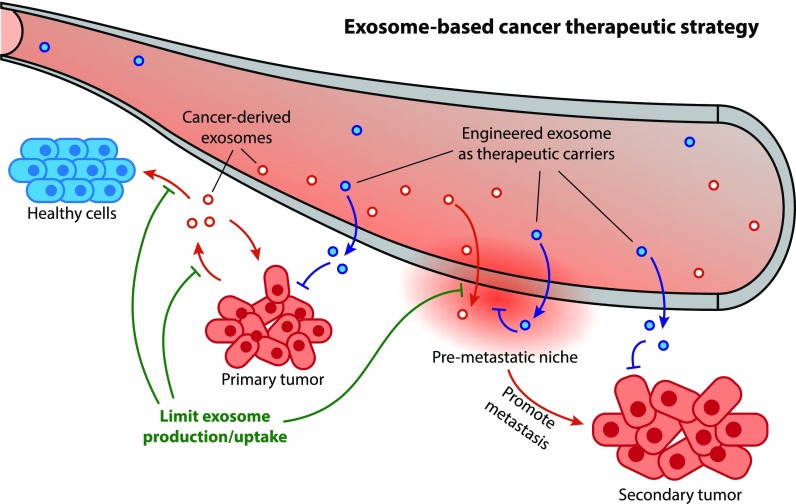
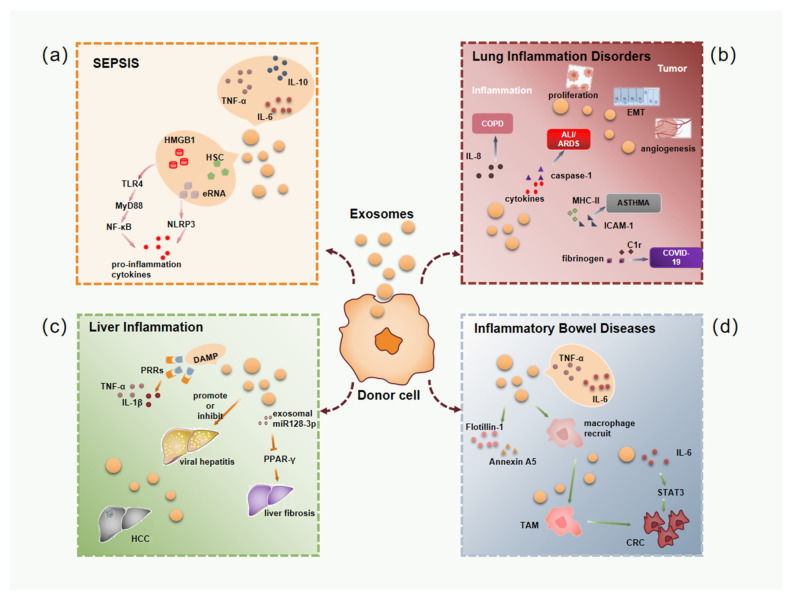
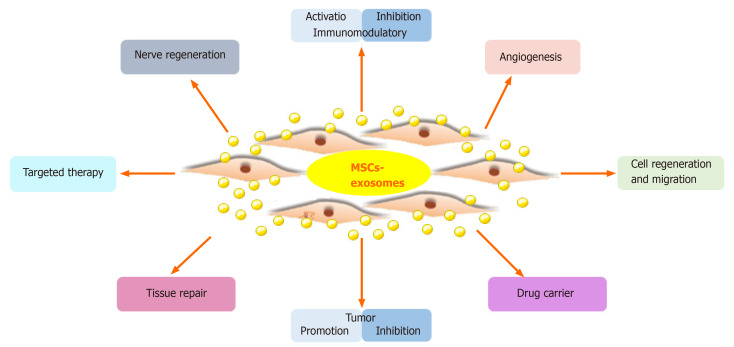
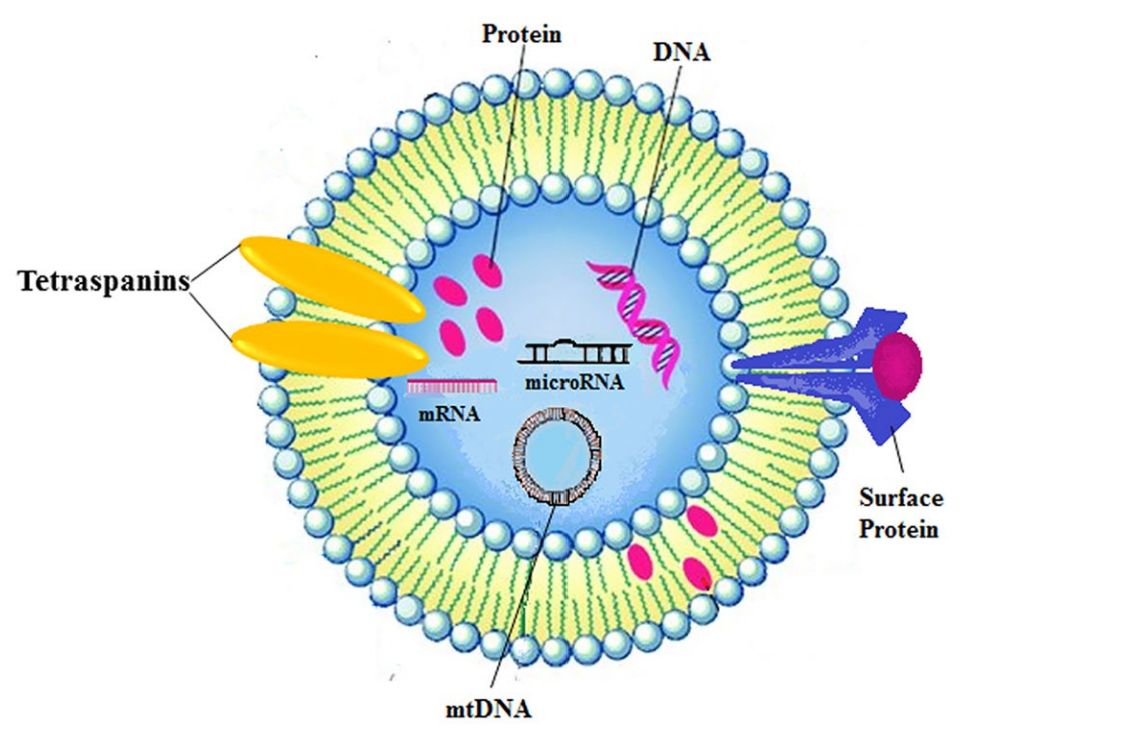
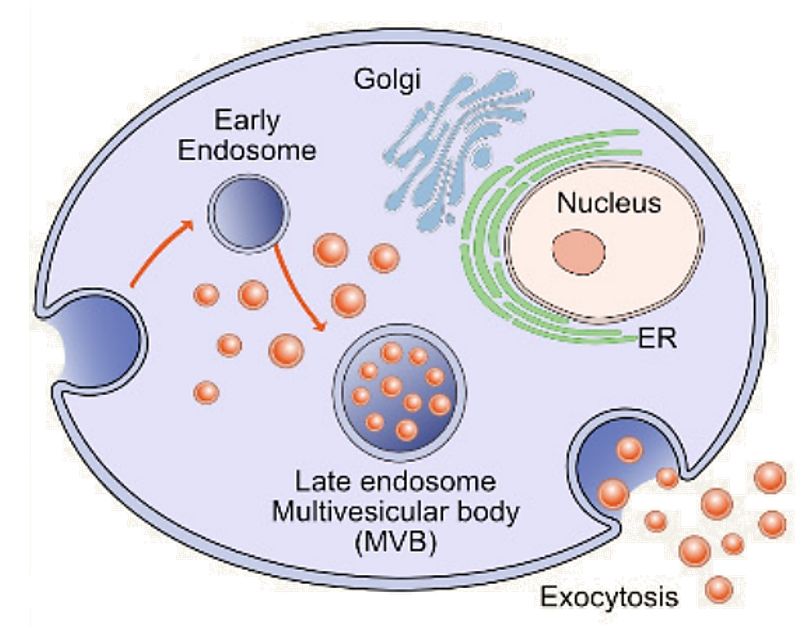
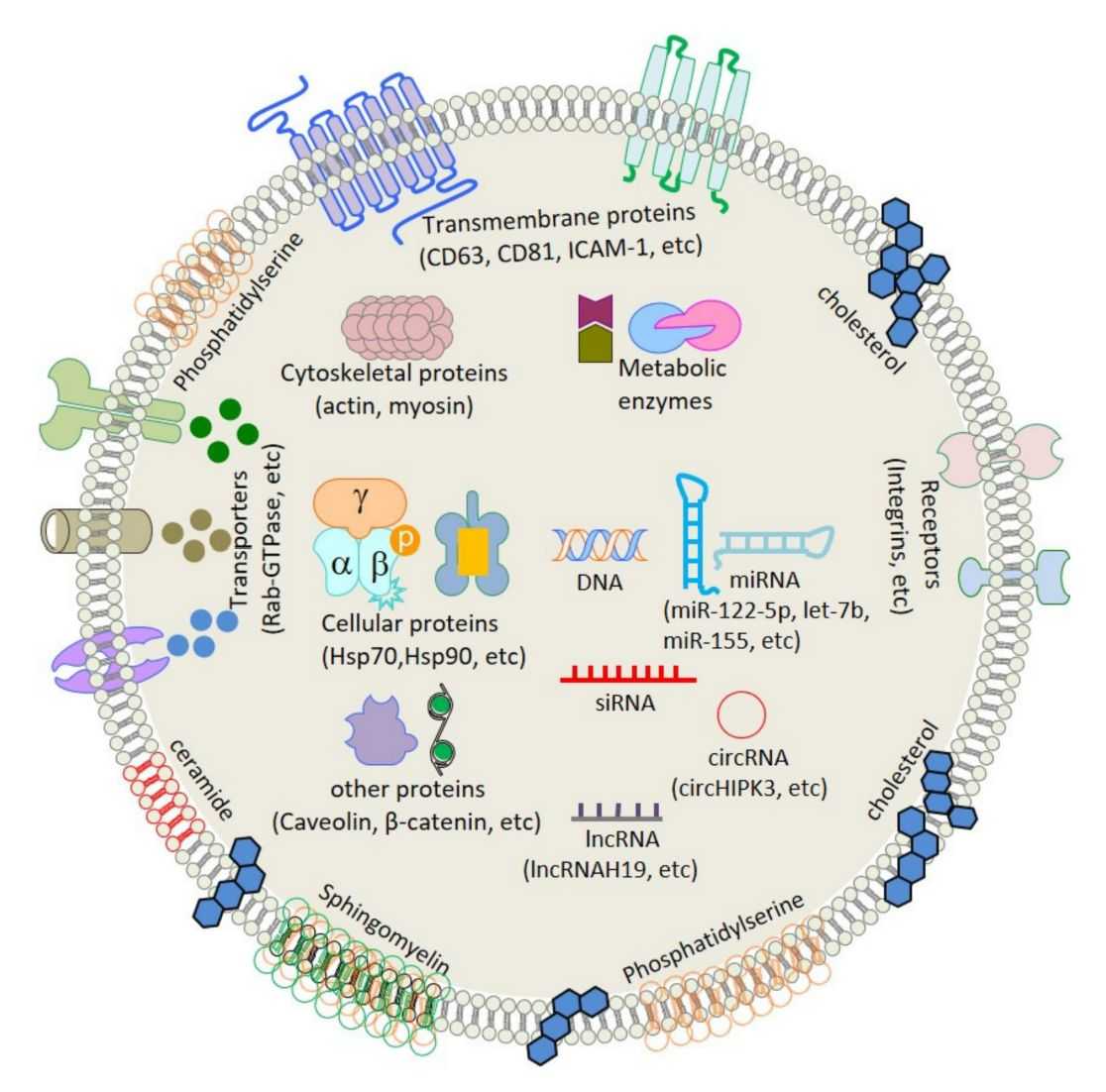
In Vivo Exosome Functional Assays
In vivo exosome functional assays are preclinical animal studies designed to evaluate the biological effect and therapeutic efficacy of an exosome intervention. Moving beyond simple biodistribution, these assays measure functional, physiological outcomes—such as tumor growth suppression, inflammation reduction, or tissue regeneration—to provide the definitive proof of your exosome's potency in a living system.
Why Validate Exosome Function In Vivo?
This is the ultimate validation step for your research. Our Exosome Tracing and Tracking service answers the critical question, "Where did my exosomes go?". This service, answers the most important question of all: "Did they work?"
- Prove Therapeutic Efficacy: An in vitro effect does not guarantee in vivo success. You must demonstrate that your exosomes loaded with therapeutic cargo can shrink a tumor, repair tissue, or modulate immunity in a complex biological environment.
- Bridge to Preclinical Data: This is the essential data package required for regulatory filings and to advance your mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes or exosome drug (e.g., exosome mediated delivery of sirna in vivo) to clinical trials.
- Integrate PK and PD: Our platform combines biodistribution confirmation (in vivo imaging) with pharmacodynamics (functional readouts like immunofluorescence and histology) to provide a complete picture of your exosome's performance in vivo.
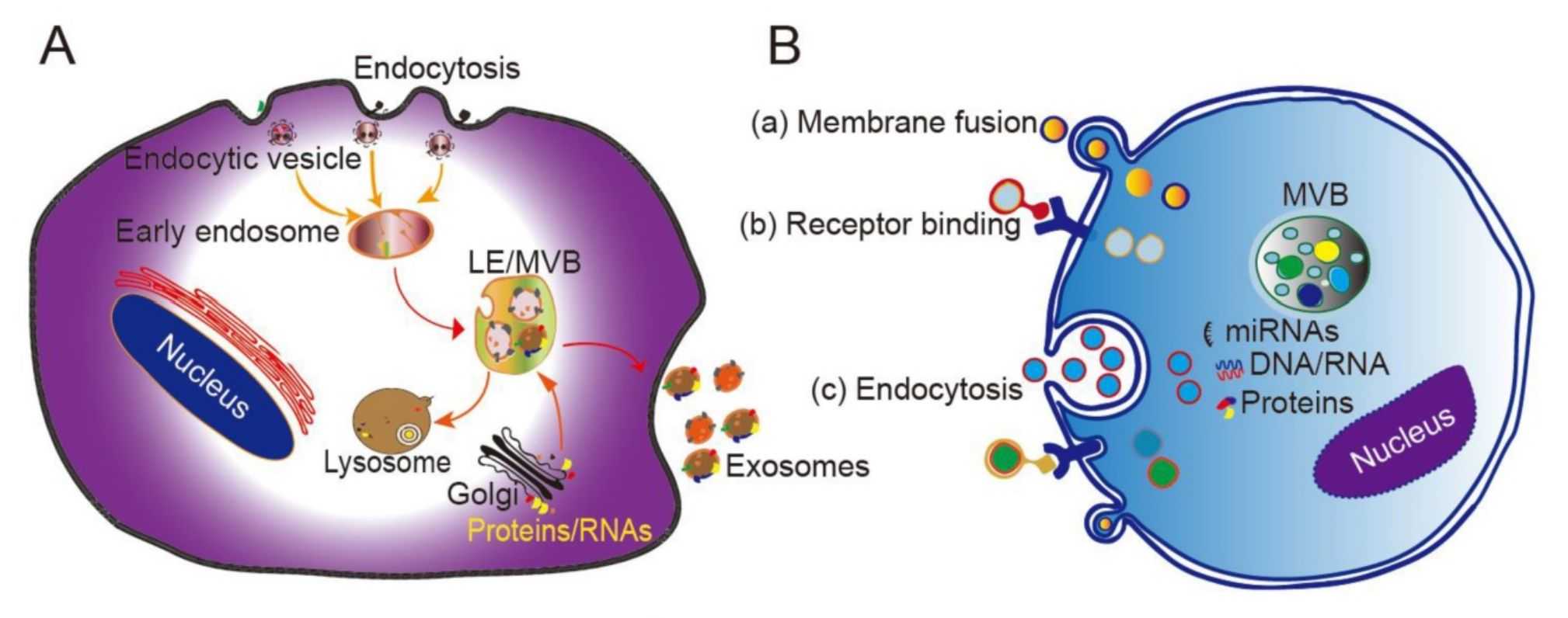
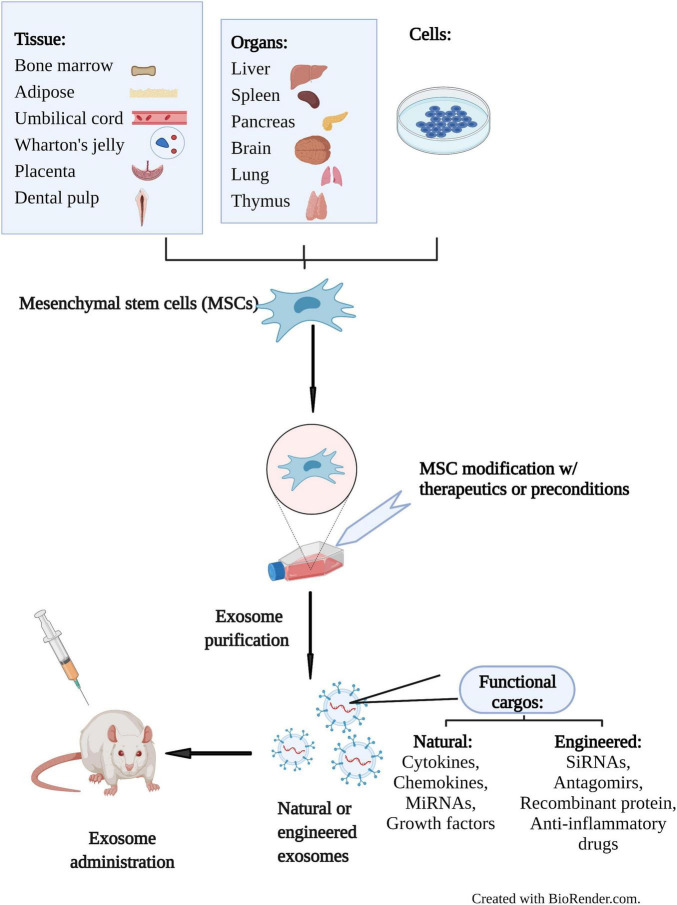 Figure 1. Therapeutic application of MSC-Exos in preclinical studies. MSCs from various sources secrete exosomes that can be engineered to deliver bioactive molecules. MSC-Exos are tested in animal models for therapeutic potential. (Cao Q, et al., 2022)
Figure 1. Therapeutic application of MSC-Exos in preclinical studies. MSCs from various sources secrete exosomes that can be engineered to deliver bioactive molecules. MSC-Exos are tested in animal models for therapeutic potential. (Cao Q, et al., 2022)
Our In Vivo Exosome Functional Assay Portfolio
Our platform is the dedicated in vivo validation hub for all your in vitro discoveries. We provide specialized animal models to confirm the therapeutic function of your exosomes.
In Vivo Therapeutic Efficacy Models (Drug Delivery)
Validates findings from Drug Delivery and Bioactivity Validation
- Service: We validate the in vivo efficacy of your exosomes loaded with therapeutic cargo, such as siRNA, mRNA, or small molecules.
- Models:
- Cancer Xenograft/Orthotopic Models: (e.g., Melanoma, prostate cancer, Colorectal, Glioblastoma). We perform exosomal injected animals and monitor tumor growth.
- Neurodegenerative Disease Models: (e.g., PD, AD models) to assess neuroprotection.
- Key Functional Readouts: Tumor Volume (caliper measurement), Animal Survival Rates, Target Gene Knockdown (qPCR/WB from tumor tissue), Neurobehavioral Scores.
In Vivo Immune Modulation Assays
Validates findings from Immunomodulation and Inflammation Assays
- Service: We assess the ability of your exosomes (e.g., macrophage exosomes) to modulate the immune response in disease models.
- Models:
- Systemic Inflammation Models: (e.g., LPS-induced Sepsis or Acute Lung Injury (ALI)).
- Chronic Inflammation Models: (e.g., IBD/Colitis, Rheumatoid Arthritis).
- Key Functional Readouts: Systemic Cytokine Levels (ELISA from serum), M1/M2 Macrophage Polarization in tissue (via Immunofluorescence), Neutrophil Infiltration (Histology, MPO assay), Disease Activity Index (DAI) scores.
In Vivo Angiogenesis & Regeneration Assays
Validates findings from Angiogenesis and Stem Cell Functional Assays
- Service: We confirm the in vivo regenerative potential of your mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes in preclinical repair models.
- Models:
- Hindlimb Ischemia Model: To assess functional angiogenesis.
- Cutaneous Wound Healing Model: To measure tissue repair.
- Bone Defect Model: (e.g., Calvarial defect) to assess osteogenesis.
- Key Functional Readouts: Blood Perfusion Recovery (Laser Doppler Imaging), Wound Closure Rate, Re-epithelialization, Neovascularization (CD31 Immunofluorescence), Bone Regeneration Volume (Micro-CT).
Core Endpoint Analysis Platforms
To measure the functional outcomes above, we utilize a multi-modal analysis platform integrated across all our in vivo models:
- In Vivo Imaging (Optical/IVIS):
- Functional Monitoring: Used non-invasively to monitor tumor burden (e.g., luciferase-tagged tumors) or inflammation (e.g., NF-κB reporters) over time.
- Biodistribution Confirmation: Can optionally be integrated with our tracking service to confirm exosome accumulation at the target site before assessing function.
- Histology & Immunofluorescence (IF):
- The core of functional validation. We harvest terminal tissues for microscopic validation of efficacy and mechanism.
- Examples: H&E staining (morphology, safety), CD31 staining (angiogenesis), F4/80+ staining (macrophage infiltration), TUNEL staining (apoptosis in tumors), specific target protein expression.
- Molecular & Cytokine Analysis:
- We process harvested tissues or serum to quantify molecular changes that underpin the functional effect.
- Examples: ELISA/Luminex (cytokine levels), RT-qPCR (target gene knockdown), Western Blot (protein expression changes).
Our End-to-End Project Workflow
We manage the entire in vivo study, from model selection and dosing to terminal analysis and data interpretation.
Key Service Steps
Model Selection & Study Design
Our experts consult with you to select the most relevant disease model, determine animal group sizes, and define the dosing strategy (e.g., number of exosomes to add in vivo, route of administration).
In Vivo Dosing & Efficacy Monitoring
We perform the exosomal injected animals dosing schedule and conduct all non-invasive functional monitoring (e.g., in vivo imaging, tumor volume measurement, behavioral tests).
Terminal Analysis & Histopathology
At the study endpoint, we perform terminal sample collection (e.g., blood, organs) and execute the key functional analyses (e.g., Histology, Immunofluorescence, ELISA) to measure the definitive therapeutic outcome.
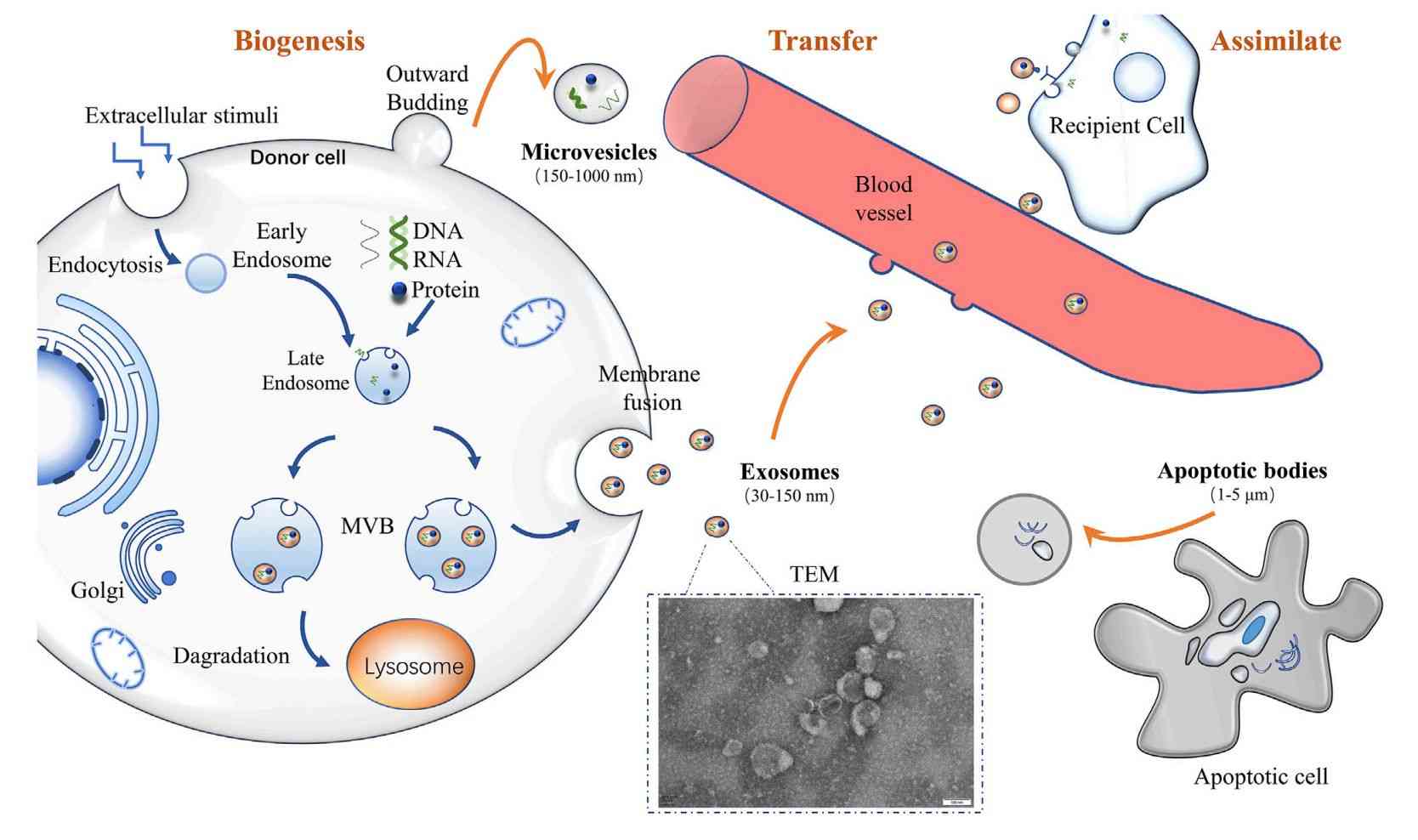
Project Workflow
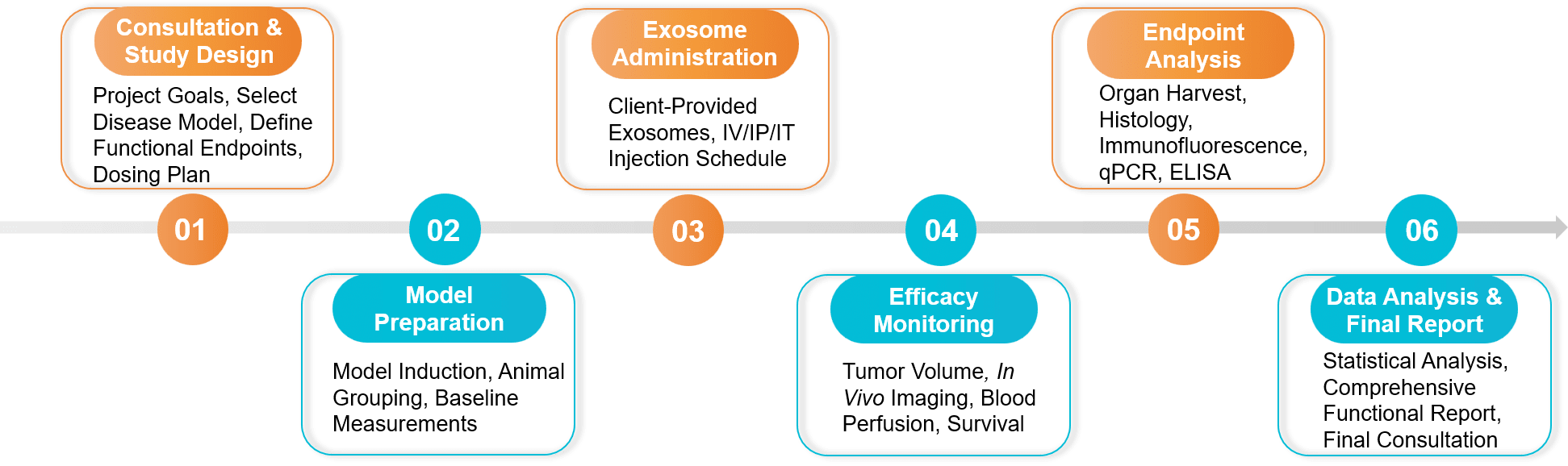 Figure 2. In Vivo Exosome Functional Assay Project Workflow. (Creative Biostructure)
Figure 2. In Vivo Exosome Functional Assay Project Workflow. (Creative Biostructure)
Sample Requirements
- Client-Provided Exosomes:
- Quantity: Large quantities are required for in vivo studies (typically 1x10¹⁰ - 1x10¹² particles per dose, multiple doses needed). Please inquire for a project-specific consultation.
- Purity & QC: Must be highly purified, sterile, and endotoxin-free. NTA and WB characterization data are required.
- Buffer: Suspended in a sterile, in vivo-grade buffer (e.g., sterile PBS).
- Controls:
- We strongly recommend providing vehicle buffer controls. For drug delivery studies, "empty" (unloaded) exosome controls are essential.
Standard Deliverables
A Comprehensive Project Report: Details the study design, animal model, dosing regimen, all protocols, and a full scientific interpretation of the functional results.
Raw and Analyzed Data: All raw data files (e.g., caliper measurements, IVIS quantification, ELISA readouts, qPCR Cq values, histology scores).
Publication-Ready Figures:
- Efficacy Plots: Tumor growth curves, animal survival plots, wound closure graphs, functional scoring graphs, etc.
- Histology/IF Images: High-resolution, publishable images of key findings (e.g., CD31, M1/M2 staining, target protein expression).
- Quantification Graphs: Bar graphs comparing functional readouts between treatment groups (e.g., cytokine levels, gene expression).
Scientific Consultation: A final meeting to discuss the functional data and its implications for your preclinical program.
Case Study
Case: In Vivo Functional Assay Confirms Exosome-Delivered siRNA/Drug Combo Inhibits Glioblastoma
Background: Glioblastoma (GBM) is highly aggressive. Researchers developed an exosome-based delivery system using blood exosomes to co-deliver siRNA (targeting cPLA2, crucial for energy metabolism) and metformin, aiming to selectively target GBM energy metabolism for therapeutic effect.
Methodology & Findings: After confirming in vitro effects, the crucial in vivo functional validation was performed. GBM tumor-bearing mice were treated with the exosome formulation (Exos-Met/sicPLA2).
- Functional Efficacy: The study demonstrated significant antitumor effects in vivo. Treatment with the exosome formulation successfully inhibited GBM growth.
- Mechanism Validation: Endpoint analysis confirmed the functional mechanism. The combination treatment delivered via exosomes effectively impaired mitochondrial energy metabolism specifically within the GBM tissue in vivo.
Conclusion: This study highlights the importance of in vivo functional assays. While delivery is necessary, this work proved the therapeutic functionality by demonstrating that the exosome-delivered siRNA and drug combination successfully modulated the target pathway (energy metabolism) in vivo, leading to a significant antitumor effect.
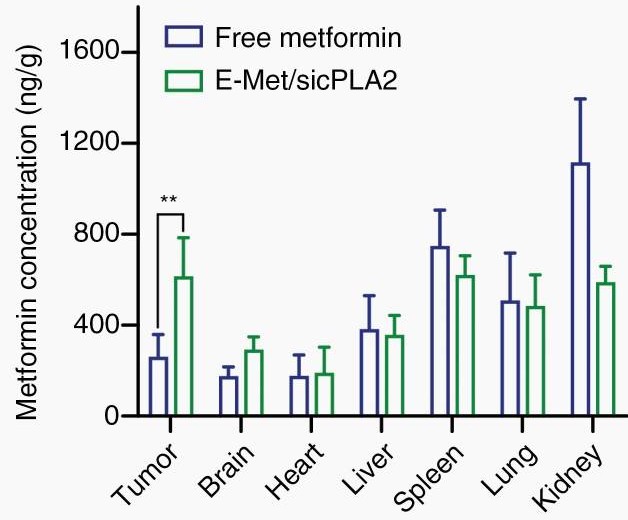 Figure 3. Metformin accumulation in GBM tissue via Exos delivery, 2.7-fold higher than native metformin. (Zhan Q, et al., 2022)
Figure 3. Metformin accumulation in GBM tissue via Exos delivery, 2.7-fold higher than native metformin. (Zhan Q, et al., 2022)
Ready to prove your exosome's therapeutic effect in vivo? Our team will help you select the right models, define dosing and endpoints, and integrate imaging, histology, and molecular readouts for decisive efficacy data. Contact us for a free consultation and a tailored study plan.
References
- Cao Q, Huang C, Chen XM, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes: Toward Cell-Free Therapeutic Strategies in Chronic Kidney Disease. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Mar 21;9:816656.
- Zhan Q, Yi K, Cui X, et al. Blood exosomes-based targeted delivery of cPLA2 siRNA and metformin to modulate glioblastoma energy metabolism for tailoring personalized therapy. Neuro Oncol. 2022 Nov 2;24(11):1871-1883.
Frequently Asked Questions
For any inquiries, our support team is ready to help you get technical support for your research and maximize your experience with Creative Biostructure.