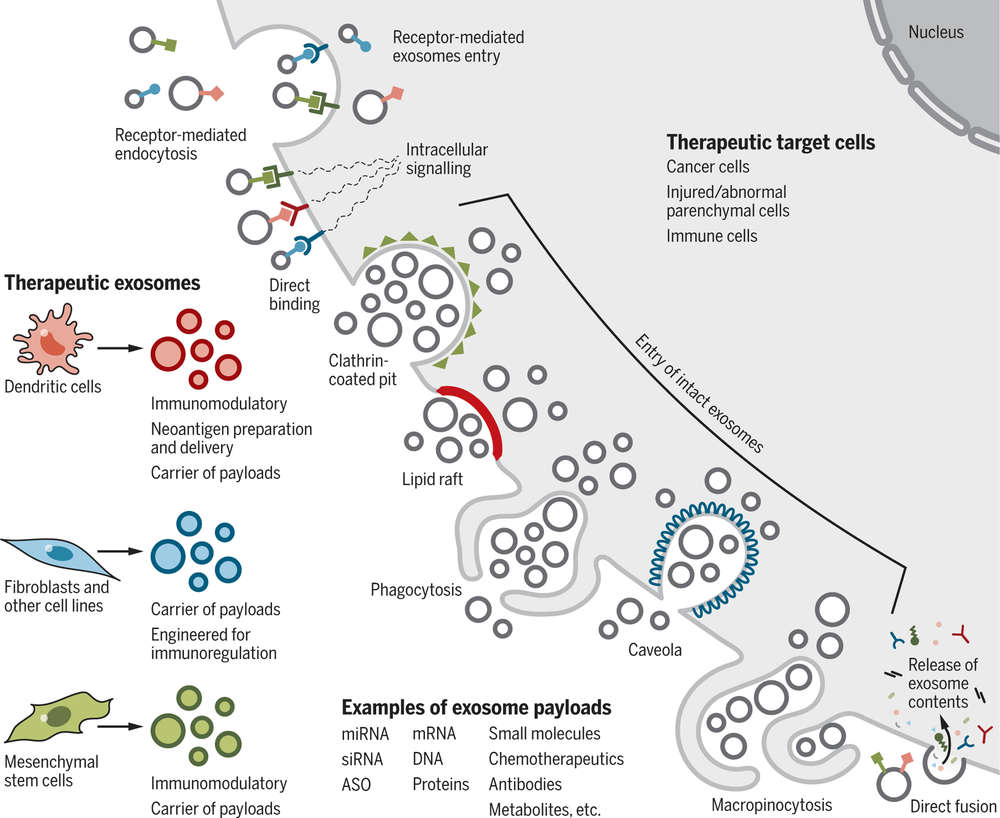
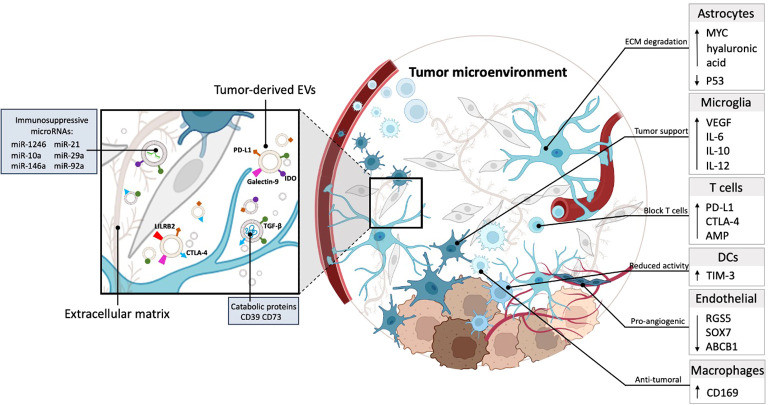
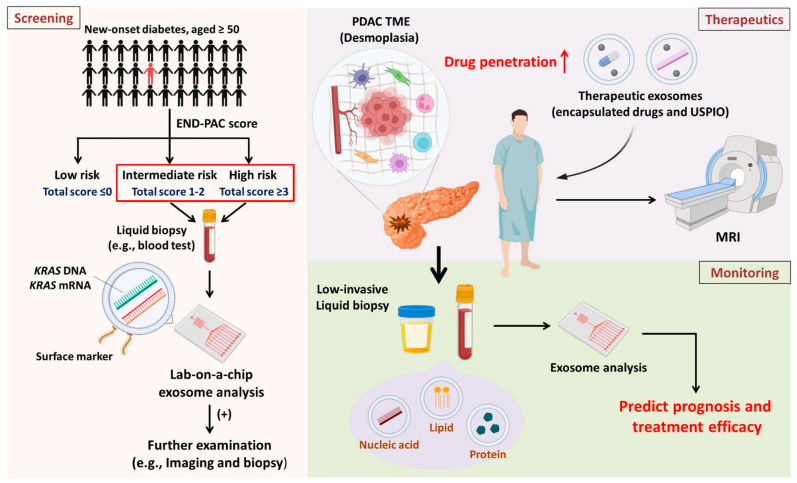 Figure 1. Overview of exosome applications in PDAC screening, therapeutics, and monitoring for high-risk populations. (Hsu SK, et al., 2023)
Figure 1. Overview of exosome applications in PDAC screening, therapeutics, and monitoring for high-risk populations. (Hsu SK, et al., 2023)
Comprehensive Service Portfolio for PDAC
We offer an integrated matrix of services tailored to your specific research focus, covering diagnosis, mechanism, and in vivo validation.
| Research Focus | Our Specialized Approach & Solution | Key Services Applied |
|---|---|---|
| Biomarker Discovery (Diagnosis) | GPC1 Enrichment & Mutation Detection: We use Immuno-Affinity Capture (Anti-GPC1) to enrich tumor exosomes, followed by Digital PCR to quantify KRAS G12D/V mutations with absolute sensitivity. | Exosome Isolation by Immunoaffinity Capture |
| TME & Stroma (Mechanism) | CAF Co-Culture & Ferroptosis: We model the interaction between CAFs and tumor cells. We test if stromal exosomes inhibit Ferroptosis (lipid peroxidation) or promote fibrosis in the microenvironment. | Exosome-protein Interactions Assay |
| Drug Resistance (Function) | Organoid Drug Screening: We utilize Patient-Derived Organoids (PDOs) to test drug sensitivity. We treat organoids with exosomes to measure shifts in IC50 values for Gemcitabine or Paclitaxel. | Exosome Organoid-based Functional Assays |
| In Vivo Validation (Animal Models) | Orthotopic & Metastasis Models: We perform Orthotopic Injection (into the pancreas) to mimic native growth. We track labeled exosomes to the liver to study the formation of the pre-metastatic niche. | In Vivo Exosome Functional Assays |
Core Technologies for Pancreatic Oncology
We highlight specialized technologies that address the unique "stromal barrier" and "low abundance" challenges of PDAC.
Digital PCR (dPCR) for KRAS
Absolute Mutation Quantification: KRAS mutations occur in >90% of PDAC cases but are diluted in blood. Our Digital PCR (dPCR) service partitions samples into thousands of droplets, allowing for the precise detection and quantification of mutant KRAS alleles (G12D, G12V) in exosomal cargo, offering a superior limit of detection compared to qPCR or NGS.
Immuno-Affinity Isolation (GPC1)
The Specificity Key: Glypican-1 (GPC1) is a specific surface marker for PDAC exosomes. We develop custom Immuno-Magnetic Bead protocols to capture GPC1+ exosomes from serum. This enrichment step is critical for downstream proteomics or transcriptomics, ensuring the signal comes from the tumor, not the host.
Exosome Organoid-Based Functional Assays
Modeling Chemoresistance: 2D cell lines cannot replicate the dense stroma of pancreatic cancer. We utilize Pancreatic Cancer Organoids (PDOs) derived from patients. By co-culturing these organoids with exosomes, we can functionally validate whether specific exosomal cargos (like lncRNAs) induce resistance to Gemcitabine or Paclitaxel in a clinically relevant model.
Application Spotlight: Stromal Exosomes Block Ferroptosis to Drive Resistance
This analysis highlights a cutting-edge mechanism where stromal exosomes confer chemoresistance by inhibiting ferroptosis, a key pathway in cell death.
Featured Technologies:
- Small RNA Sequencing
- In Vitro Cellular Functional Assays (Drug Resistance)
Literature Interpretation:
Gemcitabine resistance remains a critical obstacle in pancreatic cancer therapy. This study investigated a novel resistance mechanism involving ferroptosis, an iron-dependent form of cell death. Researchers discovered that Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts (CAFs) within the tumor microenvironment secrete exosomes enriched with miR-423-5p. Upon uptake by pancreatic cancer cells, this exosomal miRNA directly targets and suppresses ACSL4, a key enzyme required for lipid peroxidation. This suppression effectively blocks the ferroptosis pathway, shielding the cancer cells from chemotherapy-induced death and promoting survival. This finding highlights the crucial role of stromal exosomes in modulating metabolic cell death pathways and validates the importance of profiling CAF-derived vesicles to uncover novel therapeutic targets.
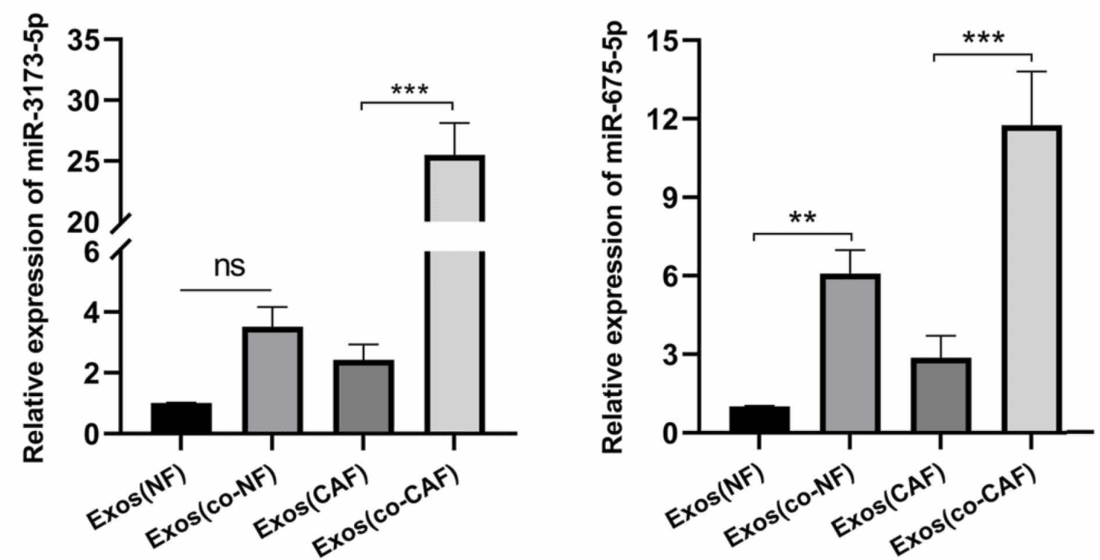 Figure 2. Amplification of miR-3173–5p levels in cancer-associated fibroblast (CAF)-derived exosomes as shown by RT-qPCR analysis. (Qi R, et al., 2023)
Figure 2. Amplification of miR-3173–5p levels in cancer-associated fibroblast (CAF)-derived exosomes as shown by RT-qPCR analysis. (Qi R, et al., 2023)
Start Your PDAC Project
Advance your research on the most challenging cancer with our specialized detection and functional tools.
How It Works: Our Project Pathway
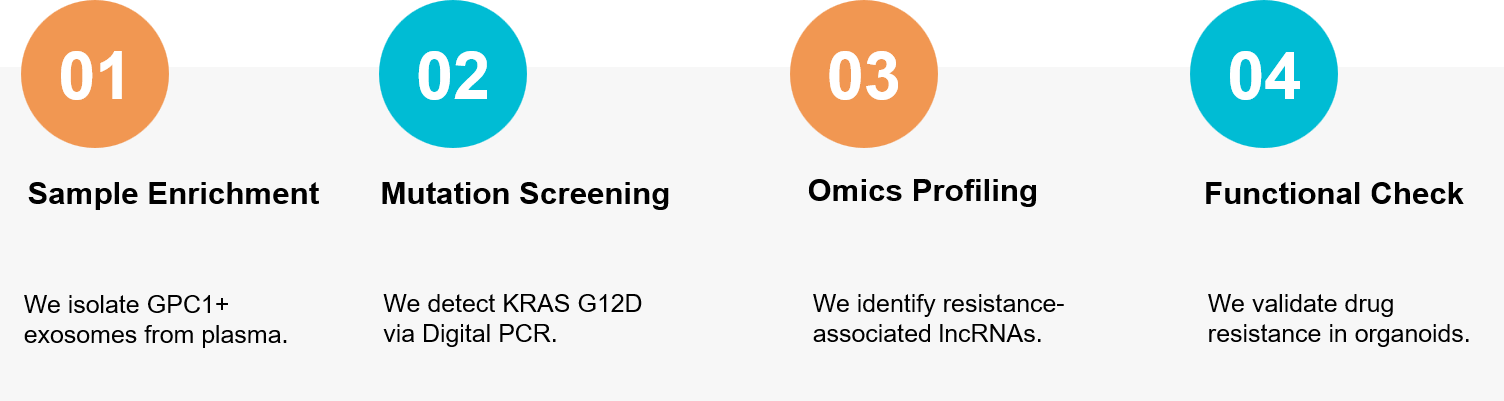 Figure 3. Our integrated workflow for identifying PDAC biomarkers (GPC1, KRAS) and unraveling the mechanisms of chemotherapy resistance using patient-derived organoids. (Creative Biostructure)
Figure 3. Our integrated workflow for identifying PDAC biomarkers (GPC1, KRAS) and unraveling the mechanisms of chemotherapy resistance using patient-derived organoids. (Creative Biostructure)
Ready to tackle the challenges of pancreatic cancer detection and therapy? Our oncology team is available to discuss your specific biomarkers or resistance models. Contact us today to discuss your project.
References
- Hsu SK, Jadhao M, Liao WT, et al. The Role of Exosomes in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Progression and Their Potential as Biomarkers. Cancers (Basel). 2023 Mar 15;15(6):1776.
- Qi R, Bai Y, Li K, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts suppress ferroptosis and induce gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic cancer cells by secreting exosome-derived ACSL4-targeting miRNAs. Drug Resist Updat. 2023 May;68:100960.