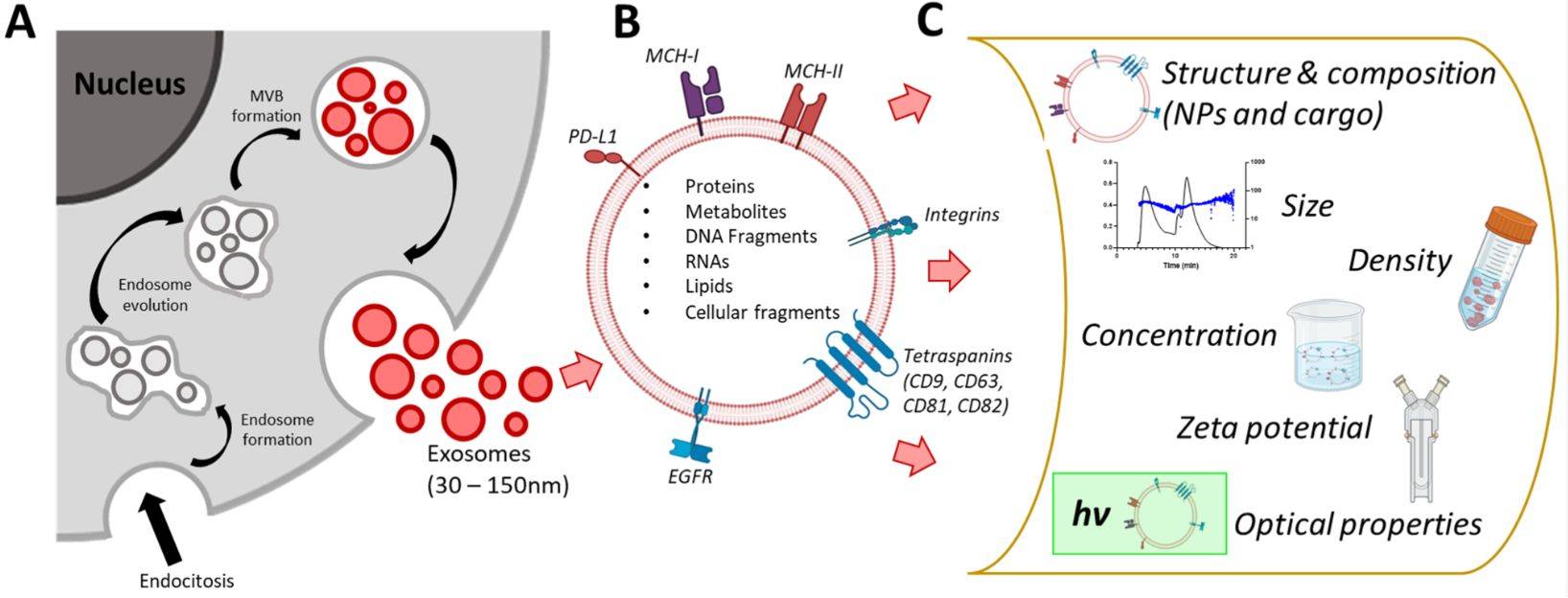
STED Microscopy Exosome Imaging Service
Exosomes are nanoscale extracellular vesicles (EVs) that play a central role in intercellular communication and have been widely studied as biomarkers and therapeutic agents. Because of their small size (typically 30-150 nm), traditional light microscopy cannot capture their fine structural and molecular details. Creative Biostructure provides stimulated emission depletion (STED) microscopy exosome imaging service, enabling researchers to visualize exosomes with nanometer precision and to gain deeper insights into their biological functions.
What is STED Microscopy?
STED microscopy is a super-resolution fluorescence imaging technology that surpasses the diffraction limit of conventional optical microscopy. By selectively switching off fluorescence in surrounding regions while retaining a single illuminated focal point, STED achieves resolutions down to 20-30 nm, far beyond the ~200 nm barrier of confocal microscopy.
This makes STED particularly powerful for exosome research, where accurate visualization of vesicle morphology, surface proteins, and cargo distribution is essential.
STED vs. Confocal Microscopy:
- Confocal: ~200 nm resolution, suitable for general cell imaging.
- STED: ~20-30 nm resolution, suitable for single-vesicle visualization and molecular mapping.
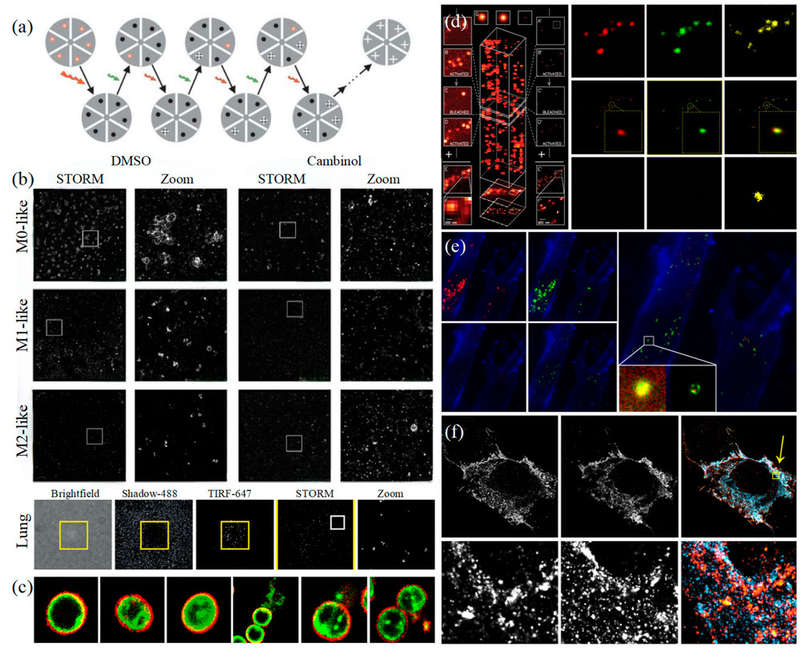
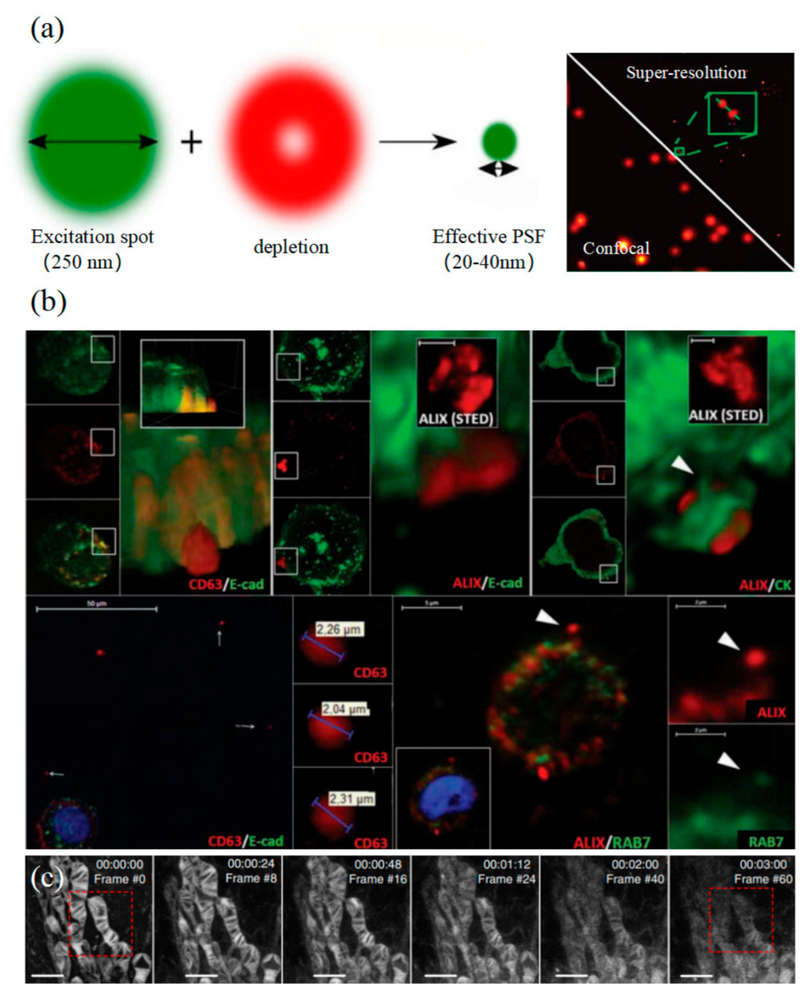 Figure 1. STED microscopy for biological imaging. (a) Principle of STED (left) and single-EV characterization with UCNP labeling (right). (b) Visualization of extracellular vesicle clusters (sEVCs) in HT29 colorectal carcinoma cells. (c) Time-lapse STED imaging of mitochondrial dynamics. (Wu S, et al., 2024)
Figure 1. STED microscopy for biological imaging. (a) Principle of STED (left) and single-EV characterization with UCNP labeling (right). (b) Visualization of extracellular vesicle clusters (sEVCs) in HT29 colorectal carcinoma cells. (c) Time-lapse STED imaging of mitochondrial dynamics. (Wu S, et al., 2024)
Comparison with Other Microscopy Techniques
| Technique | Resolution | Key Applications | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Confocal Microscopy | ~200 nm | General cell imaging | Insufficient for nanoscale EVs |
| STED Microscopy | ~20-30 nm | Exosome imaging, protein mapping | Requires fluorescent labeling |
| TEM (Transmission EM) | ~1-2 nm | High-resolution morphology | Requires fixed/dehydrated samples, no live imaging |
| Cryo-EM | Sub-nm | Native exosome ultrastructure | Limited throughput |
| AFM (Atomic Force Microscopy) | <10 nm | Surface topology, mechanical properties | Limited molecular specificity |
STED stands out as a bridge between live-cell fluorescence imaging and nanoscale resolution, making it highly suitable for both functional and structural studies of exosomes.
Our STED Microscopy Exosome Imaging Workflow
Consultation & Experimental Design
We collaborate with you to define research goals and design the optimal labeling and imaging strategy for your specific targets.
Sample Preparation & Labeling
Your cells or purified exosomes are expertly immobilized and stained using STED-validated antibodies and high-performance fluorescent dyes.
Microscope Configuration & Calibration
Before each session, the microscope's lasers are precisely aligned and the system is calibrated with nanoparticles to guarantee nanoscale accuracy.
STED Super-Resolution Imaging
A specialized two-laser system scans your sample, overcoming the diffraction limit to capture images with ultra-high resolution.
Image Processing & Quantitative Analysis
Images are computationally enhanced using deconvolution software. We then quantify key metrics like vesicle diameter, protein distribution, and co-localization.
Reporting & Data Delivery
You receive a complete package with publication-ready images, data plots, and a detailed methods report. Raw data is always available upon request.
 Figure 2. Project Workflow for Exosome Imaging by STED Microscopy. (Creative Biostructure)
Figure 2. Project Workflow for Exosome Imaging by STED Microscopy. (Creative Biostructure)
Sample Requirements for STED Exosome Imaging
To achieve the highest quality super-resolution data, please ensure your samples adhere to the following guidelines.
| Requirement | Description |
|---|---|
| Accepted Sample Types | Purified EVs/exosomes, adherent cells on coverslips, or reviewed tissue sections. Biofluids require prior EV isolation. |
| Purity (Purified EVs) | High purity is essential. Must be free of large debris and protein aggregates that can cause background signal. |
| Concentration (Purified EVs) | 108 - 1010 particles/mL recommended for achieving optimal density on imaging surfaces. |
| Buffer (Purified EVs) | Suspended in a clean, filtered, low-fluorescence buffer (e.g., PBS). Avoid detergents or high-viscosity additives. |
| Culture Conditions (Cells) | Must be grown on No. 1.5H high-precision glass coverslips. Use of exosome-depleted media is strongly recommended. |
| Storage & Shipping | Fresh, fixed samples are preferred. For frozen samples, store at -80 °C and ship overnight on dry ice. |
What Deliverables Will You Receive
- High-resolution STED images (single- and multi-channel).
- Quantitative size and intensity analysis reports.
- Customized data interpretation on request.
- Publication-ready figures and statistical outputs.
Leveraging STED Microscopy in Your Exosome Research
Our STED microscopy platform supports a wide range of exosome studies, including:
- Morphological characterization: direct visualization of exosome shape, membrane topology, and nanoclusters.
- Protein localization: detection of exosomal markers (e.g., CD9, CD63, CD81) and tracking of specific cargo proteins.
- Nucleic acid imaging: mapping DNA and RNA molecules, including microRNAs, within exosomes.
- Quantitative analysis: accurate measurement of vesicle size, distribution, and molecular density.
- Dynamic studies: monitoring exosome uptake by recipient cells and release from donor cells.
These applications support research in oncology, neurology, immunology, and drug delivery, providing data suitable for both fundamental science and translational development.
Advantages of Our STED Microscopy Exosome Imaging Service
- Nanometer-level resolution for precise visualization of individual exosomes and their molecular cargo.
- Reliable quantitative analysis with standardized protocols for size, intensity, and localization measurements.
- Customizable workflows optimized for cell culture and biofluid samples.
- Integrated characterization platform combining STED with NTA, nanoFCM, proteomics, and lipidomics.
- Publication-ready deliverables generated under strict compliance with ISEV/MISEV2023 guidelines and backed by expert experience.
Case Study
Case: STED Microscopy Reveals Exosome Footprints in Glioma Cells
In a recent study on glioma cells, researchers combined CD63 immunostaining with STED super-resolution microscopy to achieve nanoscale characterization of exosomes. Key findings include:
- Enhanced visualization: STED resolved CD63-positive cellular footprints and extracellular exosome deposits, which were not detectable by confocal microscopy.
- Quantitative precision: Analysis of ~450 vesicles showed diameters ranging from 36-157 nm, with an average of 76.6 ± 25 nm, aligning with exosome size distribution.
- Superior resolution: Deconvolution of STED images achieved ~35 nm lateral resolution, enabling detailed single-vesicle analysis.
- Biological relevance: STED imaging highlighted the close association between exosome secretion and actin dynamics, providing insights into glioma cell migration and communication.
Conclusion
This case demonstrates that STED microscopy offers the resolution and analytical power necessary for single-vesicle exosome characterization, advancing our understanding of exosome biology in the tumor microenvironment.
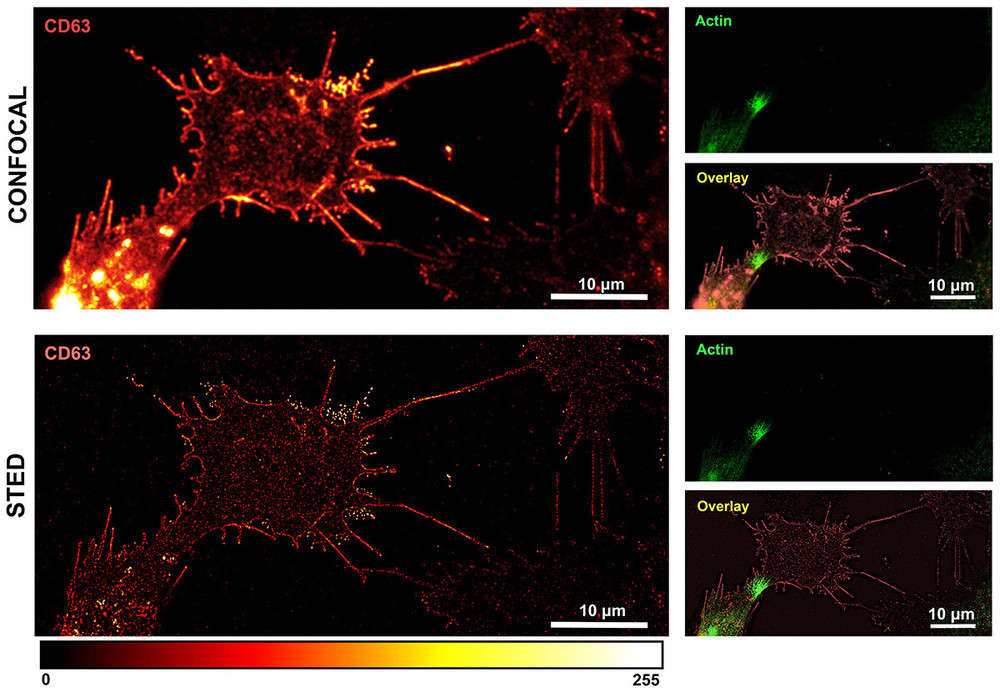 Figure 3. Confocal vs. STED microscopy of OPBG-GBM001 glioma cells immunostained with anti-CD63 (red) and anti-actin (green). Confocal imaging (upper panel) shows clusters of CD63-positive vesicles near the plasma membrane. Deconvolved STED imaging (lower panel) resolves single CD63-positive dots at the nanoscale, revealing a discontinuous membrane-associated pattern. (Petrini S, et al., 2025)
Figure 3. Confocal vs. STED microscopy of OPBG-GBM001 glioma cells immunostained with anti-CD63 (red) and anti-actin (green). Confocal imaging (upper panel) shows clusters of CD63-positive vesicles near the plasma membrane. Deconvolved STED imaging (lower panel) resolves single CD63-positive dots at the nanoscale, revealing a discontinuous membrane-associated pattern. (Petrini S, et al., 2025)
At Creative Biostructure, we empower researchers with nanometer-resolution imaging and quantitative insights into exosome biology. Whether your study focuses on morphology, protein mapping, or molecular interactions, our STED microscopy exosome imaging service provides the precision and reproducibility you need. Contact us to discuss your project or request a consultation.
References
- Welsh J A, Goberdhan D C I, O'Driscoll L, et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles (MISEV2023): From basic to advanced approaches. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles. 2024, 13(2): e12404.
- Wu S, Zhao Y, Zhang Z, et al. The advances and applications of characterization technique for exosomes: from dynamic light scattering to super-resolution imaging technology. Photonics. MDPI, 2024, 11(2): 101.
- Petrini S, Eghiaian F, Apollonio V, et al. Super-resolution microscopy reveals glioma cell footprints and exosome deposits. Cell Adhesion & Migration. 2025, 19(1): 2534759.
Frequently Asked Questions
For any inquiries, our support team is ready to help you get technical support for your research and maximize your experience with Creative Biostructure.