Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA)-Based Exosome Characterization Service
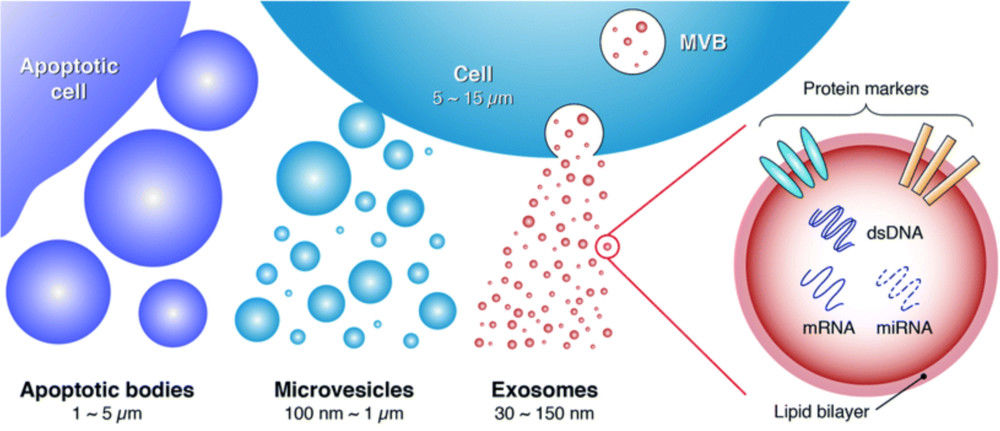
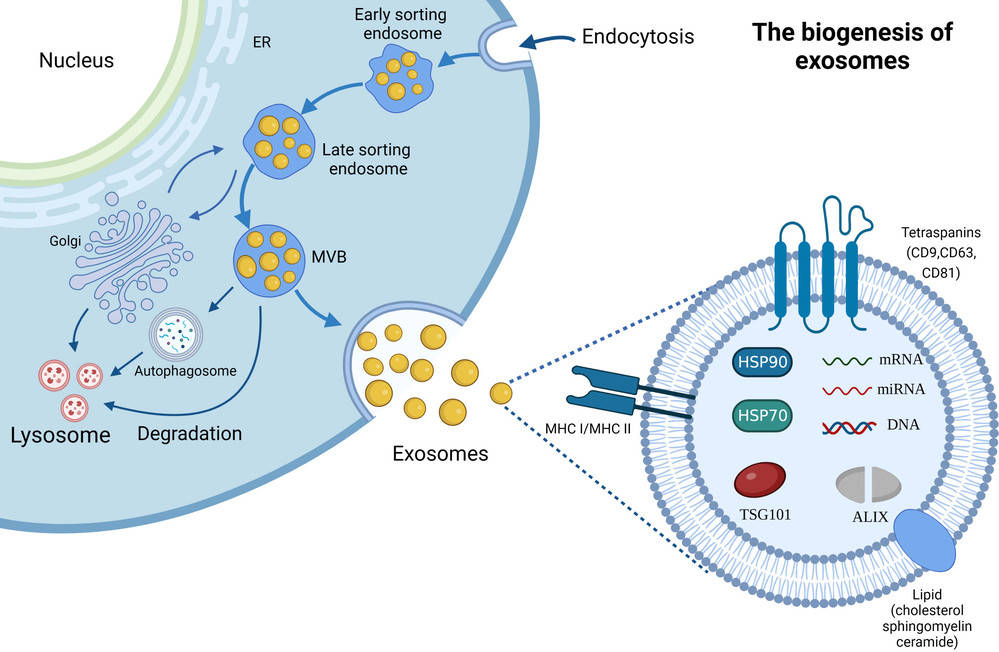
Exosomes are nanoscale extracellular vesicles (EVs) released by nearly all cell types and are increasingly recognized as key mediators of intercellular communication. Their size distribution, concentration, and molecular composition provide valuable insights for biomedical research, ranging from biomarker discovery to therapeutic development.
Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA) is one of the most widely adopted techniques for exosome characterization. By tracking the Brownian motion of particles under laser illumination, NTA provides quantitative data on particle size and concentration. At Creative Biostructure, we offer a comprehensive NTA-based exosome characterization service, fully aligned with the MISEV2023 guidelines to ensure data reliability, transparency, and reproducibility.
What is Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA)?
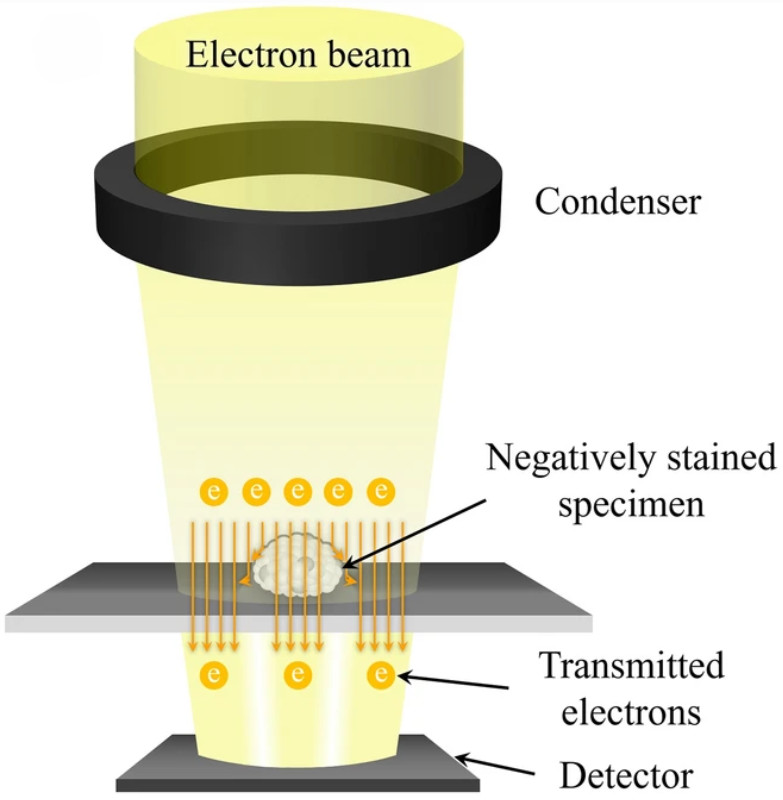
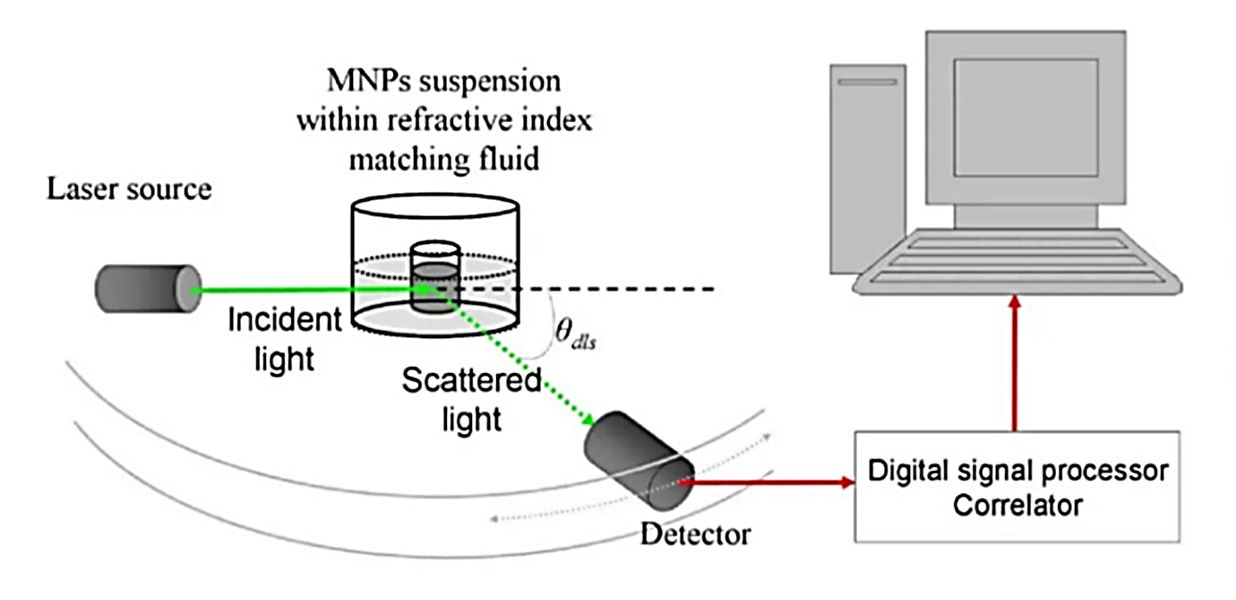
NTA is an optical technique that measures the hydrodynamic diameter of nanoparticles, including exosomes, by analyzing their diffusion behavior in liquid suspension. A laser beam illuminates the particles, which scatter light that is captured by a high-resolution camera. Software algorithms then calculate particle size distribution and concentration on a particle-by-particle basis.
Compared with Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS), which provides bulk measurements, NTA offers:
- Higher resolution for heterogeneous samples.
- Direct particle-by-particle tracking instead of ensemble averaging.
- Quantitative concentration measurements in addition to size distribution.
This makes NTA particularly well suited for extracellular vesicle research where heterogeneity and low abundance present significant challenges.
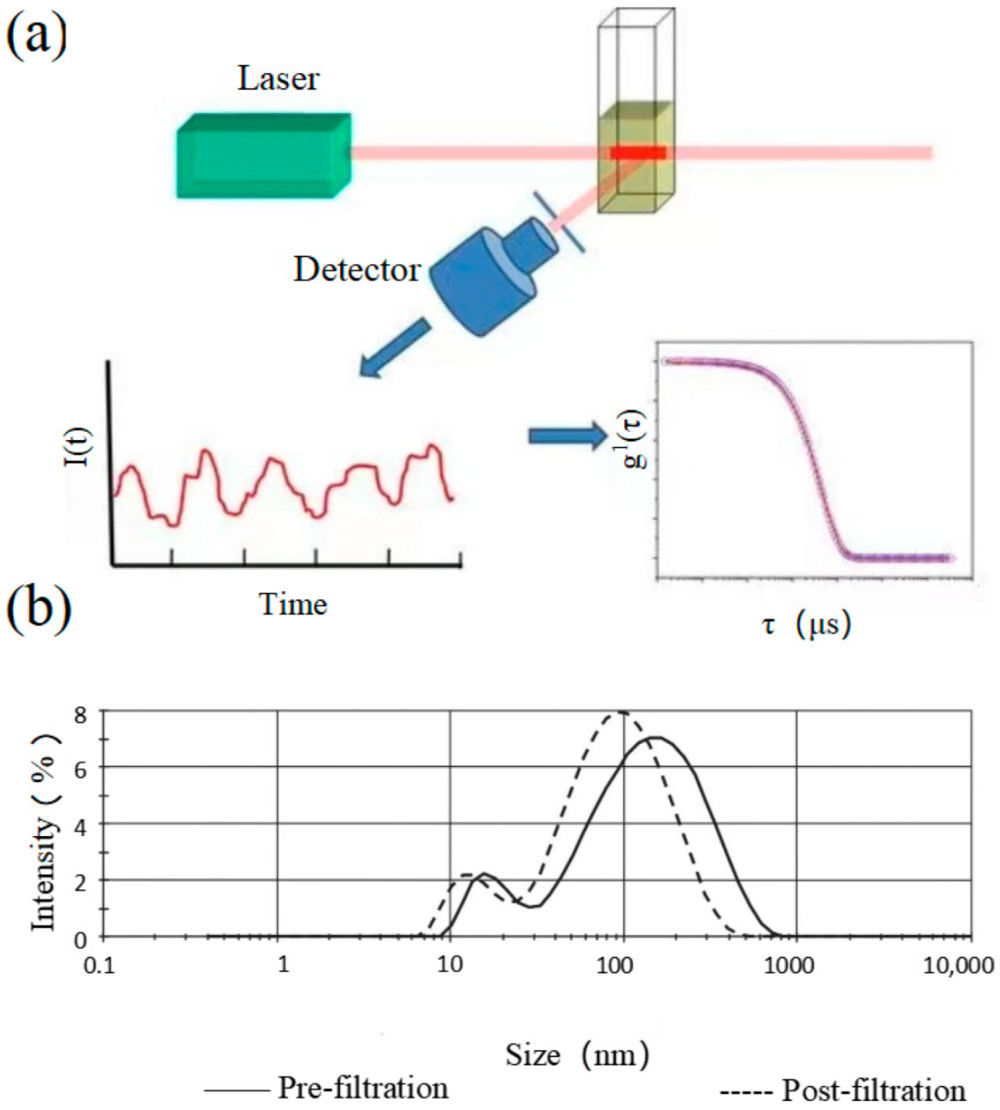
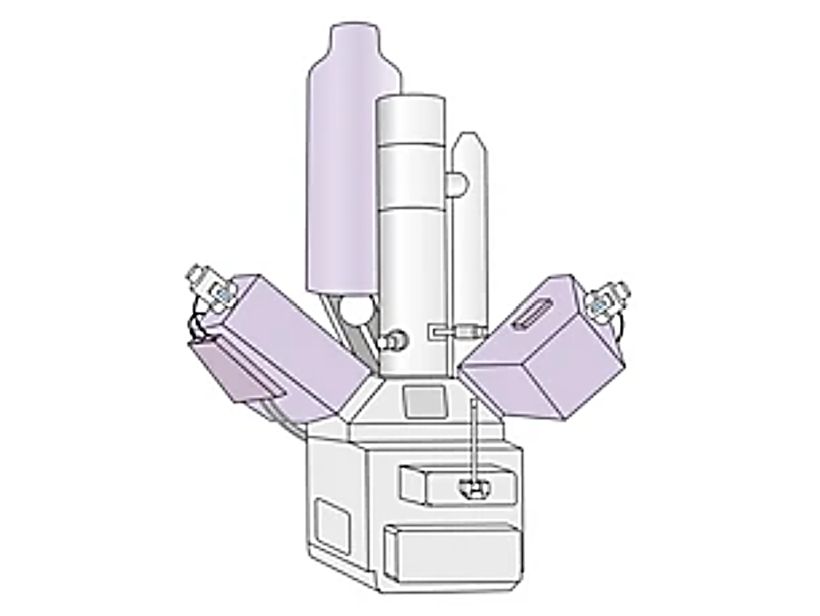
![]() Figure 1. Schematic illustration of a nanoparticle tracking analyzer (NTA) system. Particles suspended in liquid are illuminated by a laser beam, and scattered light is captured by a CMOS camera positioned at a 90° angle within an ultramicroscope setup. A fluorescence filter between the sample holder and microscope enables fluorescent particle detection. Particle tracks are displayed in the software's live-view window, and Brownian motion analysis is applied to calculate particle size and concentration simultaneously. (Sharma V, et al., 2023)
Figure 1. Schematic illustration of a nanoparticle tracking analyzer (NTA) system. Particles suspended in liquid are illuminated by a laser beam, and scattered light is captured by a CMOS camera positioned at a 90° angle within an ultramicroscope setup. A fluorescence filter between the sample holder and microscope enables fluorescent particle detection. Particle tracks are displayed in the software's live-view window, and Brownian motion analysis is applied to calculate particle size and concentration simultaneously. (Sharma V, et al., 2023)
Why Choose NTA for Exosome Characterization?
NTA has become a cornerstone technology in exosome research because it provides:
- High-resolution particle size distribution (30 nm-1000 nm).
- Accurate concentration measurements essential for dose-response studies.
- Compatibility with diverse sample types, including plasma, urine, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), synovial fluid, and cell culture supernatants.
- Fluorescence-NTA (fl-NTA) capability for subpopulation analysis, allowing selective detection of labeled vesicles while excluding non-vesicular contaminants.
However, like all technologies, NTA has limitations. Measurements may include co-isolated particles such as lipoproteins or protein aggregates, and vesicles larger than a few hundred nanometers can be difficult to quantify. Our team mitigates these issues by incorporating buffer-only controls, fluorescence validation, and replicate measurements, ensuring high-quality and interpretable results.
Our NTA-Based Exosome Characterization Service
Creative Biostructure provides end-to-end NTA characterization tailored for both academic and industrial projects.
Step-by-Step Workflow of Our NTA Exosome Analysis
Consultation & Project Design
Define research goals, select conventional or fluorescence NTA, and establish customized protocols.
Sample Submission
Clients provide exosome isolates or raw biofluids. Optional exosome isolation service is available.
Sample Preparation & Quality Control
Samples are prepared under standardized conditions with buffer-only controls and replicates.
NTA Measurement
Particle size distribution and concentration are measured in triplicate using advanced NTA instruments. Both light-scattering and fluorescence-NTA modes are available.
Data Analysis
Generate size distribution curves, concentration values, and subpopulation data using validated algorithms.
Reporting & Delivery
Provide a comprehensive report including raw video files, statistical outputs, and expert interpretation.
![]() Figure 2. Project Workflow for Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis of Exosomes. (Creative Biostructure)
Figure 2. Project Workflow for Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis of Exosomes. (Creative Biostructure)
Sample Types Supported for NTA Analysis
We accept a wide range of biological samples for NTA-based exosome characterization, with clear guidelines to ensure sample integrity and reliable results.
| Sample Type | Minimum Volume | Preparation & Storage | Shipping |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purified Exosomes | ≥ 100 µL | Store in PBS or other suitable buffer at -80 °C; avoid repeated freeze–thaw cycles | Ship on dry ice |
| Plasma / Serum / Urine | ≥ 1 mL | Freeze at -80 °C immediately after collection | Ship on dry ice |
| Cell Culture Supernatant | ≥ 5 mL | Remove cells and debris by centrifugation; store at -80 °C | Ship on dry ice |
| Other Biological Fluids* | Contact us | Follow sample-specific preparation guidelines provided upon request | Ship on dry ice |
Examples include saliva, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), bile, breast milk, amniotic fluid, plant-derived fluids, and tissue homogenates. For less common sample types, please contact us for tailored instructions.
What Deliverables Will You Receive
At the completion of our NTA-based exosome characterization service, you will receive a comprehensive data package designed for transparency, reproducibility, and compliance with MISEV2023 guidelines.
Our reports include:
- Size distribution curves (not single-value statistics).
- Particle concentration data.
- Instrument settings (model, laser wavelength, camera specifications, software version, analysis settings).
- Fluorescence controls and label validation where applicable.
- Raw video data upon request.
This structured reporting format ensures that your results are publication-ready, comparable across studies, and suitable for both academic research and industrial applications.
Applications of NTA in Exosome Research
Our NTA-based exosome characterization service supports a wide range of research and industrial applications, including:
- Cancer Research & Biomarker Discovery: Identification of exosomal signatures linked to tumor progression, metastasis, and immune modulation.
- Drug Delivery & Gene Therapy: Characterization of engineered exosomes to assess drug loading, stability, and delivery efficiency.
- Neuroscience & Immunology: Evaluation of vesicle-mediated signaling in neurodegeneration, immune activation, and inflammation.
- Metabolic Disease Studies: Analysis of exosomal roles in lipid and glucose metabolism, with implications for diabetes and obesity research.
- Quality Control & Standardization: Supporting reproducible EV-based product development for biotechnology and translational research.
Key Features of Our Service
- High-Resolution Particle Profiling: Precise determination of size distribution and vesicle concentration for accurate characterization.
- Fluorescence-NTA Capability: Subpopulation analysis using membrane dyes or antibody labeling to identify specific exosome markers.
- Advanced Instrumentation: State-of-the-art nanoparticle tracking analyzers equipped with fluorescence detection for enhanced sensitivity.
- Compliance with MISEV2023: Rigorous quality standards ensure data transparency, reproducibility, and publication readiness.
- Customizable Workflows: Flexible protocols tailored to sample type, research goals, and project requirements.
- Expertise & Support: A team with years of experience in structural biology and extracellular vesicle research, offering integrated services from isolation to functional assays.
Case Study
Case: Quantification of HCC-Derived Exosomes Using fNTA
Background
To improve non-invasive diagnostics for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), researchers developed a single-step immunocapture assay combined with fluorescence nanoparticle tracking analysis (fNTA).
Methods
- PE-conjugated antibodies against GPC3 and AFP were used to capture HCC-specific exosomes.
- Column purification removed unbound antibodies before fNTA quantification.
- Validation performed with cell lines (Huh7, HuCCA-1) and patient serum (healthy, cirrhosis, HCC).
Results
- Detection range: 10⁴-10⁸ particles/mL.
- Cell lines: HCC cells released 100-200 marker-positive exosomes/cell vs. 10-40 in non-HCC.
- Clinical serum: GPC3+ exosomes significantly enriched in HCC (AUC=0.79); AFP+ moderate (AUC=0.71).
- Correlation: GPC3+ exosome levels strongly correlated with MRI-confirmed tumor size.
Conclusion
![]() Figure 3. Quantification of AFP and GPC3 Double-Positive Exosomes in HCC. (A) Representative images from EV analysis in light scatter mode (LSM) and fluorescence mode (FM) with PE-conjugated AFP and GPC3 antibodies. (B) Size distribution (mean and mode) of immunocaptured EVs detected in LSM and FM. (C) Quantification of GPC3/AFP double-positive EVs in serum from normal, cirrhosis, and HCC patients. Particle numbers from FM were normalized to LSM. (D) ROC analysis showing sensitivity and specificity of AFP/GPC3 double-positive EVs for distinguishing HCC from normal and cirrhosis groups. (Koksal A R, et al., 2023)
Figure 3. Quantification of AFP and GPC3 Double-Positive Exosomes in HCC. (A) Representative images from EV analysis in light scatter mode (LSM) and fluorescence mode (FM) with PE-conjugated AFP and GPC3 antibodies. (B) Size distribution (mean and mode) of immunocaptured EVs detected in LSM and FM. (C) Quantification of GPC3/AFP double-positive EVs in serum from normal, cirrhosis, and HCC patients. Particle numbers from FM were normalized to LSM. (D) ROC analysis showing sensitivity and specificity of AFP/GPC3 double-positive EVs for distinguishing HCC from normal and cirrhosis groups. (Koksal A R, et al., 2023)
fNTA enables sensitive, quantitative detection of HCC-specific exosomes from minimal serum volumes, supporting its use in early cancer detection and biomarker validation.
At Creative Biostructure, we are committed to delivering reliable, reproducible, and publication-ready NTA exosome characterization services. Whether your project focuses on biomarker discovery, therapeutic development, or quality control, our team provides the expertise and technology you need. Contact us to discuss your project and receive a tailored analysis plan.
References
- Sharma V, Nikolajeff F, Kumar S. Employing nanoparticle tracking analysis of salivary neuronal exosomes for early detection of neurodegenerative diseases. Translational Neurodegeneration. 2023, 12(1): 7.
- Koksal A R, Ekmen N, Aydin Y, et al. A single-step immunocapture assay to quantify HCC exosomes using the highly sensitive fluorescence nanoparticle-tracking analysis. Journal of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. 2023: 1935-1954.
- Welsh J A, Goberdhan D C I, O'Driscoll L, et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles (MISEV2023): From basic to advanced approaches. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles. 2024, 13(2): e12404.
Frequently Asked Questions
For any inquiries, our support team is ready to help you get technical support for your research and maximize your experience with Creative Biostructure.