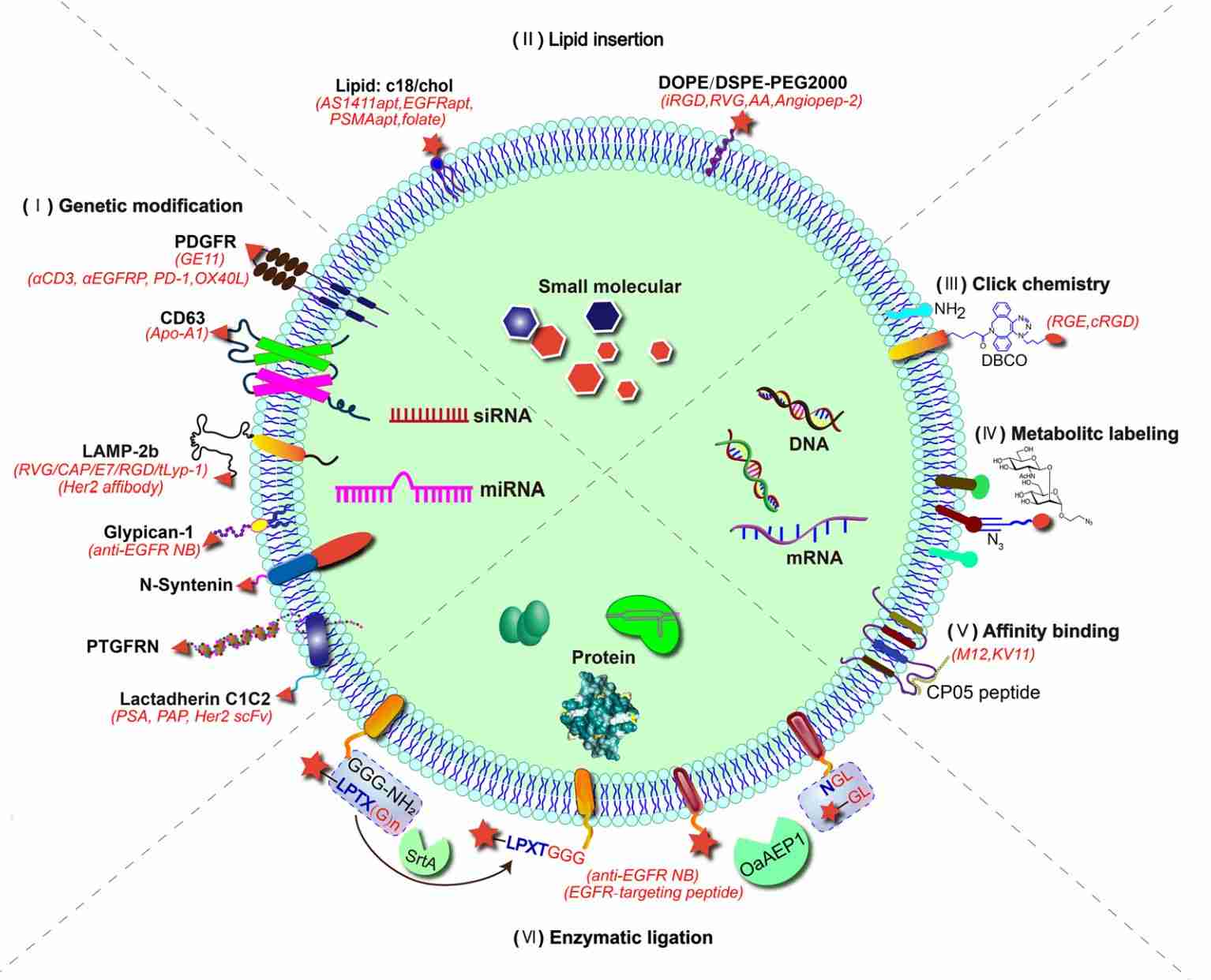
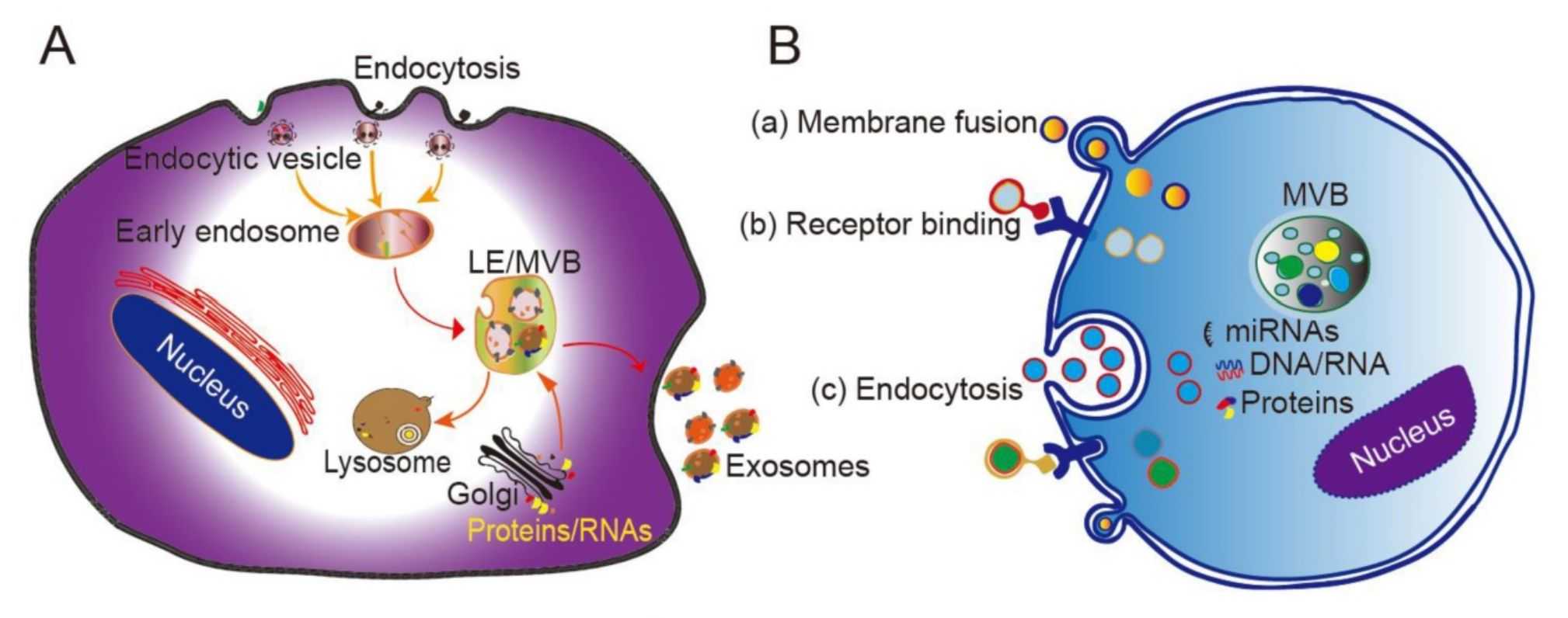
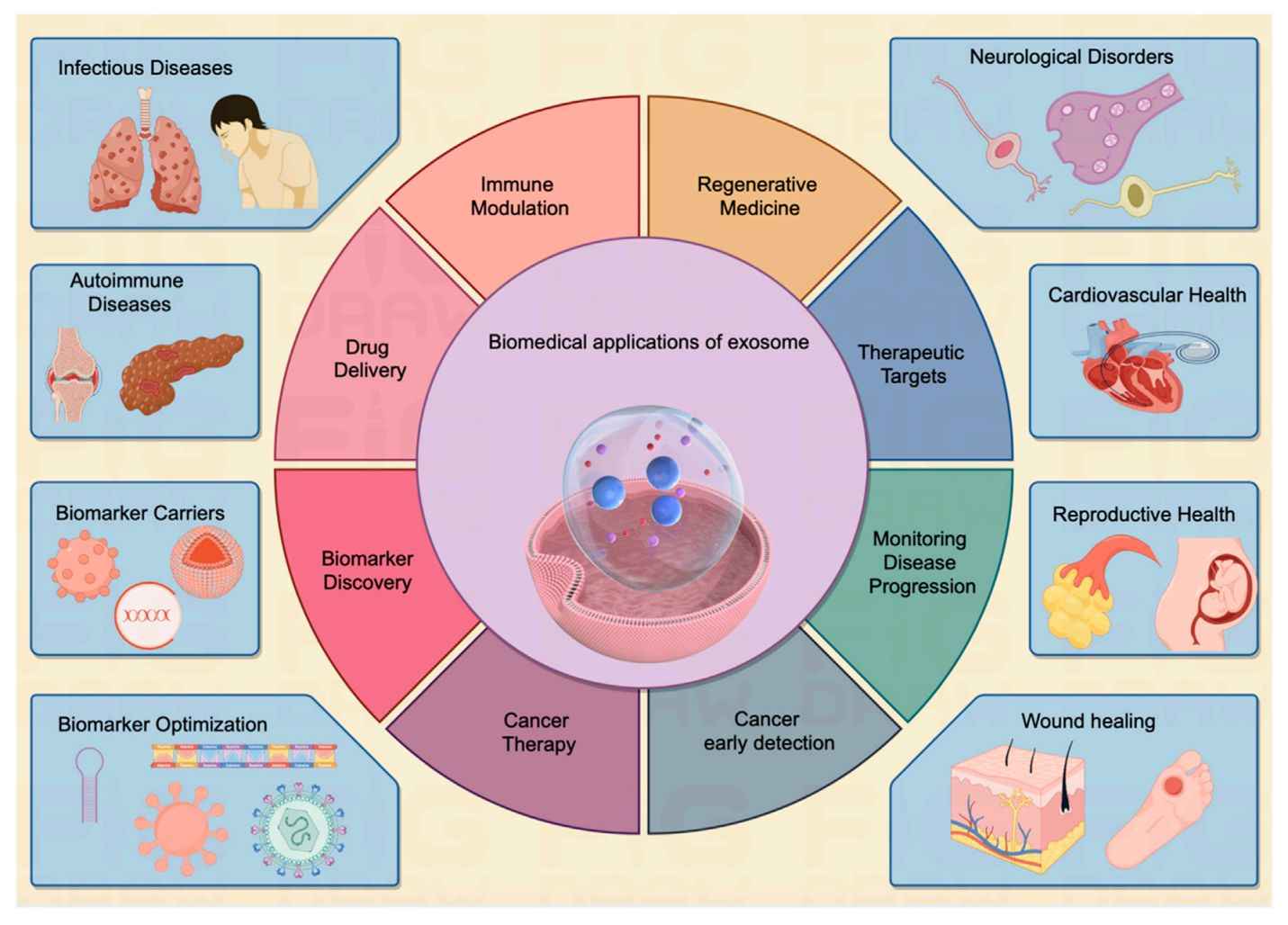
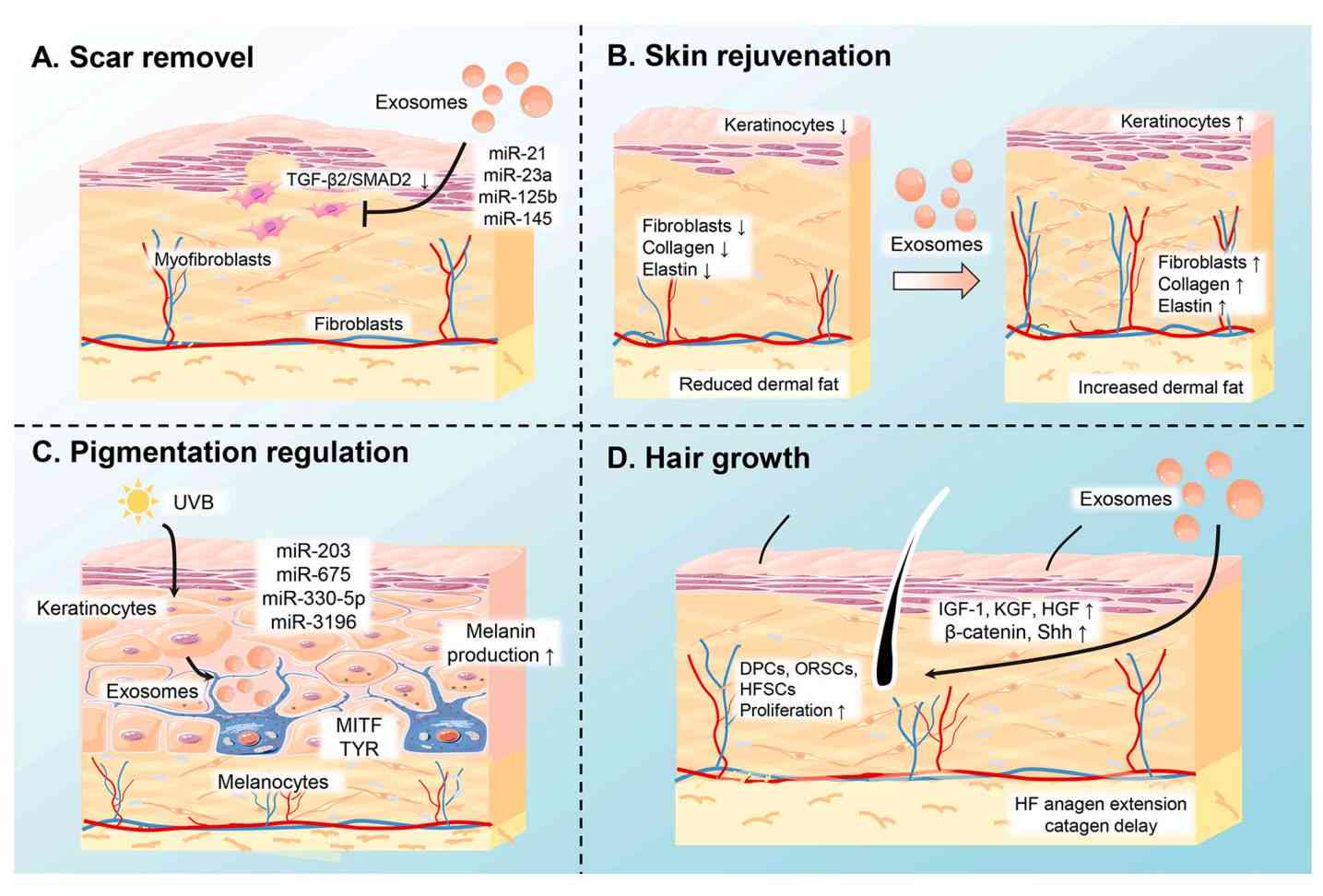
Exosome Organoid-based Functional Assays
Traditional 2D cell cultures and animal models often fail to accurately predict human responses to therapies. Organoids—self-organizing, 3D multi-cellular structures that mimic the architecture and function of real human organs—represent the next frontier in preclinical testing. Our Exosome Organoid-Based Functional Assays provide a cutting-edge platform to test your exosome's function in these highly physiological "mini-organs."
This service allows you to move beyond simplified models and assess your exosome's therapeutic efficacy, toxicity, and mechanism of action in a complex, human-relevant microenvironment. We enable the live tracking of inter-organ communication at a micro-scale, providing unparalleled insights into how your exosome in vitro treatment impacts organ-specific biology.
Why Use Organoids for Exosome Functional Testing?
Organoids offer a level of biological complexity that is simply unattainable in other in vitro systems.
- Unmatched Physiological Relevance: Comprised of multiple, organ-specific cell types (e.g., epithelial, stromal, immune), organoids replicate the intricate cell-cell interactions of a real organ.
- Ideal for Disease Modeling: We can use patient-derived organoids (PDOs) to create personalized disease models (e.g., a specific patient's tumor), allowing you to test your exosome's efficacy on a truly relevant target.
- Predictive Power: Data generated from organoid studies has shown a high correlation with human clinical outcomes, making it a powerful tool for de-risking your therapeutic pipeline.
- Complex Endpoint Analysis: Allows for advanced readouts, including high-content imaging of 3D structures, cell-type specific responses, and biomarker expression changes.
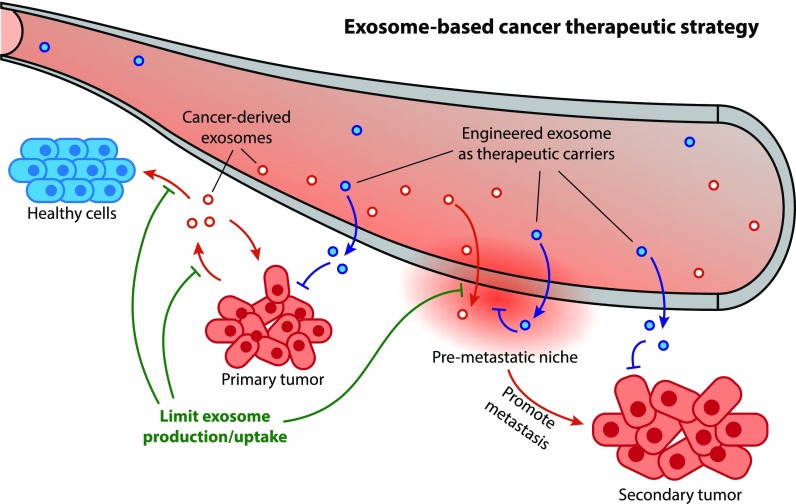
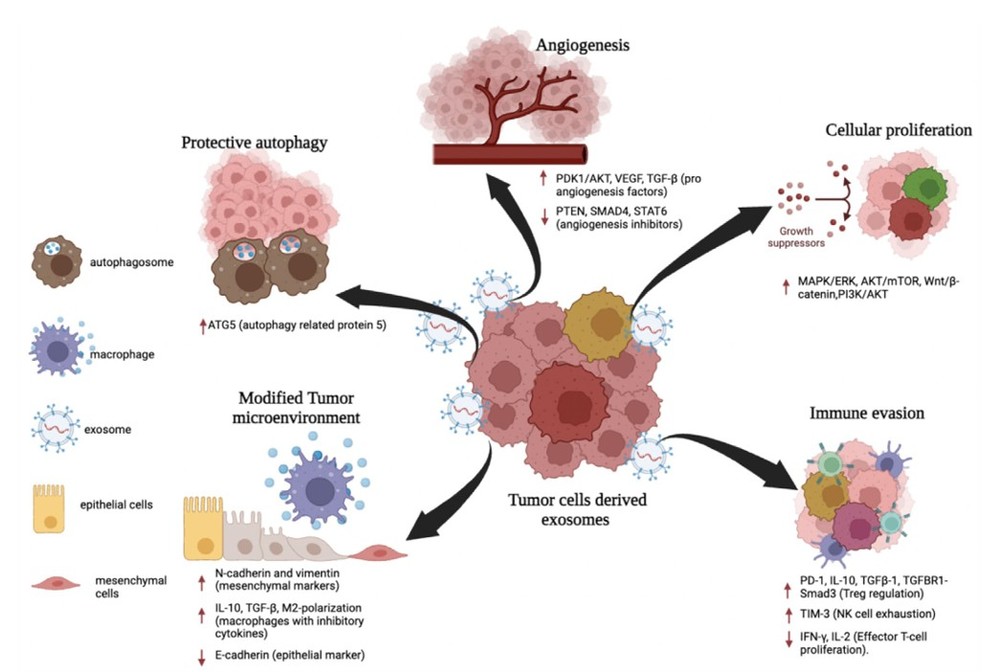
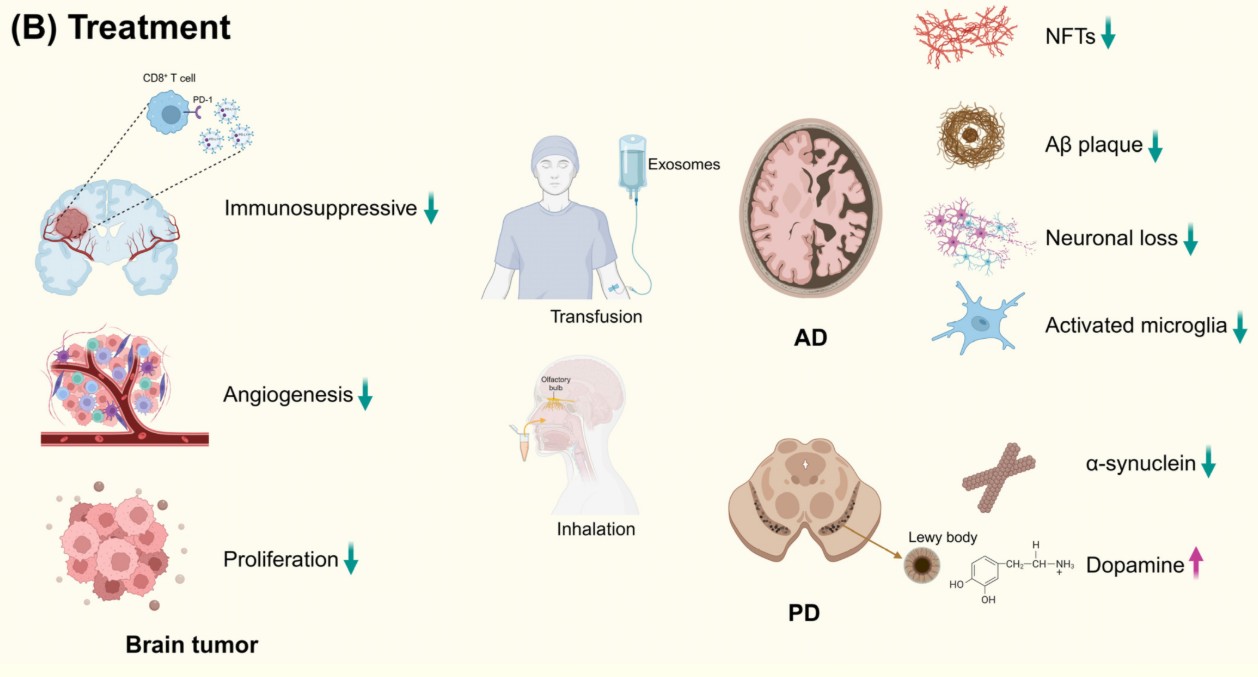
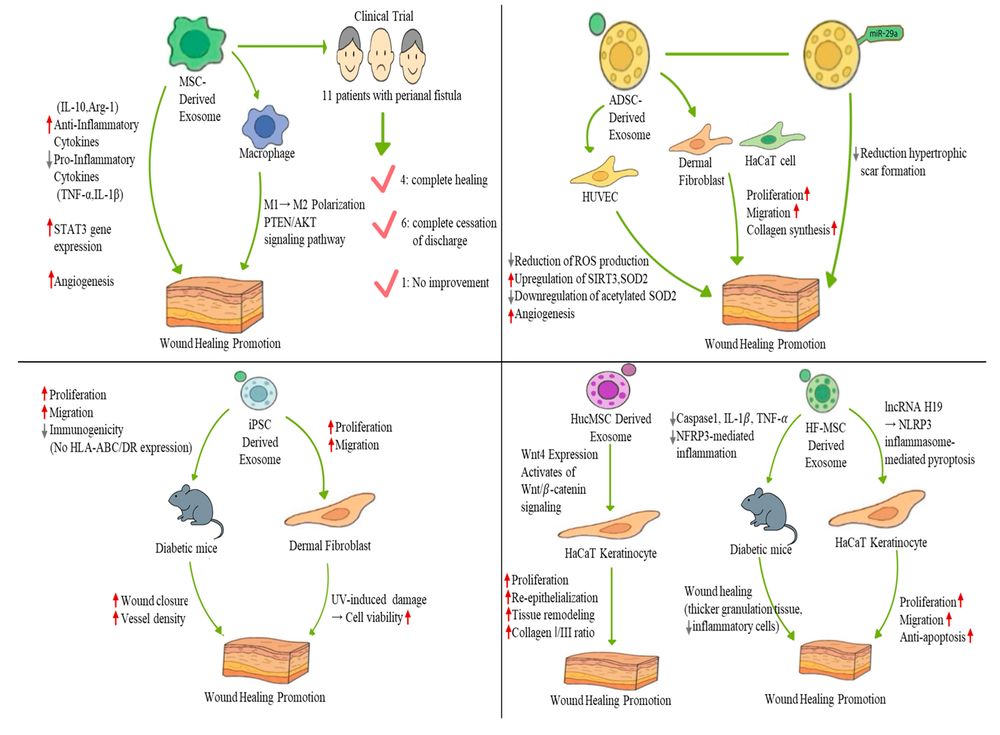
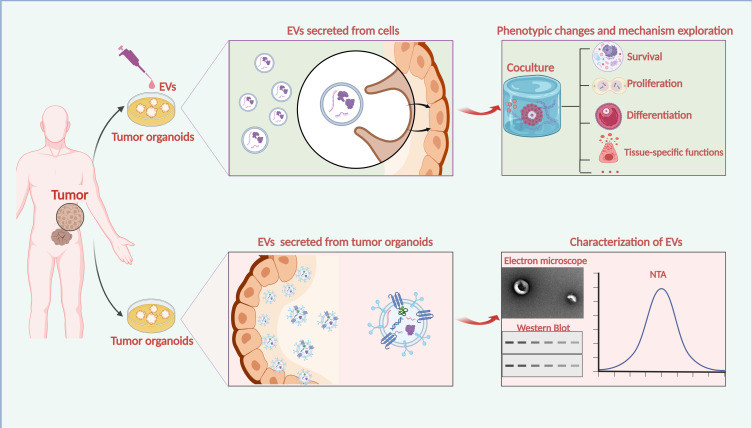 Figure 1. Organoids as a promising model to study EVs in tumors. (Zhang Y, et al., 2023)
Figure 1. Organoids as a promising model to study EVs in tumors. (Zhang Y, et al., 2023)
Our Platform of Organoid-based Assays
Our services are structured by organ type, allowing you to select the model that best fits your research area, from oncology to neurobiology.
1. Tumor Organoid (Tumoroid) Assays
This is the ultimate platform for evaluating exosome drug delivery cancer strategies and anti-cancer efficacy. We use patient-derived tumor organoids (PDOs) or cancer cell line-derived spheroids.
- Key Applications:
- Anti-Tumor Efficacy: Measure the ability of your therapeutic exosomes to inhibit tumoroid growth, induce apoptosis, or kill cancer cells.
- Chemoresistance/Sensitivity: Test if your exosomes can re-sensitize drug-resistant tumoroids to chemotherapy.
- Tumor Microenvironment (TME) Modulation: Co-culture with immune cells to assess the in vitro exosome immune response within the TME.
2. Intestinal Organoid Assays
Ideal for studying gut health, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and oral drug delivery platforms like milk exosomes drug delivery.
- Key Applications:
- Barrier Integrity and Repair: We can damage the intestinal organoid barrier and measure your exosome's ability to restore it.
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Induce an inflammatory state and quantify your exosome's ability to reduce inflammatory markers.
- Nutrient/Drug Transport: Assess how exosomes modulate transport functions within the gut epithelium.
3. Neurological Organoid Assays
Using brain organoids or neurospheroids derived from sources like human iPSC exosome in vitro cell models, we can model complex neurological functions and diseases.
- Key Applications:
- Neuroprotection: Test if your exosomes can protect neurons from toxic insults (e.g., models of Parkinson's or Alzheimer's disease).
- Neurogenesis and Differentiation: Measure the effect of exosomes on neural stem cell proliferation and differentiation.
- BBB Penetration and Efficacy: Can be combined with BBB models to test for both transport and subsequent bioactivity.
4. Other Organoid Models
We also offer developing assays for other models, including:
- Liver Organoids: For hepatotoxicity testing and metabolic studies.
- Lung Organoids: For modeling respiratory diseases and viral infections.
- Custom Organoids: Tailored to your research project.
Our Organoid Assay Workflow
Our workflow is meticulously designed to handle the complexities of 3D organoid culture, co-treatment, and advanced imaging analysis.
Key Stages of Our Service
Consultation and Model Selection
We start by working with you to select the most appropriate organoid model to address your scientific question, whether it is a Patient-Derived Organoid (PDO), a cancer cell line-derived spheroid, or an iPSC-derived model.
Organoid Culture and Maturation
The selected organoids are cultured within a 3D matrix (e.g., Matrigel). This crucial stage allows the cells to self-organize and mature, developing the complex, multi-cellular architecture characteristic of the target "mini-organ".
Exosome Co-culture and Treatment
Your exosome preparation is carefully added to the mature organoid culture. The treatment protocol is customized to your needs, whether it involves a single dose or repeated applications over a period of several days.
Our 5-Step Assay Pathway
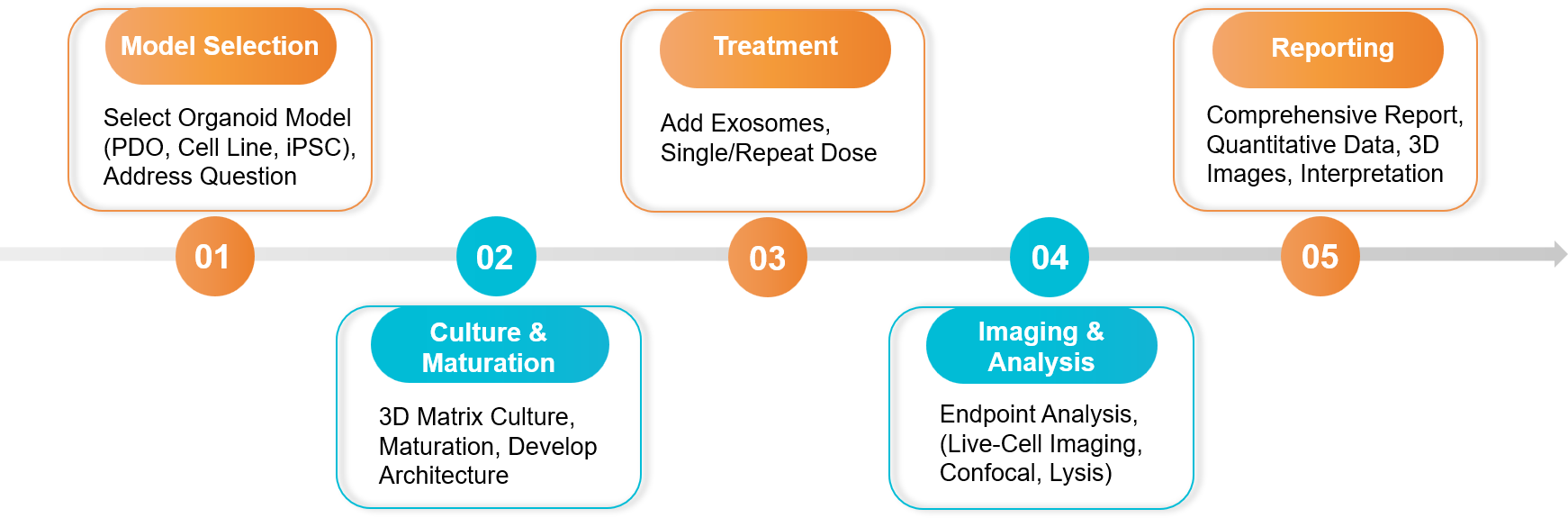 Figure 2. Exosome Organoid-based Functional Assay Project Workflow. (Creative Biostructure)
Figure 2. Exosome Organoid-based Functional Assay Project Workflow. (Creative Biostructure)
Sample Requirements
- Exosome Test Article:
- Purified exosome solutions are required. Please provide the suspension buffer as a control.
- Quantity: Typically ≥ 1x10¹¹ particles, as organoid studies often require longer incubation times and higher doses.
- Organoid Source:
- We can source commercially available cell lines for organoid generation.
- We can work with your specific patient-derived xenograft (PDX) lines or iPSC lines under a collaborative agreement.
Standard Deliverables
- A comprehensive project report with detailed methodology.
- Quantitative data for all key endpoints (e.g., organoid growth curves, dose-response curves, biomarker expression levels).
- High-resolution, publication-quality images (e.g., 2D cross-sections and 3D reconstructions from confocal microscopy).
- A final consultation to discuss the data and its implications.
Case Study
Case: Exosome-Loaded Hydrogel Rescues Human Cardiac Organoids from Infarction Injury
Background: Repairing heart tissue after a myocardial infarction (heart attack) is a major challenge. Researchers developed a hydrogel patch containing therapeutic exosomes from mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) to promote cardiac repair.
Methodology: To test their therapeutic concept in a highly relevant human model, the researchers created an in vitro model of a heart attack using human cardiac organoids (hCO-MI model).
- Model: The cardiac organoids were subjected to hypoxia/reoxygenation to mimic the injury of a heart attack.
- Treatment: The injured organoids were then treated with the exosome-loaded hydrogel (Exo-Gel).
- Endpoint Analysis: Advanced imaging techniques were used to measure cell viability and apoptosis (cell death) within the 3D organoid structure.
Key Findings:
Using the human cardiac organoid model showed that the Exo-Gel treatment significantly improved the viability of the heart muscle cells after the simulated infarction.
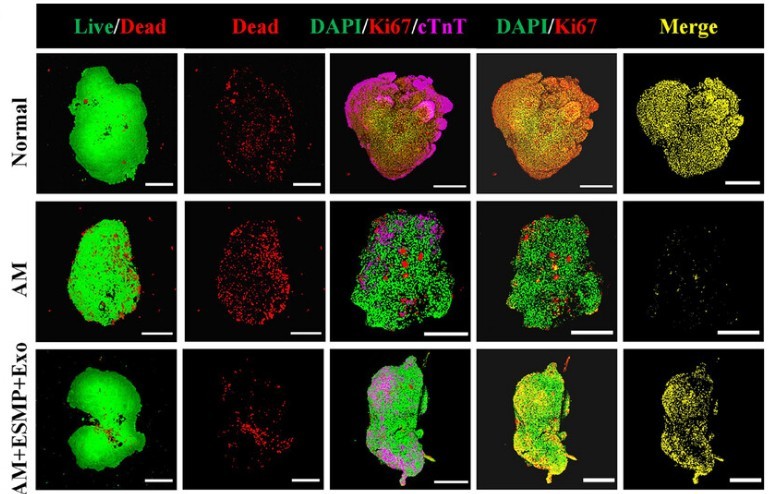 Figure 3. Live-dead fluorescence staining and Ki67 staining of HCOs in different groups, showing lower mortality and higher proliferation in ESMP+Exo group, suggesting potential for MI treatment. (Wang F, et al., 2025)
Figure 3. Live-dead fluorescence staining and Ki67 staining of HCOs in different groups, showing lower mortality and higher proliferation in ESMP+Exo group, suggesting potential for MI treatment. (Wang F, et al., 2025)
- The exosome-loaded gel also dramatically reduced the apoptosis within injured organoids.
- These positive results from the organoid model provided the crucial, human-relevant data needed to justify advancing the therapy to animal testing.
Conclusion: By using a sophisticated cardiac organoid model, the researchers were able to generate powerful, human-relevant preclinical data. The assay proved the therapeutic efficacy of their exosomes in a complex "mini-organ," demonstrating a protective and regenerative effect that would be impossible to observe in simple 2D cell culture.
Ready to validate exosomes in human-relevant organoids? We select the right models and endpoints, design a fit for purpose study, and generate quantitative efficacy, toxicity, and mechanism data. Contact us for a free consultation.
References
- Zhang Y, Lu A, Zhuang Z, et al. Can Organoid Model Reveal a Key Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Tumors? A Comprehensive Review of the Literature. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023 Sep 27;18:5511-5527.
- Wang F, Xu Z, Zheng F, et al. Cardiac Organoid Model Inspired Micro-Robot Smart Patch to Treat Myocardial Infarction. Adv Mater. 2025 Jul;37(26):e2417327.
Frequently Asked Questions
For any inquiries, our support team is ready to help you get technical support for your research and maximize your experience with Creative Biostructure.