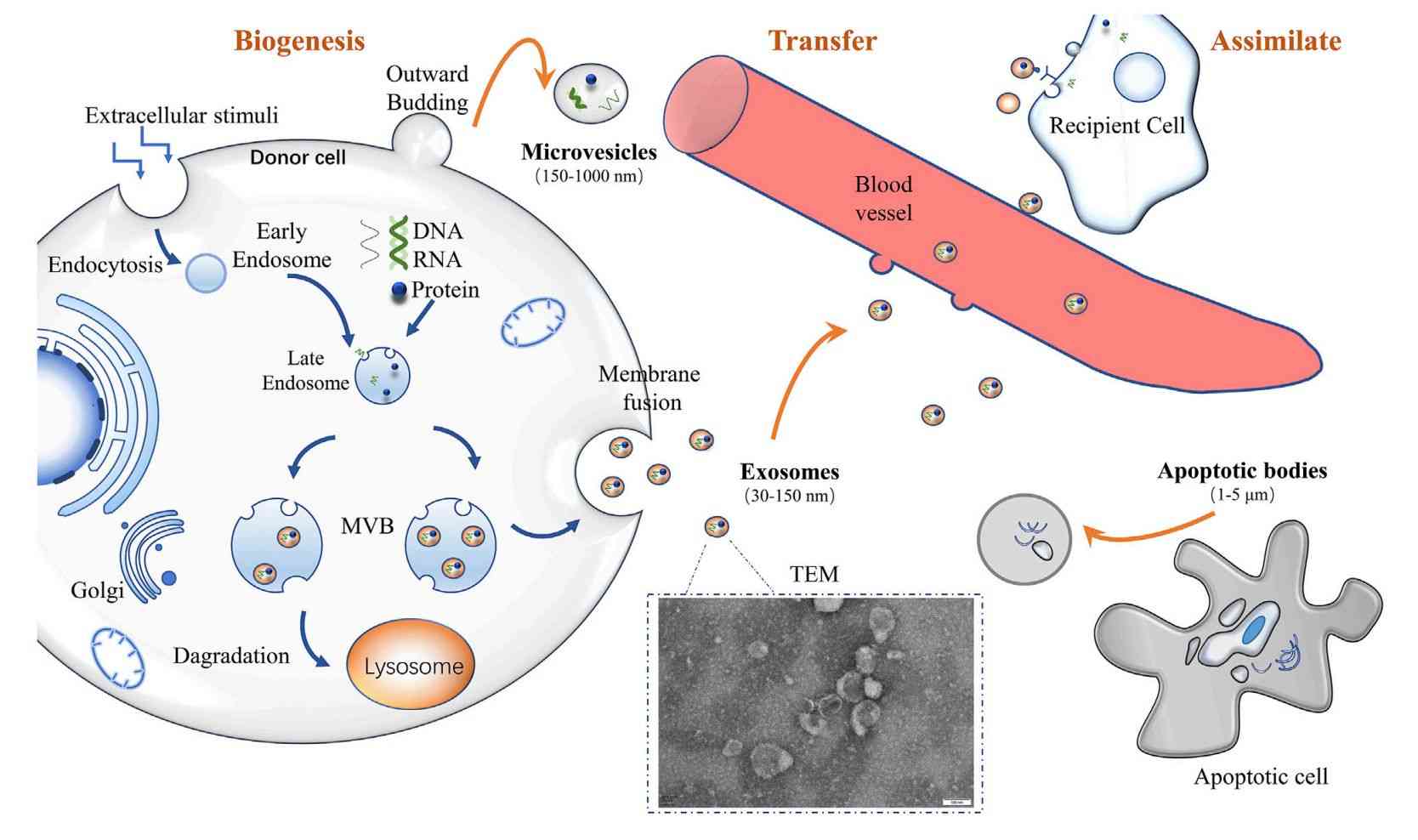
Plant-Derived Exosome Isolation Service
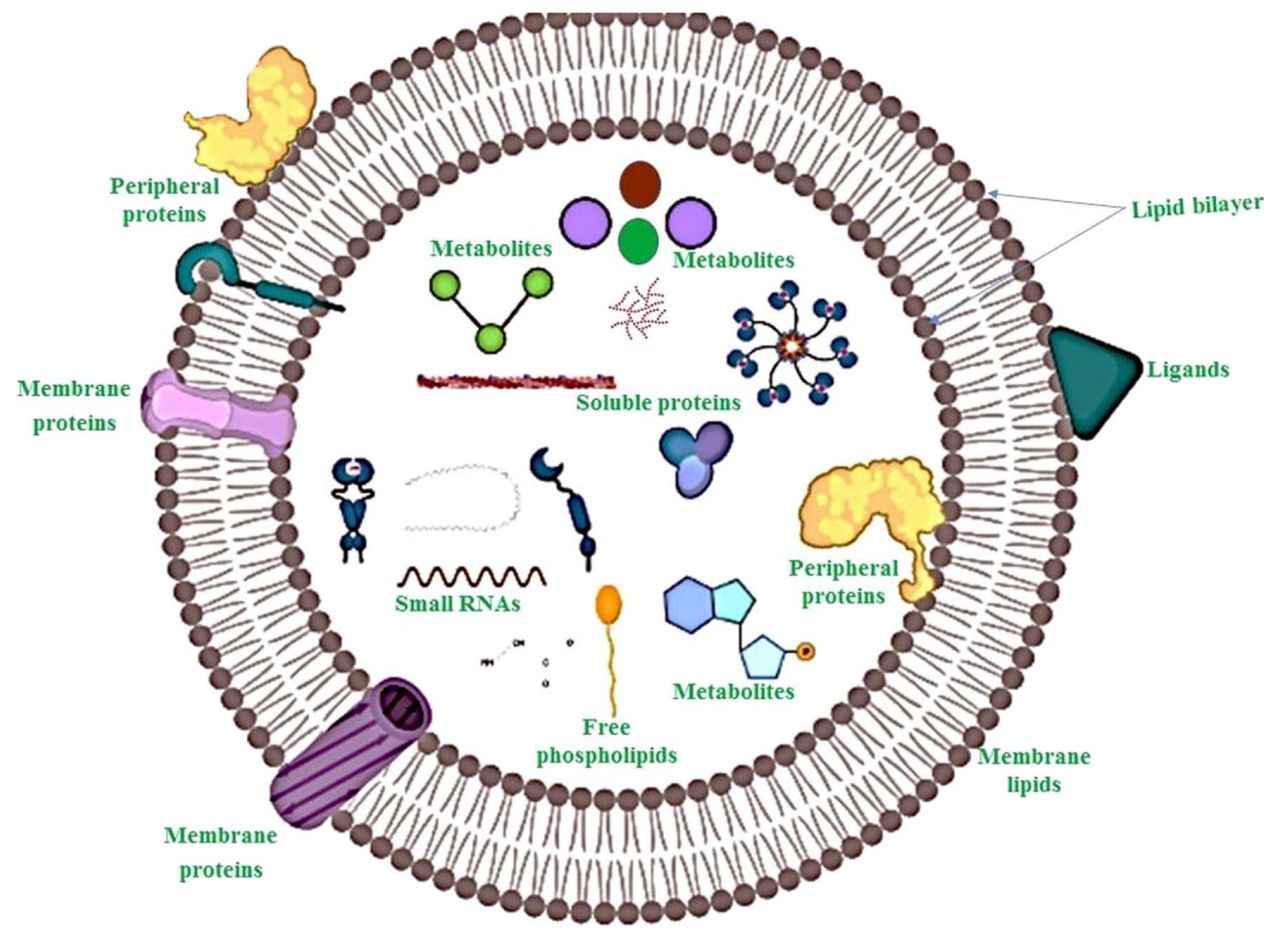
Plant-derived exosomes, also referred to as exosome-like nanovesicles (ELNs), are naturally occurring extracellular vesicles secreted by plant cells. These nanoscale carriers play critical roles in intercellular signaling and defense mechanisms within plants. Increasingly, they are being harnessed in biomedical, cosmetic, and nutraceutical research due to their ability to encapsulate and deliver bioactive compounds such as proteins, lipids, and small RNAs across biological systems.
At Creative Biostructure, we offer professional isolation and purification services for plant-derived exosomes from a wide range of plant tissues and species. Leveraging our proprietary techniques and state-of-the-art equipment, we ensure reproducible yield, structural integrity, and downstream compatibility of exosomes for your research and development needs.
Why Develop Plant-Derived Exosomes?
Plant-derived exosomes offer key advantages that support their growing use in biomedical and industrial applications:
- Naturally biocompatible and low in immunogenicity
- Stable lipid bilayer protects RNA, protein, and lipid cargo
- Sourced from edible plants, safe and easy to scale
- Distinct lipid composition (e.g., PA, DGDG, MGDG) enables unique cellular effects
- Comparable in size and function to animal exosomes, but more accessible
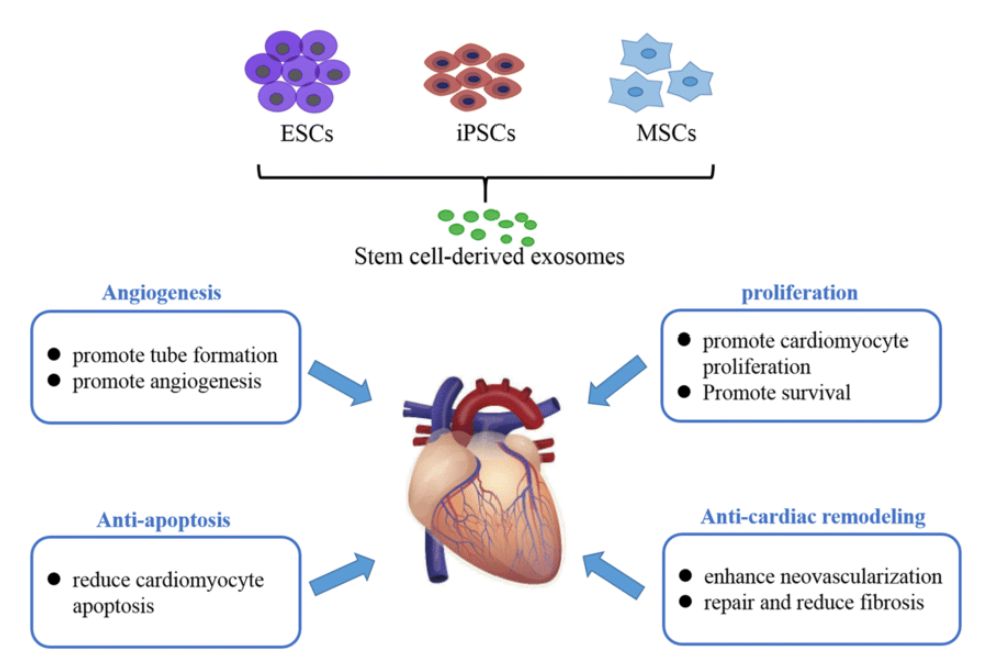
These vesicles are used in drug delivery, regenerative medicine, microbiome modulation, skincare, and functional foods.
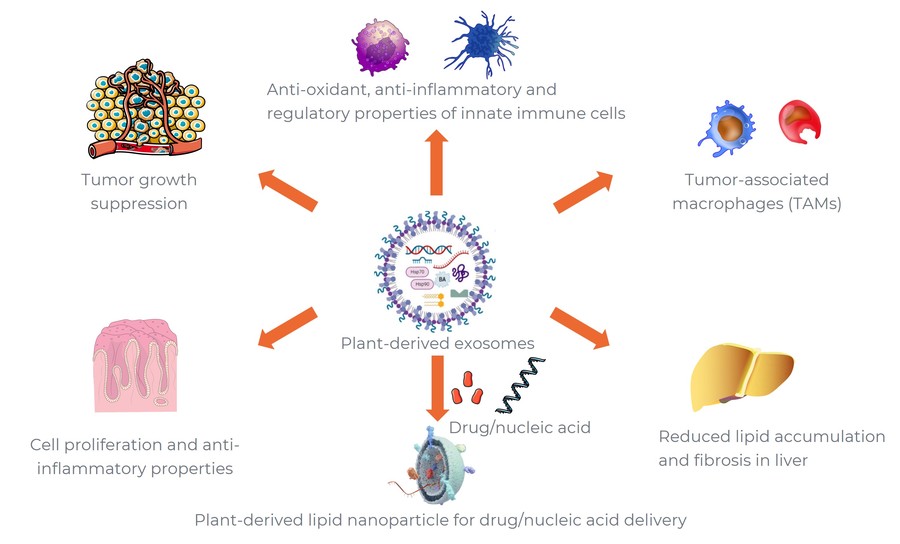 Figure 1. Biomedical applications of plant-derived exosomes. (Creative Biostructure)
Figure 1. Biomedical applications of plant-derived exosomes. (Creative Biostructure)
Plant Exosome Isolation Techniques We Offer
Creative Biostructure utilizes multiple validated isolation methods to meet diverse plant tissue characteristics, target vesicle purity levels, and intended downstream uses. The table below outlines our core techniques, including their technical features and typical applications:
| Technique | Description | Recommended Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Differential Ultracentrifugation | Sequential high-speed centrifugation to pellet exosomes based on size and density | General isolation from homogenized plant tissues |
| Density Gradient Centrifugation | Separation of vesicles using sucrose or iodixanol gradients for high-purity fractions | Therapeutic studies, RNA profiling, functional assays |
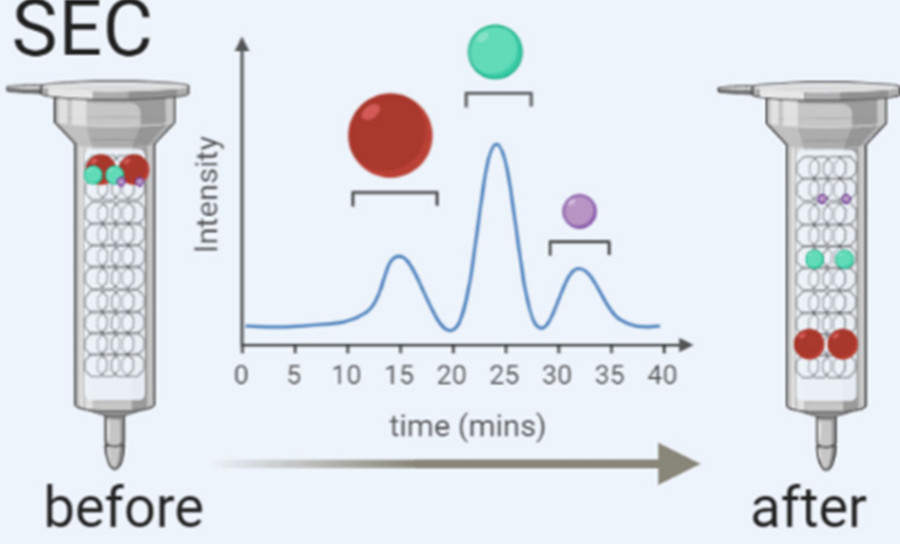
| Size-Exclusion Chromatography (SEC) | Column-based separation by particle size with minimal structural disruption | Sensitive downstream analysis, structural integrity preservation |
| Polymer-Based Precipitation | PEG-induced vesicle precipitation for scalable, equipment-light workflows | High-throughput screening, pilot-scale sample preparation |
| Tangential Flow Filtration (TFF) | Membrane-based method allowing concentration and buffer exchange in scalable volumes | Large-batch purification, formulation compatibility studies |
| Affinity-Based Isolation | Capture of vesicles using surface markers or ligands where applicable | Targeted vesicle enrichment, downstream functional validation |
We also offer integrated workflows combining methods such as SEC and gradient centrifugation to enhance yield and purity without compromising vesicle functionality.
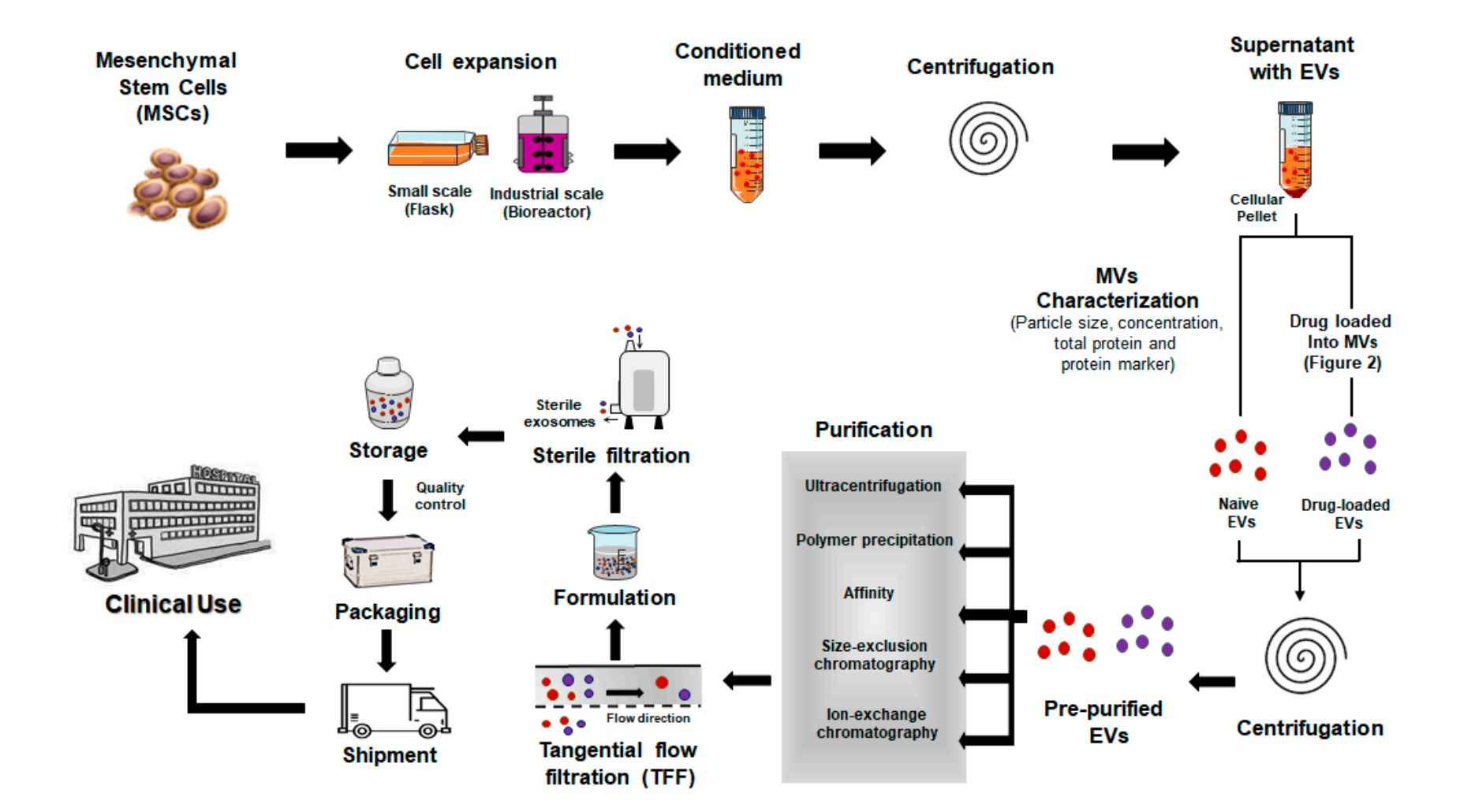
Our Plant Exosome Isolation Workflow
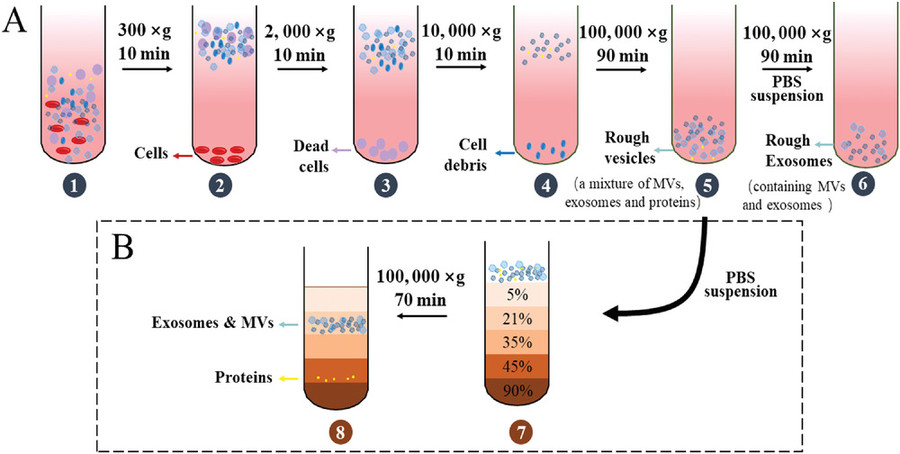
Isolating exosomes from plant tissues presents unique challenges due to rigid cell walls, variable tissue compositions, and complex matrices. At Creative Biostructure, we have developed a modular, customizable workflow tailored to different plant species, tissue types, and downstream applications. Our process ensures high-quality vesicle recovery while maintaining structural and functional integrity.
Tissue Preparation & Homogenization
Fresh or pre-treated plant tissues (e.g., roots, leaves, fruits) are homogenized through mechanical grinding or enzymatic digestion to release vesicles into solution.
Primary Clarification
The crude extract is filtered and sequentially centrifuged at low to medium speeds to remove large particles, fibrous debris, and organelles.
Exosome Isolation
We apply one or more of the following methods depending on project goals:
- Differential ultracentrifugation
- Density gradient centrifugation (sucrose or iodixanol)
- Size-exclusion chromatography
- PEG-based precipitation
Purification & Buffer Exchange
Exosomes are concentrated and transferred into research-grade buffers using ultrafiltration or dialysis to support intended applications.
Optional Characterization & Assays
Upon request, we provide nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA), TEM imaging, protein/RNA quantification, or bioactivity testing to support vesicle quality validation.
This workflow is adaptable based on plant species, sample format, and intended use such as drug delivery, molecular profiling, or bioactivity testing. Integrated workflows combining techniques are also available to improve yield, purity, and scalability.
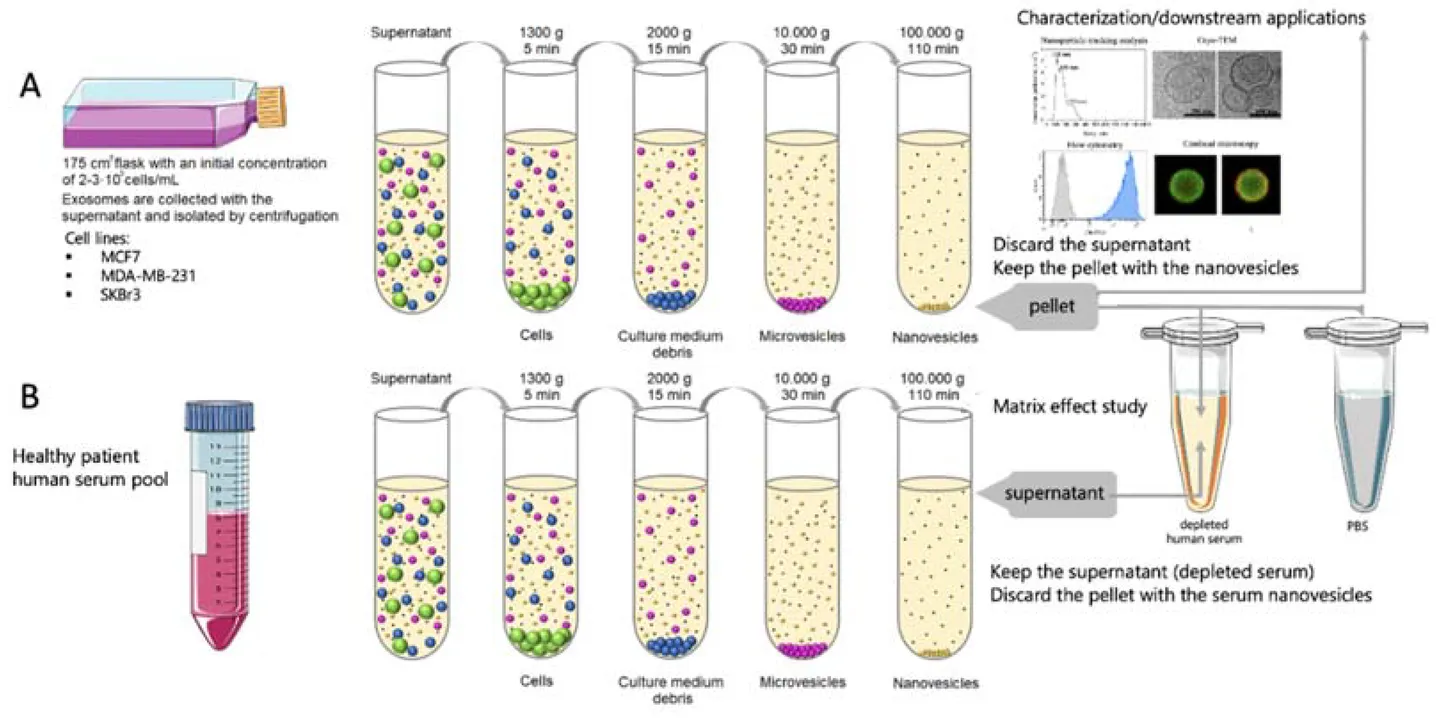
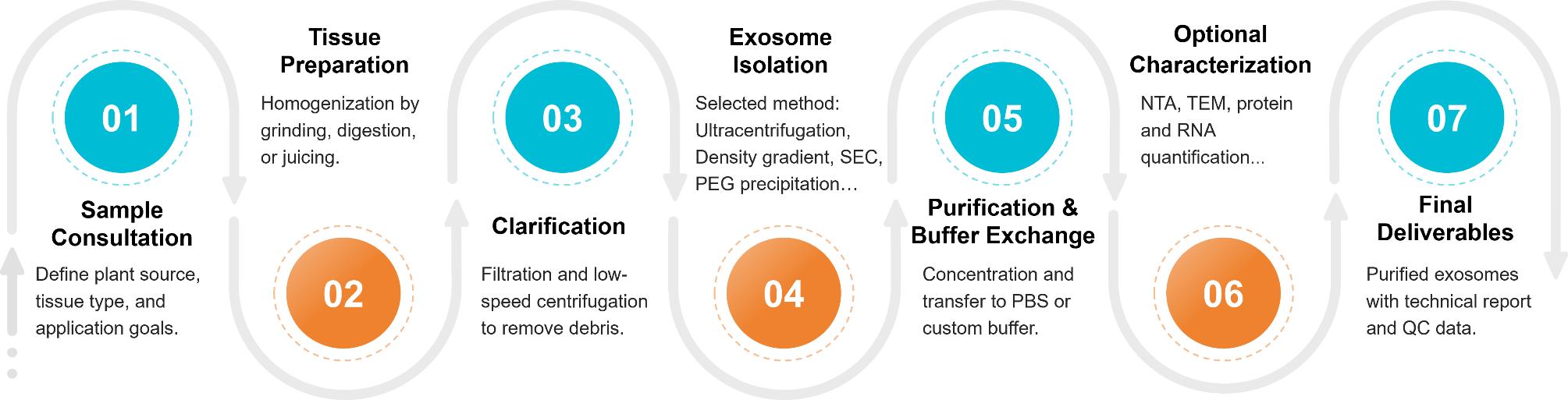 Figure 2. Plant Exosome Isolation Project Workflow. (Creative Biostructure)
Figure 2. Plant Exosome Isolation Project Workflow. (Creative Biostructure)
Sample Requirements
Creative Biostructure supports exosome isolation from a wide range of plant sources, including fruits, vegetables, herbs, roots, flowers, seeds, and algae. We customize each workflow based on the biological properties of the sample to ensure optimal yield and downstream compatibility.
Supported Sample Types
- Fruits: Grape, lemon, papaya, blueberry…
- Leaves & Herbs: Ginseng, Centella asiatica, Houttuynia cordata…
- Roots & Rhizomes: Ginger, Panax notoginseng, Pueraria lobata…
- Vegetables: Broccoli, tomato, onion…
- Flowers & Seeds: Aloe, sesame, dandelion…
- Other: Seaweed, sprouts, and specialty plant extracts
Submission Guidelines
- Fresh or flash-frozen plant material (≥50 g recommended)
- Clearly labeled species and tissue type
- Optional: Indicate preferred isolation method or target analyte (e.g., RNA, lipid, protein)
Please contact us in advance if working with rare or unconventional plant species, as we can provide customized protocol development support.
Quality Control and Deliverables
At Creative Biostructure, we are committed to providing high-quality, well-documented exosome preparations to support your downstream research with confidence.
Quality Control Options
- Vesicle size and concentration (via nanoparticle tracking analysis)
- Morphology verification (via transmission electron microscopy)
- Protein and RNA content quantification
- Optional functional assays for bioactivity assessment
- Endotoxin and sterility testing, if required
Final Deliverables
- Purified plant-derived exosomes in the requested buffer or format
- Technical report detailing isolation methods and QC results
- Data summary including size distribution, cargo content, and yield
- Optional: Interpretation of results and recommendations for next steps or publication use
We also provide consultation upon delivery to ensure seamless integration of exosome samples into your research pipeline.
Case Study
Case: Isolation of Grape Callus-Derived Exosome-like Nanoparticles for Functional and Therapeutic Study
Background
To explore the therapeutic potential of plant-derived nanovesicles, this study established a reproducible protocol for isolating exosome-like nanoparticles from Vitis vinifera callus cultures, offering a controlled and scalable alternative to fruit-derived sources.
Methods
- Callus cultures were washed, homogenized, and subjected to sequential centrifugation (7000 × g to 100,000 × g) to remove debris and concentrate exosome-like nanoparticles.
- Ultracentrifugation pellets were washed in PBS and resuspended for downstream analysis.
- Purity and morphology were confirmed by:
- Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM): vesicles ~79 nm with intact structure
- Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA): monodisperse population, zeta potential -13.9 mV
- Western blot: positive for HSP70 and TET8, confirming EN identity
Conclusion
This protocol enables efficient isolation of high-quality exosome-like nanoparticles from plant cell cultures. The method supports scalable production and downstream functional studies, highlighting its utility for plant-based nanocarrier development in biomedical applications.
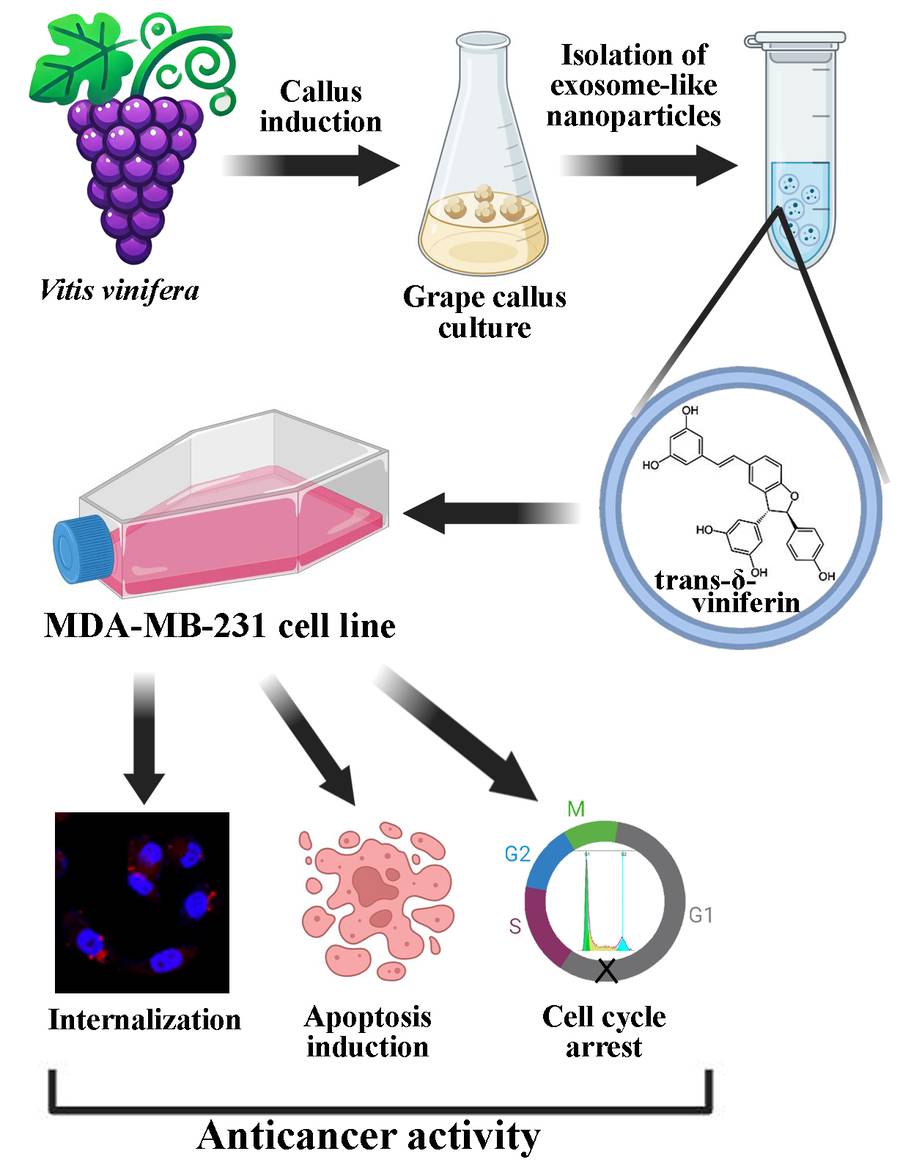 Figure 3. Exosome-Like Nanoparticles from Grape Cell Cultures with Anticancer Potential. (Shkryl Y, et al., 2024)
Figure 3. Exosome-Like Nanoparticles from Grape Cell Cultures with Anticancer Potential. (Shkryl Y, et al., 2024)
At Creative Biostructure, we specialize in isolating high-quality plant-derived exosomes tailored to your research and development needs. Whether you're working on drug delivery, bioactive compound studies, or nutraceutical innovation, our expert team is ready to support your goals. Contact us to discuss your project and receive a customized service quote.
References
- Mu N, Li J, Zeng L, et al. Plant-derived exosome-like nanovesicles: current progress and prospects. International Journal of Nanomedicine. 2023: 4987-5009.
- Sarasati A, Syahruddin M H, Nuryanti A, et al. Plant-derived exosome-like nanoparticles for biomedical applications and regenerative therapy. Biomedicines. 2023, 11(4): 1053.
- Shkryl Y, Tsydeneshieva Z, Menchinskaya E, et al. Exosome-like nanoparticles, high in trans-δ-Viniferin derivatives, produced from grape cell cultures: Preparation, characterization, and anticancer properties. Biomedicines. 2024, 12(9): 2142.
- Mun J G, Song D H, Kee J Y, et al. Recent advances in the isolation strategies of plant-derived exosomes and their therapeutic applications. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025, 47(3): 144.
Frequently Asked Questions
For any inquiries, our support team is ready to help you get technical support for your research and maximize your experience with Creative Biostructure.