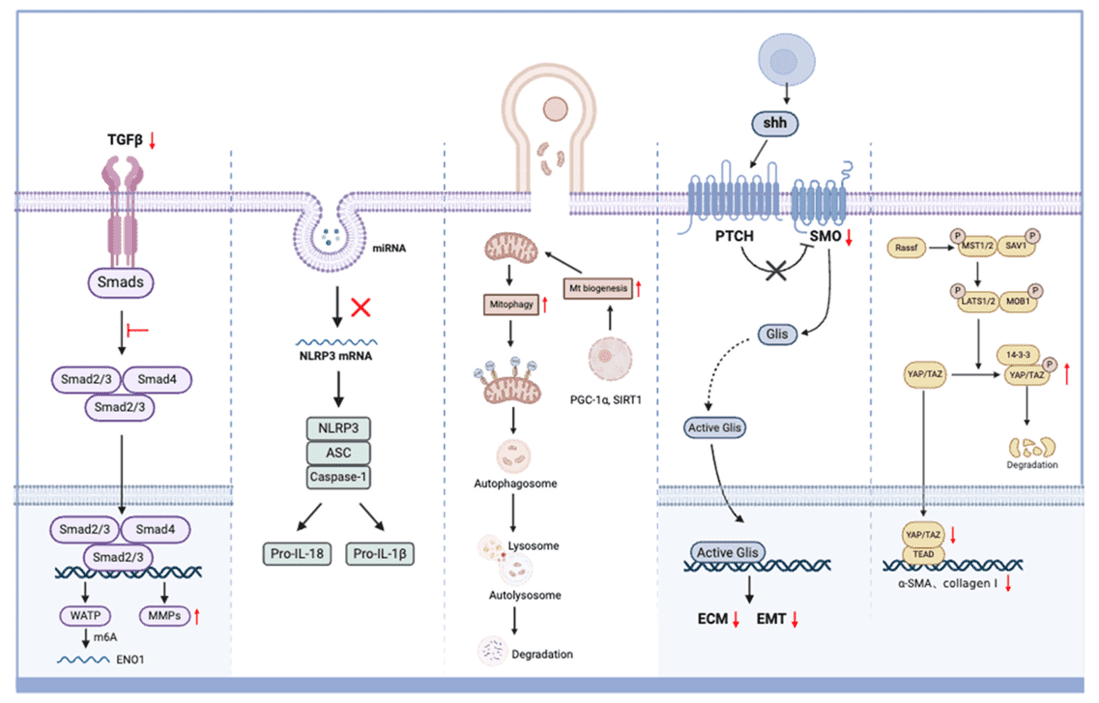
Liver Disease Exosome Characterization Services
The liver is a central hub of metabolic activity and intercellular communication, releasing vast quantities of Extracellular Vesicles (EVs) into circulation and bile. These exosomes carry specific molecular signatures—including lipids, miRNAs, and enzymes—that directly reflect the health status of hepatocytes and non-parenchymal cells. Consequently, they hold immense promise as non-invasive "liquid biopsies" for diagnosing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), differentiating NASH from simple steatosis, and monitoring Liver Fibrosis progression without the need for invasive needle biopsies.
However, hepatology research faces a unique and critical technical bottleneck: the Lipoprotein Matrix Effect. Blood samples from liver disease patients are typically hyperlipidemic, containing high concentrations of VLDL, LDL, and chylomicrons that mimic exosomes in size and density. Traditional isolation methods often co-precipitate these lipids, masking low-abundance exosomal markers and severely distorting lipidomic profiles. We have developed a specialized workflow integrating exclusion-based purification and deep multi-omics to overcome these challenges, ensuring high-purity inputs for reliable discovery.
Critical Frontiers in Hepatology Research
Research in liver diseases is rapidly evolving from basic description to mechanistic dissection and precision diagnostics. Key frontiers include:
- Deciphering Lipotoxicity in NASH: Understanding how "lipotoxic" exosomes released by stressed hepatocytes recruit macrophages (Kupffer cells) and trigger the inflammatory cascade. Profiling the specific lipid species (e.g., ceramides, oxidized phospholipids) in these vesicles is key to understanding NASH progression.
- The Fibrosis Signaling Axis: Investigating the crosstalk between hepatocytes and Hepatic Stellate Cells (HSCs). Exosomes carrying fibrogenic cargoes (such as miR-214 or PDGF) act as shuttles that drive HSC activation and transdifferentiation into collagen-producing myofibroblasts.
- Early HCC Surveillance: Moving beyond Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), researchers are validating panels of exosomal miRNAs and lncRNAs that can detect Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) at very early stages, particularly in high-risk cirrhotic patients.
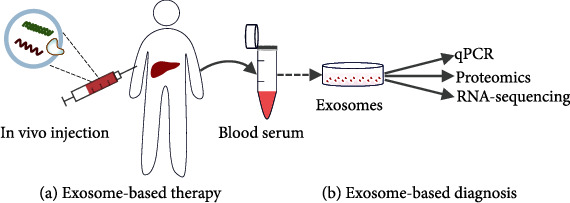 Figure 1. Exosome-based theranostics in liver disease management, illustrating both therapeutic injection and diagnostic isolation from various liver cell types. (Luo N, et al., 2022)
Figure 1. Exosome-based theranostics in liver disease management, illustrating both therapeutic injection and diagnostic isolation from various liver cell types. (Luo N, et al., 2022)
Accelerating Hepatic Discovery with Targeted Solutions
We provide a comprehensive portfolio of solutions designed to address specific research questions in hepatology, utilizing our specialized technologies to overcome lipoprotein interference.
| Research Focus | Our Specialized Approach & Solution | Key Services Applied |
|---|---|---|
| NASH & Metabolic Profiling | Deep Lipidomics & Metabolomics: We employ high-resolution LC-MS/MS to quantify hundreds of exosomal lipid species. By combining this with SEC purification, we ensure the lipid profile reflects the vesicle membrane cargo, not plasma lipoproteins. | Human Exosome Lipidomics Analysis, Rodents Exosome Lipidomics Analysis |
| Fibrosis Mechanism Studies | Functional Validation Assays: We isolate exosomes from injured liver cells and test their ability to activate HSCs in vitro (measuring $\alpha$-SMA and collagen). We also use NanoFCM to trace hepatocyte-derived EVs in complex media. | Exosome Characterization by NanoFCM, Exosome Cellular Functional Assays |
| Liver Cancer (HCC) Biopsy | High-Sensitivity Sequencing: Using our optimized Small RNA Sequencing workflow, we screen for oncogenic miRNAs and lncRNAs in serum/plasma exosomes, identifying signatures associated with tumor recurrence or metastasis. | Biofluid Exosome Isolation, Oncology Exosome Profiling and Functional Analysis |
Featured Technologies for Liver Disease
Visualizing Purity in High-Lipid Matrices (Cryo-EM)
In liver disease research, distinguishing true exosomes from co-isolated lipoprotein particles (VLDL, LDL) is a major challenge, as standard NTA cannot differentiate them based on size alone. We employ Cryo-Electron Microscopy (Cryo-EM) to provide definitive morphological validation. Unlike traditional TEM, Cryo-EM visualizes samples in a near-native frozen state without dehydration, allowing researchers to clearly resolve the characteristic lipid bilayer membrane of exosomes versus the monolayer or solid structure of lipid droplets. This provides the "gold standard" proof of purity required for high-impact hepatology publications.
Exosomal Lipidomics Profiling Suite
Given that lipotoxicity is a hallmark of NAFLD/NASH, standard protein analysis is often insufficient. Our platform integrates High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) and Mass Spectrometry (MS) to perform quantitative profiling of the exosomal lipidome. This technology allows researchers to identify distinct "lipid fingerprints" (e.g., specific sphingolipids or phosphatidylcholines) that correlate with steatosis grade and inflammation scores, providing mechanistic insights into lipid-mediated cell-cell communication.
Hepatocyte-Specific EV Tracing (NanoFCM)
Distinguishing exosomes originating from hepatocytes from those released by other liver cells (like sinusoidal endothelial cells or Kupffer cells) is challenging in bulk analysis. We employ Nano-Flow Cytometry (NanoFCM) with a detection threshold of 40 nm to analyze single vesicles. By labeling exosomes with hepatocyte-specific surface markers (e.g., ASGPR1), we can quantify the fraction of liver-derived exosomes in circulating blood, offering a precise tool for monitoring liver-specific injury.
Application Spotlight: Exosomal miRNAs Predict NASH Severity
This case study highlights the utility of circulating exosomal miRNAs as non-invasive biomarkers to distinguish NASH from simple steatosis.
Featured Technologies:
- Lipoprotein-Free Isolation (SEC)
- Small RNA Sequencing
Literature Interpretation:
Distinguishing Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) from Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver (NAFL) currently requires invasive liver biopsy. In a pivotal study, researchers isolated exosomes from the serum of NAFLD patients using size-exclusion methods to minimize lipid contamination. Sequencing revealed a distinct profile of miRNAs, specifically miR-122 and miR-192, which were significantly upregulated in exosomes from NASH patients compared to those with simple steatosis. The abundance of these exosomal miRNAs correlated strongly with liver histological features like ballooning and fibrosis. This confirms that rigorously purified circulating exosomes can serve as a "liquid biopsy" for grading liver disease severity.
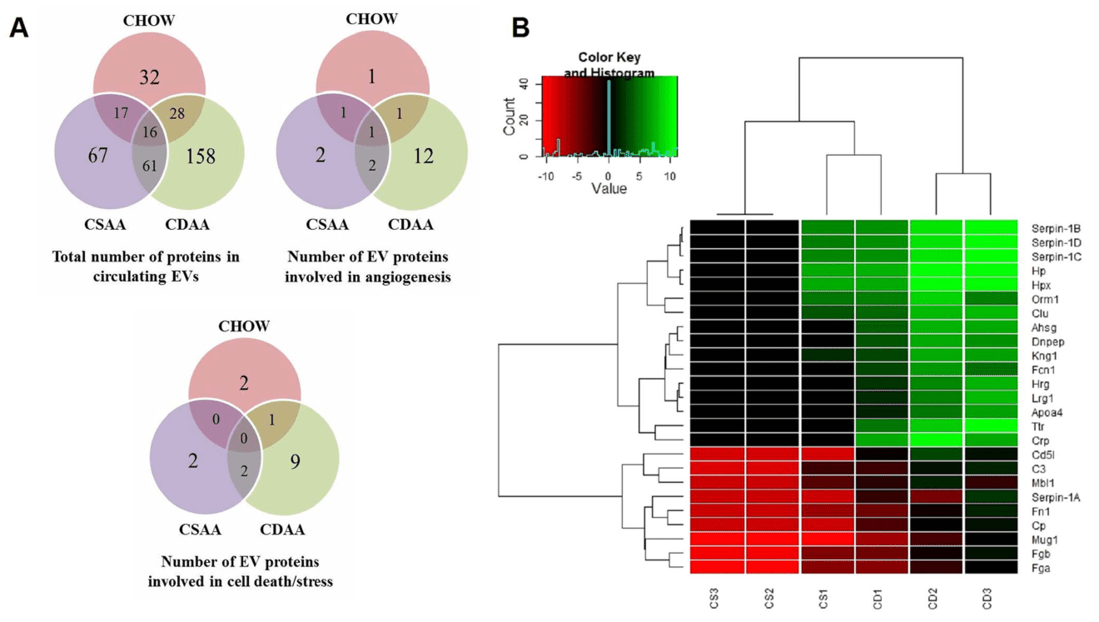 Figure 2. Proteomic changes in extracellular vesicles from diet-induced NASH and control mice. (A) Venn diagrams showing protein numbers related to cell death, stress, and angiogenesis. (B) Heatmap and dendrogram illustrating protein expression differences between CDAA and CSAA groups. (Povero D, et al., 2014)
Figure 2. Proteomic changes in extracellular vesicles from diet-induced NASH and control mice. (A) Venn diagrams showing protein numbers related to cell death, stress, and angiogenesis. (B) Heatmap and dendrogram illustrating protein expression differences between CDAA and CSAA groups. (Povero D, et al., 2014)
Start Your Liver Exosome Analysis
We have optimized a robust workflow to handle the complex matrix of hepatic biofluids, ensuring lipoprotein removal and high-quality multi-omics data.
How It Works: Our Project Pathway
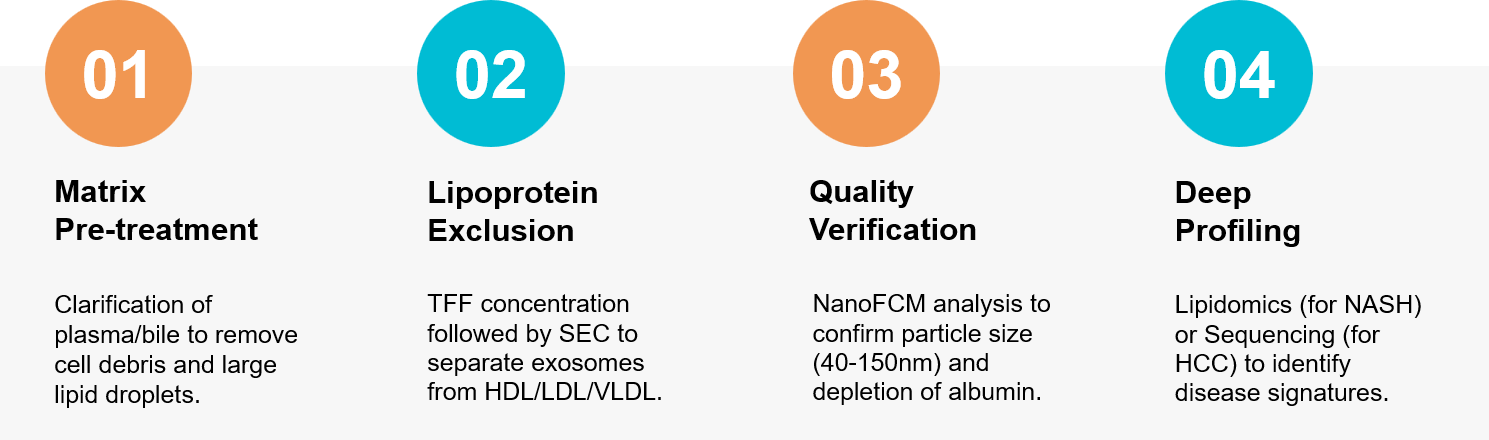 Figure 3. Integrated workflow for liver exosome isolation using SEC for lipoprotein removal followed by lipidomic analysis. (Creative Biostructure)
Figure 3. Integrated workflow for liver exosome isolation using SEC for lipoprotein removal followed by lipidomic analysis. (Creative Biostructure)
Ready to find the next breakthrough in NASH or Liver Fibrosis? Our hepatology experts are available to build a custom study plan tailored to your needs. Contact us today to discuss your project.
References
- Luo N, Li J, Dong R, et al. Exosome-Based Theranostics for Liver Diseases. Dis Markers. 2022 Nov 2;2022:7888906.
- Povero D, Eguchi A, Li H, et al. Circulating extracellular vesicles with specific proteome and liver microRNAs are potential biomarkers for liver injury in experimental fatty liver disease. PLoS One. 2014 Dec 3;9(12):e113651.