Single Molecule Localization Microscopy (SMLM) Exosome Imaging Service
At Creative Biostructure, we deliver cutting-edge Single Molecule Localization Microscopy (SMLM) services that empower researchers to probe exosomes with nanometer precision. By visualizing vesicles and their molecular components at the single-molecule level, we provide a window into the ultrastructure and dynamic functions of extracellular vesicles (EVs) that conventional microscopy cannot resolve.
Why Advanced Imaging for Exosomes Matters
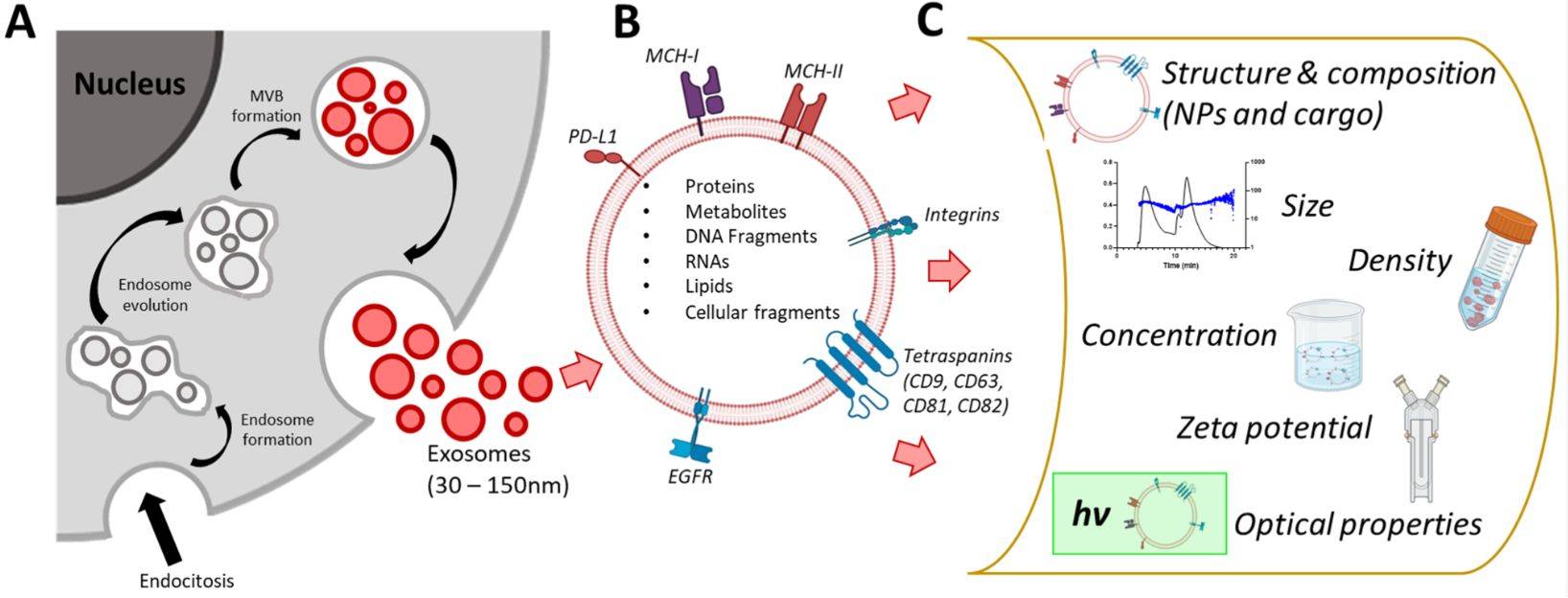
Exosomes (30-150 nm) orchestrate essential intercellular communication by transporting proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. Their role in cancer, neurodegeneration, infection, and regenerative medicine has positioned them as powerful diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic carriers. Yet, their nanoscale size places them beyond the reach of standard light microscopy. SMLM bridges this gap, offering clarity where conventional imaging leaves only blurred halos.
What is Single Molecule Localization Microscopy (SMLM)?
SMLM is a family of super-resolution imaging techniques that achieve nanometer precision by capturing the stochastic blinking of fluorescent molecules and reconstructing their coordinates into high-resolution images.
- STORM (Stochastic Optical Reconstruction Microscopy): Relies on fluorophore switching (e.g., Cy3-Cy5, Alexa Fluor 647) to achieve nanoscale localization.
- PALM (Photoactivated Localization Microscopy): Uses photoactivatable proteins (e.g., PA-GFP, mCherry) for live-cell compatible imaging.
- dSTORM: Direct STORM using optimized dyes for improved temporal resolution.
- DNA-PAINT: Utilizes transient DNA hybridization to achieve single-molecule resolution and quantitative protein mapping.
Unlike traditional fluorescence or electron microscopy, SMLM provides both spatial resolution and dynamic tracking capabilities, making it ideal for real-time exosome studies.
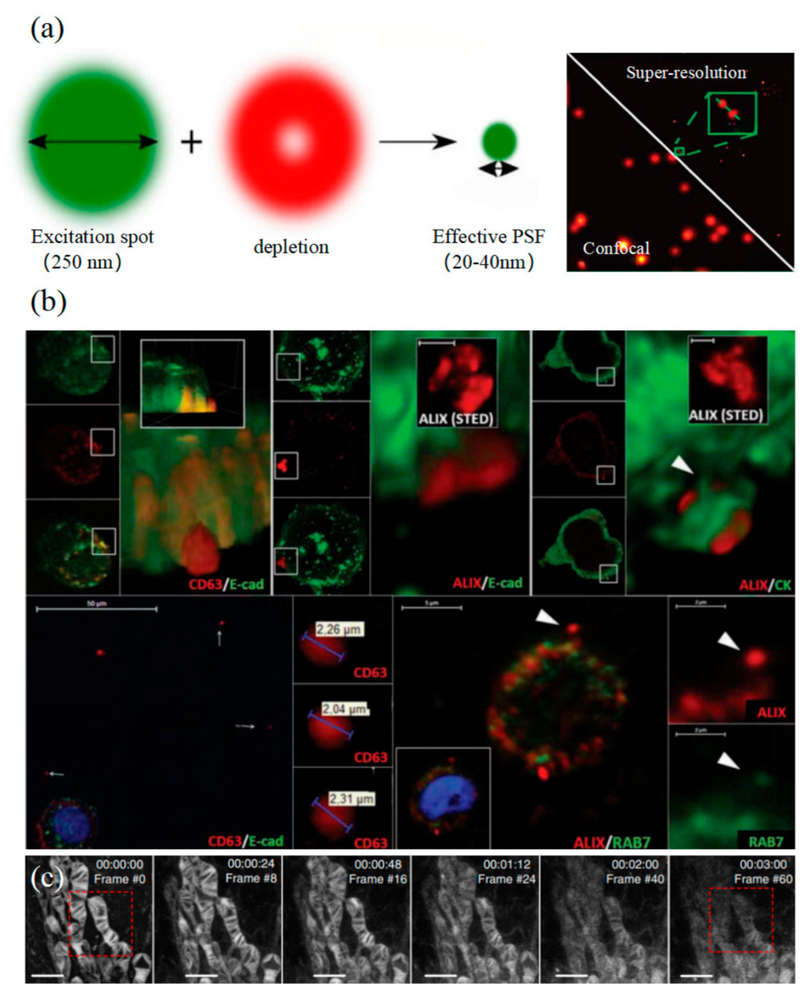
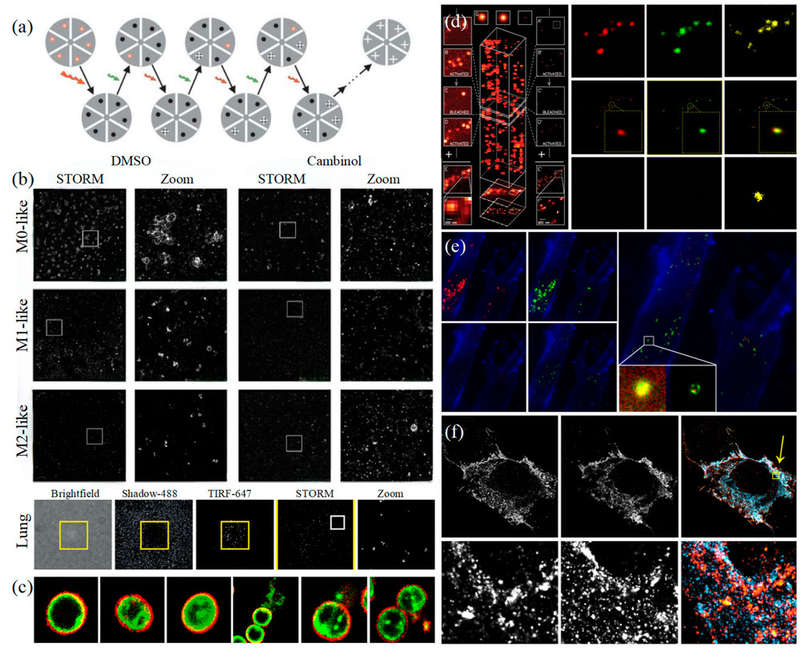 Figure 1. Super-resolution microscopy for exosome studies. (a) Principle of STORM. (b) STORM reveals EV colocalization with actin reticulum wells (inhibited by Cambinol) and secretion from activated human lung macrophages via FcγRI. (c) Multi-color STORM imaging of EV compositions in Gram-positive bacteria. (d) Principle of PALM (left) and dual-color PALM imaging of CD63 and HER2 in SKBR3-derived exosomes (right). (e) PALM/STORM visualization of colocalization between SKBR3 exosomes and MRC-5 lysosomes. (f) dSTORM imaging of U-2 OS cells expressing CD63-GFP and CD81-mCherry. (Wu S, et al., 2024)
Figure 1. Super-resolution microscopy for exosome studies. (a) Principle of STORM. (b) STORM reveals EV colocalization with actin reticulum wells (inhibited by Cambinol) and secretion from activated human lung macrophages via FcγRI. (c) Multi-color STORM imaging of EV compositions in Gram-positive bacteria. (d) Principle of PALM (left) and dual-color PALM imaging of CD63 and HER2 in SKBR3-derived exosomes (right). (e) PALM/STORM visualization of colocalization between SKBR3 exosomes and MRC-5 lysosomes. (f) dSTORM imaging of U-2 OS cells expressing CD63-GFP and CD81-mCherry. (Wu S, et al., 2024)
Key Advantages of Our SMLM-Based Exosome Analysis
- Ultra-High Spatial Resolution: Map the spatial organization of tetraspanins (CD9, CD63, CD81) and cargo proteins at ~20 nm scale.
- Quantitative Single-Molecule Data: Move from descriptive imaging to absolute molecular counting, uncovering exosome heterogeneity.
- Live-Cell Compatibility: Low phototoxicity allows tracking exosome release, uptake, and intracellular routing in real time.
- Multi-Color & 3D Imaging: Visualize multiple biomarkers simultaneously and reconstruct 3D nanoscale landscapes.
- High Specificity: Antibody-, aptamer-, or genetically encoded probes ensure precise molecular targeting.
Technical Approaches We Offer
Our laboratory integrates multiple SMLM modalities to meet diverse research needs:
| Approach | Description |
|---|---|
| STORM Imaging of Exosomes | High-resolution mapping of exosome proteins and molecular cargo. |
| PALM for Live-Cell Exosome Tracking | Real-time visualization of exosome trafficking in living cells. |
| DNA-PAINT for Quantitative Analysis | Precise mapping and counting of protein copy numbers on individual vesicles. |
| Multi-Color & 3D SMLM | Co-localization of multiple markers and nanoscale 3D reconstruction. |
| AI-Enhanced Analysis | Machine learning-based algorithms accelerate data processing and classification of exosome subsets. |
Our SMLM Exosome Imaging Workflow
Initial Consultation
Define project scope, sample type, labeling strategy, and choice of SMLM modality: STORM, PALM, or DNA-PAINT.
Sample Submission & Preparation
Exosome isolation and purification from cell culture, biofluids, or tissues; labeling with fluorophores, antibodies, or aptamers following MISEV2023 guidelines.
Quality Control
Optional pre-imaging checks: exosome size/distribution by NTA, surface marker verification, buffer compatibility.
Super-Resolution Image Acquisition
High-speed imaging using EMCCD/sCMOS cameras; optimized laser lines, filters, and buffer conditions for minimal phototoxicity.
Image Reconstruction & Processing
Localization of single fluorophores; reconstruction into nanoscale maps; correction for chromatic aberration; multi-color alignment.
Quantitative Data Analysis
Single-molecule counting, cluster/segmentation analysis, protein density mapping, AI-assisted exosome classification.
Final Report & Deliverables
Raw image data, reconstructed super-resolution images, quantitative analysis results, publication-quality figures, and expert consultation session.
 Figure 2. Project Workflow for Exosome Imaging by Single-Molecule Localization Microscopy. (Creative Biostructure)
Figure 2. Project Workflow for Exosome Imaging by Single-Molecule Localization Microscopy. (Creative Biostructure)
Applications of SMLM in Exosome Research
Our SMLM exosome imaging platform supports a wide range of applications, including:
- Structural imaging: Visualization of exosome membranes, surface proteins (CD9, CD63, CD81), nucleic acids, and cargo molecules.
- Dynamic tracking: Monitoring exosome uptake, intracellular trafficking, and release in live cells.
- Quantitative analysis: Measuring vesicle size, protein density, and distribution at the single-molecule level.
- Biomarker discovery: Identifying cancer- or disease-specific exosome signatures for diagnostic applications.
- Functional studies: Understanding how exosomes mediate intercellular communication, immune modulation, and drug delivery.
Why Choose Creative Biostructure?
- Cutting-edge platforms: Advanced STORM, PALM, and DNA-PAINT systems.
- Expert team: Decades of experience in exosome biology, super-resolution microscopy, and quantitative imaging.
- MISEV2023 compliance: Ensuring standardization and reproducibility in EV studies.
- Integrated services: From exosome isolation to imaging, proteomics, lipidomics, and functional assays.
- Tailored solutions: Customized service packages for academic research, biopharma projects, and diagnostic development.
Case Study
Case: Imaging Surface Microdomains on EVs Using dSTORM
Background
This study used dSTORM to visualize tetraspanin microdomains (CD81 and CD63) on individual EVs.
Methods
- Cell Line Preparation: U-2 OS cells were engineered to express CD81-mCherry and CD63-GFP for fluorescent labeling.
- EV Isolation: EVs were purified via tangential flow filtration and affinity beads targeting CD81.
- dSTORM Imaging: Multi-color dSTORM achieved a 16 nm lateral and 42 nm axial resolution to visualize EV surface microdomains.
Results
- Microdomain Clustering: CD81 and CD63 formed tetraspanin-rich microdomains on EV surfaces.
- Subpopulation Quantification: CD81+ EVs made up 25.26% of the total, while CD9+ EVs accounted for 17.23%.
- 3D Imaging: dSTORM revealed tetraspanin clustering in EVs, confirmed by Cryo-EM.
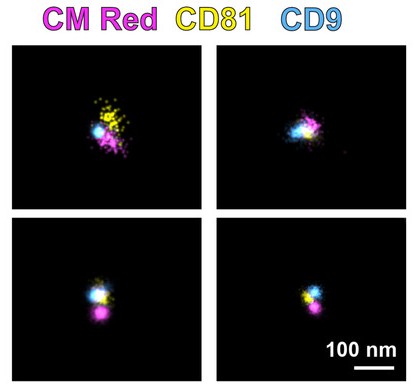 Figure 3. Three-color dSTORM imaging of total EVs using emissions from CM Red, CD81-mCherry, and anti-CD9 Alexafluor-488. Four representative images show distinct EV populations with scale = 100 nm. (McNamara R P, et al., 2022)
Figure 3. Three-color dSTORM imaging of total EVs using emissions from CM Red, CD81-mCherry, and anti-CD9 Alexafluor-488. Four representative images show distinct EV populations with scale = 100 nm. (McNamara R P, et al., 2022)
Conclusion
This study demonstrates that dSTORM effectively maps surface microdomains on EVs, enhancing our understanding of their structural complexity. These findings are critical for advancing EV-based diagnostics and drug delivery applications.
At Creative Biostructure, we combine advanced SMLM platforms with expert EV biology knowledge to deliver nanoscale insights you can trust. Whether you aim to map structural details, track dynamic processes, or identify disease-specific biomarkers, our team provides reliable, publication-ready results. Contact us to discuss your project and let us support your research with state-of-the-art exosome imaging solutions.
References
- McNamara R P, Zhou Y, Eason A B, et al. Imaging of surface microdomains on individual extracellular vesicles in 3‐D. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles. 2022, 11(3): e12191.
- Wu S, Zhao Y, Zhang Z, et al. The advances and applications of characterization technique for exosomes: from dynamic light scattering to super-resolution imaging technology. Photonics. MDPI, 2024, 11(2): 101.
- Welsh J A, Goberdhan D C I, O'Driscoll L, et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles (MISEV2023): From basic to advanced approaches. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles. 2024, 13(2): e12404.
Frequently Asked Questions
For any inquiries, our support team is ready to help you get technical support for your research and maximize your experience with Creative Biostructure.