Exosome Metabolomics Services
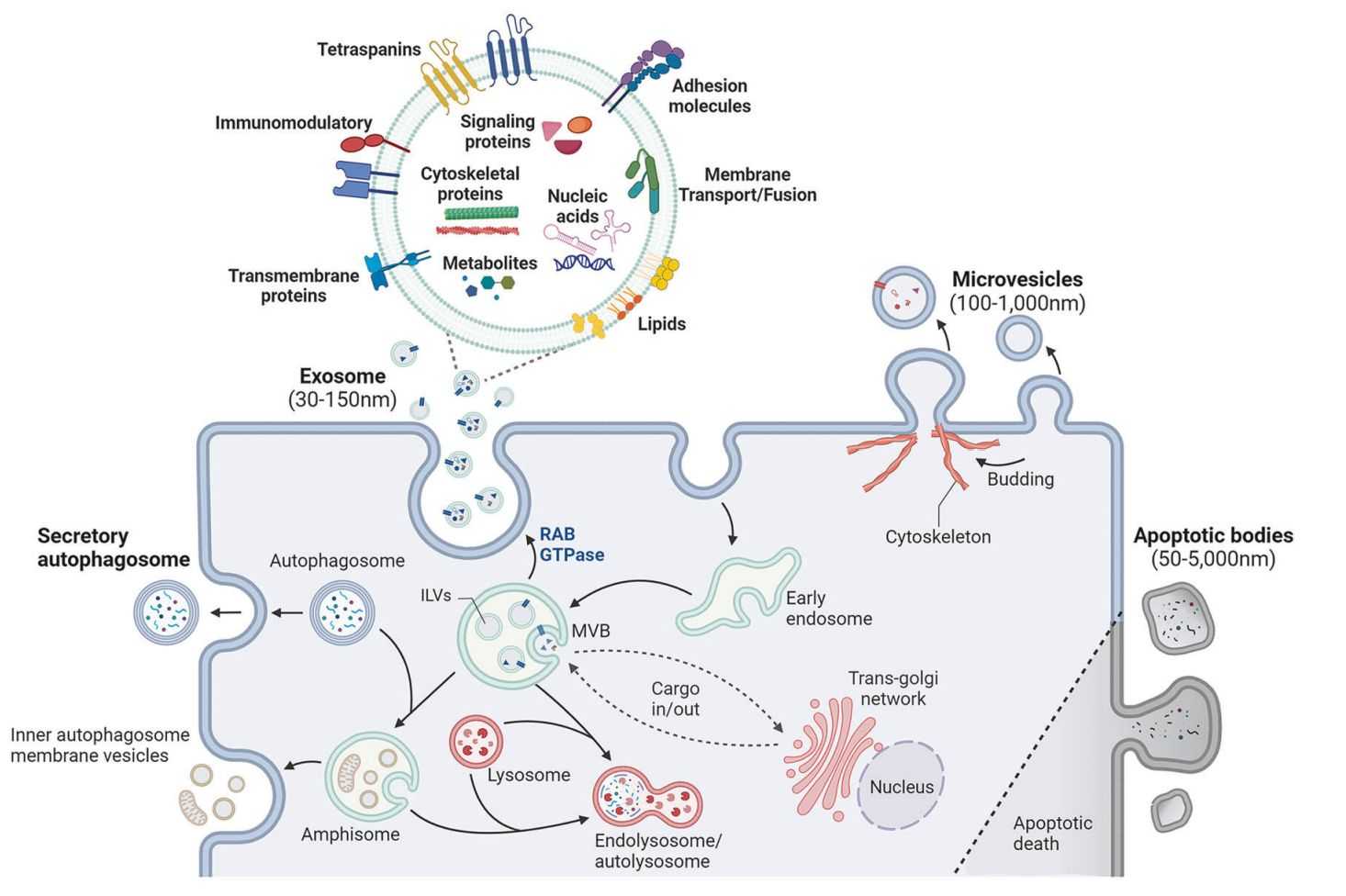
Exosomes carry a diverse range of bioactive molecules, including proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, and metabolites, that faithfully reflect the physiological and pathological states of their parent cells. While exosomal proteins and nucleic acids have been extensively studied, small-molecule metabolites within exosomes are emerging as powerful indicators of cell-cell communication, metabolic rewiring, and disease progression.
Creative Biostructure offers advanced untargeted and targeted exosome metabolomics services using high-resolution LC-MS/MS platforms, optimized EV isolation workflows, and expert bioinformatics interpretation.
What Is Exosome Metabolomics?
Exosome metabolomics refers to the systematic identification and quantification of small molecules encapsulated within or associated with extracellular vesicles. Because exosomes originate from multivesicular bodies and mirror the metabolic activity of donor cells, analyzing their metabolite composition can reveal:
- Early metabolic changes preceding phenotypic alterations
- Non-invasive biomarker signatures detectable in biofluids
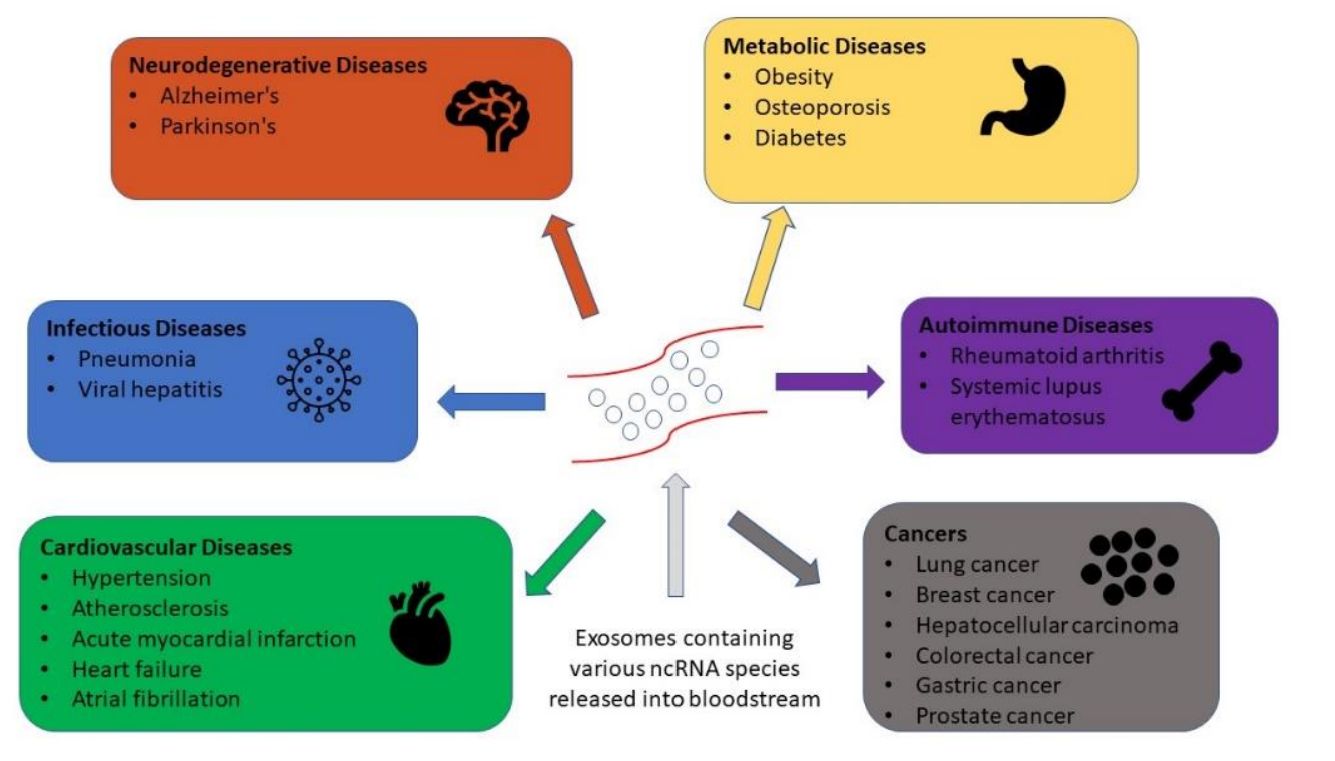
- Altered metabolic pathways in cancer, neurodegeneration, inflammation, infection, and metabolic disorders
- Drug-induced shifts in cellular metabolism
Both untargeted metabolomics (global, discovery-oriented) and targeted metabolomics (precise quantification of known metabolite classes) provide complementary insights for translational research and precision medicine.
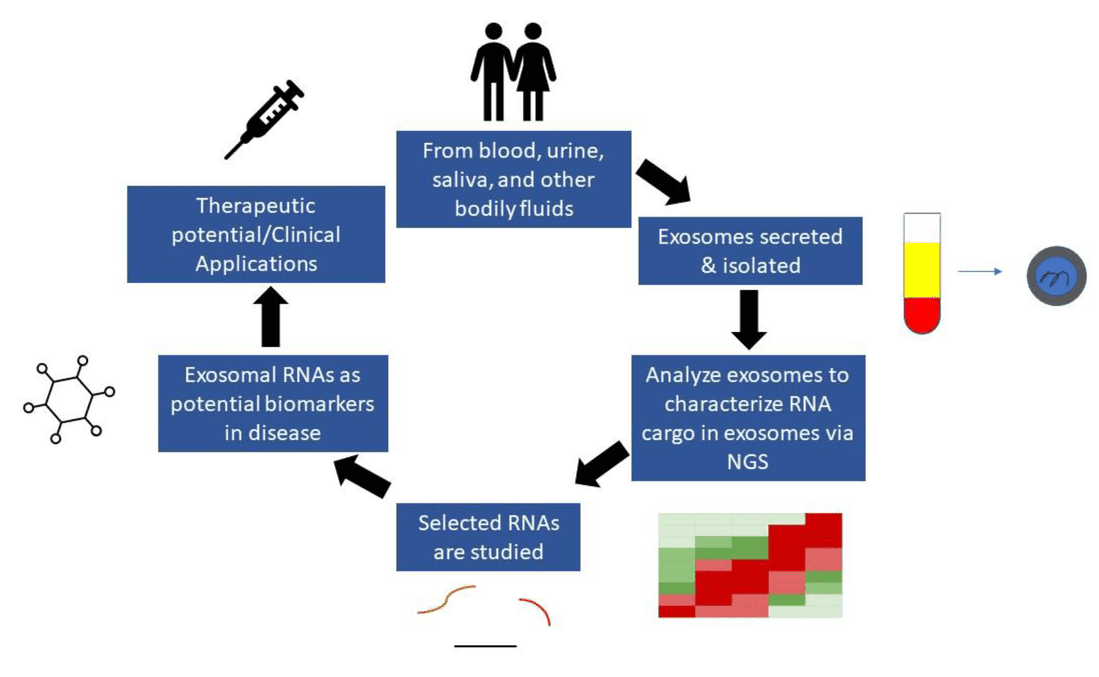
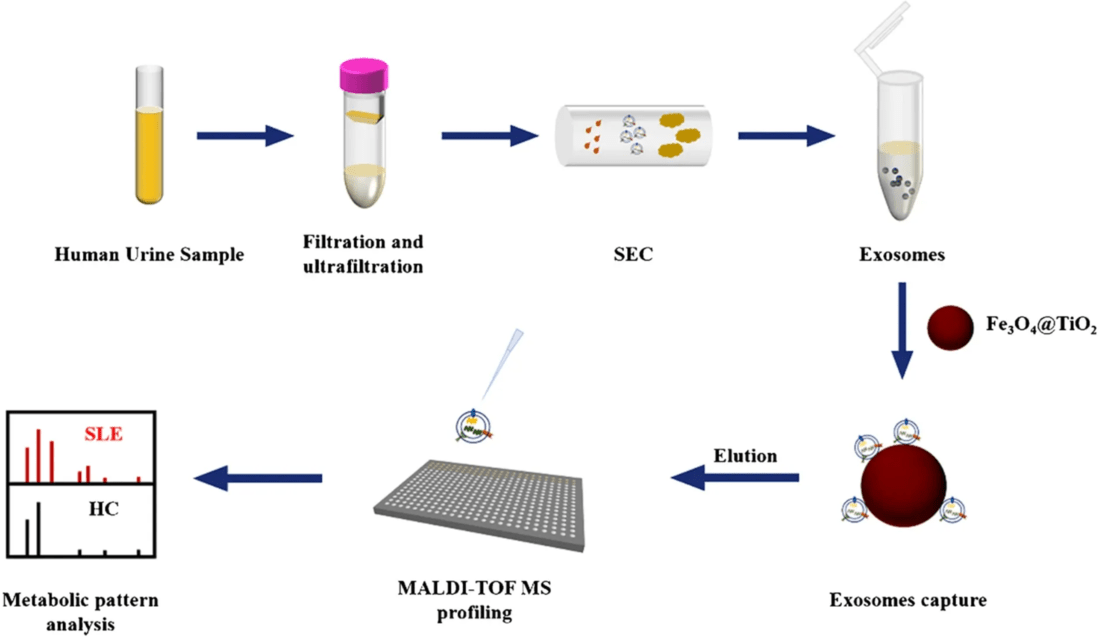 Figure 1. Overview of Urinary Exosome Isolation and Metabolomics Workflow. (Yan S, et al., 2023)
Figure 1. Overview of Urinary Exosome Isolation and Metabolomics Workflow. (Yan S, et al., 2023)
Why Conduct Exosome Metabolomics?
Researchers choose exosome metabolomics to:
- Detect disease-associated metabolic fingerprints
Exosomal metabolites can serve as sensitive biomarkers because they are shielded from degradation by the vesicle membrane.
- Elucidate metabolic reprogramming
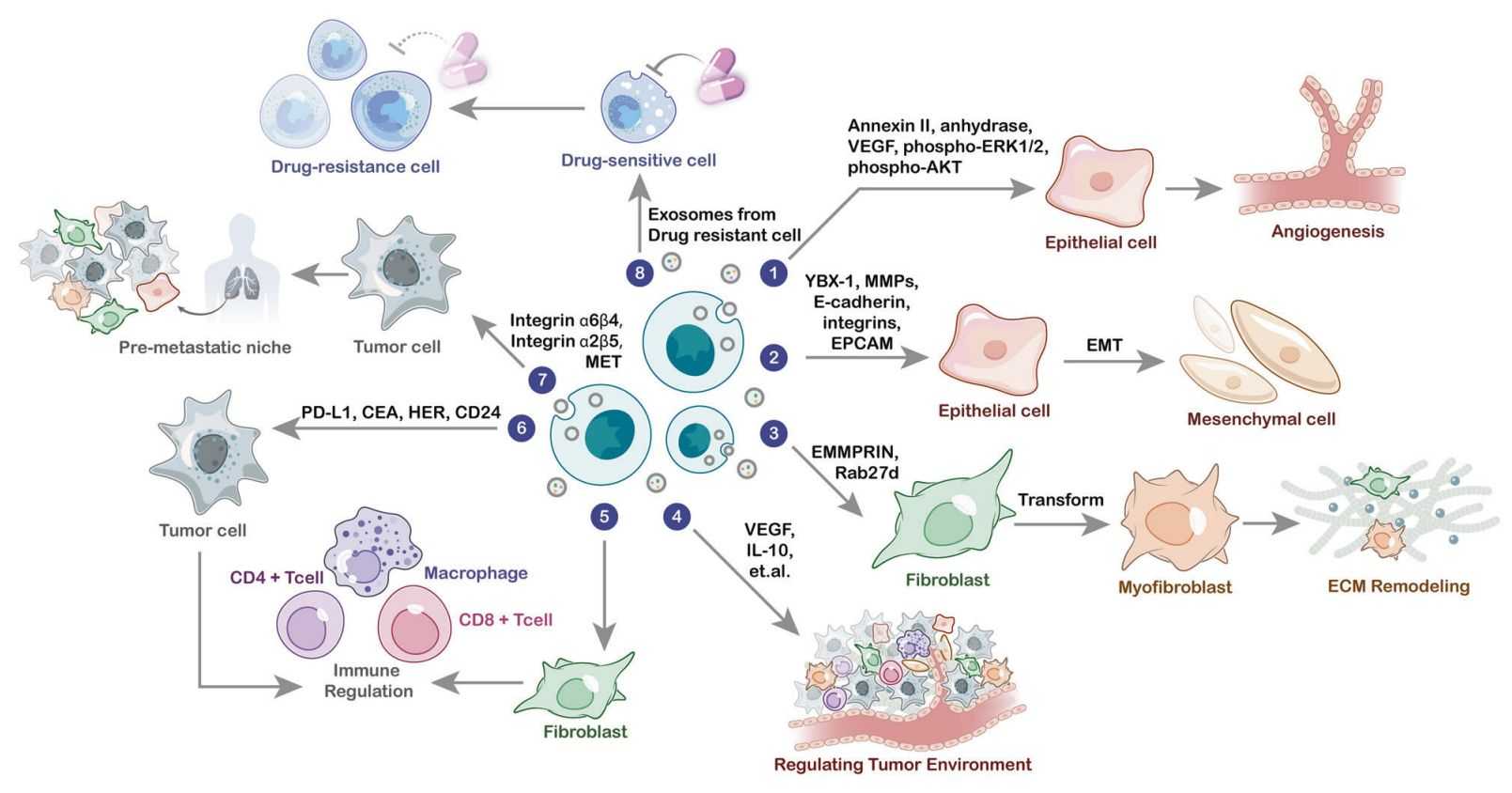
Exosomes transmit metabolic intermediates, lipids, and signaling molecules that influence immune modulation, tumor progression, and tissue physiology.
- Map pathway perturbations
Profiling metabolites helps reconstruct metabolic networks (e.g., glycolysis, TCA cycle, fatty acid oxidation).
- Support drug mechanism and toxicity studies
Tracking metabolite changes enables evaluation of therapeutic response and off-target effects.
- Study intercellular communication
Exosome-borne metabolites act as messengers that shape recipient cell behavior.
Our Exosome Metabolomics Solutions
| Category | Untargeted Exosome Metabolomics | Targeted Exosome Metabolomics |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Discovery of global metabolic changes | Accurate quantification of defined metabolite panels |
| Analytical Platform | High-resolution LC-MS/MS (Orbitrap / Q-TOF) | Triple quadrupole LC-MS/MS |
| Ideal For |
|
|
| Key Features |
|
|
| Typical Metabolite Panels | Not predefined (discovery-based) |
|
Technical Platforms
Our metabolomics facility integrates multiple analytical platforms:
- Orbitrap high-resolution mass spectrometers
- Q-TOF LC-MS for broad coverage
- Triple quadrupole systems for high-precision quantification
- GC-MS for volatile or derivatized metabolites
- Software: Compound Discoverer, MetaboAnalyst, Skyline, XCMS, MS-DIAL
Our Exosome Metabolomics Workflow
Our optimized workflow ensures high-purity vesicles and reliable metabolite profiling:
Sample Receipt & Quality Control
Samples are checked for volume, integrity, and handling history to ensure they meet the criteria for reliable exosome metabolomics analysis.
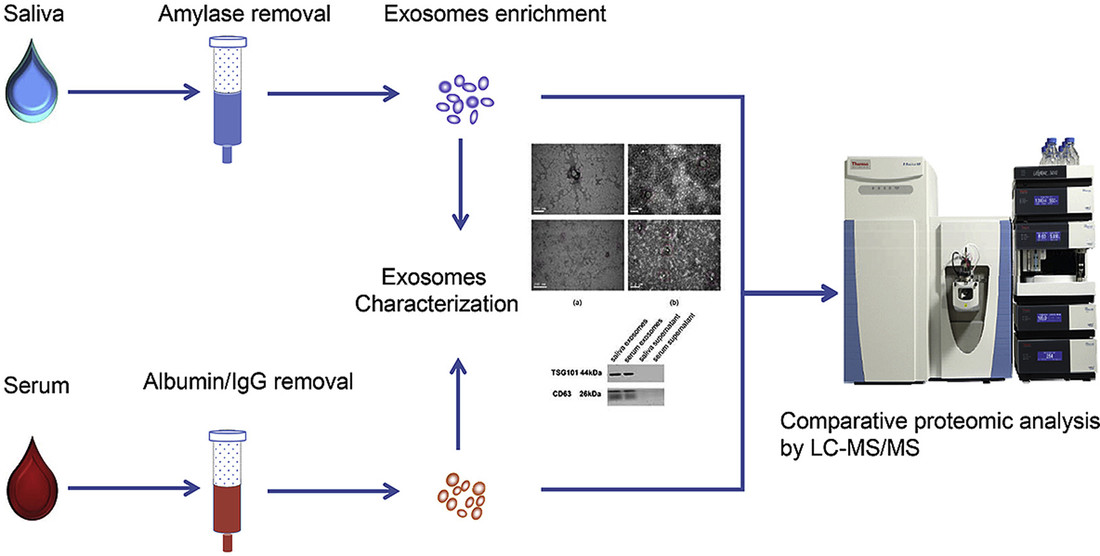
Exosome Isolation & Exosome Characterization
Exosomes are isolated and characterized using validated methods to obtain high-purity vesicles suitable for downstream metabolite profiling.
Metabolite Extraction & LC-MS/MS Run
Hydrophilic and hydrophobic metabolites are extracted with optimized protocols, then injected onto LC-MS/MS platforms for sensitive detection.
Data Processing & Metabolite Identification
Raw spectra are processed for peak picking, alignment, normalization, and metabolite identification using curated databases and QC filters.
Pathway Interpretation & Reporting
Significant metabolites are linked to pathways, visualized, and summarized in a publication-ready report with statistics and interpretation.
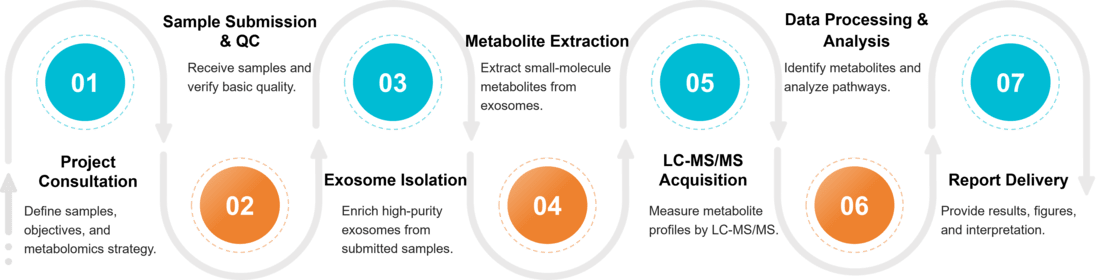 Figure 2. Project Workflow for Exosome Metabolomics. (Creative Biostructure)
Figure 2. Project Workflow for Exosome Metabolomics. (Creative Biostructure)
Sample Requirements
We support a wide range of sample types:
| Sample Type | Recommended Amount | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Biofluids (serum, plasma, urine, CSF) | ≥ 100-500 μL | Store at -80°C; avoid hemolysis and freeze-thaw cycles |
| Tissue | 50-200 mg | Snap freeze immediately post-collection |
| Cell culture supernatant | ≥ 2 mL | Collect debris-free conditioned medium |
| Cell pellets | ≥ 1 × 107 cells | Wash gently to avoid metabolite leakage |
Our experts can advise on sample preparation to maximize EV yield and metabolite integrity.
Reporting & Deliverables (Publication-Ready)
Clients receive a complete analysis package, including:
- Raw LC-MS/MS data
- Peak tables and normalized intensity matrices
- Identified metabolites with confidence levels
- Differential metabolite analysis (FC, p-value, FDR)
- Volcano plots, PCA, PLS-DA, heatmaps
- Pathway enrichment and metabolic network interpretation
- Detailed methods, instrument parameters, and QC metrics
- Optional multi-omics integration with exosome proteomics/lipidomics
Key Applications Supported by Exosome Metabolomics
Our exosome metabolomics services support a wide range of research objectives:
- Disease Mechanism Research: Understand metabolic signaling in cancer, cardiovascular disorders, neurodegeneration, and inflammatory diseases.
- Biomarker Discovery & Validation: Identify metabolite signatures from blood, urine, CSF, or other biofluids for diagnosis or prognosis.
- Drug Efficacy & Toxicity Assessment: Monitor metabolic shifts induced by small molecules, biologics, or cell therapies.
- Metabolic Pathway Reconstruction: Explore alterations in energy metabolism, amino acid metabolism, lipid turnover, and redox balance.
- Precision Medicine & Patient Stratification: Reveal metabolic heterogeneity between patient subgroups.
Why Choose Creative Biostructure
- Specialized EV Metabolomics Platform: Dedicated workflows optimized specifically for exosome-derived metabolites
- Advanced Mass Spectrometry: Orbitrap, Q-TOF, and triple quadrupole systems for accurate identification and quantification.
- Expert Bioinformatics Team: PhD-level data scientists provide deep biological interpretation.
- Multi-Omics Integration Available: Combine metabolomics with proteomics, lipidomics, glycomics, or transcriptomics.
- Flexible Study Design: Customizable protocols to meet unique scientific or translational goals.
- Transparent Reporting & Strong QA/QC: Detailed documentation ensures reproducibility and publication readiness.
Case Study
Case: Succinate-Activated Exosomes Reveal TCA-Driven Remodeling
Background
Bone marrow-derived stromal cells were stimulated with succinate to generate bioenergetic exosomes (Suc-EXO) and compared with native exosomes (N-EXO). EV identity was confirmed before metabolomics to avoid non-EV bias.
Methods
- Identification: TEM verified vesicle morphology; EV markers (e.g., CD81, TSG101) were enriched, while non-EV proteins were reduced.
- Metabolomics: Untargeted LC-MS profiled exosomal metabolites, followed by multivariate statistics and pathway analysis.
Results
- Suc-EXO and N-EXO showed clear separation in PCA/PLS-DA models.
- Dozens of metabolites significantly changed, with TCA cycle and amino acid–related metabolites prominently increased in Suc-EXO (e.g., succinate, citrate).
- Metabolic shifts were consistent with higher ATP content, indicating enhanced bioenergetic status.
Conclusion
Succinate stimulation reshaped the exosomal metabolome toward intensified TCA activity and amino acid metabolism. This case illustrates how well-controlled untargeted exosome metabolomics can capture donor cell metabolic reprogramming and support mechanism-focused biomarker discovery.
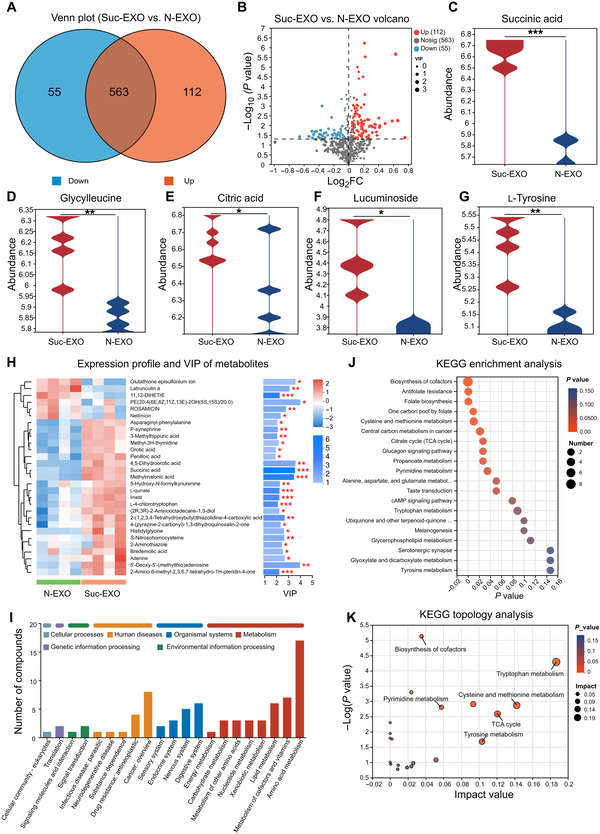 Figure 3. Metabolomic comparison of Suc-EXO and N-EXO. (A) Venn diagram and (B) volcano plots of differential metabolites. (C-G) Relative abundances of selected metabolites. (H) Heatmap and VIP scores of differential metabolites. (I-K) KEGG pathway classification, enrichment, and topology analysis. FC, fold change; cAMP, cyclic adenosine 3′,5′-monophosphate. (Liu X, et al., 2024)
Figure 3. Metabolomic comparison of Suc-EXO and N-EXO. (A) Venn diagram and (B) volcano plots of differential metabolites. (C-G) Relative abundances of selected metabolites. (H) Heatmap and VIP scores of differential metabolites. (I-K) KEGG pathway classification, enrichment, and topology analysis. FC, fold change; cAMP, cyclic adenosine 3′,5′-monophosphate. (Liu X, et al., 2024)
Ready to transform exosome metabolite profiles into meaningful biological insights? Whether you aim to discover new metabolic biomarkers, quantify defined metabolite panels, or uncover pathway-level alterations, our advanced LC-MS/MS platforms and expert bioinformatics support deliver precise, publication-ready results. Contact us to discuss your study goals and receive a fast, customized project quotation.
References
- Yan S, Huang Z, Chen X, et al. Metabolic profiling of urinary exosomes for systemic lupus erythematosus discrimination based on HPL-SEC/MALDI-TOF MS. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry. 2023, 415(26): 6411-6420.
- Liu X, Jiang S, Jiang T, et al. Bioenergetic-active exosomes for cartilage regeneration and homeostasis maintenance. Science Advances. 2024, 10(42): eadp7872.
Frequently Asked Questions
For any inquiries, our support team is ready to help you get technical support for your research and maximize your experience with Creative Biostructure.