Exosomal Phosphoproteomics Analysis Services
Exosomes, as pivotal messengers in intercellular communication, carry phosphorylated proteins that hold the key to unraveling the core mechanisms of life activities and diseases. Although exosomal phosphoproteins play critical roles in processes such as the tumor microenvironment, their comprehensive landscape remains a terra incognita. Creative Biostructure offers professional exosomal phosphoproteomics analysis solutions. Our advanced technology platform and specialized services enable reliable identification, quantification, and functional interpretation of exosomal phosphorylated proteins, empowering clients to discover novel biomarkers and uncover new functions of phosphorylation signaling in cellular communication.
Why is Exosomal Phosphoproteomics Important?
Exosomes, as nanoscale vesicles secreted by cells, can carry biomolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids from their source cells, mediating long-distance intercellular signaling within the body. Protein phosphorylation, one of the most critical post-translational modifications in eukaryotes, serves as a core switch in cellular signaling pathways (e.g., proliferation, apoptosis, metabolic regulation). Exosomal phosphoproteomics analysis holds significant applications in the following areas:
- Non-invasive Biomarkers: Exosomes are stable in biofluids, making their analysis a less invasive method for detecting disease biomarkers compared to traditional biopsies.
- Disease Diagnosis & Monitoring: Changes in exosomal phosphoproteome can provide clues about disease conditions, such as cancer and neurodegenerative diseases.
- Understanding Signaling Pathways: The analysis reveals how protein phosphorylation regulates cellular processes and intercellular communication, providing insights into disease mechanisms.
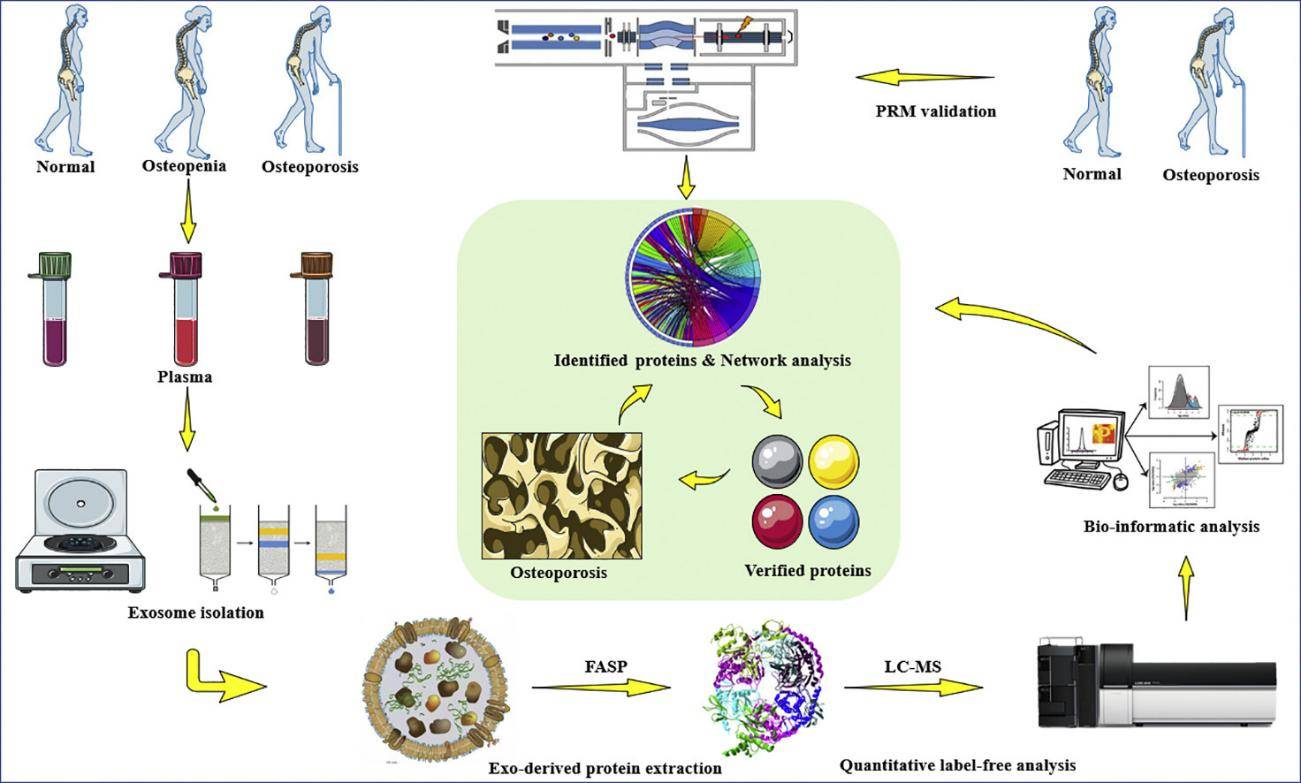
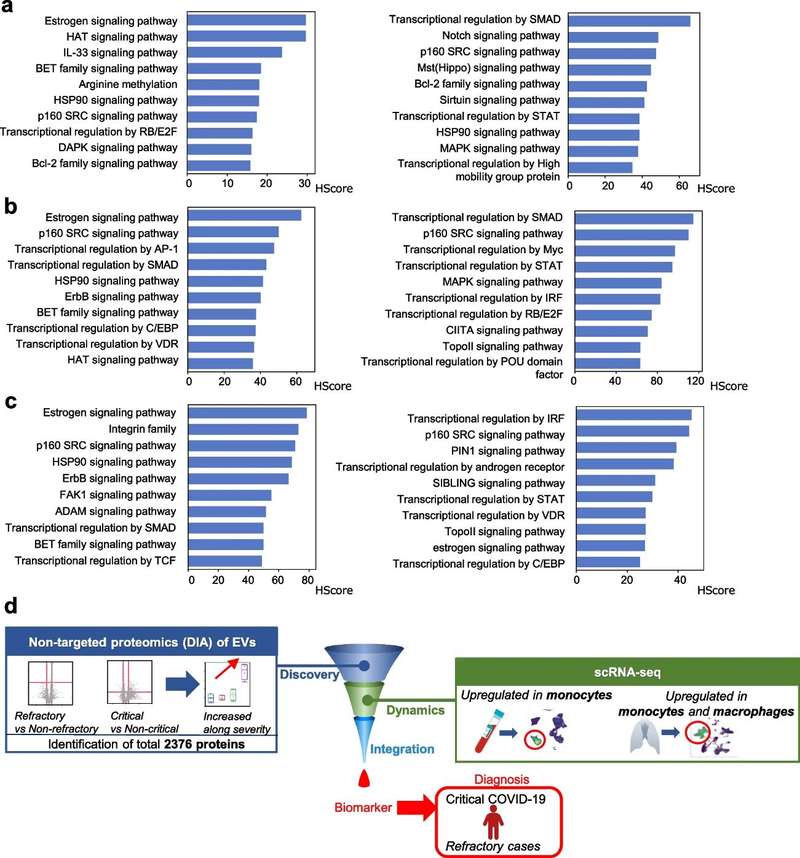
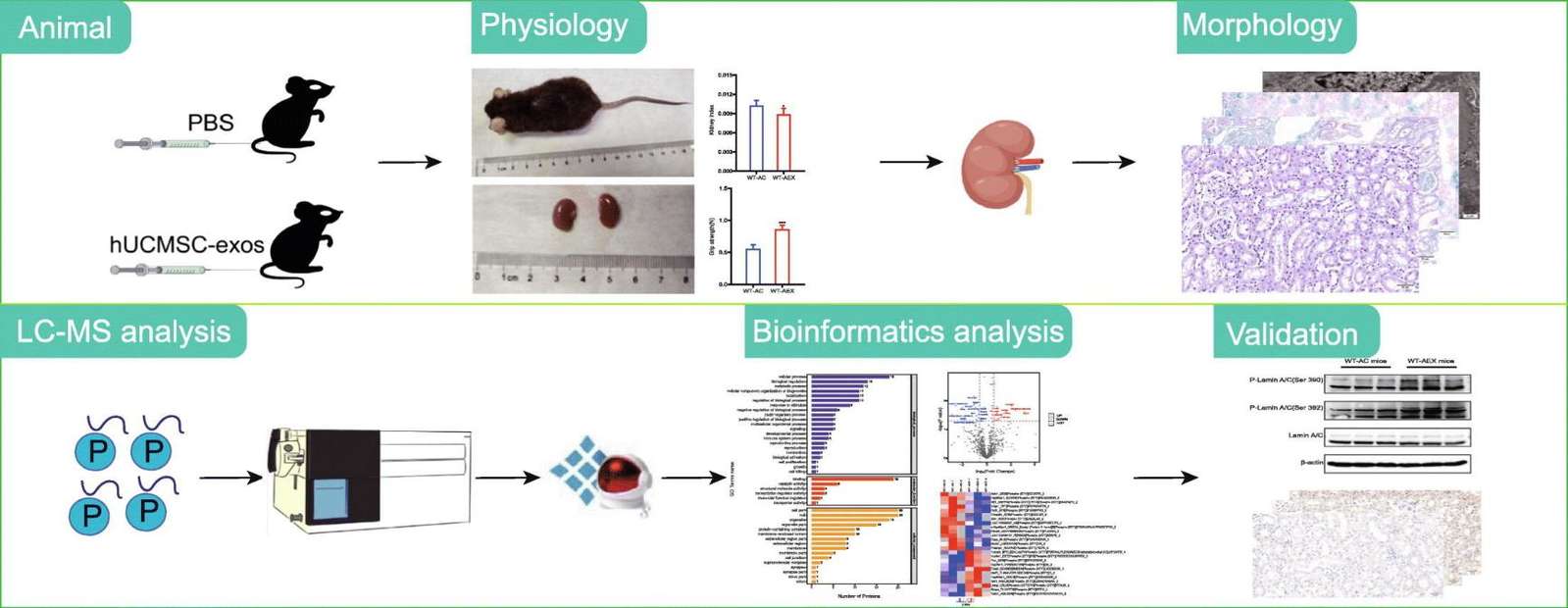 Figure 1. Phosphoproteomics reveals anti-aging mechanisms of hUCMSC-exosomes in kidney. (Yu W, et al., 2025)
Figure 1. Phosphoproteomics reveals anti-aging mechanisms of hUCMSC-exosomes in kidney. (Yu W, et al., 2025)
Our Exosomal Phosphoproteomics Analysis Service
Creative Biostructure leverages its advanced high-precision mass spectrometry platform, optimized phosphopeptide enrichment strategies, and stringent quality control system to achieve precise identification, absolute/relative quantitation, and functional analysis of phosphorylated proteins in complex exosome samples.
We begin with robust protocols for exosome isolation and protein extraction, ensuring the preservation of labile phosphorylation states. Our workflow then employs advanced phosphopeptide enrichment techniques coupled with high-sensitivity mass spectrometry, enabling deep, unbiased profiling of even low-abundance phosphoproteins in your samples.
The true power of our service lies in the integrated bioinformatics analysis. We deliver:
- Identification and Quantification of phosphorylation sites and their relative abundance.
- Kinase Activity Prediction to link phosphosignatures to upstream regulatory kinases.
- Pathway and Network Analysis to place the phosphoproteomic data into a meaningful biological context.
- Comparative Phosphoproteomics to identify signaling pathways activated or suppressed between experimental conditions.
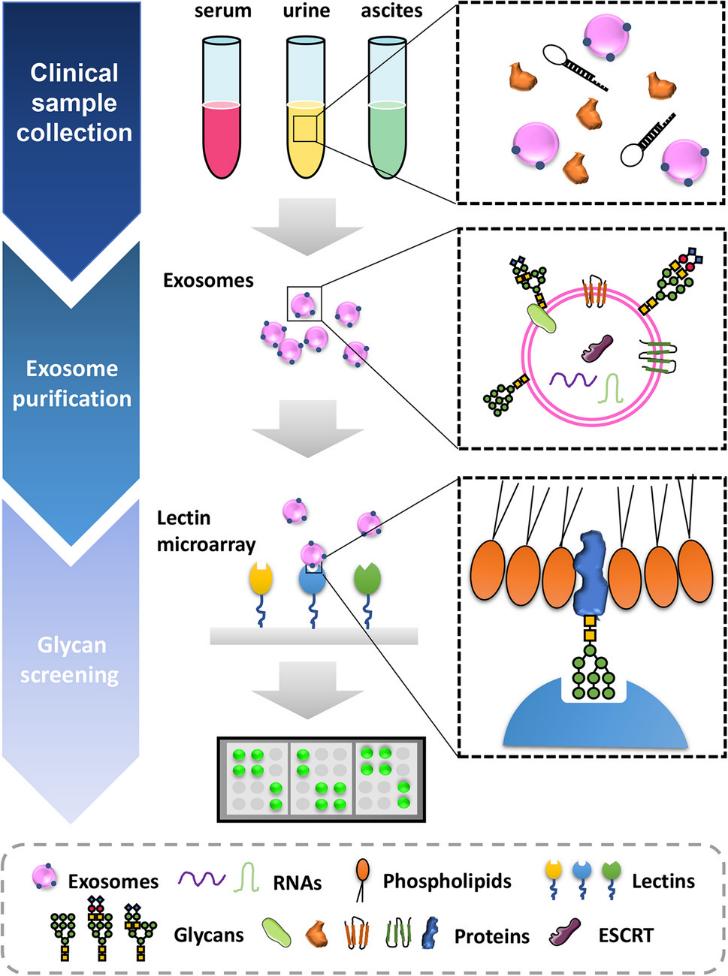
Workflow of Exosomal Phosphoproteomics Analysis Service
We provide accurate phosphoprotein profiling via a streamlined, end-to-end workflow. This process covers all critical stages, from sample preparation through data analysis, with each optimized step detailed in the following section.
Sample Receipt and Evaluation
- Samples such as blood, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), and cell culture supernatant are accepted, with accompanying sample information collected simultaneously.
- Exosome concentration/size distribution is determined by Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA), and marker expression is confirmed by Western Blot to ensure sample quality.
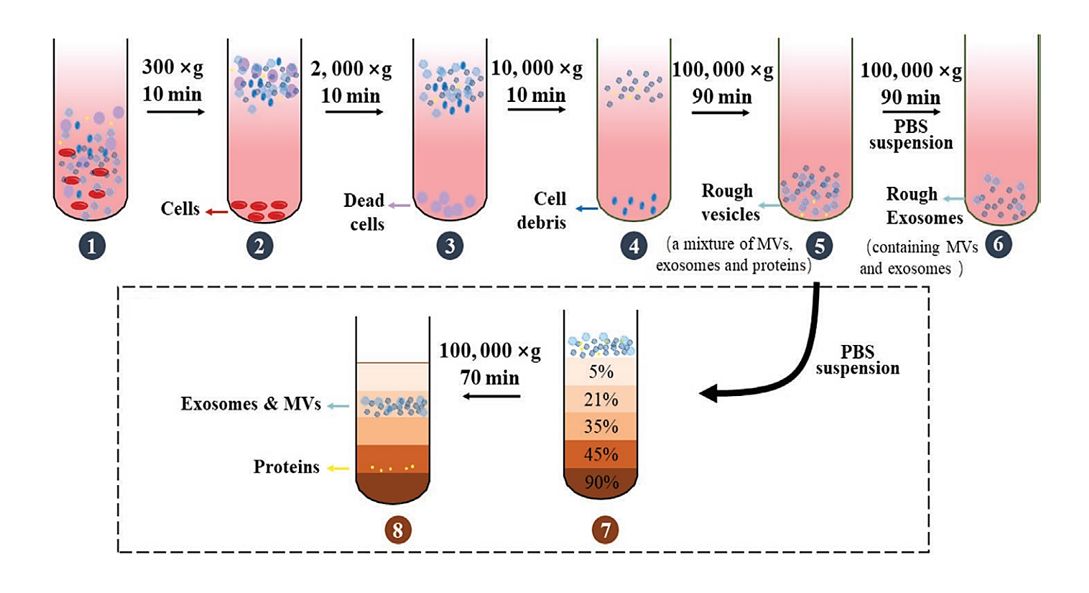
Exosome Purification
- Select the appropriate protocol based on sample type (Body fluids: Centrifugation + Immuno-magnetic beads; Cell supernatants: Centrifugation + Density gradient).
- To ensure a purity of >90%, purified samples are characterized by BCA assay for protein concentration and Western Blot for verification.
Phosphoprotein Extraction and Peptide Enrichment
- Proteins are extracted using RIPA lysis buffer containing phosphatase inhibitors, followed by trypsin digestion and desalting.
- Enrich phospho-peptides using TiO₂/Fe³⁺-IMAC magnetic beads, ensuring removal efficiency of non-phosphorylated peptides exceeds 95%.
High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry Detection and Quantification
- Select the QE-HF/Orbitrap Exploris 480 mass spectrometer for label-free or TMT/iTRAQ quantitative analysis as required.
- MaxQuant filters data to ensure phosphopeptide confidence >99% (FDR <1%).
Bioinformatics Analysis
- Basic Analysis: Identification of phosphorylated proteins/sites, screening of differentially expressed phosphoproteins, and prediction of upstream kinases.
- Functional Analysis: GO annotation, KEGG pathway enrichment, and construction of PPI networks.
- Customized Analysis: We provide biomarker screening analysis or drug pathway enrichment analysis based on client requirements.
 Figure 2. Exosomal phosphoproteomics analysis service workflow. (Creative Biostructure)
Figure 2. Exosomal phosphoproteomics analysis service workflow. (Creative Biostructure)
Sample Requirements
| Sample Type | Minimum Volume/Amount | Storage Condition | Shipping Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| Serum/Plasma | 50μL | -80°C (no repeated freeze-thaw) | Dry ice, <72h transit |
| Cerebrospinal Fluid | 100μL | -80°C | Dry ice |
| Cell Supernatant | 5mL (1×10⁶ cells) | -80°C | Avoid cell debris |
| Tissue Homogenate | 20mg | -80°C | Add protease inhibitor |
Final Deliverables
- Comprehensive Analysis Report (experimental protocol + QC results + differential phosphoprotein list)
- Raw mass spectrometry data (.raw format)
- Editable visualization files (volcano plot, heatmap, PPI network; .svg/.pdf)
- Supplementary tables (phosphorylation sites, kinase prediction, KEGG enrichment results)
Service Advantages
- Low Sample Requirement: 50μL fluid samples (competitors: 100-200μL)
- Clinical-Grade QC: Exosome purity >90% (Western Blot: CD63/CD81/TSG101)
- Customized Analysis: ROC curve for clinical biomarkers + drug target mapping
- 1-on-1 Support: Mass spectrometrists + bioinformaticians for result interpretation
Case Study
Case: Phosphoproteomics of Breast Cancer sEVs Identifies Disease-Specific Phosphoenzymes
Background
Small membrane-derived extracellular vesicles have been proposed as participating in several cancer diseases, including breast cancer (BC). This study performed a phosphoproteomic analysis of breast cancer-derived small extracellular vesicles (sEVs) to provide insight into the molecular and cellular regulatory mechanisms important for breast cancer tumor progression and metastasis.
Methods
- Cell Culturing and sEV Isolation
- Differential Ultracentrifugation (UC)
- Quantification of sEVs by Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA)
- Sample Preparation for Phosphoproteomics
- Phosphopeptide Enrichment by IMAC and TiO2
- Nano-LC-MS/MS
- MS Spectra Processing
- Data Filtering and Phosphorylation Site Localization
- Disease and Functional Annotation Analysis
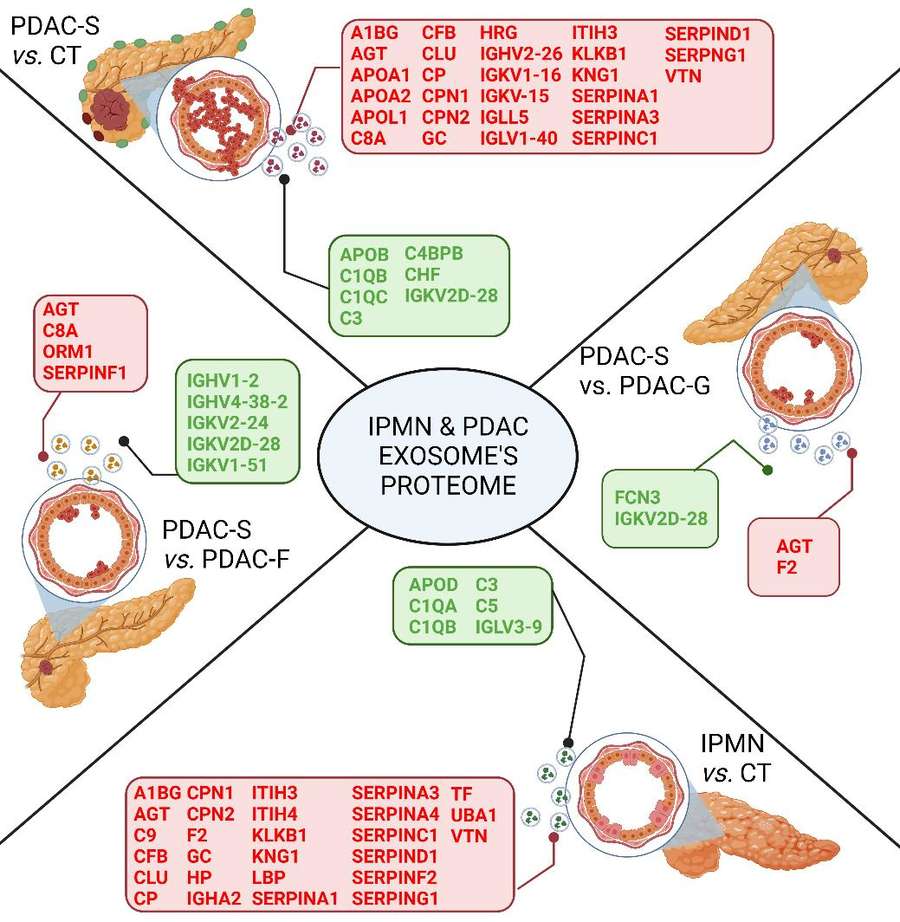
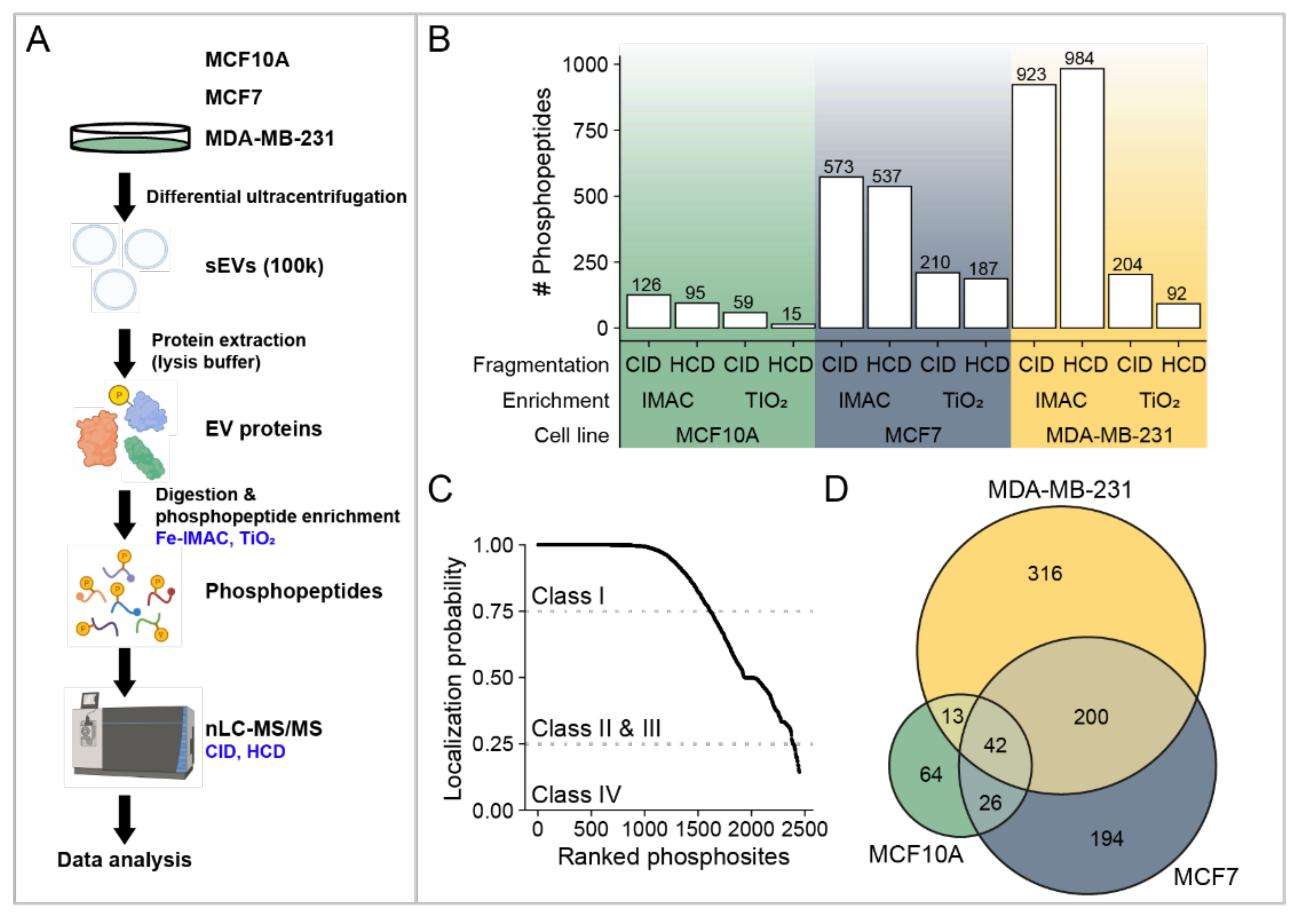 Figure 3. Overview of the identified phosphopeptides and phosphoproteins. (Minic Z, et al., 2022)
Figure 3. Overview of the identified phosphopeptides and phosphoproteins. (Minic Z, et al., 2022)
Conclusion
This study conducted a phosphoproteomic analysis of breast cancer-derived extracellular vesicles from the MCF10A, MCF7, and MDA-MB-231 cell lines. A total of 855 distinct phosphoproteins were identified across the cell lines, covering a wide range of functions, most of which are cancer-associated. The three phosphorylated enzymes ACLY, SIRT1, and SIRT6 showed a significantly higher specific enzymatic activity in MDA-MB-231 in comparison to MCF10A-derived sEVs. These three enzymes might serve as a potential prognostic biomarker for BC.
Creative Biostructure provides clients with end-to-end solutions spanning from experimental design to data interpretation. We are committed to collaborating with our clients to jointly drive breakthrough advancements in their research projects. Contact us to learn more about applying this technology to your specific research needs.
References
- Minic Z, Hüttmann N, Poolsup S, et al. Phosphoproteomic analysis of breast cancer-derived small extracellular vesicles reveals disease-specific phosphorylated enzymes. Biomedicines. 2022, 10(2): 408.
- Yu W, Jia X, Qiao H, et al. Phosphoproteomic analysis reveals the mechanisms of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes attenuate renal aging. Journal of Proteomics. 2025, 310: 105335.
Frequently Asked Questions
For any inquiries, our support team is ready to help you get technical support for your research and maximize your experience with Creative Biostructure.