Exosomal Long Non-coding RNA (lncRNA) Sequencing Service
Exosomal long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are >200 nt non-protein-coding RNAs enriched in exosomes, acting as key regulators of gene expression, cell signaling, and intercellular communication. Creative Biostructure's exosome-based lncRNA sequencing service captures full-length lncRNAs, revealing their roles in disease progression, tissue repair, and therapeutic response. Leveraging IncRNA-specific sequencing workflows and advanced bioinformatics tools, we deliver high-precision data and comprehensive lncRNA annotation.
What is Exosomal lncRNA Sequencing and Why is it important?
Exosomal lncRNA sequencing is a next-generation sequencing (NGS) technique used to comprehensively detect and profile long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) found in exosomes, which are small extracellular vesicles that facilitate intercellular communication. By quantifying the expression levels of these exosomal lncRNAs, researchers can elucidate their functional roles in various physiological and pathological processes, especially in cancer. As a result, they represent highly promising biomarkers for both diagnostic and prognostic applications.
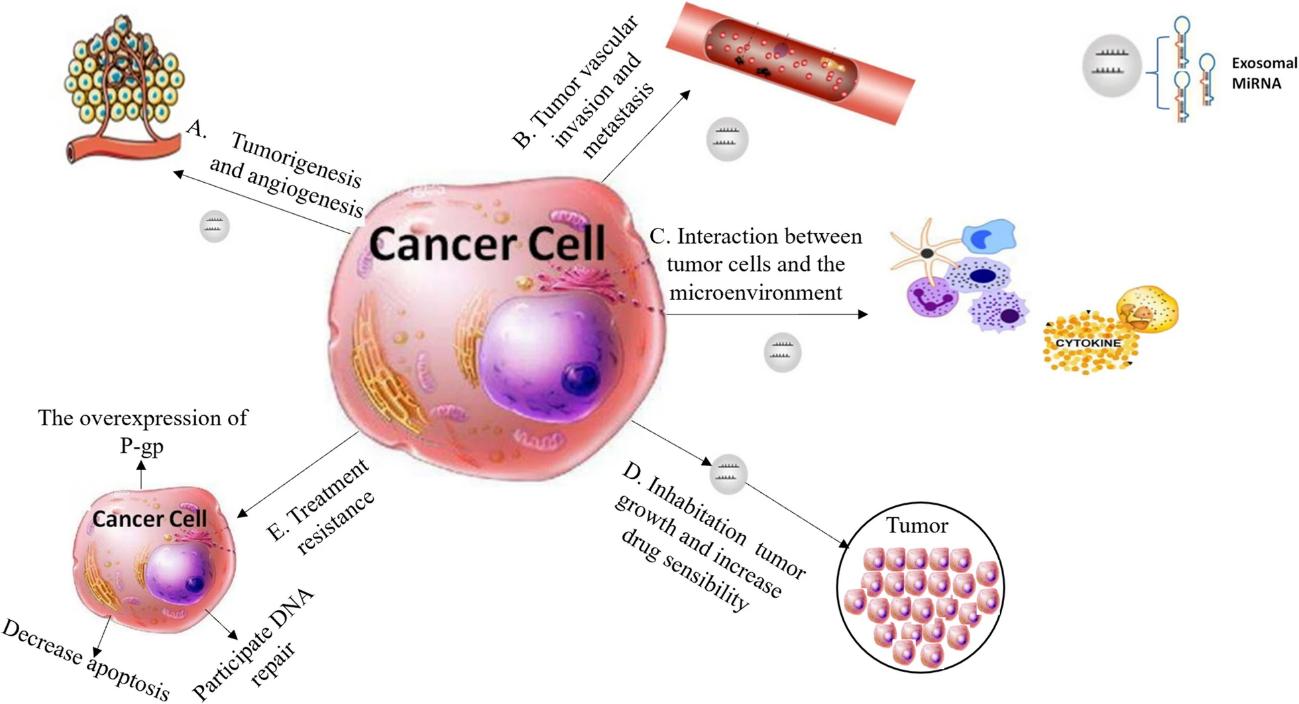
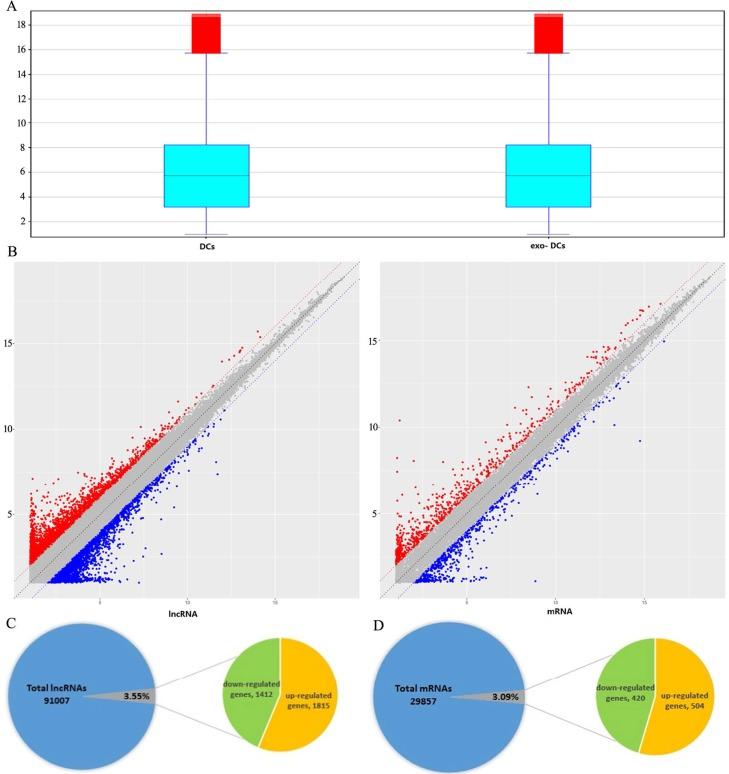
 Figure. 1 An exosome-related lncRNA signature. (Peng W, et al. 2023)
Figure. 1 An exosome-related lncRNA signature. (Peng W, et al. 2023)
Our Exosomal lncRNA Sequencing Services
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are key players in gene regulatory networks. However, their low abundance, complex splice variants, and lack of a polyadenylated (polyA) tail make their capture and characterization challenging. Creative Biostructure offers professional end-to-end lncRNA sequencing solutions to help customers overcome these challenges. From experimental design, sample quality control, and sequencing operations to data analysis, our expert team provides comprehensive technical support throughout the entire process to ensure high-quality results for every project.
We employ the Illumina NovaSeq 6000 platform combined with an lncRNA-optimized protocol to provide the following technologies and services tailored to the characteristics of long non-coding RNAs:
| Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| rRNA Depletion Technology | This method ensures≥95% rRNA removal and comprehensive lncRNA capture by using probe-based rRNA removal (targeting 18S/28S rRNA) rather than polyA+ enrichment, which misses most lncRNAs due to their lack of polyA tails. |
| Long-fragment Library Construction | Tailored to the structural characteristics of lncRNAs, we have optimized the library construction process to preferentially obtain long fragments of 300-500 bp. This approach maximizes the preservation of complete lncRNA structural information, laying a solid foundation for the accurate analysis of their splice variants and secondary structures. |
| High Read Depth | 40-60 million clean reads per sample, covering low-abundance exosomal lncRNAs (down to 0.5 copies per cell) and enabling accurate detection of lncRNA expression and co-expression patterns. |
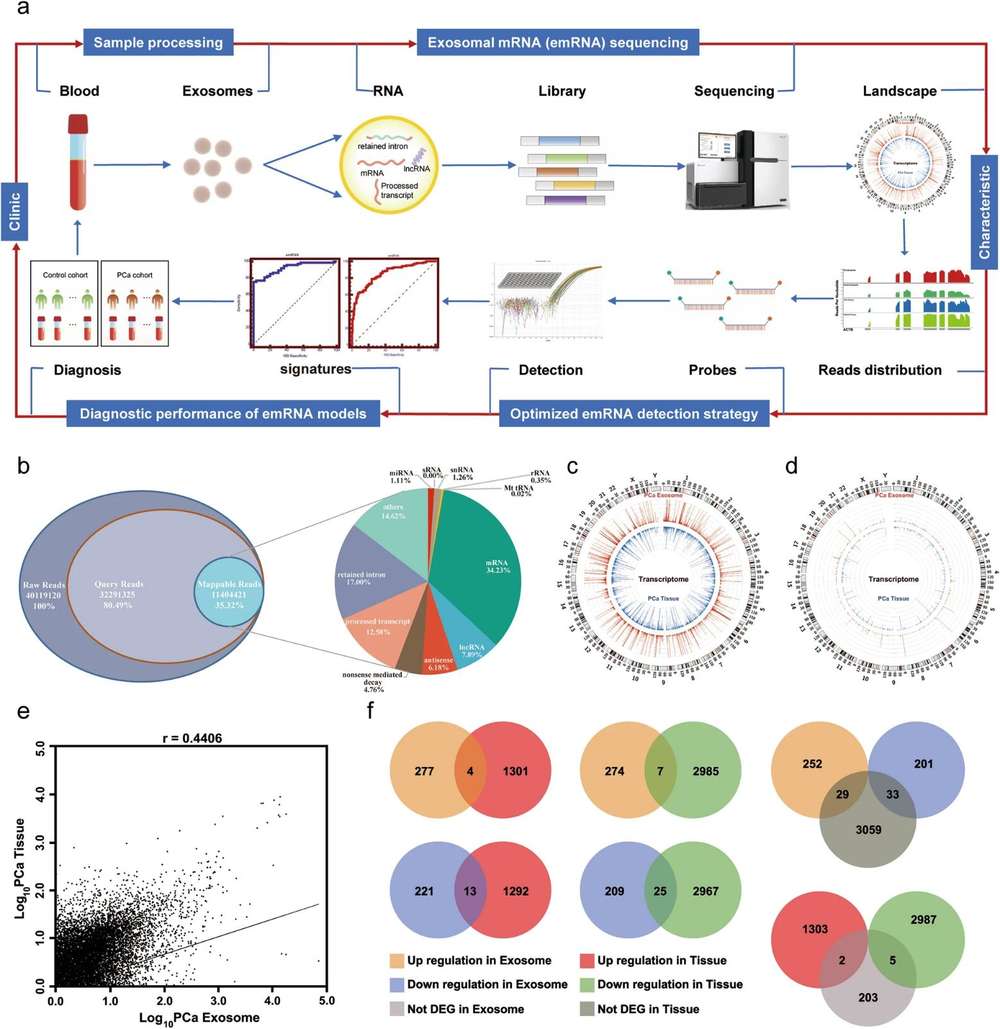
lncRNA Sequencing Analysis Service Workflow
Exosome Isolation (Optional for Raw Samples)
For raw samples (e.g., serum, cell supernatants), use "ultracentrifugation + density gradient centrifugation" to remove lipoprotein and protein contaminants (lncRNA is more sensitive to protein binding than mRNA/small RNA).
lncRNA-Specific RNA Extraction
Use RNase-free kits to extract total RNA from exosomes; avoid polyA+ selection (to retain non-polyadenylated lncRNAs); add DNase I to eliminate genomic DNA.
- rRNA Depletion & Library Construction
- Deplete rRNA using species-specific probes.
- Fragment total RNA into 300-500 bp segments (optimized for lncRNA length).
- Synthesize cDNA and add Illumina adapters to construct strand-specific libraries (preserves lncRNA's transcriptional direction, critical for regulatory analysis).
High-Throughput Sequencing
Load libraries onto Illumina NovaSeq 6000 for paired-end sequencing (2×150 bp), ensuring sufficient coverage for lncRNA splice variant detection.
lncRNA-Focused Data Analysis
- Basic Analysis: FastQC (quality control), STAR (genome alignment with lncRNA annotation), HTSeq (lncRNA expression quantification);
- Advanced Analysis: DESeq2 (differential lncRNA screening), lncRNA annotation (using NONCODE/lncRNAdb), target gene prediction (cis/trans regulation), lncRNA-mRNA/protein interaction network construction, GO/KEGG enrichment of target genes.
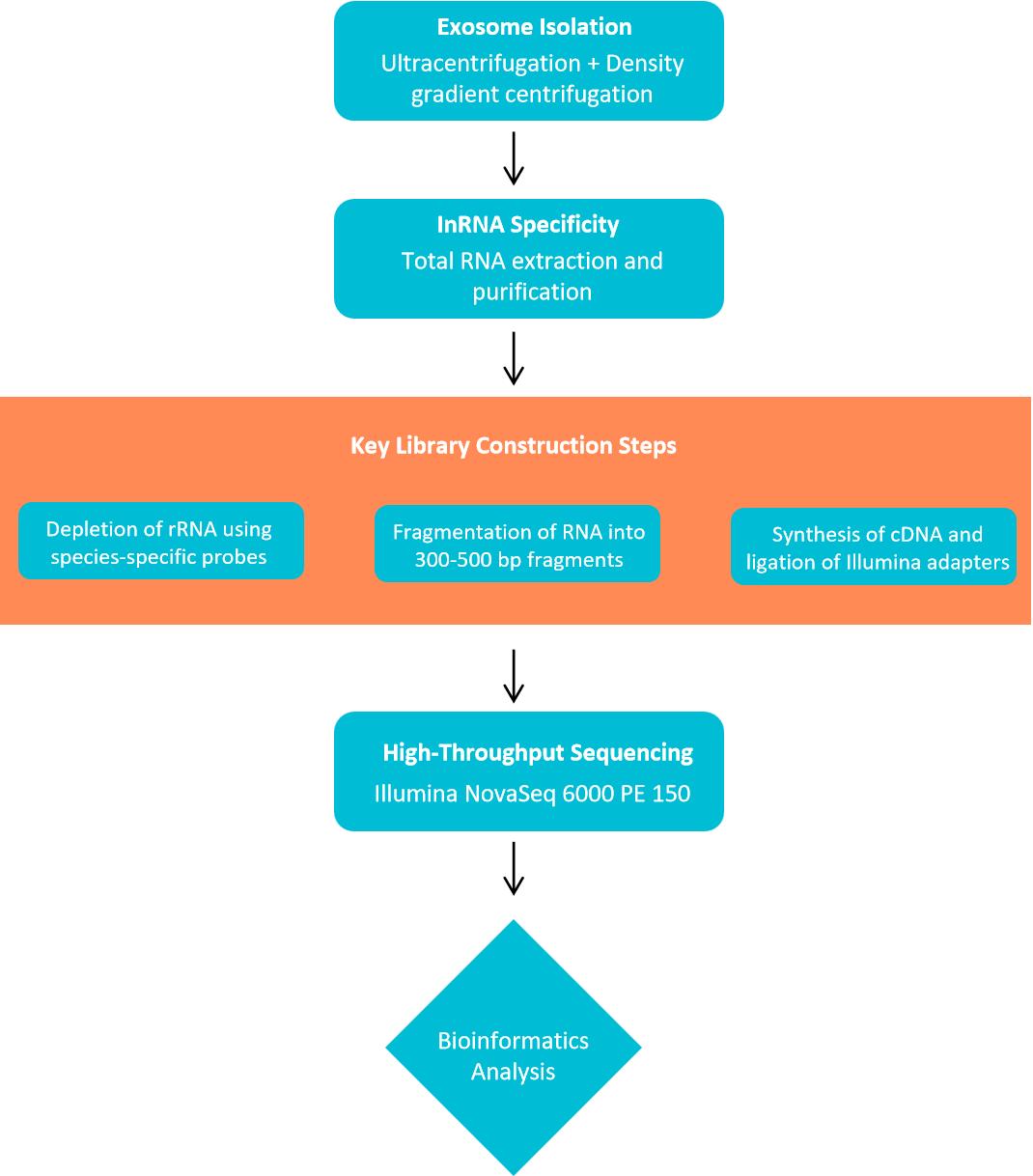 Figure 2. Workflow of lncRNA sequencing analysis. (Creative Biostructure)
Figure 2. Workflow of lncRNA sequencing analysis. (Creative Biostructure)
Supported Sample Range
Familiarize yourself with the supported sample types and submission guidelines to ensure your specimens comply with laboratory standards.
| Samples | Submit Request |
|---|---|
| Serum/plasma | ≥300 μL, no hemolysis (hemoglobin degrades lncRNA) |
| Cell culture supernatants | ≥15 mL, freshly collected (avoid RNA degradation) |
| Cerebrospinal fluid | ≥150 μL, stored at -80°C immediately |
| Urine | ≥800 μL, add RNA protection agent at collection. |
Deliverables
Clients receive a comprehensive, publication-ready report including:
- QC Report: Total RNA integrity (RIN value), rRNA depletion efficiency (>95%), library concentration/uniformity, sequencing Q30 score (>95%), alignment rate (>92%).
- Raw & Processed Data: FASTQ files (raw reads), BAM files (aligned reads), lncRNA expression matrix (TPM values), lncRNA annotation table (name, location, length, source database).
- Advanced Analysis Results:
Differential lncRNA list (fold change ≥2, p<0.05) with volcano plots and heatmaps.
Target gene prediction results (cis/trans targets, binding sites).
lncRNA-mRNA/protein interaction network diagrams (e.g., lncRNA HOTAIR targeting PTEN mRNA).
GO/KEGG enrichment of target genes (revealing lncRNA's regulatory pathways).
Case Study
Case: Improved Exosome Yield from MSCs Using One-Step Sucrose Cushion Ultracentrifugation
Background
The role of exosomal long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in type 1 diabetes (T1DM) remains unclear. This study profiles plasma exosomal lncRNA expression in T1DM to explore their potential functions in disease pathogenesis.
Methods
- Exosomal lncRNA expression profiles were detected by Illumina Hiseq platform.
- Six exosomal lncRNAs were selected to validate their expression level by using quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR).
- Bioinformatics analysis approaches were carried out to explore the potential biological function of differentially expressed lncRNAs.
Conclusion
A total of 162 differentially expressed exosomal lncRNAs were identified in T1DM patients compared with control subjects, among which 77 up-regulated and 85 down-regulated. These results highlighted the potential role of exosomal lncRNAs in T1DM pathogenesis. A better understanding of exosomal lncRNA profiling will provide novel insights into its molecular mechanisms.
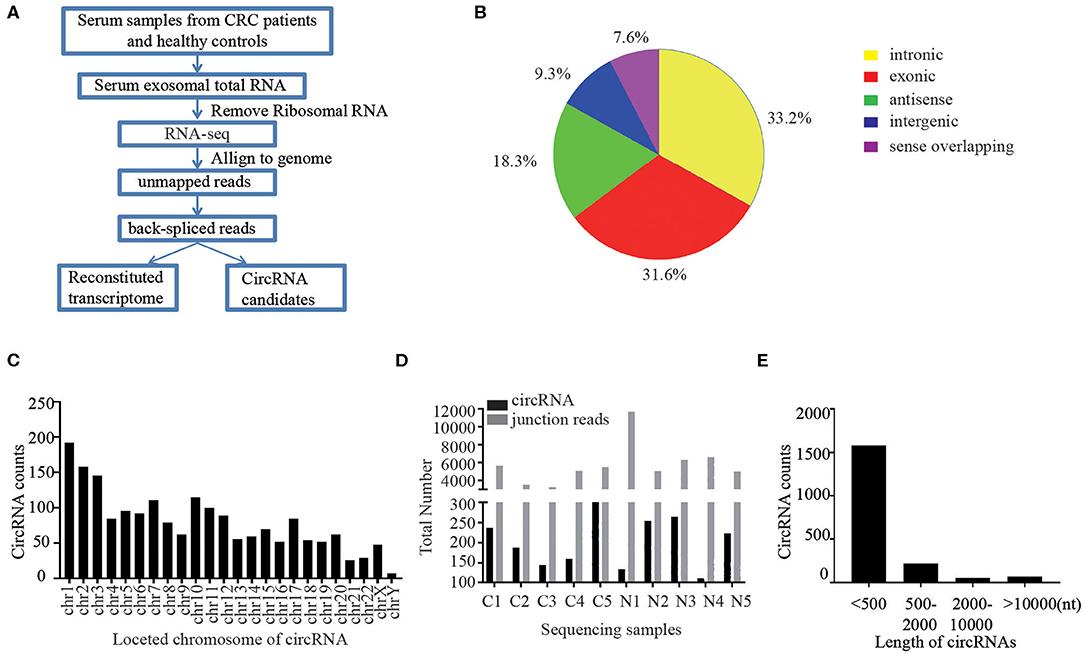
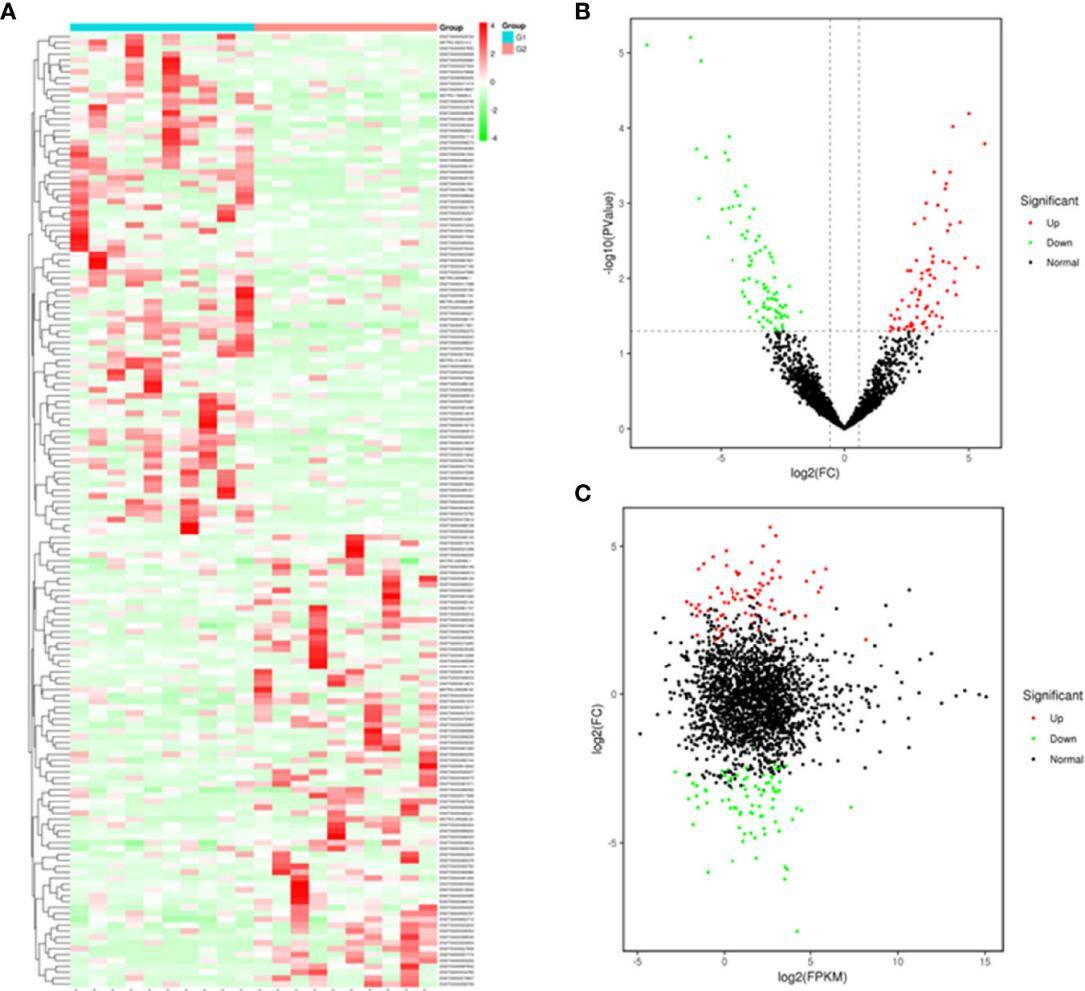 Figure 3. Plasma-derived exosomal lncRNA profiles of case and control group. (Pang H, et al., 2022)
Figure 3. Plasma-derived exosomal lncRNA profiles of case and control group. (Pang H, et al., 2022)
Creative Biostructure's exosomal lncRNA sequencing service leverages precise strand-specific library preparation and professional bioinformatics workflows. Our integrated solution provides end-to-end support, spanning complete exosome isolation, high-quality library construction, and in-depth data mining. Contact us today to obtain a customized solution that will accelerate your research progress.
References
- Peng W, Bai S, Zheng M, et al. An exosome-related lncRNA signature correlates with prognosis, immune microenvironment, and therapeutic responses in hepatocellular carcinoma. Translational Oncology. 2023, 31: 101651.
- Pang H, Fan W, Shi X, et al. Characterization of lncRNA profiles of plasma-derived exosomes from type 1 diabetes mellitus. Frontiers in Endocrinology. 2022, 13: 822221.
Frequently Asked Questions
For any inquiries, our support team is ready to help you get technical support for your research and maximize your experience with Creative Biostructure.